
目录
介绍
聚氯乙烯 (PVC) 和氯化聚氯乙烯 (CPVC) 管道和导管因其耐用性、耐化学性和成本效益而广泛应用于各个行业。为了确保这些材料的质量和性能,美国材料与试验协会 (ASTM) 制定了一系列标准。这些标准对于制造商、工程师和承包商遵守行业最佳实践和监管要求至关重要。
在本综合指南中,我们将探讨适用于 PVC 和 CPVC 管道 和导管、它们的重要性以及它们如何有助于管道系统的安全性和效率。
ASTM 概述及其作用
美国材料与试验协会 (ASTM),现称为 ASTM International,是一家全球公认的组织,负责制定和发布自愿性共识标准。ASTM 成立于 1898 年,其使命是通过材料、产品、系统和服务的标准化来提高产品质量、增强安全性并促进贸易。
对于 PVC 和 CPVC 管道,ASTM 标准涵盖材料成分、物理特性、性能标准和测试方法等方面。这些标准有助于确保不同应用和环境中的一致性、可靠性和兼容性。
PVC/CPVC 导管和管道的主要 ASTM 标准
有几项 ASTM 标准专门适用于 PVC 和 CPVC 管道。了解这些标准对于工程师、承包商和质量控制人员选择适合其项目的管道材料至关重要。一些最常引用的 ASTM 标准包括
ASTM D1784 – 20: 硬质聚氯乙烯 (PVC) 化合物和氯化聚氯乙烯 (CPVC) 化合物的标准分类体系和规范依据
ASTM D1784 – 11: 硬质聚氯乙烯(PVC)化合物和
氯化聚氯乙烯 (CPVC) 化合物
ASTM D2665: 聚氯乙烯(PVC)塑料排水、废物和通风管道的标准规范
管道及配件
ASTM E662 – 17a: 固体烟雾比光密度的标准试验方法
材料
ASTM F442/F442M-23: 氯化聚氯乙烯(CPVC)塑料管材标准规范(SDR–PR)
ASTM F512 – 12: 光滑壁聚氯乙烯(PVC)导管和
地下安装配件
ASTM D1785 – 21: 聚氯乙烯 (PVC) 塑料管材标准规范,40、80 和 120 号
每项标准都涉及管道制造和性能的特定方面,确保符合安全和监管要求。在以下章节中,我们将深入探讨适用于 PVC 和 CPVC 管道的特定 ASTM 标准,重点介绍其范围和相关性。
ASTM D1784-20 和 D1784-11:硬质 PVC 和 CPVC 化合物的标准分类和规范

ASTM D1784 是一项标准规范,涵盖了用于生产管道、导管和配件的硬质 PVC 和 CPVC 化合物的分类系统和物理性能要求。它是各种应用中材料选择、质量控制和性能评估的基础。
目的
ASTM D1784 的主要目的是为硬质 PVC 和 CPVC 化合物建立统一的分类系统。该标准确保制造过程中使用的材料满足特定的质量、强度和耐用性要求,从而确保在不同应用中具有一致的性能。
分类
ASTM D1784 根据 PVC 和 CPVC 化合物的物理特性对其进行分类,其中包括:
- 基础树脂
- 抗冲击性(伊佐德)
- 拉伸强度和拉伸弹性模量
- 负荷变形温度
- 易燃
这些属性在标准的表 1 中定义,其中每类材料都由唯一的单元分类代码表示,例如 12454。此代码依次表示树脂类型、冲击强度、拉伸强度、弹性模量和热变形温度等级。
材质成分
根据 ASTM D1784 规定的 PVC 和 CPVC 化合物通常由以下成分组成:
基体树脂: 至少 80% 氯乙烯 (PVC) 或氯化氯乙烯 (CPVC)
润滑剂: 辅助加工并防止表面缺陷
稳定剂: 增强耐热和抗紫外线能力
填料: 有时添加以改善机械性能或降低成本
机械和物理性能
ASTM D1784 规定了化合物要符合该标准必须满足的不同材料特性。
对于 PVC 化合物:
冲击强度(悬臂梁式): ≥ 34.7 焦耳/米(0.65 英尺磅力/英寸)(ASTM D256)
抗拉强度: ≥ 48.3 兆帕(7000 磅/平方英寸)(ASTM D638)
拉伸弹性模量: ≥ 2758 兆帕(400,000 磅/平方英寸)
热变形温度(HDT): 1.82 MPa 负载下温度≥ 70°C (158°F) (ASTM D648)
对于 CPVC 化合物:
冲击强度(悬臂梁式): ≥ 34.7 焦耳/米(0.65 英尺磅力/英寸)(ASTM D256)
抗拉强度: ≥ 48.3 兆帕(7000 磅/平方英寸)(ASTM D638)
弹性模量: ≥ 2758 兆帕(400,000 磅/平方英寸)(ASTM D638)
热变形温度: 退火 24 小时后温度≥ 50°C (122°F)
阻燃性: 燃烧范围≤25毫米,10秒内熄灭(ASTM D635)
包装和标识
