目录
In the world of electrical conduits, customers often ask about the distinctions between DB2 conduit and Schedule 40 conduit. While both are widely used for protecting electrical wiring, each has unique properties, compliance standards, and application benefits. Choosing the right conduit depends on a project’s specific needs, such as strength requirements, installation environment, and regulatory compliance. This article provides a comprehensive comparison of DB2 and Schedule 40 conduits, covering their definitions, standards, mechanical properties, fitting options, and applications, to help you choose the right conduit for your project.
DB2 conduit, or Direct Burial 2 conduit, is a type of rigid, non-metallic conduit specifically engineered for underground installations. It is designed to endure external pressures from soil and resist environmental corrosion. DB2 conduit complies with CSA C22.2 NO. 211.1, a Canadian standard that certifies its durability for direct burial in diverse soil conditions.
Schedule 40 conduits is a rigid PVC (polyvinyl chloride) conduits designed for both above-ground and below-ground installations. Known for its durability, it can be installed in exposed or concealed spaces and provides excellent protection for electrical wiring in both indoor and outdoor environments. Which appliable for Low-voltage cables are used for telephone, internet, television, and security system wiring protection. Schedule 40 conduit must meet the UL651 standard, which specifies the performance and safety requirements for plastic conduit.

DB2 Conduit: CSA C22.2 NO.211.1, this standard sets guidelines for direct burial use in underground applications in Canada.
Schedule 40 PVC Conduit: UL651, the standard governs the performance, durability, and safety requirements for PVC conduit in the U.S.
These standards ensure that each conduit type meets specific mechanical and safety performance metrics, making them reliable choices for their intended applications.
Both DB2 and Schedule 40 conduits must adhere to a set of properties as outlined in their respective standards. Here are comes common required properties:

Schedule 40 Conduit
According to UL651, Schedule 40 rigid PVC conduit must meet a specific tensile strength requirement. It must not be less than 5000 psi (34.5 MPa) in unaged specimens. This strength ensures the conduit can withstand significant stress without elongation or breaking, making it suitable for both above-ground and underground applications where exposure to environmental variations, movement, or handling might introduce tensile stresses. In any case, tensile strength of conduit shall not be less than:
- a) 5,000 psi (34.5 MN/m2) (3.45 kN/cm2) (3515 gf/mm2) for Schedule 40 and 80 rigid PVC conduit
- b) 4000 lbf/in2 (27.6 MN/m2 or 2.76 kN/cm2 or 2812 gf/mm2) for Type A and EB rigid PVC conduit
To assess this requirement, three unaged specimens of Schedule 40 conduit are tested to determine their baseline tensile strength. These specimens are then aged, and the average tensile strength of the aged samples must equal or exceed 95% of the average tensile strength of the unaged specimens. This aging test follows procedures similar to those described in the Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics (ASTM D 638), ensuring the conduit retains its strength under different conditions.
These specifications make Sch 40 conduit an excellent choice for applications that require durable, high-strength conduits, even in environments where temperature fluctuations or potential exposure to stressors are more common.
DB2 Conduit Tensile Strength
For DB2 conduit, used primarily in direct burial applications, there is no specific tensile strength requirement defined by the CSA C22.2 NO. 211.1 standard. Since DBii conduit is installed underground, where the temperature remains relatively stable and protected from the above-ground elements, it experiences less exposure to stressors that might necessitate strict tensile strength benchmarks. This stability in the installation environment helps minimize thermal expansion and contraction issues, reducing the need for high tensile strength performance in DB2 conduit.
Schedule 40 Conduit Impact Resistance
According to UL651 (Article 6.6, Table 6.2), Schedule 40 conduit must undergo a specified impact test. During this test, a 20-pound (9.1 kg) weight is dropped onto the conduit from a set height, with the weight shaped as a cylinder with a 2-inch (51 mm) diameter. This requirement ensures that Schedule 40 conduit can handle physical impact, making it suitable for exposed installations where accidental impacts may occur, such as in above-ground applications.
