
目录
在电气安装领域,接线盒是体现布线系统组织性、安全性和效率的关键部件。接线盒是一种专门设计用于在统一结构内容纳多个电气设备的外壳, 联机箱 在电网内各种组件的无缝集成中发挥着不可或缺的作用。
接线盒的定义和用途
联动箱,通常称为导管盒或电气箱,是专门设计的外壳,用作集中枢纽,用于容纳和组织单个单元内的多个电气设备,例如开关、插座或插座。这些盒子经过精心制作,为安装和连接各种电气元件提供安全且结构化的环境,从而促进简化和有凝聚力的布线设置。
接线盒的主要用途是将多个电气设备整合到一个紧凑且有序的外壳内并加以保护。接线盒为各种组件的安装提供了一个集中位置,因此不仅增强了接线系统的功能性和美观性,还有助于提高电气安装的安全性和效率。
为什么联动箱如此重要?

接线盒在电气系统中的重要性怎么强调都不为过。这些专用外壳是结构化布线安装的基石,使电工和安装人员能够在住宅、商业和工业环境中创建连贯可靠的电网。接线盒为多个设备提供集中且安全的外壳,有助于高效安装、连接和管理电气元件,从而提高布线系统的整体性能和安全性。
在本综合指南的后续章节中,我们将深入探讨接线盒的各个方面,探索其类型、材料、应用、技术规格、安装程序等。通过了解接线盒在电气安装中的定义、用途和重要性,读者可以获得宝贵的见解,了解这些多功能外壳在电气工程和建筑领域发挥的重要作用。
了解接线盒
接线盒有哪些不同类型?
4 种不同材质的组合盒
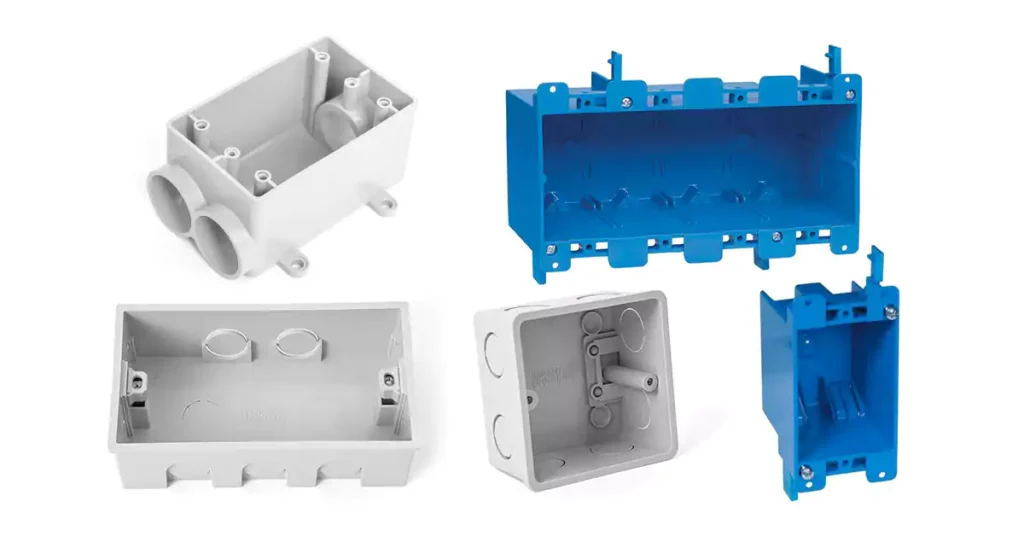
接线盒通常由各种材料制成,每种材料都具有独特的特性和优势。接线盒结构中使用的常见材料包括:
金属接线盒: 金属接线盒由钢或铝制成,具有耐用性和强度,适用于重型应用。
塑料接线盒: 塑料接线盒重量轻并且经济高效,通常是易于操作的住宅安装的首选。
玻璃纤维接线盒: 玻璃纤维接线盒以其耐腐蚀和电绝缘性能而闻名,非常适合恶劣环境。
PVC接线盒: PVC(聚氯乙烯)接线盒具有出色的防潮和防化学腐蚀性能,适合用于户外和潮湿的地方。
接线盒的材料选择取决于安装环境、所需的耐用性和预算考虑等因素。
电气接线盒尺寸、配置和特点

