
目录
Electrical conduit plays a crucial role in protecting and housing electrical wiring systems. It serves as a conduit for electrical cables, providing a safe and organized pathway that helps prevent damage and ensures the smooth flow of electricity. In this article, we will delve into the important topic of fire and UV resistance rating for electrical conduits. Understanding these ratings is essential for selecting the appropriate conduit types and ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical installations.
Fire Resistance Rating
定义

Fire resistance rating refers to the ability of an electrical conduit to withstand fire and prevent the spread of flames and smoke. In the event of a fire, a conduit with a high fire resistance rating can help contain the fire within a limited area, minimizing damage and allowing for a safer evacuation. Fire resistance ratings are typically determined through rigorous testing procedures, which evaluate the conduit’s performance under elevated temperatures and exposure to flames.
Actual Importance
The fire resistance rating of an electrical conduit is of utmost importance for the safety of electrical installations. It plays a crucial role in containing a fire within a specific area and preventing its rapid spread to other parts of a building or facility. By withstanding the effects of fire, a conduit with a high fire resistance rating enables more time for evacuation and reduces the risk of property damage.
Rating Dimensions
The Fire Resistance Rating of PVC electrical conduit is determined through standardized testing methods conducted by recognized testing laboratories such as Underwriters Laboratories (UL) and the Canadian Standards Association (CSA). These tests evaluate the conduit’s ability to withstand fire exposure and measure its performance in terms of flammability and resistance to fire propagation.
UL Flammability Testing for PVC Electrical Conduit:
UL (Underwriters Laboratories) also conducts flammability testing for PVC electrical conduit using the UL 94 standard (Standard for Tests for Flammability of Plastic Materials). This standard evaluates the material’s response to ignition and flame propagation. The testing methods specified by UL 94 assess the behavior of PVC conduit when exposed to a flame source.
UL 94 defines specific flammability ratings for PVC materials, including electrical conduits. The ratings are as follows:
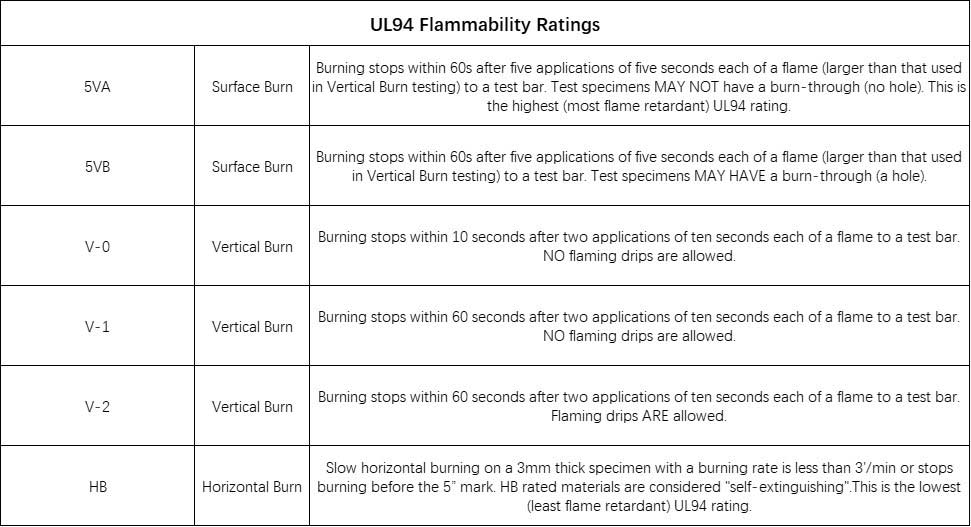
UL Flammability Testing Standard
CSA Flame Test
CSA standards have specify the fire resistance rating for electrical conduit, CSA C22.2 No. 211.0 is the Canadian standard that covers flame tests for wires and cables. This standard specifies the testing methods and performance requirements for various flame ratings, including FT4 and FT6. Here are the details of the testing methods and assessment criteria:
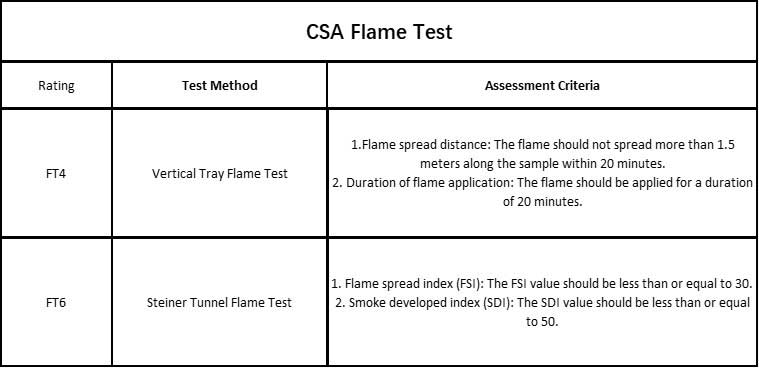
CSA Flame Test Standard
UV Resistance Rating
UV Resistance Rating for electrical conduit refers to the ability of the conduit material to withstand the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun over a prolonged period. Here’s an overview of UV and its definition, hazards, and rating standards:
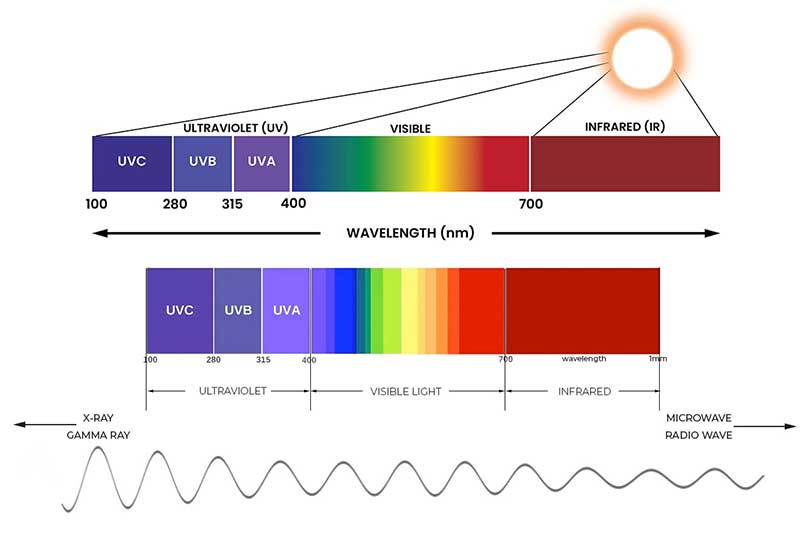
UV Definition:
UV radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation with shorter wavelengths than visible light. It is divided into three categories based on wavelength: UVA, UVB, and UVC. UVA has the longest wavelength and is the least harmful, while UVB and UVC have shorter wavelengths and can cause more damage to materials and living organisms.
UV Hazards:
Prolonged exposure to UV radiation can have several harmful effects on electrical conduit and other materials:
- Discoloration: UV radiation can cause the conduit material to fade, discolor, or develop a yellowish tint over time.