交易规模 | Height above the Specimen (Schedule 40) | |
脚 | (m) | |
1/2 | 2-1/2 | 0.762 |
3/4 | 4 | 1.22 |
1 | 5 | 1.52 |
1-1/4 | 6 | 1.83 |
1-1/2 | 7-1/2 | 2.29 |
2 | 9-1/2 | 2.90 |
2-1/2 | 10-1/2 | 3.20 |
3 – 6 | 11 | 3.35 |
DB2 Duct Impact Resistance
For DB2 conduit, CSA C22.2 NO. 211.1 (Clause 6.2) specifies a different impact testing method. DB2 conduit must withstand an impact energy of 61 joules at 23 ℃ (73.4 ℉) and 34 joules at –18 ℃ (0 ℉). This method ensures that DB2 conduit maintains its integrity under varying temperatures, particularly in colder conditions where the material may be more brittle. Given its direct burial application, DB2 conduit’s impact resistance is optimized for underground environments where it may encounter forces from soil or equipment.
If you are interested in the Impact Resistance section, you can click here to read the Impact Resistance performance insights of PVC conduit written by our technical team.
导管类型 | Impact Test Method | Weight/Force | Temperature |
Schedule 40 Conduit | UL651, Article 6.6, Table 6.2 | 20 lbs (9.1 kg) | 23.0 ± 2.0℃
|
DB2 Duct | CSA C22.2 NO. 211.0, Clause 6.3.1, Method A | 1.36 kg ± 10 g 61 J at 23 ℃, 34 J at -18 ℃ | 23 ℃ and -18 ℃ |
Resistance to crushing is a critical property for conduits, ensuring they can withstand external pressures without deformation.
Schedule 40 Conduit Resistance to Crushing
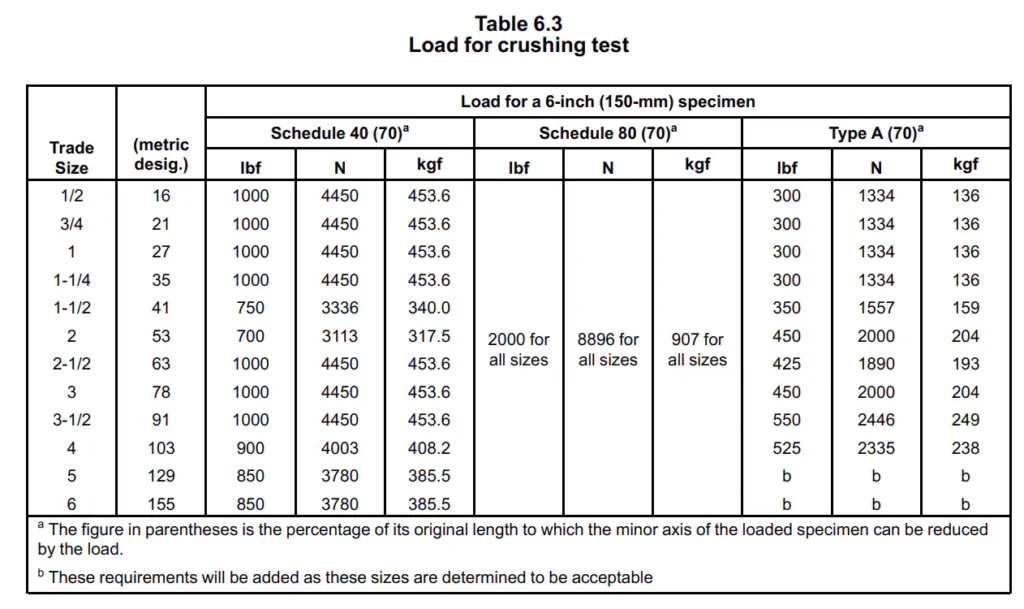
Under UL651 (Article 6.9), Schedule 40 conduit is subjected to a crush test to evaluate its resistance to deformation. And the conduit shall not flatten under the load indicated in table 6.3 to the point where they buckle, and the minor axis measured inside each loaded specimen shall not be less than 70 percent of the inside diameter of the specimen measured before loading.
- Plate Movement Rate: The plate is to be moved toward the other at the rate of rate of 1/2 ±1/8 inch (10.0 ±2.5 mm) per minute, until the load specified in Table 6.3 is applied as indicated on the dial on the machine.
The standard requires Sch 40 conduit to maintain its structural integrity up to a specific threshold, which simulates real-world conditions where the conduit may be exposed to weight or pressure from above-ground installations, such as traffic loads or heavy machinery. This ensures the conduit remains functional and safe even in environments where it might face significant physical compression.