为了确保正确处理和可追溯性,ASTM D1784 规定 PVC/CPVC 材料应采用商业包装并带有详细标签,包括:
材料名称及牌号
制造商名称
批次和批号
数量
配送信息
合同或订单参考
适当的包装和标签有助于保持产品完整性并确保符合行业标准。
ASTM D1784 规定的 PVC/CPVC 管道产品类型
根据 ASTM D1784 分类的化合物用于制造各种挤压和模塑产品,包括:
挤压管 (用于给水、排水和工业应用)
注塑配件 (用于压力和非压力管道系统)
额定压力管道系统 (需要额外考虑长期压力)
对于高温 CPVC 应用,通常使用 10/11 级,因为它具有优异的耐热性和在热水或工业化学环境中的长期性能。
ASTM D1784 作为 PVC 和 CPVC 材料分类的基础,确保产品满足机械、热和化学性能要求。
ASTM D2665:PVC 塑料排水、废水和通风管道及配件标准

定义和目的
ASTM D2665 是一项广泛认可的标准,规定了 聚氯乙烯 (PVC) 塑料排水、废水和通风 (DWV) 管道和配件。该标准确保 PVC DWV 管道系统满足严格的材料、尺寸和机械性能要求,以确保卫生排水应用中的长期性能、安全性和耐用性。
根据 ASTM D2665 制造的 PVC 管道和配件主要用于住宅和商业管道系统中的重力供水卫生排水、废物处理和通风应用。该标准为材料成分、物理特性、抗冲击性和管道刚度提供了基本指导,以确保 DWV 系统的高可靠性。
测试方法和要求
尺寸和公差
测量方法: 所有尺寸,包括外径 (OD)、壁厚和长度,均须按照 ASTM D2122 确定。
标准长度: 管道通常长度为 10 英尺(3.05 米)和 20 英尺(6.10 米),允许公差为 +1.0 英寸。
外径和壁厚: 外径和壁厚必须符合 ASTM D2665 表 2 中详细列出的规格。
配件:排水、废水和通风配件应符合 ASTM F1866 的规定,以确保管道系统内正确安装和运行。
管道刚度要求
管道刚度 (PS) 是 PVC DWV 管道系统的关键性能标准,可确保在负载下抵抗变形。管道刚度使用 ASTM D2412 确定,该标准测量管道承受 5% 偏转而不发生结构故障的能力。
ASTM D2665 表 3 提供了不同管道直径的最小刚度值,以确保埋地和地上应用中的结构完整性。
冲击强度
测试方法: 抗冲击性采用 ASTM D2444 来确定,其中包括落锤冲击试验 (Tup C)。
验收标准: 通常情况下,10 个样本中必须有 9 个能够通过测试,且不得出现开裂或分裂的迹象。
配件冲击强度: 单个配件,特别是分型线处的配件,必须承受至少 750 lbf/ft (11 kN/m) 的力,且不得出现任何可见的裂缝,如 ASTM D2665 第 6.3.2 节所规定的那样。
管件类型
ASTM D2665 涵盖 DWV 系统必需的各种配件,其中包括:
标准配件: 符合 ASTM D3311 的弯头、三通、Y 型管和联轴器,确保尺寸和配置标准化。
短管道: 符合 ASTM F2135 的 DWV 管道短段,适合特定的安装要求。
螺纹配件: 带有螺纹的组件必须符合 ASTM F1498 的规格,以确保适当的密封和机械强度。
合规与质量保证
为了确保产品质量始终如一,制造商必须定期进行测试并遵守规定的要求。这包括计算管道刚度的置信下限 (LCL),以确保所有制造的管道 99% 均达到或超过所需的刚度值,从而提供额外的质量保证和可靠性。
通过遵守 ASTM D2665,制造商和管道专业人员可以确保 PVC DWV 管道系统可靠、耐用且适合其预期用途,从而保障公众健康和基础设施的完整性。
ASTM E662-17:烟雾产生光密度的标准测试方法
ASTM E662-17 是一种标准测试方法,旨在评估固体材料在热解(非燃烧)和火焰(燃烧)条件下的发烟量和光密度特性。主要目的是量化材料通过产生烟雾而衰减光的程度,以特定光密度 (Ds) 表示。
目的
ASTM E662-17 的主要目的是测量材料在特定暴露条件下产生的烟雾量。这对于在烟雾密度会影响火灾期间能见度和疏散的环境中评估材料至关重要。但是,需要注意的是:
- 测试结果提供特定的光密度 (Ds) 值,该值仅适用于给定形式和厚度的测试样品。
- 该方法没有考虑烟雾的毒理学效应或其对人体视觉的生理影响。
- 该测试无法预测真实火灾条件下的烟雾行为,因为通风、燃烧动力学和多物质相互作用等因素都会影响烟雾的产生。
测试方法
测试在封闭的烟雾密度室内进行,材料样品暴露在受控热源下。使用光度测量系统测量烟雾累积,该系统跟踪光随时间衰减,从而计算出特定光密度 (Ds)。测试包括两个条件:
1. 无焰(热分解)条件
样品暴露在 2.5 W/cm² 的辐射热通量中,无需直接使用火焰。
此条件模拟材料在没有点火的情况下因受热而产生烟雾的场景。
2. 有焰燃烧条件
The same 2.5 W/cm² heat flux is applied, but with the addition of a six-tube burner that introduces a direct flame to ignite the material.
This setup evaluates the smoke production when the material is actively burning.
The smoke generated under both conditions is analyzed through a photometric system that measures light transmission through the chamber. The reduction in light intensity is used to calculate the specific optical density.
Calculation of Specific Optical Density (Ds)
The specific optical density (Ds) is determined using the following formula:
Ds=G⋅{log(100/T)+F}
Where:
Ds = Specific optical density
G = Geometric factor (typically 132)
T = Percentage of light transmitted through the smoke
F = A correction factor accounting for the initial light transmission conditions
This equation expresses how much the smoke reduces visibility by measuring the logarithmic decrease in light transmission.
Data Interpretation and Limitations
- The results are expressed as specific optical density (Ds) values, indicating the concentration of smoke in the chamber.
- Samples must be uniform in composition, and their thickness should not exceed 1 inch (25.4 mm).
- If a sample exhibits self-ignition or any unexpected combustion behavior, additional testing is required to ensure data reliability.
- The values obtained are not inherent properties of the material and may vary under different fire conditions.
Significance in Material Selection
ASTM E662-17 plays a crucial role in assessing materials for applications where smoke production is a concern, such as:
- Building materials (e.g., wall panels, flooring, insulation).
- Electrical conduit and piping systems, where smoke density can affect fire safety compliance.
- Transportation sectors, including aircraft, railways, and automotive industries, where reduced visibility due to smoke can impact passenger safety.
