
Table of Contents
When it comes to electrical installations, concealed conduit wiring should be a good choice for safety and aesthetics factors.
Concealed conduit wiring involves the installation of electrical cables within rigid metal conduits or PVC conduits, which are then hidden behind walls, ceilings, or floors. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth understanding of concealed conduit wiring, exploring its benefits, installation process, and compliance with electrical codes and regulations.
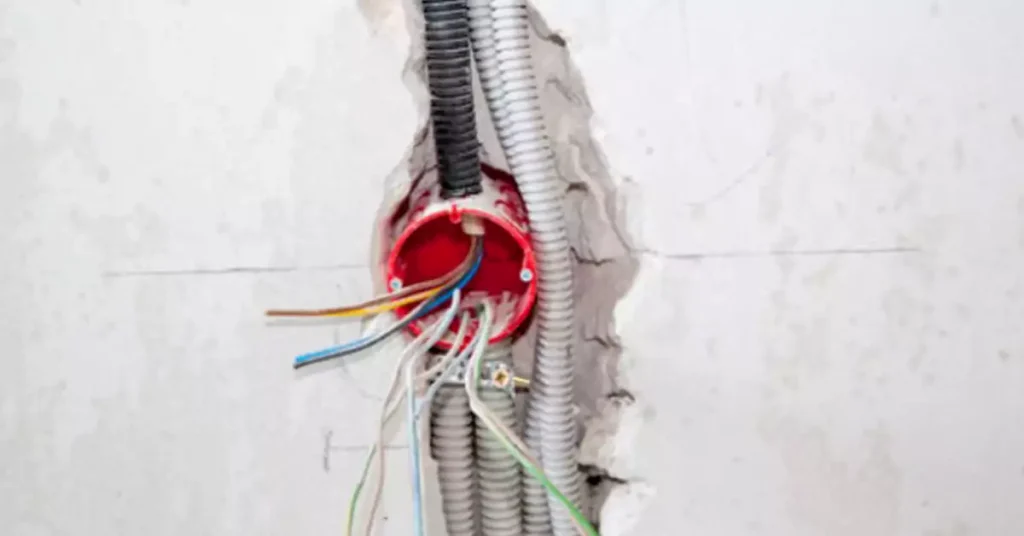
Concealed conduit wiring refers to the practice of running electrical cables within rigid metal conduits or PVC conduits that are hidden behind walls, ceilings, or floors. This method involves concealing the wiring infrastructure to enhance safety, aesthetics, and functionality in electrical installations. The conduits act as protective channels, enclosing the electrical cables and shielding them from potential damage or exposure.
Concealed conduit wiring offers a more organized and streamlined approach compared to traditional surface conduit or open wiring methods. Instead of having visible wires and cables running along the surfaces of walls or ceilings, concealed conduit wiring keeps the electrical infrastructure hidden, providing a clean and uncluttered appearance.
