
目录
C22.2 No.211.1-06 标准在提供评估性能和确保 DB2 PVC 导管安全性的基本指导方面发挥着关键作用。该特定标准适用于两种不同类型的硬质 PVC 导管,即 EB1(设计用于包裹在混凝土或砖石中)和 DB2/ES2(用于直接埋入或包裹在混凝土或砖石中)。此外,它还包含相关配件,所有这些配件都必须遵守《加拿大电气规范》第 I 部分中概述的规定,特别是针对普通位置的规定。通过遵守此标准,客户可以自信地评估 DB2 PVC 导管的质量和可靠性,同时保持一致地了解与性能和安全措施相关的期望。
本文所提及的相关标准测试方法及表格数据均来源于 CSA C22.2 编号 211.1-06 和 ASTM官方标准 供参考之用的文件。
直径和壁厚:
为了符合官方文件 C22.2 No.211.1-06 中规定的标准,导管必须满足直径和壁厚的必要要求,按照 ASTM D 2122 进行测量。
对于多层导管,各内层和外层必须具有下表中指定的壁厚的最小厚度 10%。此外,与内层和外层相比,多层导管的中心层应具有对比色。
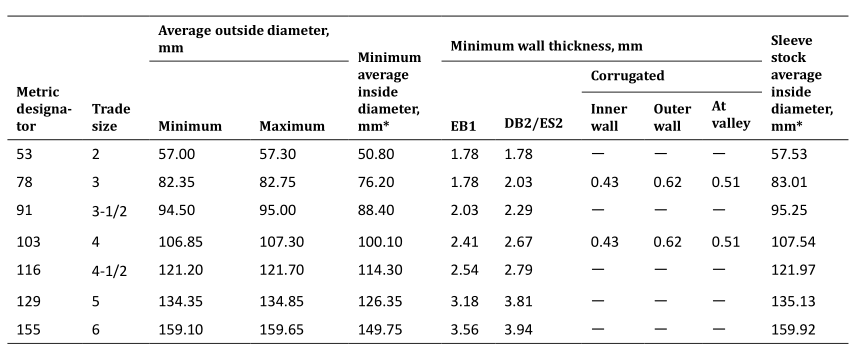
硬质 PVC 导管的直径和壁厚要求
外径与测量的平均外径的最大允许差 根据 ASTM D 2122 中概述的标准,不应超过 2%。
评估导管的直线度时,偏差不应超过每米 10 毫米,按照 ASTM D 2122 进行测量。
包含的测试要求:
调质
为确保结果一致,所有导管和配件都必须按照 ASTM D 618 进行调节过程。这包括将它们置于温度为 23 ± 2°C 且相对湿度为 50 ± 5% 的受控环境中至少 40 小时。调节的目的是建立标准化的测试基线,确保所有样品都暴露在相同的温度和湿度条件下。
抗冲击性
导管按照 CSA C22.2 No. 211.0 中第 6.3.1 条的方法 A 进行冲击测试。 该测试评估导管承受冲击而不破裂或分裂的能力。 测试时使用的冲击能量在 23°C 温度下为 61 J,在 -18°C 温度下为 34 J。
在冲击试验期间,每个温度下测试十个样本。值得注意的是,十个样本中至少有九个不应在导管内部或外部出现任何可见的裂纹或裂缝,这些裂纹或裂缝可使用正常或矫正视力观察到。这可确保导管保持其结构完整性并可承受潜在冲击,而不会损害其性能和安全性。
抗压强度
为了评估导管承受挤压力的能力,在 23 ± 2 °C 的温度下对五个样本进行了测试, 按照 CSA C22.2 No. 211.0 第 6.9 条规定. 测试测量每个样本在负载下和恢复后的直径减少百分比。
然后计算平均值并与特定限值进行比较。对于 EB1 型,负载下直径的平均百分比减小不应超过 12%,而对于 DB2/ES2 型,则不应超过 10%。此外,两种类型的恢复后直径的平均百分比减小不应超过 5%。这些标准确保管道能够承受挤压力而不会发生明显变形。
耦合挤压
联轴器的强度通过联轴器挤压试验进行评估,如 CSA C22.2 No. 211.0 条款 6.10 所述。该试验涉及使用正常或矫正视力进行目视检查,以检测任何裂纹或故障迹象。
此外, 联轴器被挤压在两个平行板之间,板材至少比接箍本身长 3 毫米。挤压过程以恒定的速率进行,逐渐将接箍的内径减小到其原始尺寸的 50%。测试持续时间为 2 至 5 分钟。
此项测试的目的是确定接头承受挤压力而不出现任何裂纹或故障的能力。通过确保接头在测试期间保持完好无损,可认为其适合使用,并在导管系统内提供可靠的连接。
残余应力测试
为了评估两个样本的尺寸稳定性,需要进行一项测试 遵循 CSA C22.2 No. 211.0 中第 6.12.1 条的方法 A。 目的是确保每个样本的内部垂直直径的减小量不超过 0.5%。
以下是测试所涉及的步骤:
- 每个样本的长度为 250±3 毫米。
- 测量并记录每个样品的垂直内径。
- 将试件放入预热至65±2℃的烘箱中,确保测量的垂直内径保持垂直位置。然后将试件在65±2℃的烘箱中保存4小时。