By adhering to this standard, manufacturers, designers, and regulatory bodies can better evaluate and compare materials based on their smoke generation potential, leading to safer product development and improved fire safety standards.
ASTM F442/F442M-23: Standard Specification CPVC Plastic Pipe (SDR-PR)

ASTM F442/F442M-23 is a standard specification that defines the requirements for Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride (CPVC) plastic pipes used in pressurized water distribution systems. This standard establishes material properties, dimensions, classification, and performance criteria to ensure the structural integrity and long-term reliability of CPVC piping under varying temperature and pressure conditions.
目的
The primary objective of ASTM F442/F442M-23 is to specify the dimensions, material properties, and pressure ratings of CPVC pipes used for water distribution. It ensures that CPVC pipes are manufactured to meet consistent quality standards for hydrostatic strength, durability, and chemical resistance, making them suitable for both hot and cold water applications in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
分类
Pipes covered by ASTM F442/F442M-23 are manufactured from chlorinated poly(vinyl chloride) (CPVC) compound, formulated to provide enhanced temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, and chemical compatibility compared to conventional PVC pipes.
The standard classifies CPVC pipes based on two key rating systems:
- Standard Dimension Ratio (SDR-PR System): Pipes are categorized based on a fixed ratio of outside diameter to wall thickness (SDR) and a corresponding pressure rating (PR).
- Class System: Pipes are assigned a specific pressure class, indicating their ability to withstand internal pressure at a defined temperature.
Covers six Standard Dimension Ratios (SDR):
SDR: 11, 13.5, 17, 21, 26, and 32.5.
SDR, calculated as the ratio of outer diameter to minimum wall thickness (rounded to 0.5), directly correlates with pressure ratings, enabling uniform performance across all nominal pipe sizes. Lower SDR values (e.g., SDR11) indicate thicker walls for higher-pressure applications, while higher SDRs (e.g., SDR32.5) suit lower-pressure environments. Hydrostatic design stresses, derived from long-term testing, further classify pipes based on their pressure-bearing capabilities at 73°F (23°C) and 180°F (82°C).
Material Requirements
The CPVC compounds used in these pipes must comply with ASTM D1784, ensuring the material meets strict mechanical and physical properties. Additionally, the hydrostatic design basis (HDB) and hydrostatic design stress (HDS) values are determined according to ASTM D2837, with the following key properties:
HDB at 73 °F (23 °C): 4000 psi (28 MPa)
HDB at 180 °F (82 °C): 1000 psi (7.0 MPa) or 1250 psi (8.6 MPa)
Each CPVC pipe is designated with a material code that includes the ASTM type and grade, followed by the design stress values at 73°F (23°C) and 180°F (82°C), expressed in units of 100 psi (0.7 MPa). The complete material code consists of four letters and six numerical figures for proper identification and classification.
Material designation codes (e.g., CPVC 4120-05 or CPVC 4120-06) reflect design stresses at both temperatures.
Rework material must be clean and meet all specification requirements.
Performance and Testing
The standard mandates stringent testing to validate pipe quality:
- Dimensional Tolerances:
Outside Diameter (OD): Conforms to Table 1 (per ASTM D2122), with tolerances for out-of-roundness applicable pre-shipment.
壁厚: Conforms to Table 2 (per ASTM D2122), with a maximum thickness variation of 12%.
- Pressure Testing:
Sustained Pressure Test: Six specimens withstand 1,000 hours at pressures. Failure of two specimens results in rejection.
Burst Pressure Test: Five specimens are pressurized to failure within 60–70 seconds, with minimum thresholds.
Accelerated Regression Test (Optional): An alternative to sustained/burst tests, this method uses regression analysis (per ASTM D2837) to project 100,000-hour hydrostatic strength.
Lower confidence limit (LCL) exceeds 15% of extrapolated LTHS.
Statistical parameters (M ≤ 0 or slope b ≥ 0) indicate unreliable projections.