DB2 Conduit Resistance to Crushing
For DB2 conduit, CSA C22.2 NO. 211.1 (Article 6.3) provides the specific requirements for crush resistance in direct burial applications. It requires the percentage decrease in diameter under and after recovery shall not exceed 10% on DB2, and shall not exceed 5% after recovery.
- 加载应用程序: A 90 kg mass (including the platen) is gradually applied and held for 60 ± 5 seconds.
- Diameter Measurement Under Load: While the mass is applied, the vertical inside diameter is remeasured.
- Recovery Measurement: After the load is removed, the conduit recovers for 300 ± 20 seconds before the diameter is measured again.
- Deformation Calculation: The percentage decrease in diameter is calculated, both under load and after recovery, indicating the conduit’s crush resistance.
This standard specifies that DBII conduit must endure a particular load per unit length to simulate the weight of soil or other materials that may be exerted on the conduit when buried underground. The CSA standard is designed to ensure DB2 conduit can withstand the unique stressors of buried installations, where it is not only protected from direct surface loads but also faces prolonged pressures from the surrounding soil.
Schedule 40 Conduit Stiffness
For Schedule 40 PVC conduit, pipe stiffness is assessed according to ASTM D 2412 (Standard Test Method for Determination of External Loading Characteristics of Plastic Pipe by Parallel-Plate Loading). Schedule 40 conduit used in directional boring applications must meet a minimum pipe stiffness of 120 psi (827 kPa) at 10% deflection. This ensures that Schedule 40 maintains structural integrity and resists deformation under external pressure.
DB2 Conduit Stiffness
DB2 conduit, tested per ASTM D 2412 as well, has stricter stiffness requirements given its direct burial application:
- Type EB1 Conduit: Must have a minimum pipe stiffness of 200 kPa at 5% deflection.
- Type DB2/ES2 Conduit: Must meet a higher threshold, with a minimum pipe stiffness of 300 kPa at 5% deflection.
These values ensure DB2 conduits withstand underground pressures more effectively, providing added resilience against soil loads and other environmental forces typical in burial applications.
导管类型 | Minimum Pipe Stiffness | Deflection Percentage | Standard Test Method |
附表40 | 120 psi (827 kPa) | 10% | ASTM D 2412 |
Type DB2/ES2 | 300 千帕 | 5% | ASTM D 2412 |

Schedule 40 Conduit
For Schedule 40 PVC conduit, sunlight resistance is essential to ensure long-term durability when exposed to UV radiation. According to UL651, Izod impact strength tests are conducted to measure how well the material withstands prolonged exposure to sunlight.
- Initial Impact Requirement: Unaged bar samples machined from Schedule 40 or Schedule 80 conduit must achieve an average Izod impact strength of at least 0.5 ft-lbf/inch (27 J/m) of notch width. This ensures that the conduit can handle mechanical impacts even before exposure to UV.
- Extended Sunlight Exposure Testing: Schedule 40 conduit specimens undergo conditioning for 720, 1080, and potentially 1440 hours to simulate extended UV exposure. After each time interval, the average Izod impact strength is measured to ensure compliance with values specified in Table 6.4 of UL651. This test uses a process similar to ASTM D 256 (Test Method for Determining the Izod Pendulum Impact Resistance of Plastics), ensuring that the material retains impact strength even after long-term sunlight exposure. The 1440-hour test is particularly rigorous, providing assurance for extended outdoor installations.
DB2 导管
Unlike Schedule 40, DB2 conduit is designed for direct burial applications, where it is typically not exposed to sunlight. Therefore, DB2 conduit has no specific sunlight resistance requirements under CSA C22.2 NO. 211.1, as its underground environment shields it from UV radiation, eliminating the need for sunlight testing.
There is always fire resistant requirement for electrical conduit, for Schedule 40 and DB2 conduit, there are different flammability requirements.
尖端: The Sunlight Resistance and Fire Rating performance is the most important performance for electrical conduit durability, you can get more professional insights from this post for analyzing Sunlight and UV for electrical conduit.
Schedule 40 Conduit
- UL651: According to article 6.11 in UL651, Schedule 40 conduit shall not flame for longer than 5 seconds following any of three 60-second applications of flame, and the conduit shall not be capable of igniting combustible materials in its vicinity during, between, or after the three applications of the test flame.