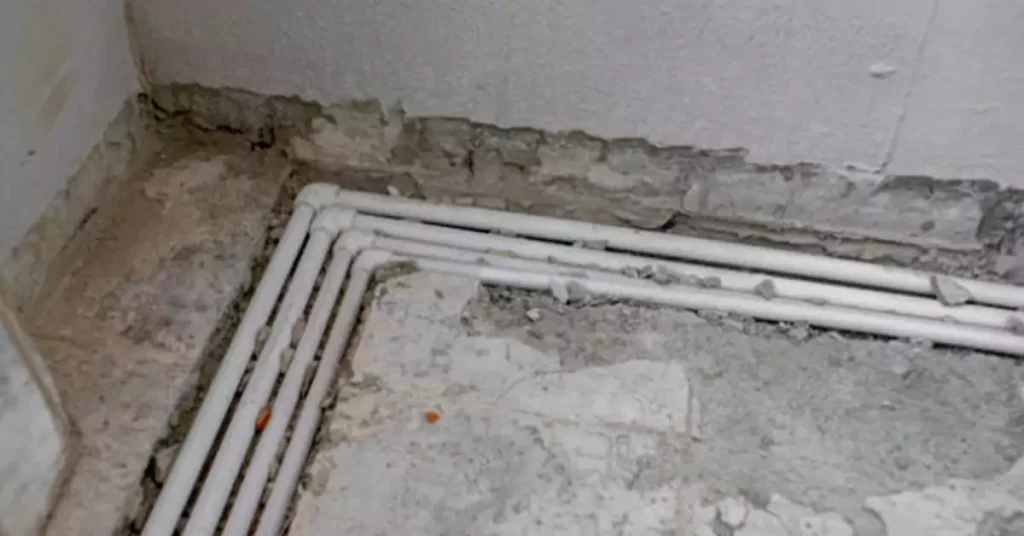

Concealing electrical wiring holds several key advantages in electrical installations:
Concealed conduit wiring prioritizes safety by providing physical protection for electrical cables. The conduits act as a barrier, safeguarding the cables from accidental damage due to factors such as physical impact, moisture ingress, or corrosive environments. By minimizing the risk of damage or exposure, concealed conduit wiring reduces the likelihood of electrical shocks, short circuits, or fires, ensuring the safety of occupants and the property.
Electrical cables can be vulnerable to external elements, such as humidity, dust, or chemicals. Concealing the wiring within conduits shields it from these environmental factors, enhancing its longevity and reducing the risk of electrical malfunctions or failures. This protection is particularly important in areas with high moisture levels, such as bathrooms, kitchens, or outdoor installations.
Concealed conduit wiring significantly improves the visual appeal of a space. By hiding the wires and cables behind walls, ceilings, or floors, the interior environment appears clean, uncluttered, and visually pleasing. This aesthetic advantage is especially desirable in settings where a sleek and professional appearance is sought, such as residential homes, offices, retail stores, or hospitality venues.
Concealing electrical wiring frees up valuable space within the room. Without exposed wires and cables, there is more flexibility in designing the layout and arrangement of furniture, fixtures, and decorative elements. The absence of visible wiring also creates a sense of spaciousness and allows for a seamless integration of electrical systems with the overall interior design.
Concealed conduit wiring offers a range of advantages that make it a preferred method for electrical installations. These benefits encompass aesthetics, protection and safety, flexibility for modifications, and enhanced durability of the wiring system.
One of the primary benefits of concealed conduit wiring is its positive impact on aesthetics. Exposed wires and cables can create a cluttered and unattractive appearance in residential and commercial spaces. Concealing the wiring behind walls, ceilings, or floors provides a clean and uncluttered environment, allowing the focus to be on the design elements and architectural features of the space. By eliminating visible wires, concealed conduit wiring enhances the overall visual appeal and creates a more pleasing and professional atmosphere.

Concealed conduit wiring prioritizes the protection and safety of electrical wiring. By routing the cables within conduits, the system is shielded from accidental damage, physical impact, and environmental factors. The conduits act as a protective barrier, reducing the risk of electrical shocks, short circuits, or fires. This added layer of protection ensures the safety of occupants and minimizes the potential for electrical hazards. Concealed conduit wiring is particularly important in areas where moisture, dust, or corrosive substances may pose a threat to the electrical system.
Concealed conduit wiring offers flexibility and ease of modifications. As electrical needs evolve or when modifications become necessary, concealed conduit wiring allows for easier access to the wiring infrastructure. Electricians can make modifications or additions without the need for extensive demolition or disruption to the walls, ceilings, or floors. The ability to access and modify the wiring system with relative ease makes concealed conduit wiring a practical choice for renovations, expansions, or future upgrades. This flexibility ensures that the electrical system can adapt to changing requirements without significant inconvenience or cost.