接线盒有多种尺寸和配置,可容纳不同数量和类型的电气设备。常见尺寸包括:
- 1 帮派: 单台设备容量
- 2 帮派: 设备容量加倍
- 3帮派: 设备容量增加三倍
- 4 帮派: 设备容量增加四倍
此外,接线盒可能具有以下功能:
- 方便电缆进出的敲除孔
- 安装支架,确保安全安装
- 内部夹具用于固定接线连接
- 电气安全接地螺钉
了解接线盒的尺寸、配置和特点对于确保在电气系统中正确选择和安装这些外壳至关重要。
接线盒用于什么用途?
居住环境

在住宅环境中,接线盒在组织和固定各种设备的电气连接方面发挥着关键作用。常见应用包括:
照明控制: 接线箱用于容纳调光开关、灯开关和其他照明控制装置,为控制不同房间的照明设备提供一个集中点。
电源插座: 接线盒对于整个家庭安装电源插座至关重要,可确保家用电器、电子设备和其他设备的安全可靠的电气连接。
数据和通信接口: 接线盒用于安装数据端口、电话插孔和其他通信插座,方便不同房间访问互联网和电话服务。
吊扇: 接线盒支持吊扇的安装,为这些装置提供安全的安装点和电气连接。
商业和工业应用
在商业和工业环境中,接线盒有多种用途,包括:
办公空间: 接线盒用于在办公室隔间、会议室和其他工作区域安装电源插座、数据端口和开关。
零售店: 接线盒支持在零售环境中安装电源插座、照明控制和安全系统,确保各种应用的有效电气连接。
生产设施: 接线盒用于组织工业环境中机械、设备控制和照明系统的电气连接,提高操作效率和安全性。
医院和医疗机构: 接线盒在为医疗机构中的医疗设备、照明设备和通信系统提供可靠的电气连接方面发挥着关键作用,可确保最佳功能和患者安全。
电缆管理和组织
接线盒在电缆管理和组织中发挥着重要作用,有助于:
减少混乱: 接线盒以整洁有序的方式容纳电气连接,从而减少混乱并提高接线装置的视觉吸引力。
方便维护: 通过将电气连接集中在接线盒内,维护和故障排除任务变得更加高效和直接,从而节省了维护人员的时间和精力。
防止电缆损坏: 接线盒可保护电缆和连接免受物理损坏、潮湿和其他环境因素的影响,确保电气系统的寿命和可靠性。
安全和合规要求

在使用接线盒时,安全性和遵守电气法规至关重要,以确保:
电气安全: 接线盒为电气连接提供了安全的封闭空间,降低了短路和电气火灾等电气危险的风险。
接地: 接线盒的正确接地对于电气安全、防止电荷积聚和确保电气设备安全运行至关重要。
遵守法规: 接线盒必须符合相关电气规范和标准,例如 UL(美国保险商实验室)和 CSA(加拿大标准协会)制定的规范和标准,以确保符合安全法规和行业标准。
在安装和使用接线盒时遵守安全和合规要求至关重要,可以提高各种应用和环境中的电气安全性和可靠性。
安装指南和安全提示
安装接线盒是电气布线项目中的关键步骤,遵循正确的指导方针和注意事项对于确保安全有效的安装至关重要。以下是一份全面的安装指南以及关键注意事项。
提示:您可以访问此页面以查看阅读完整的配电箱安装指南。
安装接线盒的 10 个步骤:
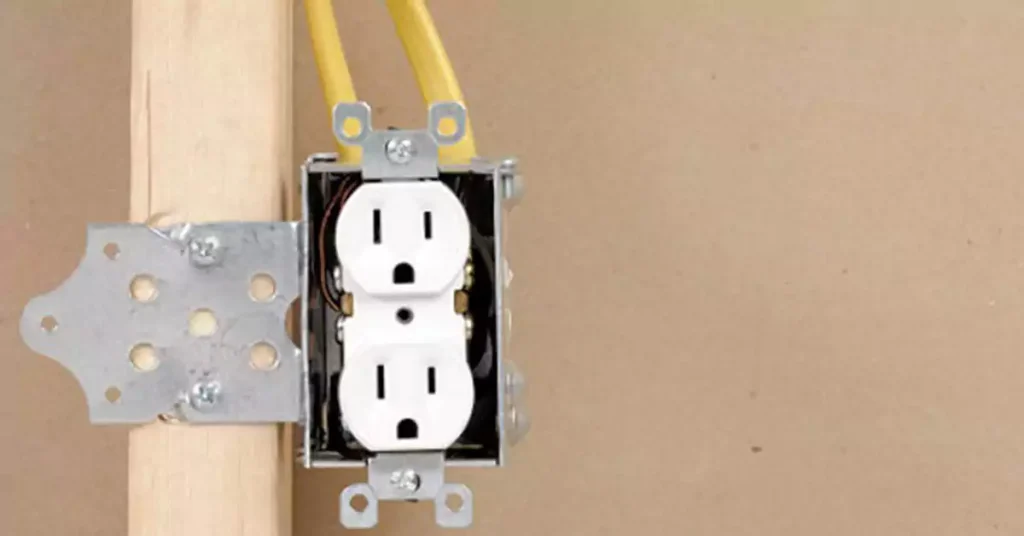