- UL94: Beside the flammability requirements in UL651, most customers also require the conduit meeting V0 rate after testing in according to UL94. he UL 94 flammability rating is a standard developed by Underwriters Laboratories (UL) to measure how likely a plastic material is to ignite. Here are the flammability classifications included in UL94:
UL94 Rating | Orientation | Requirements |
5VA | Vertical | Burning stops within 60 seconds after five applications of flame (each application 5 seconds), no flaming drips and specimens have no burn through hole; |
5VB | Vertical | Burning stops within 60 seconds after five applications of flame (each application 5 seconds), no flaming drips and specimens may have a burn though hole; |
V0 | Vertical | Burning stops within 10 seconds after two applications of flame (each 10 application seconds), no flaming drips; |
V1 | Vertical | Burning strops within 60 seconds after two application of flame (each 10 application seconds), no flaming drips; |
V2 | Vertical | Burning stops within 60 seconds after two applications of flame (each application 10 seconds), flaming drips are allowed; |
HB | Horizontal | Burning stops before 100mm. |
DB2 导管
DB2 conduit, designed primarily for direct burial applications, follows the standards in Canada, which includes flammability classifications like FT4 and FT6:
FT4 Flame Test
The FT4 certification is highly regarded due to its stringent testing requirements. The FT4 test subjects cables to a 70,000 BTU/hour flame in a vertical tray configuration. The test procedure is demanding:
- 测试设置: Cables are mounted on a vertical tray and exposed to a 70,000 BTU/hour flame for 20 minutes. This setup simulates the intense heat a cable or conduit might be exposed to in real-world industrial fires.
- 标准: For a cable or conduit to pass FT4, the charred material must not extend more than 1.5 meters (5 feet) from the lower edge of the burner face. This requirement is specified under CSA C22.2 No. 38 and is nearly identical to the IEEE 1202 flame test. Because of the reduced char height limits, the FT4 test is considered slightly more rigorous than the UL1685 vertical tray test.
- 应用: FT4 certification is crucial for industrial and commercial spaces where vertical flame spread could pose a hazard. Passing the FT4 test ensures that the conduit will limit flame spread, enhancing fire safety in densely cabled environments.
FT6 Flame Test
The FT6 certification, often known as the Steiner Tunnel flame test (similar to the NFPA 262 in the U.S.), is even more rigorous, primarily assessing flame spread and smoke production in air-handling plenums. This is critical in HVAC systems and any environment with circulated air, where low smoke and limited flame spread are essential.
- 测试设置: The test uses a 25-foot Steiner Tunnel equipped with intake and exhaust ducts to control airflow. Cables or conduits are mounted in a tray within the tunnel, with two circular burners at the intake end. Methane is burned at 240 ft./min airflow through the tunnel for 20 minutes.
- 标准: To pass the FT6 test, the flame travel distance must not exceed 1.52 meters (5 feet). Additionally, the test monitors smoke density, requiring that the peak optical smoke density does not exceed 0.5, with an average optical density below 0.15. These criteria ensure that materials rated FT6 have excellent fire resistance and low smoke production, suitable for sensitive environments where air quality must be preserved.
- 应用: FT6-certified materials are used in air plenums, HVAC systems, and other spaces where minimizing smoke and flame spread is essential for safety and air quality.
DB2 导管配件
DB2 conduit fittings are manufactured to be compatible with direct burial applications. These fittings are designed to form watertight seals, preventing moisture ingress and protecting the electrical wiring from underground elements.
Schedule 40 Conduit Fittings
Schedule 40 fittings offer flexibility in both above-ground and underground installations. They include elbows, couplings, adapters, and junction boxes that can adapt the conduit to various layouts. These fittings are easy to install and are compatible with most Schedule 40 conduit pipes.
Fittings’ Dimension Comparison
Commonly used solvent cement fittings for both conduit types, such as couplings and elbows and bends are offer the same functions, they may also have similar outlook, but dimensions requirements are quite different, here we take elbows for example to have a dimension comparison:
交易规模 | Schedule 40 Conduit | DB2 导管 | ||
Radius R (mm) | Length Ls (mm) | Radius R (mm) | Length Ls (mm) | |
1/2 | 100 | 38 | / | / |
3/4 | 114 | 38 | / | / |
1 | 146 | 48 | / | / |
1-1/4 | 184 | 50 | / | / |
1-1/2 | 210 | 50 | / | / |
2 | 241 | 50 | 241 | 38 |
2-1/2 | 267 | 76 | / | / |
3 | 330 | 79 | 330 | 38 |
3-1/2 | 380 | 83 | 381 | 44.5 |
4 | 400 | 86 | 406 | 50.5 |
4-1/2 | / | / | 508 | 57 |
5 | 600 | 92 | 610 | 63.5 |
6 | 760 | 95 | 762 | 82.5 |

DB2 Conduit Applications: Ideal for direct burial applications, DB2 is commonly used in underground infrastructure projects, including utility lines, street lighting, and public works. Its corrosion resistance and pressure tolerance make it suitable for locations with variable soil conditions.
