
目录
电气导管系统 导管系统是住宅、商业和工业建筑中安全高效布线的支柱。无论是新建项目还是现有建筑的升级,导管系统对于保护电缆和确保安全都至关重要。在这些系统中,一个至关重要但经常被忽视的组件起着关键作用:导管体。
电气安装中的重要性
在电气安装中,导管体对于提供保护和进入电气导管内的线路至关重要。它们的主要功能是允许电工更改导管系统内的方向或连接,为电线接头、连接点和拉点提供空间。如果没有导管体,电气系统将缺乏绕过拐角或弯道的灵活性,并且电线将更难以维护或更换。
导管体还起到保护作用,确保导管内的电线免受物理损坏、环境危害和潮湿的影响。这种保护对于系统的使用寿命和安全性至关重要,可防止短路或火灾等问题。此外,导管体可帮助电工满足法规合规性要求,确保安装符合既定的安全标准。
导管体兼具实用性和安全性,在现代电气安装中不可或缺,特别是在复杂的布线系统中,例如工业或商业环境中使用的系统。
您可以从本文中学到什么
本文将作为导管体的综合指南,分解其各种类型、应用和规范遵从性。在本文结束时,您将对以下内容有扎实的了解:
- 什么是导管体及其不同类型
- 导管体的优点
- 导管体规范和标准
- 如何安装导管体
- 导管体的应用
定义:什么是导管体?
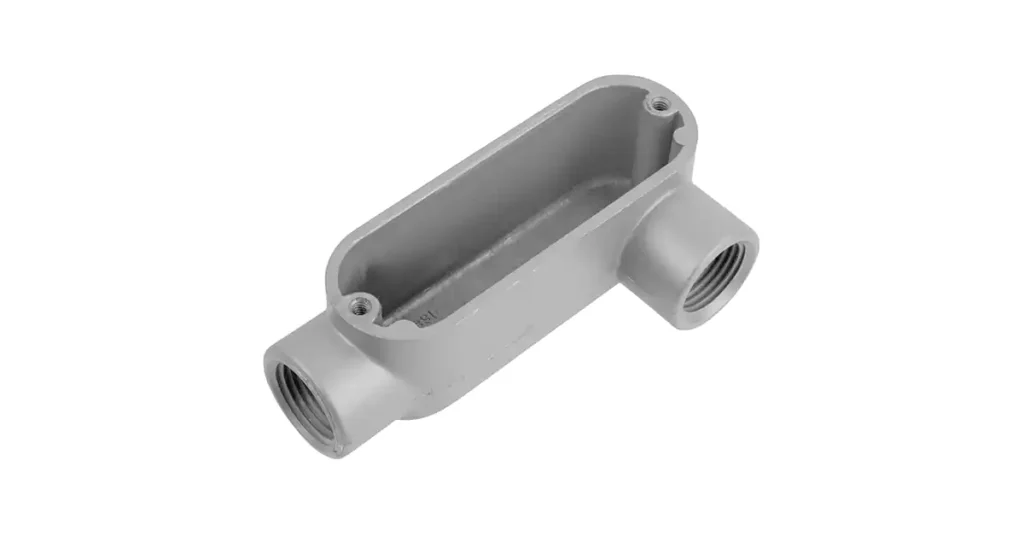

导管体是导管系统中使用的一种电气配件,旨在允许改变方向、提供拉线的接入点以及方便导管各部分之间的连接。它本质上是一个盒子或外壳,安装在导管管路中,通常安装在连接处、拐角处或需要进入导管进行维护或维修的位置。
导管体由各种材料制成,包括铝、钢和塑料,具体取决于安装和环境的具体要求。这些导管体容纳电线连接,为电线接头提供空间,并使电导体能够安全高效地穿过系统。
导管体用途
导管体最常用于 Schedule 40 和 Schedule 80 刚性导管,这两种导管都是 PVC(聚氯乙烯)导管。选择这些类型的导管是因为它们的耐用性、抗腐蚀性和易于安装。
导管体主要用于以下用途:
- 方向变化: 当导管系统需要转弯或弯曲时,导管体可实现从一个部分到另一个部分的平稳过渡。它可以适应不同程度的弯曲(例如 90°、45°),并有助于保持电线的正确排列。
- 导管连接部分: 导管体充当两个或多个导管部分相接的连接点。这些连接点对于确保系统连续性以及电线在整个安装过程中安全布线至关重要。
- 电线接入和拉动: 导管主体的主要功能之一是提供电工可以拉动、检查或安装电线的接入点。当电线需要穿过较长或复杂的导管时,这些主体特别有用,使电缆的导航和安装更加容易。
- 电线连接和端接: 导管体还允许电线拼接和端接,从而可以在导管系统内进行电气连接。这在需要连接电线或需要延长线来连接其他电路的系统中特别有用。
- 电气连接外壳: 在某些情况下,导管体充当导管内的小型接线盒。这些外壳有助于保护电气连接免受物理损坏、潮湿和污染,确保系统的安全性和使用寿命。
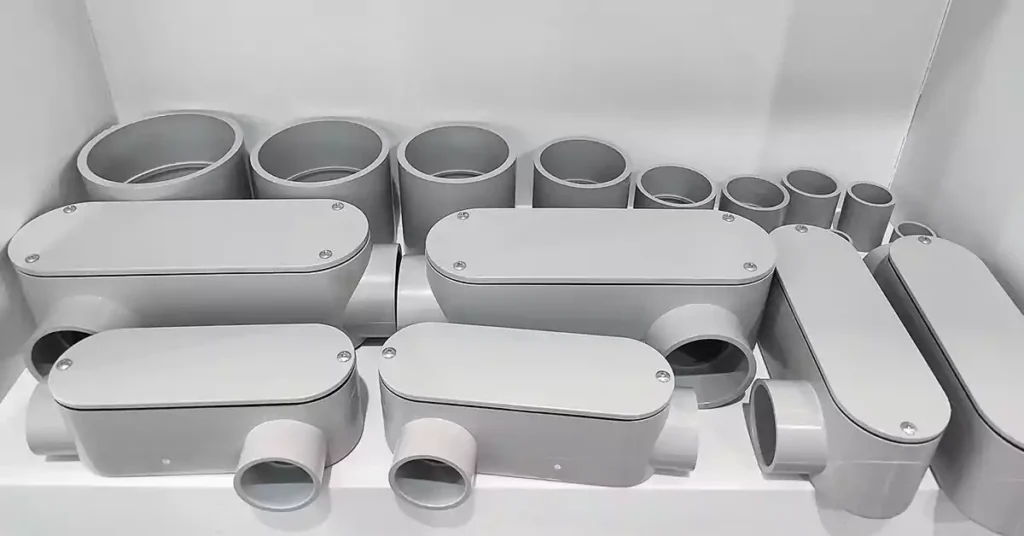
导管体类型
导管体有各种形状和设计,每种都经过量身定制,以满足电气导管系统的特定需求。这些配件用于改变导管运行方向、提供布线通道以及允许电线拼接或维护。下面,我们将介绍电气安装中常用的标准导管体类型,以及为大型系统设计的更专业的导管体类型。此外,我们将区分导管体和接线盒,因为这两个组件虽然在某些方面相似,但用途不同。
导管体的标准类型
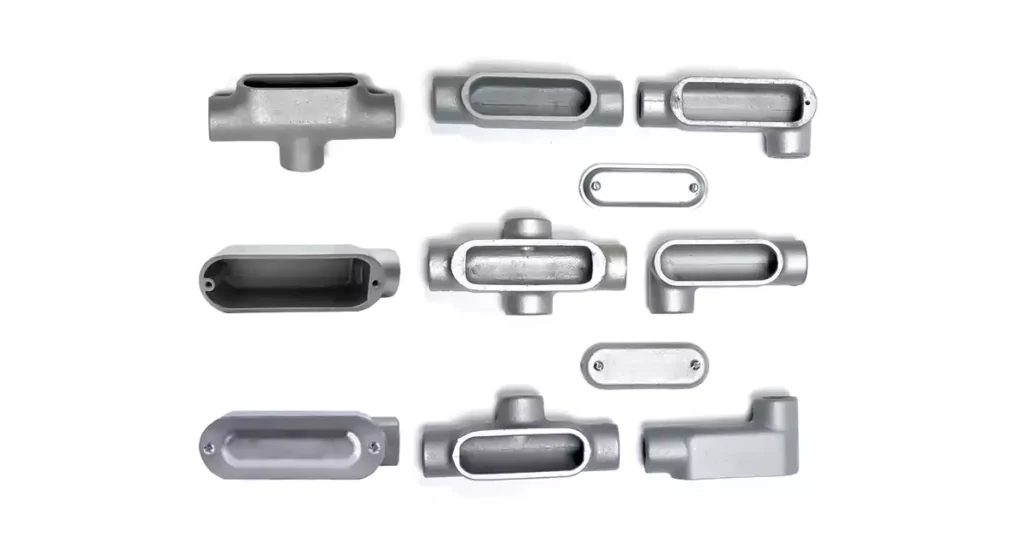

LB 导管体(侧后部):
LB 导管体是最常用的类型之一,用于在导管管路中进行 90 度转弯,同时还可用于拉线和拼接。它包括两个导管集线器(一个用于进线,另一个用于出线),允许电工绕过拐角布线。LB 导管体上的接入点位于导管体背面,非常适合穿过墙壁或表面布线。
常见用途: 非常适合导管需要以 90 度角改变方向的情况,特别是当电线需要从结构外部布线到内部时。
LL 导管体(左外侧):
与 LB 类似,LL 导管主体也形成 90 度转弯,但接线从主体左侧而不是右侧引出。此版本包括两个导管集线器:一个用于顶部的电线入口,另一个用于左侧的电线出口。与 LR 主体一样,LL 主体可用于沿同一平面重新定向接线。