- 4 小时后,打开烘箱门,让试样在烘箱内冷却至 23±2 ℃。
- 然后将样品从炉中取出,重新测量垂直内径。通过比较初始测量值与最终测量值来计算直径的百分比变化。
通过遵循这些步骤,测试有助于确定样品在暴露于高温时是否能保持其尺寸稳定性。它确保内部垂直直径不会过度收缩,从而验证样品是否适合其预期用途。
耐化学性
为了评估测试样品的耐化学性,按照 CSA B137.0 中规定的指导方针进行耐化学性测试。目的是确保样品在暴露于下表列出的指定溶液时质量变化不超过 2%。浸泡期持续 7 天。
浸泡期过后,每个样品用于制备测试和对照样本。 这些样品的表观抗拉强度按照 CSA B137.0 确定。测试在从试剂中取出样品后 1 小时内进行。 从每个大样本中选取至少三个测试样本并以 12.7 mm/min ± 25% 的横梁速度进行测试。
然后将测试样本的平均抗拉强度与对照样本的平均抗拉强度进行比较。这两个平均值之间的可接受差异不应超过 15%。该标准确保化学品暴露不会显著影响样本的抗拉强度,表明其具有抵抗化学降解和保持结构完整性的能力。
通过进行这些测试并遵守指定的参数,可以准确评估样品的耐化学性,确保其适合预计接触各种化学物质的应用。
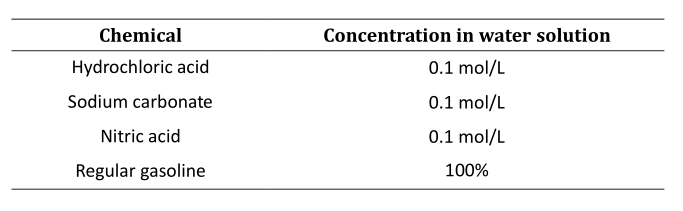
耐化学性测试要求
关节紧张
为了评估接头的密封性,需要按照 CSA C22.2 No. 211.0 中第 6.11.2 条的方法 A 进行测试。目的是确定接头是否能承受一定时间的水压而不破裂。
以下是测试所涉及的步骤:
- 将两根长度各为 1 ± 0.1 米的导管用溶剂粘合到接头上。然后让组件在室温下固化 24 小时。
- 在导管末端采用合适的封闭装置,形成密封的组件。
- 组件内充满水,确保所有空气均被适当排出。
- 对组件施加 35 kPa 表压,持续 4 小时。
通过对接头进行水压测试,可以评估其密封性。目的是验证接头是否能承受规定的压力而不会发生任何泄漏或故障。该测试可确保接头密封牢固,提供可靠的密封,并防止水或液体从导管系统中逸出。
刚性
为了评估导管的硬度,需要按照 ASTM D 2412 的指导方针进行测试。对于 EB1 型导管,其最小管道硬度应为 200 kPa,而 DB2/ES2 型导管的最小管道硬度应为 300 kPa。该测试测量导管在指定 5% 偏转下抵抗变形的能力。
粘结强度
导管样品的粘合强度通过尝试使用尖锐探针或刀尖在波纹谷处干净地分离内壁和外壁来评估。测试在导管圆周周围八个等距点处进行。
如果无法将壁完全分开,则测试视为成功。这表明内壁和外壁之间结合牢固,确保了导管的完整性和结构稳定性。通过进行此测试,可以评估导管保持其结构完整性和抗分层的能力,从而确保其可靠性和耐用性。
C22.2 No.211.1-06 标准对于确保 DB2 PVC 导管的质量和安全至关重要。该标准建立了全面的测试参数和要求框架,以保证导管符合基本性能标准。通过评估阻燃性、抗冲击性、抗压性、柔韧性、拉拔强度和环境适应性等各个方面,该标准确保 DB2 PVC 导管可靠、耐用且适用于广泛的电气应用。
遵守这些严格的要求不仅可以提高电气装置的安全性,还可以提高电气系统的整体效率和有效性。该标准确保 DB2 PVC 导管能够承受火焰和撞击等潜在危险,同时保持其结构完整性。它还验证了导管是否具有必要的灵活性和抗压性,以承受具有挑战性的环境条件。此外,该标准还评估了导管的拉拔强度,确保连接安全可靠。
通过遵守 C22.2 No.211.1-06 标准,制造商可以提供满足电气安装严格要求的高质量 DB2 PVC 导管。而 LEDES 作为中国领先的电气导管供应商之一,当然获得了这项 CSA 认证。这反过来又增强了人们对导管可靠性和耐用性的信心,从而促进了整个电气系统的安全性和效率。
接触
如果您有任何疑问或对我们的产品感兴趣,您可以通过以下方式联系我们 提交联系表格.我们的销售团队将在一个工作日内回复您的消息。