Schedule 40 Conduit Applications: Schedule 40 conduit is used in residential, commercial, and industrial installations, where its versatility allows it to be installed in walls, ceilings, and outdoor areas. It is suitable for applications that may be exposed to sunlight, making it popular for building wiring systems.
重量:
Schedule 40 Conduit: Schedule 40 conduit is manufactured with a thicker wall compared to DB2, which gives it greater durability and weight. This construction allows Schedule 40 to be used in both above-ground and exposed applications. Due to the thicker walls, Schedule 40 conduit is heavier than DB2, making it more robust but also more challenging to handle in certain applications. This added weight contributes to its durability and strength for both underground and exposed environments.
DB2 Duct: DB2 conduit is engineered for direct burial applications, where it does not require the same level of structural thickness as Schedule 40. With thinner walls, DB2 conduit is lighter than Schedule 40, making it easier to manage for underground installation projects where material weight and handling are critical considerations.
Wall Thickness and Socket Dimensions
To have a better understanding of their dimension requirements, here we will compare some important dimension data of them:
de Size | Schedule 40 Conduit | DB2 导管 | ||||
Max. OD | Min. Avg. ID | 最小温度 | Max. OD | Min. Avg. ID | 最小温度 | |
1/2 | 21.54 | 14.68 | 2.77 | / | / | / |
3/4 | 26.92 | 19.81 | 2.87 | / | / | / |
1 | 33.66 | 25.50 | 3.38 | / | / | / |
1-1/4 | 42.47 | 33.90 | 3.56 | / | / | / |
1-1/2 | 48.56 | 39.72 | 3.68 | / | / | / |
2 | 60.63 | 51.33 | 3.91 | 57.30 | 50.80 | 1.78 |
2-1/2 | 73.41 | 61.31 | 5.16 | / | / | / |
3 | 89.28 | 76.40 | 5.49 | 82.75 | 76.20 | 2.03 |
3-1/2 | 102.87 | 88.54 | 5.74 | 95.00 | 88.40 | 2.29 |
4 | 115.57 | 100.60 | 6.02 | 107.30 | 100.10 | 2.67 |
4-1/2 | / | / | / | 121.70 | 114.30 | 2.79 |
5 | 142.57 | 126.36 | 6.55 | 134.85 | 126.35 | 3.81 |
6 | 169.54 | 152.04 | 7.11 | 159.65 | 149.75 | 3.94 |
交易规模 | 附表40 | DB2 导管 | ||||
At entrance | At bottom | Min socket depth(mm) | At entrance | At bottom | Min socket depth(mm) | |
1/2 | 21.64 | 21.23 | 16.56 | / | / | / |
3/4 | 27.03 | 26.57 | 18.26 | / | / | / |
1 | 33.78 | 33.27 | 22.22 | / | / | / |
1-1/4 | 42.60 | 42.04 | 23.83 | / | / | / |
1-1/2 | 48.72 | 48.11 | 26.97 | / | / | / |
2 | 60.78 | 60.17 | 28.58 | 57.53 | 57.02 | 18.92 |
2-1/2 | 73.41 | 72.85 | 37.31 | / | / | / |
3 | 89.28 | 88.70 | 40.49 | 83.08 | 82.42 | 37.97 |
3-1/2 | 101.98 | 101.40 | 42.85 | 95.38 | 94.51 | 38.10 |
4 | 114.68 | 114.07 | 44.45 | 107.57 | 106.91 | 43.94 |
4-1/2 | / | / | / | 122.43 | 121.06 | 50.80 |
5 | 142.06 | 141.05 | 49.20 | 135.38 | 134.47 | 62.99 |
6 | 169.11 | 168.00 | 53.98 | 160.15 | 159.26 | 74.93 |
There are different marking requirements for Schedule 40 conduit and DB2 conduit according to UL and CSA standards, bellow are the marking requirements from CSA C22.2 No.211.1 and UL651:
加拿大航空
Each standard length of conduit and each elbow and bend shall be marked legibly and durably to show the
- a) manufacturer’s name, trademark, or other recognized symbol of identification;
- b) product designation;
- c) trade size;
- d) date of manufacture or manufacturer’s code; and
- e) CSA Standard number.