常见用途: 常用于需要将电线转 90 度后向左布线的安装中。
LR 导管体(右外侧):
LR 导管体是另一种 90 度弯头配件,可让电工重新调整导管布线。此版本具有两个导管集线器:一个位于顶部用于电线入口,另一个位于右侧用于电线出口。这种设计允许调整线槽的方向而无需改变平面。
常见用途: 当需要将导管中的电线引导到正确的方向时使用,特别是在狭窄的空间或跨同一平面布线时。
T 型导管体(T 形):
T 型导管体是本列表中第一个具有两个以上集线器的导管体。它形成一个 T 形接头,其中一个导管集线器指向 90 度角,而其他两个则彼此平行。这允许电工将来自两个不同位置的电线合并到单个导管中,或者从单个导管分支到两个不同的方向。
常见用途: 通常用于需要将导管分成多个方向的情况,例如向现有系统添加新电路时。
C 导管体(直线):
C 型导管体用作直接头体。它以直线方式连接两段导管,而不会改变布线方向。它采用可拆卸板设计,方便进入导管,在管道上提供可维修点。这种类型非常适合连接不需要改变方向的导管段。
常见用途: 用于需要以直线连接或延伸导管的系统,沿途提供接入点。
E 导管体(端部接入):
E 型导管主体设计为在主体末端有一个接入点。它允许在导管末端轻松进出电线。虽然设计简单,但 E 型导管主体对于需要在导管段末端拉线或维护的安装非常有效。
常见用途: 通常用于直管道铺设,只需要一个接入点进行电线拉动或检查。
TB 型导管体:
TB 导管主体除了后部接入点外,还设计有顶部和底部接入点。这种额外的灵活性使得从多个方向拉线和拼接电线更加容易,这在狭小空间或复杂的电气系统中尤其有用。
非常适合需要多个接入点进行维护、检查或从不同方向拉电线的安装。
X 导管体(十字形):
X 型导管主体与 T 型导管主体类似,但具有四个导管中心(两组平行的导管中心形成十字形)。这种配置允许线路从同一点以多个方向进入或退出。当多个导管线路需要在中心连接处汇合时,X 型导管主体是理想的解决方案,使其成为复杂电气系统的关键组件。
常见用途: 通常用于大型商业或工业电气系统,其中多个导管需要从中心点连接或分支。
专用型导管体
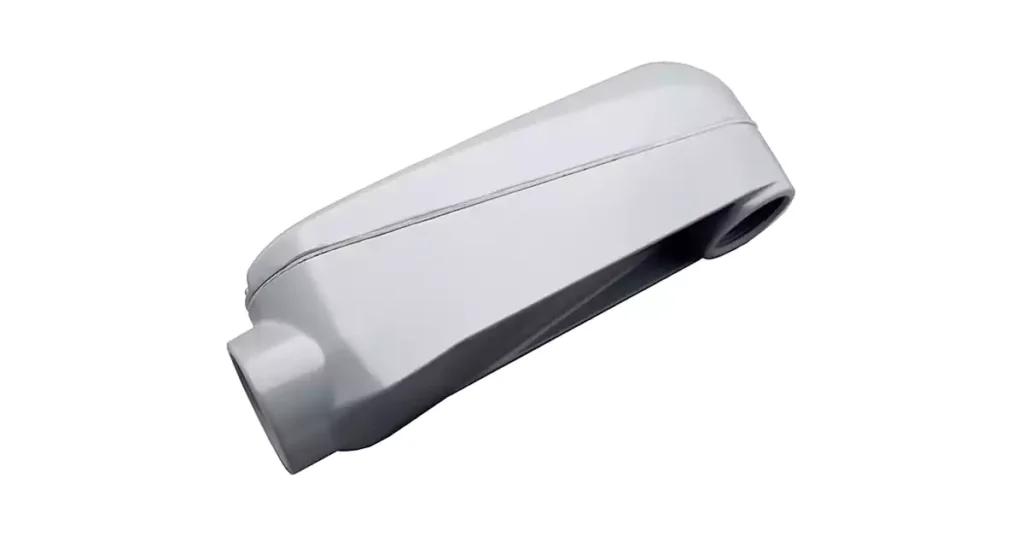

Mogul 导管体
Mogul 导管体是标准导管体的更大、更耐用的版本。它们旨在容纳更大的导管尺寸,通常用于工业应用或导管系统处理高容量的大型电气安装。Mogul 导管体非常适合需要更大、更坚固的配件来管理电线的情况。
常见用途: 通常用于需要大型导管配件来管理重载电路的工业或高容量商业电气系统。
导管体与接线盒
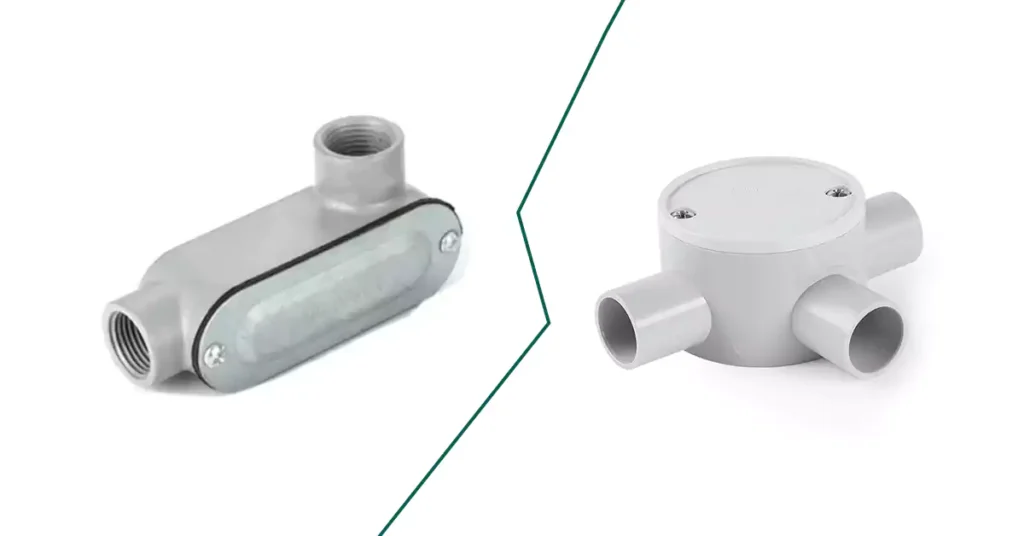

虽然导管体和接线盒都是电气装置不可或缺的一部分,但它们的用途不同,并且在不同的环境中使用。
特征 | 导管体 | 接线盒 |
目的 | 提供访问、允许方向改变或在导管系统内布线。 | 容纳并保护电气连接、接头和端接。 |
主要功能 | 改变导管的方向,方便拉线,并创建用于拼接的接入点。 | 保护和封闭电气连接,确保安全和合规。 |
地点 | 集成到导管系统中;是管道的一部分。 | 位于导管系统外部,用于保护和访问。 |
设计 | 通常具有多个用于连接导管部分的轮毂。 | 带有一个或多个用于线路连接的入口/出口点的封闭容器。 |
安装要求 | 不需要单独支撑,因为它是滚道的一部分。 | 必须独立支撑,通常安装在表面上。 |
类型 | LB、LL、LR、C、T、X、TB、E 等(各种形状用于不同功能)。 | 方形、矩形、圆形或椭圆形的盒子,通常带有可拆卸的盖子。 |
接入点 | 可直接从导管系统本身访问接线。 | 提供对接线连接的访问,以便进行维护或检查。 |
导管体的特点
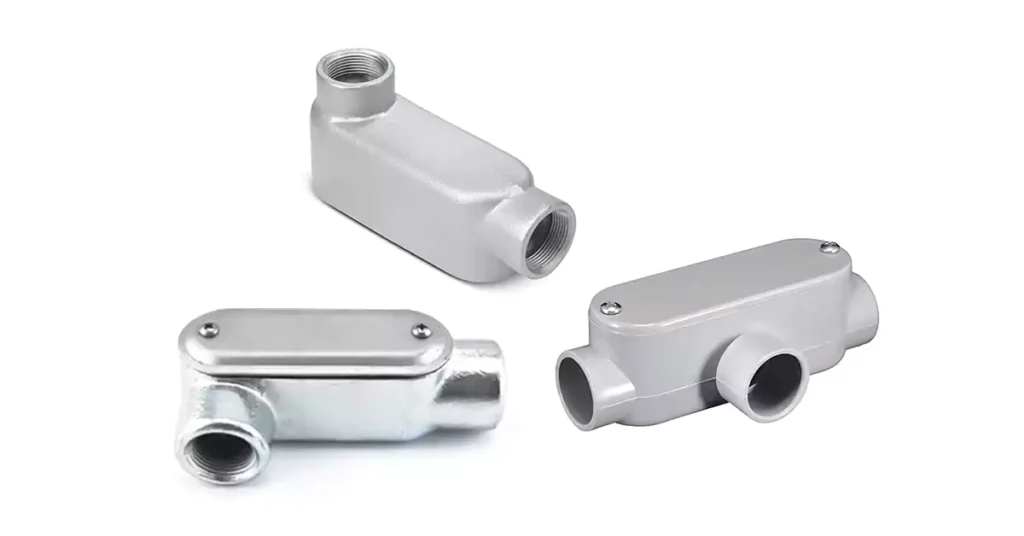

导管体是电气系统的重要组成部分,其设计因材料成分、耐候性、与导管类型的兼容性以及特定应用需求而异。本节将探讨不同的材料选择、其优缺点以及使导管体适用于各种应用的各种设计特点。
导管主体的材料选项