Flattening Test: Three specimens compressed to 40% of their diameter must show no cracks or breaks.
Marking Requirements
Legible, permanent markings spaced ≤5 ft (1.5 m) include:
Nominal Pipe Size (e.g., NPS 2 or NPS 50).
Material code (e.g., CPVC4120-05).
SDR (e.g., SDR13.5).
Pressure ratings at 73°F and 180°F (e.g., “400 psi at 73°F, 100 psi at 180°F”).
ASTM designation (F442, F442M, or F442/F442M).
Manufacturer’s name/trademark and production code.
Potable water pipes: Evaluator laboratory’s seal/mark.
Requirements and Compliance
CPVC pipes must meet strict performance and quality criteria as outlined in ASTM F442/F442M-23. This includes compliance with:
- Minimum hydrostatic design stress requirements to ensure long-term pressure resistance.
- Wall thickness and dimensional tolerances for uniformity and reliability.
- Material purity and consistency to guarantee high performance in demanding applications.
Manufacturers producing CPVC pipes under this standard must conduct regular quality control checks to maintain compliance, ensuring that every batch meets the specified standards.
应用
The standard explicitly excludes pipes for venting combustion gases. Its primary focus is water supply systems, where CPVC’s corrosion resistance, thermal stability, and cost-effectiveness make it ideal for residential, commercial, and industrial use.
ASTM F512-12: Standard for PVC Conduit & Fittings for Underground Installation

定义和目的
ASTM F512-12 is a standard specification that defines the requirements for smooth-wall polyvinyl chloride (PVC) conduit and fittings designed for underground applications, primarily in electrical and communication systems. The standard categorizes conduits into two main types based on their intended installation method: Encased Burial (EB) conduit, which requires concrete encasement for structural support, and Direct Burial (DB) conduit, which can be buried directly in the ground without additional reinforcement. The primary purpose of this standard is to ensure uniformity in conduit performance, durability, and compatibility while providing protection for electrical and communication cables in underground environments.
Material and Classification
The conduits and fittings covered under ASTM F512-12 are manufactured from rigid polyvinyl chloride (PVC), complying with ASTM D1784 material specifications. The acceptable PVC cell classifications include 12254-A/B and 12164-B5, ensuring high durability, mechanical strength, and resistance to environmental stressors. Additionally, the specification allows for both single-wall conduit and coextruded honeycomb-core conduit designs, with conduit joints available in either integral bell or separate coupling configurations.
ASTM F512-12 classifies conduits into five types based on pipe stiffness and intended burial method:
EB-20 – Designed for encasement in concrete.
EB-35 – Designed for encasement in concrete with higher stiffness than EB-20.
DB-60 – Designed for direct burial without concrete encasement.
DB-100 – Designed for direct burial, offering greater stiffness than DB-60.
DB-120 – Designed for direct burial, providing the highest stiffness among DB conduits.
Additionally, the specification covers molded and fabricated fittings that are compatible with all conduit types listed above.
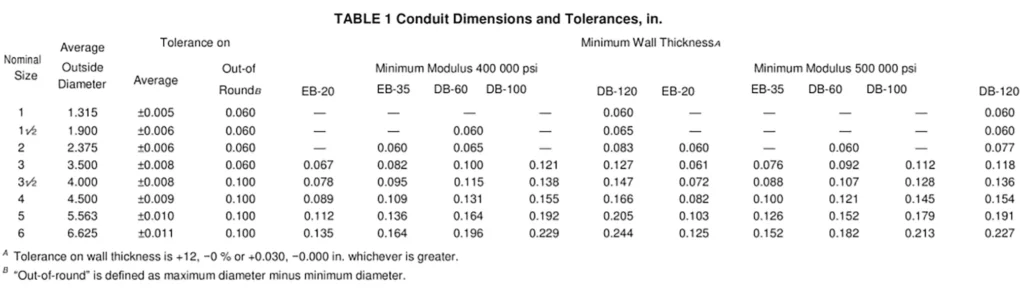
方面
The standard specifies conduit dimensions and tolerances, including wall thickness, socket depths, and length requirements. These dimensions are determined in accordance with ASTM D2122 test methods.