Concealed conduit wiring contributes to the overall durability and longevity of the electrical system. By enclosing the cables within conduits, they are protected from external elements such as moisture, dust, or corrosive substances. This protection reduces the risk of cable degradation, insulation damage, or premature wear and tear. Concealed conduit wiring helps maintain the integrity of the electrical system over an extended period, resulting in a more reliable and long-lasting installation. This benefit is particularly significant in areas with challenging environments or where the electrical system may be subjected to regular use and potential hazards.
Concealed conduit wiring consists of various components that work together to create a safe and efficient electrical installation. Here are some main components:
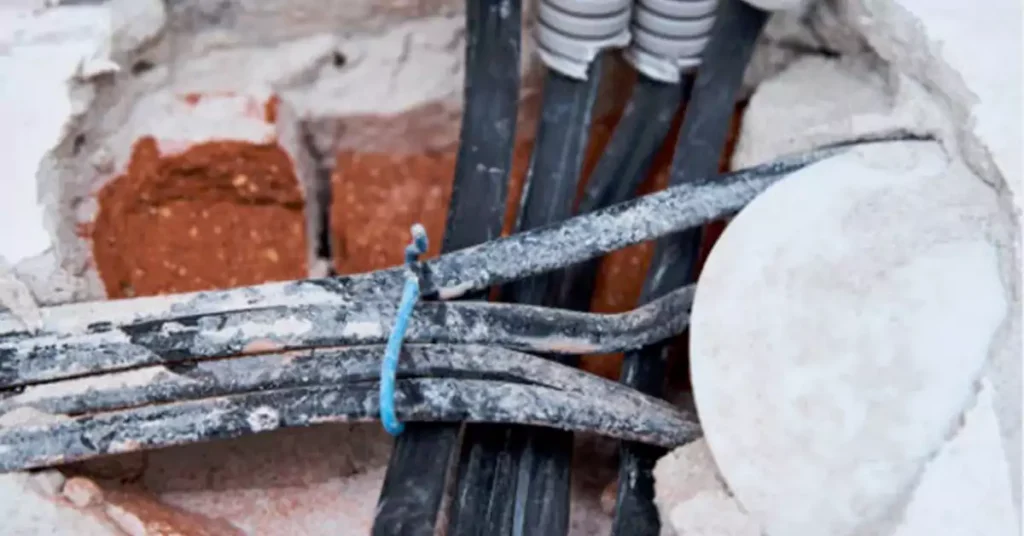

Conduits are the protective channels that house and conceal electrical cables within concealed conduit wiring. Conduits can be made of different materials, including metal and PVC (polyvinyl chloride). Metal conduits, such as galvanized steel or aluminum, are known for their strength, durability, and resistance to physical impact. PVC conduits, on the other hand, are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easy to work with. The choice of conduit material depends on factors such as the installation environment, electrical code requirements, and personal preferences.
Electrical cables are the conductive wires that transmit electricity within the concealed conduit wiring system. Different types of electrical cables are used depending on the specific application, voltage requirements, and load capacity. Common types of electrical cables include:
NM cable, also known as Romex, is a widely used type of cable that consists of insulated conductors within a flexible plastic sheath. It is commonly used for residential electrical installations.
AC cable features conductors protected by a flexible metal armor, which provides additional mechanical protection. It is commonly used in commercial and industrial settings where increased durability is required.
UF cable is designed for underground installations, such as outdoor lighting or buried electrical lines. It is resistant to moisture and can withstand direct burial without the need for conduit.