导管体由多种材料制成,每种材料根据环境和应用要求具有不同的优势。最常用的四种材料是铝、钢、PVC 和镀锌材料。
铝导管体
铝制导管主体重量轻、耐腐蚀且非常耐用。它们广泛用于导管主体可能暴露于潮湿或环境压力的应用中。
钢导管体
钢制导管体坚固耐用,可为高冲击或恶劣环境下的电线提供出色的强度和保护。钢通常用于需要额外机械保护的工业或商业设施。
PVC 导管体
PVC 导管体由具有耐腐蚀性的塑料材料制成,常用于需要低成本、非金属解决方案的应用。
镀锌导管体
镀锌(或镀锌)导管主体通常由钢制成,但具有保护性锌涂层以提高耐腐蚀性。它们用于导管可能暴露于潮湿、化学品或其他腐蚀性元素的环境。
优点和缺点:
防风雨、耐腐蚀
导管体的主要特性之一是其能够承受风吹日晒,因此既适合室内应用,也适合室外应用。以下是不同材料的防风雨和耐腐蚀性能的细分:
- 铝:天然耐腐蚀,但会随时间氧化。在潮湿或含盐环境中表现良好。
- 钢:坚固耐用,但除非镀锌或涂层,否则容易生锈。适用于工业环境,但需要维护以避免腐蚀。
- PVC:具有出色的耐腐蚀性,非常适合潮湿环境。它还不具有反应性,非常适合接触化学品的区域。
- 镀锌钢:提供增强的耐腐蚀性能,但仍需要维护以确保锌涂层保持完好。
选择导管主体的材料时,必须考虑天气条件、暴露于潮湿环境以及物理磨损的可能性。
与导管类型的兼容性
导管体设计为与各种类型的电气导管兼容,确保无缝集成到整个导管系统中。与导管体配合使用的一些常见导管类型包括:
- 刚性金属导管 (RMC):这是工业环境中使用的重型导管。导管体由 钢 或者 铝 是 RMC 系统的理想选择。
- 中间金属导管 (IMC):RMC 的更薄替代品, 钢 导管体最常用于 IMC 系统。
- PVC 导管:对于非金属导管系统, PVC 导管体 用于确保与导管的兼容性,并保持对潮湿或地下安装的腐蚀保护。
导管体必须与要连接的导管类型相匹配,因此兼容性是选择适合您的项目的正确类型的关键因素。
针对特定应用的设计变化
导管体有多种设计,可满足特定应用的需求。一些设计变化包括:
- 尺寸:导管体有多种尺寸,以适应导管直径并容纳需要穿过的电线数量。选择正确的尺寸可确保有足够的空间进行电线拉动和维护。
- 接入点:许多导管体都带有 可拆卸盖板 或者 多个接入点 方便拉线、拼接和系统检查。可打开和关闭机身,便于长期维护。
- 重型选件:适用于恶劣环境、重载 钢 或者 镀锌 可以使用导管体。这些导管体设计用于承受 高影响力 情况并提供增强的耐用性。
每种类型的导管体都是根据特定项目的需求而定制的,在各种安装中提供多功能性和灵活性。
导管体的规范和标准

导管体必须遵守各种监管标准,以确保其满足安全性、耐用性和性能要求。在本节中,我们将讨论 NEC(国家电气规范)对导管体的要求,包括管理其使用的关键规范、UL(保险商实验室)列表和 CSA(加拿大标准协会)认证。我们还将介绍安装的最佳实践,以确保符合这些标准。
NEC(国家电气规范)要求
国家电气规范 (NEC) 是美国为确保电气安装安全而制定的一套法规。NEC 的几个具体部分适用于电气系统中导管体的使用。这些部分概述了必要的安全措施、正确的安装做法和性能标准。
NEC 第 300.15 条 接线盒、导管体或配件:如有需要
NEC 300.15 规定了电气安装中需要接线盒、导管体或配件时的一般要求。这些组件对于在布线系统的各个点为导体提供适当的接入和保护至关重要。该规范概述了在出口点、接合点、连接点和其他关键位置使用它们的具体要求。
一般要求:
每个插座点、开关点、导体拼接点、导体连接点、导体终端点、接线方法转换点或导体拉点都必须安装盒体或导管体。此要求适用于使用导管、管材、AC 型电缆、MC 型电缆、MI 型电缆、非金属护套电缆或其他电缆的情况,除非 300.15(A) 至 (L) 明确允许例外。
NEC 第 314 条
导管体是用于连接、保护和提供各种布线安装中电导体的通道的重要部件。根据 NEC 第 314 条,导管体被归类为用作布线系统连接点的盒子或配件,可实现安全连接并确保将来维护或修改的可访问性。本文提供了有关导管体的安装、尺寸和具体用例的全面指南,以保持电气系统的安全性、效率和规范合规性。