- Degradation: Continuous exposure to UV rays can lead to the breakdown of the conduit material’s molecular structure, resulting in brittleness, cracking, and reduced mechanical strength.
- Reduced Lifespan: UV damage can shorten the lifespan of the electrical conduit, leading to premature failure and the need for replacement.
UV Resistance Rating Standards:
There are various standards and rating systems used to assess the UV resistance of electrical conduit. These standards typically involve exposure to accelerated weathering tests that simulate long-term UV exposure. The following are some commonly used UV resistance rating standards:
UL651: Underwriters Laboratories (UL) standard for PVC conduit and fittings. It includes UV resistance requirements and testing procedures to ensure the conduit’s durability under outdoor conditions.
ASTM D2565: American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) standard that provides guidelines for conducting xenon-arc weathering tests to evaluate the weatherability and UV resistance of plastics, including conduit materials.
NEMA TC 2: National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) standard for PVC conduit. It includes requirements for UV resistance and other performance characteristics for electrical conduit systems.
UV Resistance Rating Levels:
The specific UV resistance rating levels can vary depending on the standard and material used. Generally, conduit materials are classified into different UV resistance categories based on their performance during testing. These categories may include:
UV Resistance Rating: Excellent
UV Resistance Rating: Good
UV Resistance Rating: Fair
UV Resistance Rating: Poor
The exact criteria and specifications for each rating level may differ based on the standard being used and the specific application requirements.
It is crucial to consult the relevant standards and specifications applicable to your region or industry to determine the specific UV resistance rating requirements for electrical conduit.
The significance and practical value of UV-resistant conduit

Building codes often include specific requirements for electrical installations, including the use of UV-resistant conduit in outdoor or exposed areas. These requirements are based on the understanding that UV radiation can cause significant damage to electrical conduit and compromise its performance and safety over time.
The benefits of using UV-resistant conduit in outdoor or solar projects are as follows:
- 增强耐用性: UV-resistant conduit is designed to withstand prolonged exposure to UV radiation without degrading or deteriorating. It maintains its structural integrity, mechanical strength, and electrical insulation properties over an extended period.
- Extended Lifespan: By protecting the conduit material from UV damage, UV-resistant conduit can have a longer lifespan compared to non-UV-resistant alternatives. This reduces the need for frequent replacements and maintenance, resulting in cost savings and improved reliability of the electrical system.
- 可靠的性能: UV-resistant conduit ensures consistent and reliable performance of the electrical system, even in harsh outdoor environments. It minimizes the risk of conduit failure, electrical shorts, or compromised insulation due to UV-induced degradation.
- 遵守规范和标准: Using UV-resistant conduit in accordance with building code requirements ensures compliance with safety regulations. It helps prevent potential hazards, such as electrical failures or fire risks, caused by UV damage to the conduit.
- Protection of Wiring and Components: UV-resistant conduit shields the electrical wiring and components inside from direct UV exposure. This protection helps maintain the integrity and functionality of the wiring, preventing premature aging, insulation breakdown, or performance degradation.