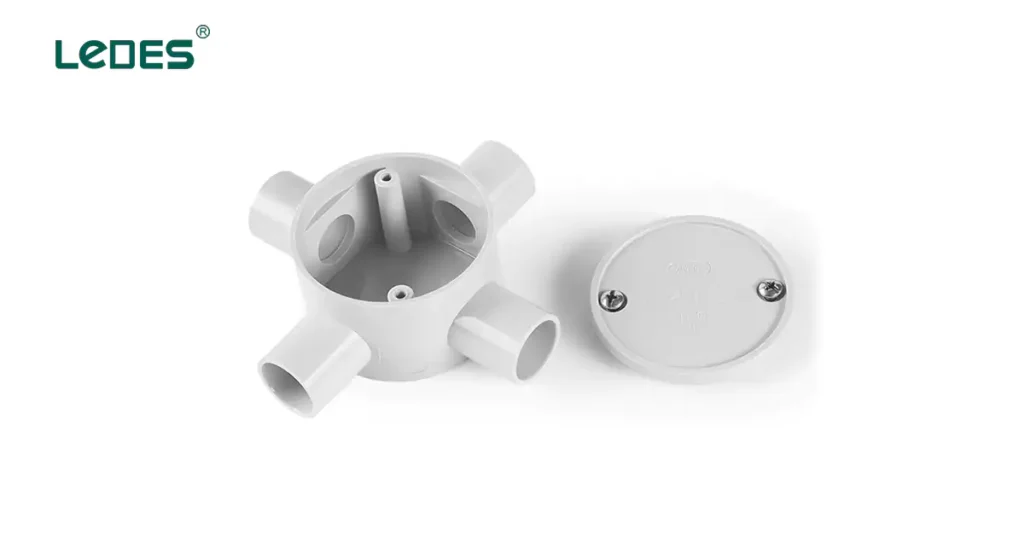

Junction boxes and electrical enclosures serve as protective housings for electrical connections and wiring junctions. These components ensure that electrical connections are secure, organized, and protected from external elements. Junction boxes are available in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different wiring needs. They are typically made of metal or PVC and have removable covers for easy access to the wiring inside. Electrical enclosures are larger boxes that provide additional space for housing electrical components such as switches, circuit breakers, or control panels.
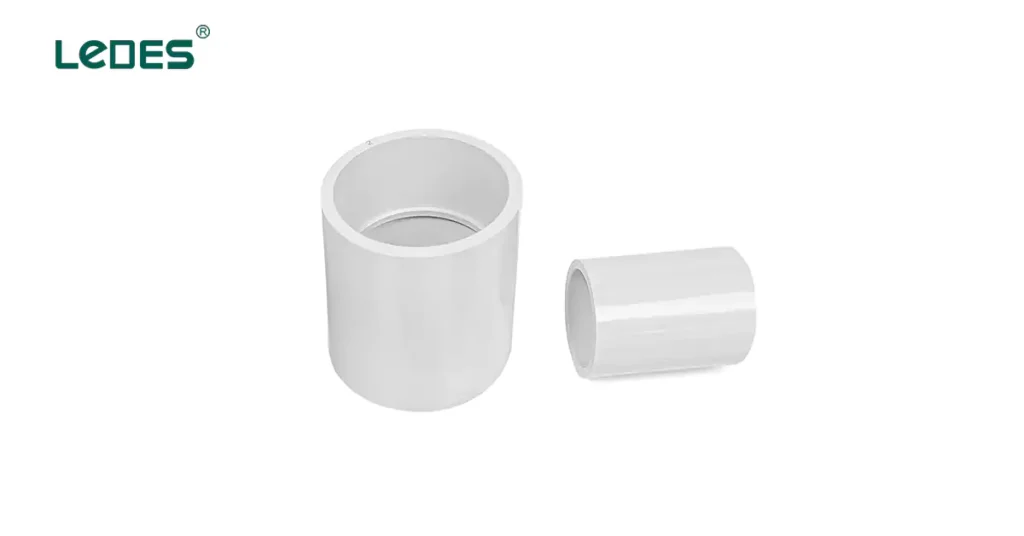
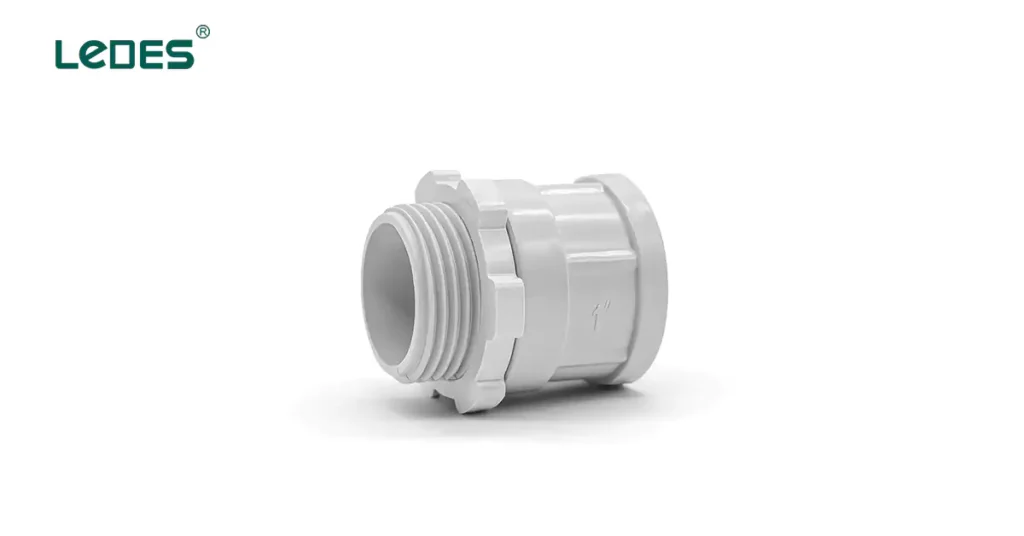


Connectors, couplings, and fittings are essential components used to join and secure conduits, cables, and junction boxes within the concealed conduit wiring system. Connectors are used to create secure electrical connections between cables and devices, while couplings are used to join sections of conduit together. Fittings, such as elbows or connectors, are used to navigate corners or changes in direction within the conduit system. These components ensure proper alignment, grounding, and protection of the concealed conduit wiring system.
Planning and designing a concealed conduit wiring system requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure a safe, efficient, and code-compliant electrical installation. The following are important considerations when planning and designing concealed conduit wiring:
Before designing a concealed conduit wiring system, it is essential to calculate the electrical load requirements of the space. This involves determining the expected power consumption of the electrical devices and appliances that will be connected to the system. Proper load calculation ensures that the wiring and circuitry can handle the anticipated electrical demand without overloading. It is also important to consider future electrical needs to allow for potential expansions or additions to the system.