第314条介绍了一些要点:
导管体类型:
导管体有多种材质,包括铸造金属、金属板和非金属类型。它们用作管道和电缆之间的连接点。
它们必须专门针对其预期用途进行设计和列出,以确保安全性和性能。
体积计算:
导管体必须足够大,以容纳其封装的导体的数量和尺寸。导管体的体积必须符合 314.16(C) 中规定的要求,确保有足够的空间容纳所有导体。
横截面积: 对于大多数导管体来说,其横截面积必须至少为其所连接的最大导管面积的两倍,以确保导体能够安全布线而不会过度拥挤。
安装和使用:
导管体需要以刚性和稳定的方式得到牢固支撑。这确保它们能够承受环境压力并长期保持结构完整性。
短半径导管体像弯头这样用于改变管道系统方向的管件,无需安装接头、分接头或设备。
潮湿或湿润的地方: 在潮湿的地方安装时,导管体必须设计成防止水分积聚在内部。此类安装中允许有排水口,以防止水进入。
带接头或分接头的导管体:
只有制造商标明容量的导管体才允许容纳接头、分接头或设备。这些必须符合容量要求,且尺寸适当,以处理电气负载。
防护和磨损:
必须保护进入导管体的导线免受磨损。当金属导管体上安装有未受保护的导线时,应使用绝缘套管。
导管体还需要具有足够的配件和封闭装置,以防止意外接触带电导体并保持布线系统的完整性。
较大导体的导管体:
对于涉及大于 6 AWG 的导体的安装,必须根据导体的总横截面积来计算导管体尺寸。这可确保有足够的空间进行适当的导体管理和散热。
维护和可访问性:
安装后,导管体必须保持可访问性,以便进行检查、维护和可能的升级。这对于确保安全以及允许将来进行任何修改或维修而不对布线系统造成重大破坏至关重要。
UL 认证导管主体
美国保险商实验室 (UL) 是一家独立的安全认证机构,确保电气产品符合既定的安全标准。导管体通常经过 UL 认证,这意味着它们已经通过了严格的测试,并且被认为可以安全用于电气系统。导管体的相关 UL 标准包括 UL514C 和 UL 514B。
UL 514C – 非金属插座盒、嵌入式设备盒和盖子
UL514C 规定了导管体的性能和测试要求。这些标准对于确保导管体在电气系统中安全、可靠和耐用至关重要。UL 514C 下的一些关键性能测试和要求包括:
方面: UL 514C 规定了导管体的尺寸要求,包括其横截面积要求、内部容积等。
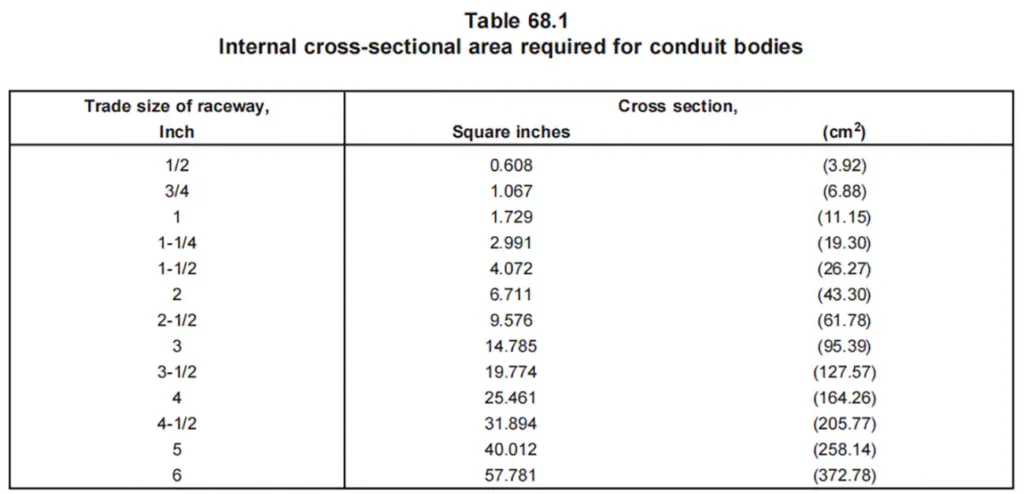
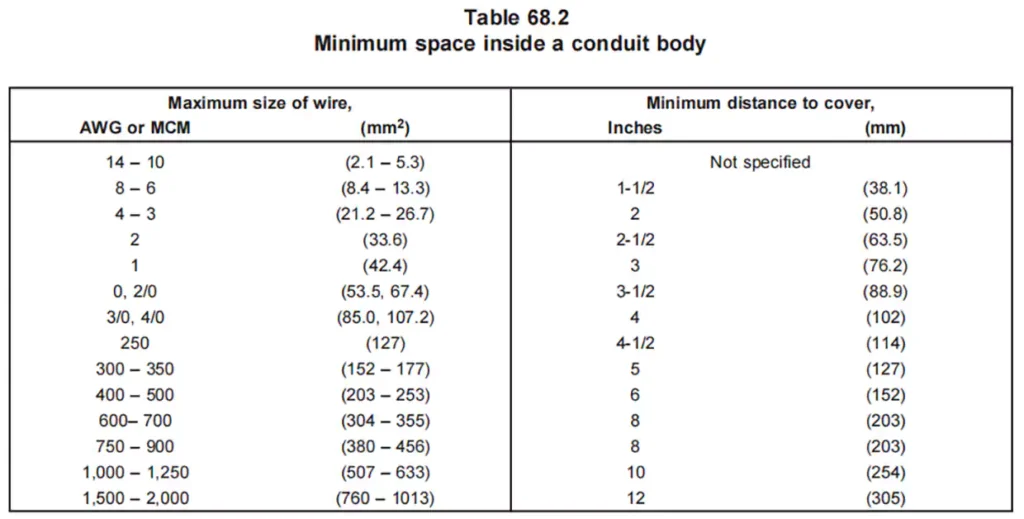
耐温性: 导管体必须承受标准规定的 92℃ 高温,且不会变形、弯曲、开裂或失去结构完整性。UL 514C 测试导管体处理极端条件的能力,确保其在高温和低温环境下都能可靠运行。
阻燃性: 要求管线盒在第三次施加火焰后 5 秒以上不助燃,且不应出现火焰滴落,管线盒不应完全烧毁。
机械强度: 导管体需接受机械应力测试,以确保其能够抵抗电气系统中常见的物理冲击、振动和其他机械应力。包括拉伸试验、冲击试验。
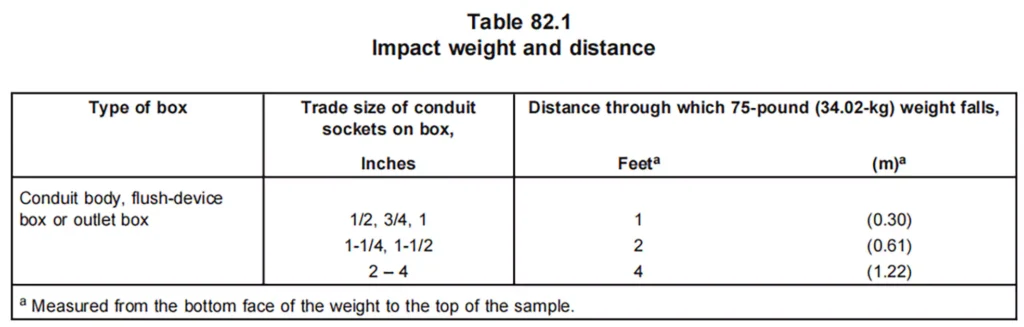
耐腐蚀性: UL 514C 要求导管体满足特定的耐腐蚀标准,特别是对于在潮湿或恶劣环境中使用的导管体。这可确保导管体不会降低或损害接线的完整性。
电绝缘性和导电性: 对于非金属导管主体,UL 514C 可验证材料是否不导电,从而防止任何电气短路或电击风险。对于金属主体,必须根据需要进行适当绝缘或接地。
防范环境因素: 在户外或恶劣环境下使用的导管体必须经过防风雨和抗湿气、灰尘和化学品等元素测试。这可确保电气系统即使在恶劣环境下也能保持安全。
UL 514B – 导管、管材和电缆配件
UL 514B 是美国保险商实验室标准,概述了导管体的结构、性能和安全要求,确保它们在电气安装中安全使用。该标准适用于用于连接管道和电缆的所有导管体,包括用于住宅、商业和工业应用的导管体。以下是 UL 514B 中概述的有关尺寸、结构材料和性能标准的关键要求。它涵盖了以下方面:
导管体尺寸:
UL 514B 规定了精确的尺寸标准,以确保导管体适合容纳导体并保持其预期功能。
施工和材料要求:
导管体制造所用的材料和施工方法对其耐用性、性能和安全性至关重要。UL 514B 规定了以下施工要求:
性能要求:
UL 514B 确保导管体符合严格的性能标准,以保证电气安全性、耐用性和整体功能性。这些包括:
体力:
抗冲击性: 导管主体必须能够承受物理冲击,不会破裂或损坏。这在受到机械应力的环境中尤为重要。
抗压强度: 材料必须足够坚固,在受到压缩时能够抵抗变形,确保导管主体在负载下保持其形状,并且在正常条件下不会崩溃或变形。
电气安全:
电气绝缘: 对于非金属导管主体,材料必须具有电绝缘性,以防止意外短路或电击危险。另一方面,金属导管主体必须正确连接和接地,以确保它们不会携带可能造成电击风险的杂散电流。
防潮、防腐蚀: UL 514B 要求导管主体具有足够的防潮和防腐蚀保护,特别是在潮湿或潮湿环境中使用时。这包括适当的密封和使用耐腐蚀材料,以长期保持电气安全。
CSA 认证 - CSA C22.2 No. 85
在加拿大,加拿大标准协会 (CSA) 制定了电气产品的安全标准。在加拿大销售的导管体必须符合 CSA C22.2 No. 85,该标准规定了电气导管和管材配件的要求。CSA C22.2 No. 85 下的一些关键要求包括:
材料和设计标准:
与 UL 标准类似,CSA 要求导管体满足特定的材料成分和设计标准,以确保它们适合在电气系统中安全可靠地使用。
导管体尺寸:
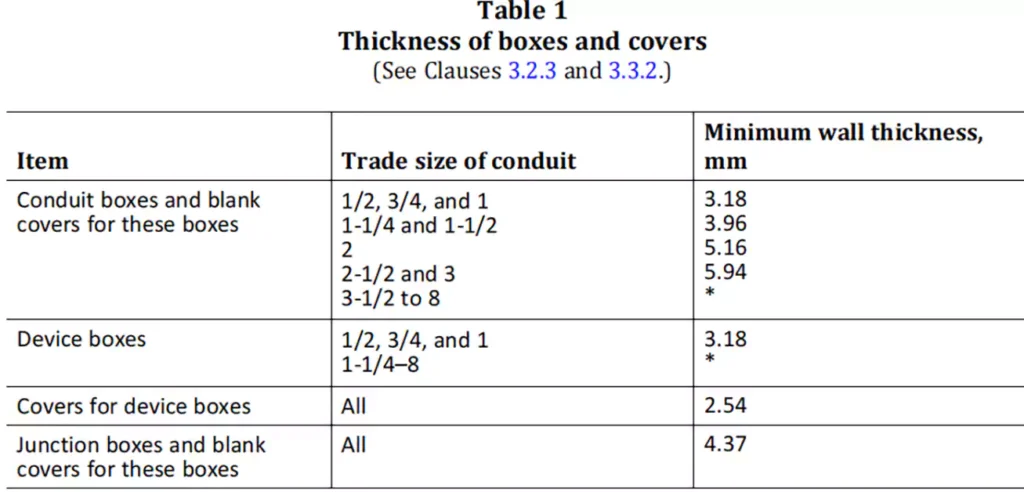
CSA C22.2 No. 85 设定了特定的尺寸标准,以确保导管体具有足够的布线空间,并可将导体容纳在管道内,而不会出现过度拥挤或安装不当的风险。
物理性能和耐久性要求:
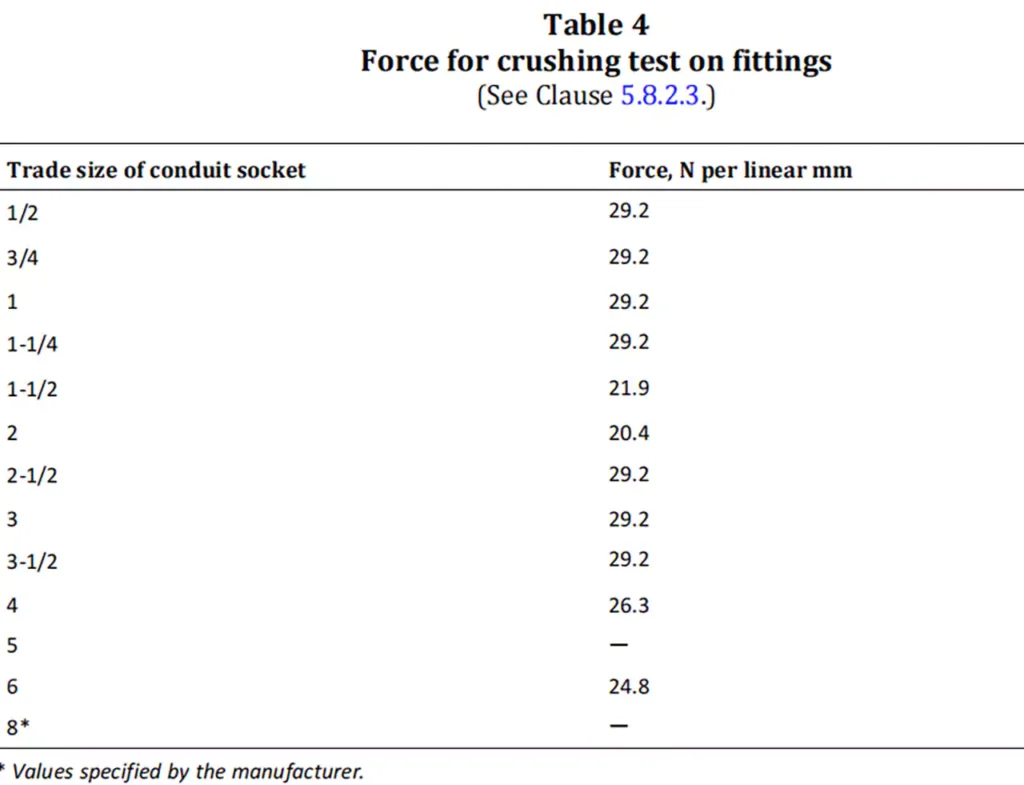
CSA C22.2 No. 85 概述了各种物理和环境性能要求,以确保导管主体能够在恶劣条件下可靠运行。这些要求包括耐热、耐火、耐-34 摄氏度冲击和耐压。
耐化学性:
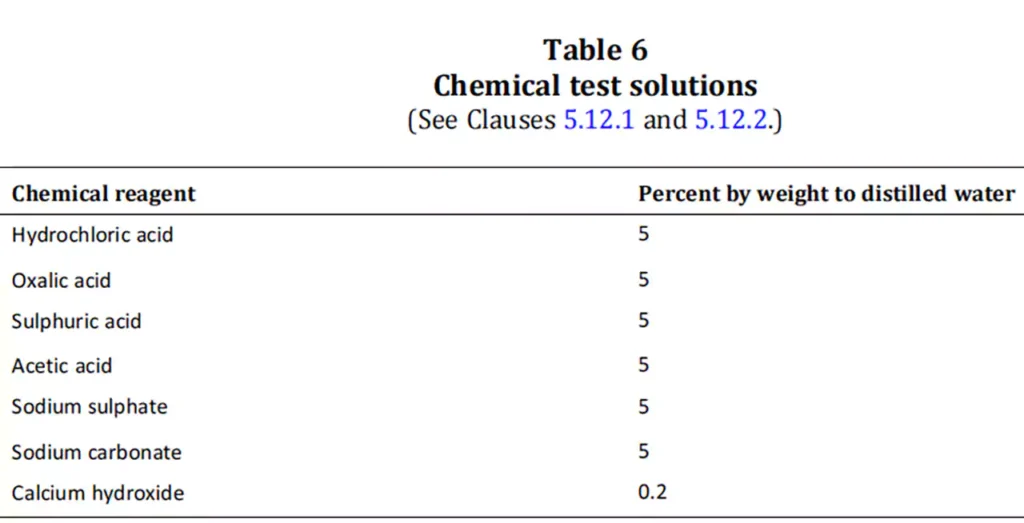
耐腐蚀性: 导管体,尤其是用于户外或工业用途的导管体,必须能够抵抗因暴露于湿气、化学品和污染物而引起的腐蚀。金属导管体尤其如此,必须对其进行处理或涂上耐腐蚀材料,以防止生锈和变质。
化学品暴露: 非金属导管体还必须具有对某些电气装置中可能遇到的常见工业化学品、油和溶剂的抵抗力,确保它们不会降解或失去结构完整性。
标记和标签:
导管体必须清晰标明制造商信息、材料类型、额定电压和 CSA 认证。耐用的标签可确保导管体得到正确使用并符合安全规定。
导管体应用
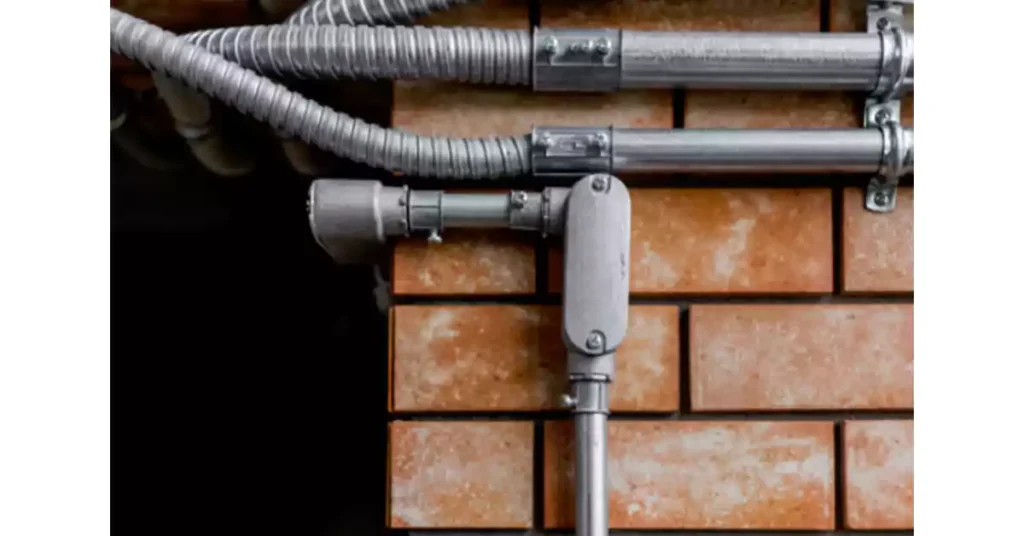
导管体是各种电气设备中用于保护和整理线路的重要部件。导管体用途广泛,适用于住宅和工业环境中的各种应用。以下是导管体的一些常见用途:
1.住宅电气系统
在家庭中,导管体用于:
接线连接: 它们为连接和连接电线提供了安全的空间。这确保了线路井然有序,便于将来维护。
保护: 它们有助于保护电线免受物理损坏和湿气、高温等环境因素的影响,尤其是在地下室或厨房等区域。
分支电路: 导管体允许电气系统分支并为多个电路供电,例如插座、灯和电器。
2. 商业和工业应用
在企业和工厂中,导管体用于:
控制面板: 它们容纳接线连接并方便访问电气系统,确保工业环境中的顺利运行。
重型系统: 它们保护工厂和仓库等高机械应力环境中的电线免受物理损坏。
自动化系统: 导管体有助于将电线安全地引导至机械、机器人和自动化设备。
3. 潮湿的地方
在暴露于潮湿的区域,导管主体的设计应满足潮湿位置的特定标准:
户外设施: 户外使用的导管体(例如用于街道照明、标牌或景观照明)旨在防止湿气侵入并保护电线免受天气相关的损坏。
潮湿环境: 在地下室、停车场或洗衣房等地方,导管体可防止湿气影响电线,从而降低短路或电气系统损坏的风险。
潮湿的地方: 在直接暴露于水的地方,例如室外游泳池、喷泉或海洋环境,适合潮湿地方的特殊导管体可以提供全面的防潮保护,确保电气系统的安全。
4.数据中心和电信
在数据中心和电信系统中,导管体用于:
管理电缆: 它们使电缆保持有序并受到保护,同时确保敏感设备基础设施内电线的安全布线。
提供安全: 导管体有助于防止电气干扰,保护电线免受外部元件的影响,并确保电气系统继续平稳运行,而不会对关键数据和通信系统造成风险。
5. 危险场所
在火灾或爆炸风险较高的环境中,例如化工厂或炼油厂,导管体的设计用于:
防爆: 防爆导管体可防止火花或电弧点燃易燃气体或蒸汽的危险,为易爆环境提供安全保障。
耐腐蚀性: 在电气系统暴露于刺激性化学物质或腐蚀性元素的区域,导管体由耐腐蚀材料制成,确保其保持其保护功能
使用导管体的 4 个好处

导管体不仅仅是功能性组件;它们具有多种优势,可提高电气设备的性能、安全性和使用寿命。以下是在电气系统中使用导管体的一些主要优势:
1. 管道布局灵活
导管体的主要优点之一是它们在设计和修改电气导管系统时提供的灵活性。
多个入口点: 导管体提供各种开口和配置,可轻松在系统内的不同位置接入。这种灵活性使更改或扩展电气系统变得更加容易,而无需完全重新设计布局。
复杂路由: 它们可以实现复杂的布线配置,例如急弯、分支或 90 度转弯,而不会损害系统的完整性或性能。这在通道受限的空间或布线必须遵循特定路径的空间中尤为重要。
Adaptability: Conduit bodies are available in many sizes and shapes, allowing them to be used in a wide variety of installations, from small residential systems to large commercial and industrial setups.
2. Simplifying Wiring Access
Conduit bodies serve as access points for wiring connections, which simplifies the maintenance, inspection, and modification of electrical systems.
Easy Maintenance: Because they are designed for easy access, conduit bodies make it much simpler to perform electrical maintenance. Technicians can easily access splices, taps, or connections housed within the conduit body without disassembling large portions of the conduit system.
Convenient Modifications: If the electrical system needs to be updated or expanded, conduit bodies provide a convenient place for adding or modifying circuits without the need to disrupt the entire installation.
Safe Access: They also provide safe and organized access to wiring, which can be important for troubleshooting or repairs, reducing the risk of accidental damage to the wiring or the system as a whole.
3. Protection of Electrical Connections
Conduit bodies play a crucial role in protecting electrical connections and ensuring the overall safety of the electrical system.