- 选择正确的框: 选择适合要安装的设备数量和类型的接线盒。根据安装的具体要求考虑尺寸、材料和功能等因素。
- 找到安装地点: 确定接线盒的理想位置,确保其易于访问且符合安全和规范要求。考虑诸如与电气设备的距离和接线连接的简易性等因素。
- 准备安装表面: 确保安装表面平整、稳定,并能支撑接线盒和连接设备的重量。根据需要对表面进行必要的调整或加固。
- 测量并标记: 使用卷尺和水平仪准确标记安装表面上接线盒的位置。仔细检查测量结果,确保对齐和间距正确。
- 切开开口: 使用适当的工具在安装表面上切割接线盒的开口。确保开口的尺寸和形状正确,以便牢固地容纳接线盒。
- 固定盒子: 使用螺钉或安装支架将接线盒固定到安装表面,确保其牢固固定到位。确保接线盒与表面齐平。
- 安装设备: 按照制造商的说明和接线图将电气设备(如开关、插座或插座)连接到接线盒。使用正确的接线技术并确保连接牢固。
- 完成接线连接: 整理并固定接线盒内的接线连接,确保适当的绝缘和应力消除。使用电缆夹或连接器固定电缆并防止损坏。
- 测试安装: 在关闭接线盒之前,请测试电气连接以确保其正常工作。使用电压测试仪检查电源和接线是否正确。
- 安全盖板: 安装完成并测试后,将盖板固定在接线盒上,以保护设备和接线连接。确保盖板对齐并正确固定。
接线盒安装的 5 个安全提示
安全预防措施: 安装过程中,请务必注意安全,遵循正确的程序、使用绝缘工具并在开始工作前关闭电路的电源。
守则合规性: 安装接线盒时,确保符合当地的电气规范和规定,包括接线盒尺寸、安装方法和接地的要求。
环境因素: 选择接线盒材料和安装位置时,请考虑湿度、温度和化学物质暴露等环境条件。
未来可访问性: 将接线盒安装在便于维护、维修和未来升级且不会造成重大中断的位置。
专业协助: 对于复杂的安装或不熟悉的情况,请考虑寻求合格电工的帮助,以确保安全且合规的安装。
By following this installation guide and considering key factors, you can effectively install gang boxes in various electrical applications, ensuring safe and reliable electrical connections within your wiring system.
Codes Compliance and Requirements of Gang Boxes

There are many standards in different regions set the requirements for gang boxes, or outlet boxes. Here we will focus on the requirements for gang boxes in UL and CSA standards.
UL 514A: Standard for metallic outlet boxes, with requirements for materials, construction, and performance.
UL 514C: UL 514C covers requirements for nonmetallic outlet boxes and fittings that are intended for use with nonmetallic conduit, tubing, and cable systems in accordance with the National Electrical Code (NEC). With requirements for materials, constructions and performance criteria.
CSA C22.2 No. 18.1: Standard for metallic outlet boxes, covering requirements for materials, construction, and performance similar to UL 514A.
CSA C22.2 No. 18.2: Standard for non-metallic outlet boxes, set safety and performance requirements for gang boxes, some requirements are similar to UL514C.
Requirements for PVC Gang Boxes - UL 514C
UL 514C outlines requirements for nonmetallic outlet boxes, gang boxes, covers, and supports used in electrical installations. Here are some typical requirements specified by UL 514C for nonmetallic gang boxes:
材质标准:
Nonmetallic gang boxes must be constructed from materials that meet specific durability, flame resistance, and impact resistance standards.
Flame - Retardant Properties:
The standard require the box for use with non-metallic tubing should not flame for more than 1 min after the fifth application of a standard test flame. And box for use with nonmetallic rigid conduit should not support combustion for more than 5 seconds after the third application of the flame test.
抗压强度