- Conduit lengths are typically supplied in 20 ft (6.1 m) or 25 ft (7.6 m) sections, unless otherwise agreed upon by the manufacturer and purchaser.
- Integral bells and socket dimensions follow two primary fitment systems:
- Interference Fit System, following ASTM D2466 specifications.
- Clearance Fit System, with tolerances defined within ASTM F512-12.
Main Tests and Test Methods
To ensure compliance with performance requirements, conduits and fittings undergo a series of standardized tests:
Acetone Immersion Test (ASTM D2152)
Validates fusion integrity by exposing specimens to acetone, ensuring no surface deterioration or laminations.
Pipe Stiffness Test (ASTM D2412)
Measures conduit stiffness at 5% deflection. The required minimum stiffness values are:
EB-20: ≥ 20 psi
EB-35: ≥ 35 psi
DB-60: ≥ 60 psi
DB-100: ≥ 100 psi
DB-120: ≥ 120 psi
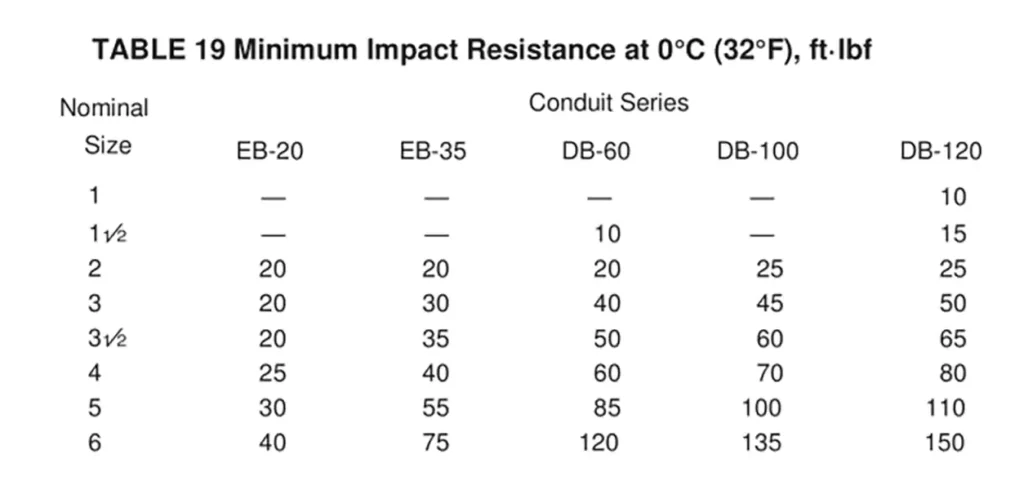
Impact Resistance Test (ASTM D2444)
Evaluates the conduit’s ability to withstand mechanical impact using Type A or Type B impact hammers. Conduits must pass impact testing with a minimum acceptable pass rate (e.g., 17 out of 20 samples meeting requirements).
Requirements: Assesses toughness at 0°C (32°F) using a Type A or B tup (hammer). For example, a batch passes if 17 out of 20 specimens withstand the specified impact energy without cracking.
Requirements
Conduits and fittings manufactured under ASTM F512-12 must meet the following quality and performance criteria:
Homogeneity: The material must be free of visible cracks, holes, foreign inclusions, or other defects that could compromise performance.
Uniformity: Conduits should be consistent in color, opacity, density, and mechanical properties to maintain product integrity.
Wall Thickness Compliance: The wall thickness of integral bells and sweeps must meet the minimum specifications to ensure structural reliability.