Shielding from Physical Damage: By enclosing wiring connections, conduit bodies protect them from external forces such as physical impacts, abrasion, or crushing. This is particularly important in environments where cables are at risk of being damaged by equipment, machinery, or everyday wear and tear.
Moisture and Dust Protection: In wet or damp environments, conduit bodies can be designed to prevent moisture or dust from entering the electrical connections, helping to maintain the integrity of the system and reducing the risk of electrical faults or failures.
提高安全性: Conduit bodies help maintain safe electrical systems by ensuring that connections are properly protected from environmental hazards. This contributes to reducing the risk of short circuits, sparks, and potential fire hazards.
4. Reducing Stress on Cables and Wires
Electrical cables and wires are often subjected to mechanical stresses, especially in systems with sharp bends or high traffic areas. Conduit bodies help alleviate this stress, contributing to the longevity of the wiring system.
Preventing Physical Stress: By providing a smooth path for cables and offering space for changes in direction, conduit bodies reduce the risk of kinks, tight bends, or other forms of mechanical stress on the wires. This helps prevent the potential for insulation damage and reduces the risk of wire breakage.
Minimizing Wear and Tear: Conduit bodies can also prevent direct contact between the cables and surfaces that might cause abrasion, further protecting the wiring and extending its service life.
Reducing Tension on Wires: They allow for smoother transitions and more room for wiring within the system, ensuring that wires do not experience undue tension, which can lead to failure or degradation of the cable insulation.
Conduit Body Installation Guide (7 Steps)
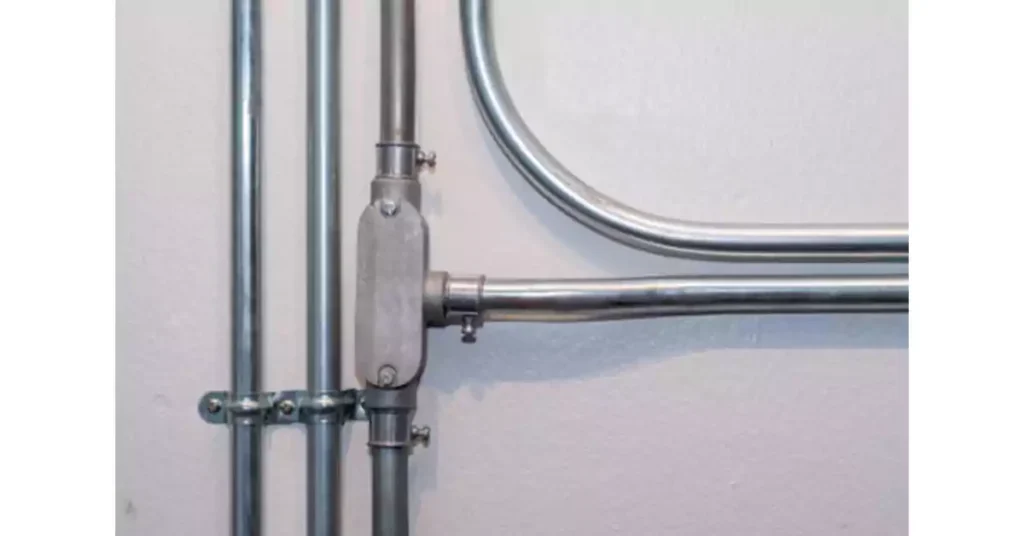

Installing conduit bodies correctly is essential for ensuring a safe and reliable electrical system. Proper installation not only helps maintain code compliance but also ensures the system operates efficiently and minimizes the risks of electrical faults or failures. This section provides a step-by-step guide to installing conduit bodies, highlights the tools needed, and emphasizes key considerations based on relevant codes of such as International Residential Code and NEC.
Tools Required for Installation
Before starting the installation, ensure you have the following tools:
- Measuring Tape: For accurately measuring distances and ensuring conduit bodies are placed in the right location.
- Screwdriver: To secure screws and fasteners in place.
- Wire Strippers: To prepare the conductors before they enter the conduit body.
- Hacksaw or Pipe Cutter: For cutting conduits to the required length.
- Conduit Bender: To bend the conduit to fit the installation layout if required.
- Drill: To create holes for mounting the conduit body if needed.
- Level: To ensure the conduit body is correctly aligned.
- Conduit Wrenches: For tightening connections securely.
Step-by-Step Installation Process (7 Steps)
1. Prepare the Conduit and Conductors
Measure and cut the conduit to the required lengths using a hacksaw or pipe cutter. Make sure the conduit ends are clean and free from burrs.
Strip the insulation from the conductors carefully, ensuring the exposed wires are ready for connection.
2. Position the Conduit Body
Select the appropriate location for the conduit body. Ensure that the position complies with NEC Code Section 314.17 for access and clearance, allowing space for wiring and other connections.
Mount the conduit body securely, using a level to ensure it is aligned correctly. Make sure it is placed at an accessible location for future maintenance.
3. Install the Conduit Entries
Connect the conduit to the conduit body by threading the conduit into the appropriate entry points on the conduit body. Use a conduit wrench to tighten the connections and ensure they are secure.
If using any fittings or bushings, ensure they are installed correctly to avoid damage to the conductors (NEC 300.4(G)).
4. Insert Conductors into the Conduit Body
Insert the prepared conductors into the conduit body, ensuring they pass through any openings smoothly and without damage. According to NEC, conductors entering the conduit body should be protected from abrasion. Use insulating fittings or bushings where necessary.
5. Close Any Openings
If there are unused openings in the conduit body, close them with approved plugs or covers as to prevent any exposure to moisture or dust, which could compromise the safety of the installation.
6. Secure and Seal the Conduit Body
Secure the cover or device to the conduit body, ensuring it is tightly fastened using appropriate screws. Follow manufacturer instructions for any specific sealing requirements.
Use non-corrosive, weather-resistant materials if installing in wet or damp environments.
7. Test the Installation
Once the conduit body and conductors are installed and secured, test the system for continuity and proper operation. Inspect all connections for tightness, ensuring that no part of the system is loose or improperly mounted.
5 Tips for Securing and Sealing
- Tighten Connections Properly: Always ensure that threaded connections between the conduit and the conduit body are tightened securely. Over-tightening can damage threads, while under-tightening can lead to leaks or faults in the system.
- Use Insulated Fittings: To protect the conductors from abrasion when entering the conduit body, use insulated fittings (per NEC 300.4(G)) where appropriate.
- Seal Unused Openings: Unused openings must be sealed using proper plugs or covers to prevent entry of moisture, dust, or debris. Ensure that these covers are properly secured.
- Waterproofing in Wet Locations: In wet or damp environments, be sure to use waterproof conduit bodies and ensure all connections are sealed with a gasket or other weatherproof material.
- Ensure Proper Grounding: Make sure that any metal conduit bodies are properly grounded as per the grounding requirements of the NEC (Section 250).
4 Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Incorrect Placement: Ensure that the conduit body is installed in a location that allows easy access for future maintenance and modification. Avoid placing the conduit body where it is difficult to reach or in locations with poor ventilation.
- Not Sealing Unused Openings: Leaving unused openings in the conduit body open can lead to moisture ingress, which could result in short circuits or corrosion over time.
- Failure to Follow Code: Make sure the installation adheres to the local code, including requirements like those outlined in NEC for securing, sealing, and mounting conduit bodies. Not complying with these can result in unsafe installations or costly repairs.
- Improper Support: Make sure the conduit body is properly supported, especially when mounted in areas with high vibration or movement. According to NEC, all enclosures should be securely mounted to prevent accidental dislodging.
Buying Guide for Conduit Bodies

Choosing the right conduit body is crucial for ensuring the safety, efficiency, and longevity of your electrical installations. With a variety of options available, it’s important to consider the specific requirements of your project, including environmental factors, installation conditions, and compliance with relevant standards. This guide will help you navigate the selection process and make an informed purchase decision.