- 美学和视觉吸引力: UV-resistant conduit can retain its color and appearance for an extended period, even under intense UV exposure. This is particularly important in outdoor installations or solar projects where visual aesthetics are desired, maintaining an attractive and professional appearance over time.
Q & A
1. What is the temperature rating of PVC electrical conduit?
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) electrical conduit typically has a temperature rating of 60°C (140°F) or 75°C (167°F), depending on the specific type and application. The temperature rating indicates the maximum temperature at which PVC conduit can safely operate without experiencing significant degradation or damage to its structural integrity and electrical insulation properties.
PVC conduit with a temperature rating of 60°C (140°F) is commonly used in residential and light commercial applications. It can safely handle the heat generated by electrical currents within this temperature range. This type of PVC conduit is suitable for most general-purpose electrical wiring installations.
PVC conduit with a temperature rating of 75°C (167°F) is often used in more demanding applications, such as commercial and industrial settings. It can withstand higher temperatures and is designed to handle the heat generated by larger electrical loads or in environments where higher temperatures may occur.
2. Does Ledes manufacture 105°C schedule 40 PVC conduits?
Based on the certification requirements and practical construction needs, our company currently does not manufacture 105°C schedule 40 PVC conduits. Generally, PVC conduits have temperature ratings of 60°C or 75°C, which are suitable for most residential, commercial, and industrial applications, meeting safety standards and performance requirements.
From a certification perspective, PVC conduits typically need to comply with UL (Underwriters Laboratories) certification standards, such as UL 651, which ensures adherence to safety and performance criteria. Additionally, NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) certification, specifically NEMA TC 2, is also important for PVC conduit compliance with industry standards for safety, durability, and performance.
In terms of practical construction requirements, the ambient temperature is crucial. In typical electrical installations, PVC conduits are designed to handle normal ambient temperatures encountered in various settings. These temperatures generally remain well below 105°C (221°F).
Moreover, PVC conduits with temperature ratings of 60°C or 75°C are commonly used and considered sufficient for most electrical installations. They effectively handle the heat generated by electrical currents while maintaining the safety and performance of the electrical system.
3. Is electrical conduit fire rated?

Whether electrical conduit is fire-rated depends on the specific material it’s made of and the standards it adheres to. Here’s a breakdown:
Generally:
Metal conduits like steel or aluminum are non-combustible but don’t have a formal fire rating. They can help protect wires from fire damage for a limited time but won’t prevent flames from spreading indefinitely.
Non-metallic conduits like PVC can have fire ratings assigned based on specific tests and standards. These ratings indicate their ability to resist flame spread and smoke generation during a fire.
LEDES PVC electrical conduits are UL and CSA certified with top fire performance ratings. They carry the stringent UL651 Aboveground Rating and UL1653 Plenum Rating, as well as a CSA FT4 Rating.
To achieve these ratings, PVC conduit must pass specific fire resistance tests:
UL651 and CSA FT4 rated conduit passes a Vertical Flame Test (UL 94 V-0). This evaluates self-extinguishing ability – the material must extinguish a flame within 10 seconds of removal from a flame source.
UL1653 is even more rigorous, as it subjects conduit to direct flame and radiant heat exposure. PVC samples must self-extinguish flames and not melt/drip for a minimum of 30 seconds.
These tests simulate the extreme heat conditions of building fires to ensure conduit maintains circuit integrity for safe evacuation and fire response.
4. How hot can conduit get?
he temperature that a conduit can reach depends on various factors, including the type of conduit material, the surrounding environment, and the electrical load being carried. Different conduit materials have different temperature ratings, which indicate the maximum temperature they can safely withstand without degrading or compromising their structural integrity and electrical insulation properties.
Metallic Conduit:
Metallic conduit, such as rigid metal conduit (RMC), intermediate metal conduit (IMC), and electrical metallic tubing (EMT), offers higher heat resistance compared to PVC conduit. The specific heat resistance can vary depending on the type and thickness of the metal used.
Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC): RMC is typically made of galvanized steel and can withstand higher temperatures. It has a heat resistance rating ranging from 200°C (392°F) to 450°C (842°F) or higher, depending on the specific application and manufacturer’s specifications.
Intermediate Metal Conduit (IMC): IMC is also made of galvanized steel and has a heat resistance similar to RMC, typically ranging from 200°C (392°F) to 450°C (842°F) or higher.
Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT): EMT, which is made of coated steel, has a slightly lower heat resistance compared to RMC and IMC. It is generally rated to withstand temperatures ranging from 100°C (212°F) to 200°C (392°F).
PVC 导管:
PVC conduit, made from polyvinyl chloride, has a lower heat resistance compared to metallic conduit. As previously mentioned, PVC conduit typically has temperature ratings of 60°C (140°F) or 75°C (167°F), indicating the maximum temperature it can safely handle in normal operating conditions.
End
That’s it. Feeling free to contact us if you have any questions. You can simply send email to us 或者 submitted contact form to us.