Box for use with nonmetallic tubing: Boxes are to be conditioned for 7 hours at a temperature of 90℃ in an air-circulating oven, then cool them at a room temperature for 16 hours to 96 hours, then place each box between two flat 1/2 inch thick steel plates, and apply a force of 2500 pounds (11,121 N) to the box until the box continues to yield to the force at a rate greater than that at which the force is applied.
Box for use with rigid nonmetallic conduit: The box is subjected to a force of 5000 pounds (22,241 N) as described in the standard, the reduction in height of 1/2-, 3/4-, or 1-inch conduit box is not more than 15 percent of its original height, and the reduction of any other box is not more than 10 percent of its original height.
— Test information and table data cite and reference UL514C, Fourth Edition.
抗冲击性
Box for use with nonmetallic tubing: Box is to be exposed for 5h to air maintained at minus 20±1℃. And drop it onto a concrete floor twice in a rapid succession from a height of 54 feet once it be removed from the cold chamber. After test the box should show any loss of integrity and should not have a 1/32 inch (0.8 mm) dill rod through any resulting crack in the box or nailing attachment.
And test some box samples at room temperature, using a 6 pound (2.72 kg) test weight with an 3/8 inch by 3/4 inch by 6 inch polyurethane striking face drop from a height of 18 inches to trike the box adjacent to the open face. After test the box should show any loss of integrity and should not have a 1/32 inch (0.8 mm) dill rod through any resulting crack in the box or nailing attachment.
Box for use with rigid nonmetallic conduit: The box is to be placed with its open side down on a steel plate and subjected to the impact of a 75 pound 6-inch diameter cylindrical steel weight free of sharp edges and having a flat impact surface. The weight is to be dropped vertically with a distance of follow table:

— Test information and table data cite and reference UL514C, Fourth Edition.
Requirements for PVC Gang Boxes - C22.2 No.18.2
CSA C22.2 No.18.2 is a recognized standard in Canada for nonmetallic outlet boxes, including nonmetallic gang boxes. Here are some of the performance requirements for the box:
Flammability:
On box sample should be conditioned in an air-circulating oven at a temperature of 90±2℃ for 168h before being tested, and other samples should be tested as received. After subjected to the flame test described in the standard, the box should not burn for more than 30 s after any of the first four applications, nor more than 1 min after the fifth application of the test flame, and any resulting openings in the material should not permit a 6.4mm diameter probe to pass through after the material has returned to approximately ambient room temperature. There should be no visible flame on the surface of the box or plaque opposite the surface to which the test flame has been applied. And there should be no glowing or burning particles during the test.
— Test information and table data cite and reference standard C22.2 No.18.2.
Crushing:
The box should be subjected to a force of 11000 N for 30 s after being conditioned for 7 h at 90±2℃, and should not crack and the amount of deflection of the boxes should not exceed 15%. The test method is clearly described in the standard.
Impact:
The box is tested at room temperature, and be placed on its side with the open face perpendicular to the bar. A 2.7kg test mass, with a 20*150mm striking face of 9.5mm thick polyurethane, dropping from a height of 460mm to strike the box adjacent to the edge of the open face. And the box should not break and not show any loss of integrity, nor permit the free passage of a 0.8mm steel rod through any resulting crack.
— Test information and table data cite and reference standard C22.2 No.18.2.
Requirements for PVC Gang Boxes | ||
Test Requirements | UL 514C | CSA C22.2 No.18.2 |
Flammability | Not flame more than 1min after fifth application for box used with nonmetallic tubing | Not burn for more than 30 s after any of the first four applications, nor more than 1 min after the fifth application |
Not flame more than 5s after third application for box used with nonmetallic rigid conduit | ||
抗压强度 | Box used with nonmetallic tubing: Condition 7h at 90℃ oven, subject to 11121 N force. | Condition 7 h at 90±2℃, subject to a force of 11000 N for 30 s |
Box used with nonmetallic rigid conduit: Subject to 22241 N force. | ||
抗冲击性 | Box for use with nonmetallic tubing: Some samples are conditioned 5h at minus 20±1℃, drop it onto a concrete floor twice from a height of 54 feet; Some using 6 pound (2.72 kg) test weight to strike the sample at room temperature. | Using a 2.7kg test mass, dropping from a height of 460mm to the box. |
Box for use with rigid nonmetallic conduit: Subject to the impact of a 75 pound 6-inch diameter cylindrical steel | ||
Fill Capacity of Gang Boxes