5 Factors to Consider When Buying Conduit Bodies
1. Size and Capacity
Conduit bodies come in different sizes, often referred to as “trade sizes,” which relate to the diameter of the conduit. You need to pick a size that suits the number of conductors (wires) you will be using, as well as any future wiring that might need to pass through. If the conduit body is too small, it could lead to crowded wires that are difficult to manage. If it’s too large, it may be unnecessary and take up too much space.
2. Material
The material of the conduit body affects its durability and ability to handle environmental factors.
3. Environmental Conditions (Indoor vs. Outdoor Use)
The environment where the conduit body will be installed is crucial. For indoor use, plastic or aluminum is often sufficient. However, for outdoor use or areas exposed to moisture, heat, or chemicals, you’ll need a more rugged material like aluminum or steel. Make sure the conduit body is sealed properly to prevent water or dust from entering.
4. Compatibility with Existing Conduit Systems
Ensure the conduit body matches the size and type of conduit you’re using. Conduit bodies come in different styles (like LB, T, LL) and sizes, so check that the trade size of the conduit body matches your conduit, and that the style works with your wiring layout.
Choosing a conduit body from a reputable manufacturer ensures you’re getting a high-quality, durable product that meets safety standards. Trusted brands typically offer better customer service, warranties, and ensure that their products meet important certifications like UL or CSA.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting for Conduit Bodies
Proper maintenance of conduit bodies is essential to ensure the continued safety and functionality of your electrical system. Regular inspections and prompt attention to any signs of wear or damage can help you avoid costly repairs and potential electrical hazards. In this section, we’ll explore some key tips for maintaining your conduit bodies and troubleshooting common issues.
Routine Inspection Tips
Routine inspections are crucial to ensure that your conduit bodies remain in good condition. Here’s how to go about it:
- Visual Inspection: Start with a visual check to spot any obvious signs of damage or wear. Look for cracks, dents, or deformations in the conduit body. Check the cover and sealing gaskets for any signs of looseness, rust, or corrosion.
- 清洁度: Make sure that the conduit body is free from debris, dirt, or any other buildup that could block openings or impede airflow. Dust or dirt can build up over time, which might also affect the performance of the seals or cause overheating.
- Secure Connections: Ensure that all fasteners are tight and that the conduit body is securely mounted. Loose connections or poorly sealed conduit bodies can lead to moisture intrusion, which could damage the wiring inside.
- Check for Ingress: Examine the conduit body for any signs of water, dust, or other contaminants entering. This is especially important for outdoor or wet-location installations. Look for moisture buildup inside the body or at the conduit entry points, as this could indicate a compromised seal.
Identifying Signs of Wear and Damage
Identifying wear and damage early can save you from more serious problems down the line. Here are some common signs to look for:
Physical Damage: Look for cracks, splits, or other physical damage to the conduit body. These can weaken the structure and compromise its protective function. Impact damage is particularly common in outdoor installations, so be sure to check for any visible dents or deformations.
Corrosion: In wet or outdoor environments, metal conduit bodies can corrode over time. If you notice rust, pitting, or any signs of oxidation, this can lead to structural weaknesses and potential failure. Corrosion can also affect the electrical grounding of the system.
Loosening or Displacement: If the conduit body cover or fittings are loose or have become misaligned, this can lead to improper sealing, exposing the internal wiring to environmental factors. Tighten any loose screws and ensure that all components are properly aligned.
Moisture or Debris Inside: If you find water, rust, or other debris inside the conduit body, it could indicate that the seal is no longer intact. Moisture is especially concerning as it can lead to short circuits or corrosion of the internal wiring.
Repair and Replacement Considerations
When a conduit body shows signs of wear, you may be faced with the decision to repair or replace it. Here are some considerations to guide your decision:
Minor Damage: If the damage is minor (such as a loose cover or a small crack), a simple repair might be sufficient. Tighten any loose fasteners or replace worn seals, gaskets, or screws. For cracks or damage in plastic conduit bodies, you might be able to apply a sealant or patch if the damage is not severe.
Corrosion or Major Damage: If the conduit body is significantly corroded or structurally compromised (such as severe cracking or rusting), it is often best to replace it entirely. Corrosion can weaken the integrity of the conduit body, making it a safety hazard. A replacement ensures that your electrical system remains secure and fully functional.
Old or Outdated Conduit Bodies: If your conduit body is outdated or no longer complies with current electrical codes, it might be worth replacing it with a newer model that meets modern standards. This is particularly true if the conduit body has been in place for a long time and shows signs of aging, such as brittle materials or outdated fittings.
Cost Considerations: While repairs might seem more cost-effective in the short term, it’s important to evaluate the long-term cost. In some cases, replacing a conduit body with a newer, more durable model may be a more cost-effective solution in the long run, as it will likely last longer and require fewer repairs.
常见问题解答:

如何密封用于户外的导管体?
Sealing conduit bodies for outdoor use is essential to protect electrical connections from moisture, dust, and other environmental elements. Here’s how to properly seal them:
- Use Weatherproof Gaskets: When installing conduit bodies outdoors, ensure that the cover and the body are equipped with a weatherproof gasket or sealant. This will help prevent water and dirt from entering the body.
- Apply Silicone Sealant: For additional protection, you can apply silicone or polyurethane sealant around the edges of the conduit body cover before securing it. This creates a more airtight and waterproof seal.
- Use Approved Outdoor-Rated Fittings: When using conduit bodies outdoors, it’s crucial to use components specifically rated for outdoor use, such as weather-resistant covers and corrosion-resistant fittings.
- Check Seals Regularly: Over time, seals and gaskets may wear out, so it’s important to inspect and replace them periodically to ensure a continued waterproof barrier.
导管体用于什么用途?
Conduit bodies serve several functions in electrical systems:
- Junction Points: They act as connection points where different sections of conduit come together. Conduit bodies provide a safe, accessible location for splicing or joining electrical wires and cables.
- Wiring Access: They provide access to the wiring within the conduit system for future maintenance or troubleshooting. This allows electricians to work on the wiring without needing to dismantle large sections of the conduit system.
- Cornering and Bending: Conduit bodies, such as the LB, LR, and LL types, allow for smooth direction changes in the conduit system, helping to run wires around corners and bends.
- 保护: They offer additional protection to wiring from external elements and damage by enclosing the wires in a safe, secure box.
怎样在拐角处布置导管?
Running a conduit around corners requires either using pre-made fittings or bending the conduit manually. Here’s how to do it:
- Use Conduit Bodies: The most common method to run conduit around corners is by using a conduit body, such as the LB, LR, or LL models, which are designed for this purpose. These conduit bodies have built-in angles that allow for smooth changes in direction without the need for bends.
- Use Elbows or 90-Degree Bends: If you’re not using a conduit body, you can use elbows or pre-formed 90-degree bends. These fittings are installed directly into the conduit system to turn the conduit at the desired angle. Ensure that the bend radius meets the requirements for the type of conduit you’re using to prevent damage to the wire inside.
- Manual Bending: For metal conduit (such as EMT or RMC), you can use a conduit bender to create a custom bend around a corner. However, be mindful of the conduit’s minimum bend radius to prevent damaging the conduit or wiring.
结论
In this article, we’ve explored the essential role that conduit bodies play in electrical systems, offering both functional and safety benefits. Conduit bodies are critical for providing accessible junction points, simplifying wiring layouts, protecting electrical connections, and ensuring smooth transitions in conduit systems. Whether you’re working with an LB, LR, or LL type, each conduit body is designed to meet specific needs while adhering to safety codes like NEC and CSA standards.
Understanding the types of conduit bodies, their applications, and the importance of code compliance ensures that your installations are both efficient and safe. Regular maintenance and correct installation will keep your electrical systems functioning smoothly and compliant with industry regulations.
If you’re ready to enhance your electrical systems with high-quality conduit bodies, contact us today or explore our wide selection of conduit bodies and fittings that meet the highest industry standards. Let us help you create safe, reliable, and efficient electrical systems with the right conduit solutions!