Identifying the optimal conduit routes is crucial for efficient installation and functionality of the concealed conduit wiring system. Factors to consider include the layout and structure of the building, accessibility to electrical devices and outlets, and minimizing the length of conduit runs. Planning the conduit routes in advance helps avoid unnecessary bends, excessive lengths, or obstructions that could impede the installation process or future maintenance.

Selecting the appropriate conduit sizes and materials is vital for accommodating the electrical cables and ensuring proper protection. The size of the conduit should be based on the number and size of the cables that will be routed through it. It is important to consider the ampacity ratings and fill capacities specified by electrical codes to prevent overcrowding and overheating of the cables. Additionally, the choice of conduit material should align with the specific installation requirements, such as environmental conditions, fire resistance, or corrosive environments.
Concealed conduit wiring must adhere to electrical codes and regulations set forth by local authorities. These codes ensure the safety and proper functioning of the electrical system. It is crucial to consult the relevant electrical codes and regulations to determine the specific requirements related to concealed conduit wiring. Compliance considerations include proper grounding, minimum conduit depth requirements, maximum fill capacities, installation clearances, and the use of approved materials and components.
Additionally, it is advisable to consult with a qualified electrical professional or engineer experienced in concealed conduit wiring to ensure the design meets all necessary safety and regulatory standards. Their expertise can help in optimizing the design, addressing any challenges, and ensuring a successful concealed conduit wiring installation.