Product Marking
To ensure traceability and compliance, conduits and fittings must be clearly marked with essential information at intervals of 5 ft (1.5 m) or less. The markings include:
Manufacturer’s name or trademark
PVC cell classification (e.g., PVC 12254-A, PVC 12254-B, PVC 12164-B)
Conduit size and type (e.g., DB-60, EB-35)
Minimum wall thickness
Control number or batch code
ASTM designation (ASTM F512 for single extrusion; ASTM F512 COEX for coextruded products)
Additionally, sweeps and bends should be marked with their bend radius and angle (e.g., 18″ R – 30°), while fittings should be labeled with size, material type (PVC), and the ASTM F512 designation. If space constraints prevent direct marking on fittings, the required information should be included on the packaging.
Applications and Industry Relevance
ASTM F512-12 is pivotal in underground infrastructure for electrical and communication networks, offering solutions that balance flexibility, strength, and corrosion resistance. Its dual focus on concrete-encased and direct-burial applications ensures adaptability to diverse installation environments, from urban utility corridors to industrial sites. By enforcing stringent material and testing protocols, the standard mitigates risks of premature failure, ensuring conduits meet the demands of modern buried infrastructure systems.
ASTM D1785-21: Standard for PVC Plastic Pipes, Schedule 40, 80, and 120

定义和目的
ASTM D1785-21 is a standard specification that defines the requirements for poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) plastic pipes manufactured in Schedule 40, 80, and 120 wall thicknesses. This specification applies to pressure-rated pipes intended primarily for the conveyance of fluids, including potable water, in various plumbing and industrial applications. The standard provides guidelines for material composition, classification, dimensional tolerances, hydrostatic pressure ratings, and performance testing to ensure the quality, safety, and durability of PVC pipes used in fluid transportation systems.
This specification establishes six types/grades of PVC pipes, categorized based on hydrostatic design stress and long-term performance testing. It also aligns with ASTM D1784, which sets the material classification requirements for PVC compounds used in the manufacturing of these pipes.
分类
ASTM D1785-21 classifies PVC pipes based on their type, grade, and hydrostatic design stress, ensuring consistent performance across different applications. This specification covers pipes produced in Schedule 40, 80, and 120 wall thicknesses, with each pipe clearly marked according to one of six designated type/grade/stress classifications.
Schedule 40: Standard-weight pipe for moderate-pressure applications.
Schedule 80: Heavy-duty pipe for higher-pressure systems.
Schedule 120: Extra-heavy pipe for specialized high-stress environments.
A key aspect of this classification is the hydrostatic design stress (HDS), which determines the long-term pressure-bearing capability of the pipe. These stresses are established through rigorous long-term testing, ensuring that the pipes can withstand sustained internal pressures without failure. The classification framework helps in selecting the appropriate pipe for different pressure applications, particularly in water distribution and industrial systems.
材料
ASTM D1785-21 specifies that PVC pipes must be made from poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) plastics with well-defined physical and chemical properties. The materials used must meet the standards set in ASTM D1784, specifically PVC 12454 or PVC 14333, ensuring durability, strength, and chemical resistance.
For potable water applications, the pipe must be tested and certified to meet NSF/ANSI Standard 14, ensuring it is safe for drinking water use. Pipes that pass this certification must display the appropriate approval mark.
Manufacturers can also use clean rework PVC material, but only from their own production process, and the final product must fully comply with ASTM D1785-21 requirements. This ensures consistent quality and performance across all PVC pipes.
尺寸和公差
The dimensional and tolerance requirements for PVC pipes are specified in Tables 1 and 2 of the standard. These dimensions are verified according to ASTM D2122, ensuring compliance with strict manufacturing tolerances. Key aspects include:
Outer diameter, wall thickness, and tolerances – ensuring pipes meet the required size specifications.
Out-of-roundness tolerances – applicable before shipment to ensure proper fit during installation.
Test Methods and Requirements
To ensure durability and safety, ASTM D1785-21 mandates several critical tests for PVC pipes:
1. Sustained Pressure Test (ASTM D1598)
Pipes must withstand hydrostatic pressure for 1,000 hours at their designated stress level without failure (such as bursting or leaking).