Understanding box fill capacity is crucial to ensure safety and compliance with electrical standards. Box fill determines the maximum number of wires and devices that can be safely accommodated inside an electrical box.
Single Gang Box:
A single gang box typically have 18 cubic inches of space and you can fit:
- 9 wires of #14 gauge
- 8 wires of #12 gauge
- 7 wires of #10 gauge
- Electrical Device for one switch or outlet.
Double Gang Box:
For double-gang boxes, which have two separate regions, with 34.3 cubic inches of space, and you fill:
- 16 wires of #14 gauge
- 15 wires of #12 gauge
- 13 wires of #10 gauge
- House two devices
Triple Gang Box:
Triple gang box typically with 52.9 cubic inches of space, and you can fill:
- 24 wires of #14 gauge
- 22 wires of #12 gauge
- 20 wires of #10 gauge
- House three devices
Four Gang Box:
Four gang box that with 71.5 cubic inches of space, you can fill:
- 32 wires of #14 gauge
- 30 wires of #12 gauge
- 28 wires of #10 gauge
- House four devices
Gang Box Fill Capacity Chart
Box Type | Box Volume(cu in) | #14 Gauge | #12 Gauge | #10 Gauge | Devices |
Single Gang | 18 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 1 |
Double Gang | 34.3 | 16 | 15 | 13 | 2 |
Triple Gang | 52.9 | 24 | 22 | 20 | 3 |
Four Gang | 71.5 | 32 | 30 | 28 | 4 |
These are just some common box types for reference, not all gang boxes are with the same dimensions and spaces, the specific number of conductors is depending on the box’s space you are using. Different regions could have different requirements and regulations for box fill, follow your local when installing the gang boxes.
Buying Guide for Gang Boxes
5 Things You Need to Know Before Purchased Gang Boxes
When selecting gang boxes for your electrical installations, consider the following factors:
- Size and Capacity: Choose a gang box size that can accommodate the number and type of devices you plan to install. Ensure it has sufficient capacity for wiring connections.
- 材料: Select a material (metal, plastic, fiberglass, PVC) based on environmental conditions, durability requirements, and compatibility with wiring methods.
- Mounting Method: Consider the mounting method (nail-on, screw-on, adjustable) that best suits the installation surface and provides secure attachment.
- 特征: Look for features such as knockouts, cable clamps, and built-in grounding screws to facilitate wiring connections and installation convenience.
- Certifications: Check for UL or CSA certifications to ensure the gang box meets safety and quality standards established by reputable testing organizations.
4 Different Applications of Gang Boxes
- Residential Use: For residential applications, consider plastic gang boxes for lightweight installations or metal gang boxes for added durability and protection.
- Commercial Settings: In commercial environments, opt for metal gang boxes with ample capacity and features like knockouts for versatile wiring configurations.
- 工业应用: Choose heavy-duty metal gang boxes with corrosion-resistant coatings for industrial settings that require robust and long-lasting solutions.
- 户外设施: Select weatherproof gang boxes made of durable materials like aluminum or PVC for outdoor installations to protect against moisture and environmental elements.
Pricing and Budget Considerations
Gang box prices can vary based on factors like material, size, features, and brand. Consider the following budget considerations:
- Quality vs. Cost: Balance quality and cost by choosing gang boxes that meet safety standards and durability requirements while staying within your budget.
- Bulk Purchases: Buying gang boxes in bulk quantities may offer cost savings per unit, especially for larger projects or ongoing installations.
- Value-added Features: Evaluate the value of additional features like built-in clamps or adjustable mounting options relative to their impact on cost.
Where to Buy Gang Boxes
You can purchase gang boxes from various sources, including:
- Local Stores: Local stores often carry a selection of gang boxes in different sizes and materials for residential and commercial use.
- Electrical Supply Retailers: Specialty electrical supply stores offer a wider range of gang boxes, including options for specific applications and industrial settings.
- Online Retailers: Explore online platforms that sell gang boxes to compare prices, read reviews, and access a broader selection of brands and models.
- Wholesale Manufacturer: Wholesale manufacturer may offer competitive pricing on gang boxes for bulk purchases or larger projects. Better choose manufacturers with reputation and product certifications. Ledes is manufacturer of electrical conduit products and fittings, including various of electrical boxes, with UL and CSA certificates, and well recognized in some large projects, it is good choice for electrical conduit relative products purchasing.
Before buying gang boxes, ensure you have considered the necessary factors, recommendations for specific applications, pricing considerations, and where to purchase them to make an informed decision that meets your electrical installation needs.
结论
In conclusion, gang box is an essential part in electrical installations, selecting the right gang boxes for your electrical installations is crucial for ensuring safety, reliability, and longevity in your wiring system. Throughout this guide, we have covered essential aspects related to gang boxes, including technical specifications, applications, standards, and purchasing considerations.
通过仔细选择符合您的安装要求和标准的接线盒,您可以延长电气系统的使用寿命和可靠性。
如有任何问题和要求,请随时联系我们 提交表格 或者 向我们发送电子邮件。