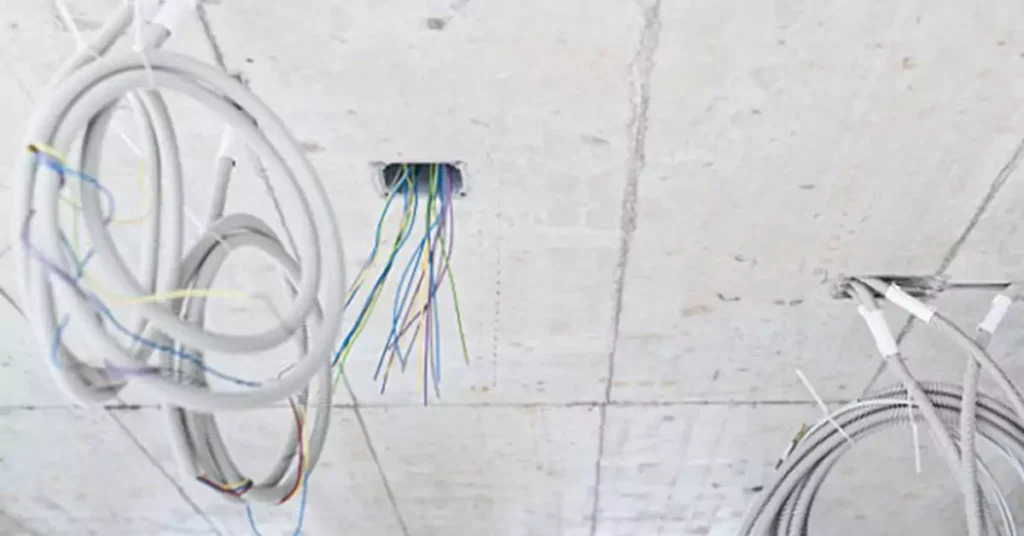

The installation process of concealed conduit wiring involves several steps to ensure a safe and efficient electrical system. It is important to follow industry best practices and adhere to electrical codes and regulations. The following outlines the general installation process for concealed conduit wiring:
Before beginning the installation, review the electrical plans and design to ensure accuracy and compliance with the project requirements. Confirm the locations of electrical fixtures, outlets, and switches, and determine the optimal conduit routes based on the building’s structure and layout.
Using the electrical plans as a guide, mark the locations where conduits will be installed. Use a stud finder and other appropriate tools to determine the path and avoid any structural obstacles or hazards within the walls, ceilings, or floors.
Begin by drilling holes or creating access points at the marked locations. Install the conduits by attaching them securely to the surfaces, such as wall studs or ceiling joists, using appropriate straps or clamps. Ensure proper alignment, support, and spacing between conduits as per electrical codes.
Using appropriate cable pulling tools, carefully pull the electrical cables through the conduits. Ensure that the cables are not damaged during the pulling process. Use cable lubricant if necessary to reduce friction and ease the cable pulling. Secure the cables to the conduits at regular intervals using cable ties or securing clips.
At junction boxes, strip the insulation from the ends of the electrical cables, exposing the conductors. Follow proper color-coding and connect the cables to switches, outlets, fixtures, or other electrical devices as per the electrical plans. Use appropriate connectors, couplings, or fittings to join cables and ensure secure connections. Install grounding wires as required and connect them to grounding points.
Mount the junction boxes and electrical enclosures at appropriate locations as specified in the electrical plans. Ensure that they are properly grounded and securely fastened. Leave sufficient space within the boxes for easy access and future modifications or additions.
Once the installation is complete, conduct thorough testing to ensure the proper functioning of the concealed conduit wiring system. Use a voltage tester to verify the presence of electricity in the circuits. Test switches, outlets, and fixtures to ensure they are working correctly. Check for any loose connections, shorts, or electrical faults, and address them promptly.