2. Burst Pressure Test (ASTM D1599)
Pipes must endure a short-term hydrostatic pressure test at four times the rated pressure for 60-70 seconds without failure.
3. Flattening Test
Pipe specimens (minimum 2 inches long) are compressed between two parallel plates until they reach 40% of their original diameter or until the walls touch.
The specimen must not crack, split, or break under this pressure.
4. Testing Conditions
- Tests are conducted in a controlled laboratory environment at 73°F ± 4°F (23°C ± 2°C) with 50% ± 10% relative humidity, unless otherwise specified.
- For impact testing, specimens are conditioned at 32-35°F (0-1.6°C) for at least 30 minutes before testing.
These stringent testing procedures ensure that PVC pipes meet performance expectations for high-pressure applications.
Marking Requirements
To ensure traceability and compliance, ASTM D1785-21 requires all pipes to be clearly marked with the following information at intervals not exceeding 5 feet (1.5 meters):
Nominal pipe size (e.g., 2 inches (50 mm))
PVC material designation code (e.g., PVC 1120)
Schedule and pressure rating (e.g., Schedule 40, 200 psi)
ASTM designation and year (e.g., ASTM D1785-21)
Manufacturer’s name or trademark
Production code (identifying date, shift, plant, and extruder used in manufacturing)
Marking for potable water use (if applicable)
Manufacturers must ensure that markings remain legible after installation and inspection.
Comparison with ASTM Standards
PVC pipes are regulated by multiple ASTM standards, depending on their intended application. The table below summarizes key differences:
6 Different ASTM Standard Comparing Chart
标准 | Core Content | Key Tests | Applicable Pipe Types | Special Requirements |
ASTM D1784-20/11 | PVC and CPVC material classification | Izod impact, tensile strength, heat deflection | Extruded/injection-molded pipes & fittings. | Pressure pipes require HDB evaluation |
ASTM D1785-21 | PVC pressure pipes for pressurized water systems | Sustained pressure, burst pressure, flattening test | Schedule 40, 80, 120 pipes | Production code traceability; integral bell joints. |
ASTM D2665 | DWV (Drain, Waste, and Vent) pipe performance | Pipe stiffness, impact test | DWV pipes, elbows, tees | Threads must meet ASTM F1498 |
ASTM F442/F442M -23 | CPVC pressure pipe | Sustained burst /pressure, flattening test | SDR series pipes | Prohibits pneumatic testing |
ASTM E662-17 | Smoke density testing | Optical attenuation | Solid materials | Sample thickness ≤ 1 inch |
ASTM E512-12 | Smooth-wall PVC conduit for underground installation | Acetone immersion, Pipe stiffness, Impact | EB/DB conduit types | Material must meet 12254-A/B grade |
结论
In summary, ASTM standards for PVC and CPVC pipes, all play a critical role in ensuring the reliability, safety, and performance of these piping systems across a variety of applications. From defining the material specifications and classifications to setting rigorous testing requirements, these standards ensure that PVC and CPVC pipes meet the necessary strength, durability, and chemical resistance criteria for use in water distribution, electrical conduit, and industrial systems.
By adhering to these established guidelines, manufacturers can produce pipes that perform consistently under pressure and environmental stress, while also complying with important safety and health regulations, such as those for potable water. The comprehensive requirements for materials, manufacturing processes, and pressure ratings outlined in these standards provide a clear framework for achieving high-quality pipe products.
Ultimately, understanding and following ASTM standards is essential for anyone involved in the design, manufacturing, and installation of PVC and CPVC piping systems, ensuring that the final products meet the highest performance and safety standards.
Contact our expert today if you still have any questions about ASTM standards or related; we will reply to you within 24 hours.
参考
ASTM D1784 – 11: Standard Specification for Rigid Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Compounds and
ASTM D2665: Standard Specification for Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Drain, Waste, and Vent
ASTM E662 – 17a: Standard Test Method for Specific Optical Density of Smoke Generated by Solid
ASTM F512 – 12: Standard Specification for Smooth-Wall Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Conduit and