Each fitting shall be marked legibly and durably on its outside surface to show the
- a) manufacturer’s name, trademark, or other recognized symbol of identification;
- b) product designation; and
- c) trade size.
UL
8.1.3 The product, package, or label marking shall include:
- a) The phrase “rigid PVC conduit,”
- b) The trade size of the conduit product,
- c) The name or trademark of the manufacturer or any other distinctive marking by means of which
the organization responsible for the product can be readily identified and
- d) The date or other dating period of manufacture not exceeding any three consecutive months.
对于弯头,制造日期应为:
1) 当挤压和弯曲同时发生在同一位置时,导管被挤压,或
2)弯头成型,其中导管在不同位置挤压。

When selecting between DB2 and Schedule 40 conduits, consider factors such as environmental conditions, budget, installation type, and regulatory requirements. DB2 conduit is better suited for underground and heavy-duty applications where additional strength and environmental protection are necessary. Schedule 40 is versatile and cost-effective, ideal for general-purpose use.
- Project Requirements
The first step is to assess the overall needs of your project. Above-ground applications are generally well-suited to Schedule 40 conduit due to its robust structural properties and compliance with outdoor exposure requirements. However, if your project involves direct burial applications, DB2 conduit is a better choice. DB2 is specifically designed for underground installations and has features optimized for soil conditions and temperature stability.
- Environmental Considerations
The environment where the conduit will be installed greatly influences the choice. For example, Schedule 40 conduit has UV-resistant properties that make it suitable for outdoor, above-ground installations where it may be exposed to sunlight. DB2 conduit, on the other hand, does not require UV resistance as it is designed to be directly buried. Consider factors such as temperature extremes, exposure to chemicals, and UV exposure when deciding on the material.
- 守则合规性
Ensuring code compliance is essential to maintain safety and quality standards. Schedule 40 conduit meets UL651 standards, while DB2 conduit adheres to CSA C22.2 No. 211.1. These standards outline specific requirements for each conduit type, including flammability, impact resistance, and crush resistance. Choose a conduit that aligns with local and national building codes for your project location.
- 成本
DB2 conduit is generally less expensive due to its lighter weight and thinner wall construction, making it a cost-effective option for underground installations. Schedule 40, being more robust, is typically more costly. Balancing upfront costs with the long-term durability requirements of the project is an important consideration when budgeting for materials.
- Installation Cost
Schedule 40 conduit is heavier and may require more manpower and resources for installation, especially in above-ground settings where supports are needed. DB2 conduit, being lighter and optimized for burial, is often easier to install underground, which can lower installation costs. Assessing installation costs based on conduit weight, accessibility, and equipment requirements can help determine the best choice for budget-conscious projects.
- Variety
Schedule 40 offers a wider range of fittings and sizes, making it versatile for various applications and configurations. If your project demands flexibility in conduit diameter, fittings, or accessory options, Schedule 40 may offer more variety to match specific design needs. DB2 conduit generally has more limited sizing and fitting options, as it’s typically optimized for straightforward underground installation.
- Consulting with Professionals
Consulting with industry professionals or conduit suppliers can provide invaluable insights tailored to your unique project needs. Professionals can assess your project specifications and environmental conditions to recommend the most suitable conduit type. Their expertise can also help you stay within budget while ensuring code compliance and optimal performance.
In summary, both DB2 and Schedule 40 conduits offer reliable protection for electrical wiring but are optimized for different environments and project requirements. DB2 conduit is designed for durability in underground, direct burial applications, with higher wall thickness and robust crush resistance. Schedule 40 conduit, on the other hand, provides versatility, affordability, and ease of installation for general-purpose applications.
At Ledes, we are committed to providing high-quality, certified conduit solutions that meet both CSA and UL standards, including options in both DB2 and Schedule 40 types. Our products are rigorously tested to ensure they meet industry standards for durability, safety, and performance, making them a trusted choice for contractors and engineers across diverse applications.
Choosing the right conduit depends on understanding each project’s specific needs, and at Ledes, we’re here to support our clients in finding the optimal solution for their electrical infrastructure needs.