After successful testing and verification, cover the conduits with appropriate wall, ceiling, or floor finishes. Replace or install cover plates for switches and outlets. Ensure all access points, such as electrical panels or enclosures, are properly closed and secured.
Schedule a final inspection with the relevant local authorities or electrical inspectors to ensure compliance with electrical codes and regulations. Address any issues or concerns raised during the inspection and make necessary corrections if required.
It is important to note that the installation process may vary based on the specific project requirements, building construction, and electrical codes and regulations in the local jurisdiction.
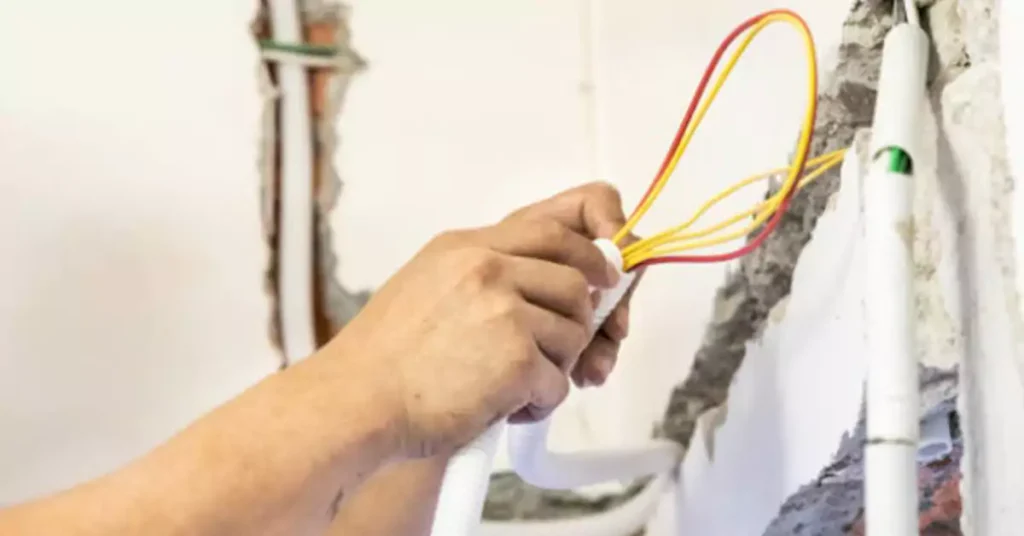
Here are 12 pro tips to take when doing concealed conduit wiring installation:
- Plan the conduit route carefully to avoid interference with other building components like HVAC ducting.
- Secure conduit firmly to the framing structure out of the way of insulation and vapor barriers.
- Cut conduit accurately and deburr/ream cuts to avoid scrapes inside when pulling wire.
- Bend conduit slowly using the proper tool to achieve minimum bend radiuses without kinks.
- When pulling wire, use a lubricant and pull cord, don’t exceed sidewall friction factors. Leave slack at boxes.
- Support junction boxes securely aligned with framing and position for easy access.
- Neatly form and label wire in boxes with appropriate connectors, leaving extra for terminations.
- Seal around boxes, conduit, and inside wires to prevent insulation damage from moisture.
- Ground and bond conduit properly considering transitions between metal and non-metallic.
- Protect wiring from physical damage in high traffic areas through conduit selection and routing.
- Document schematics, labeling, and test results for future reference and code compliance.
- Consider low-voltage lighting inside ceiling/wall cavities to facilitate inspections.

Concealed conduit wiring is a popular method of electrical installation that involves running electrical cables and wiring inside concealed conduits within walls, ceilings, or floors. This method offers several advantages and disadvantages, which should be considered when deciding on the appropriate wiring system for a specific application. The following outlines the advantages and disadvantages of concealed conduit wiring:
Concealed conduit wiring provides a clean and uncluttered appearance as the wiring is hidden from view. This helps maintain the architectural integrity of the space and allows for more flexibility in interior design and decoration.
Concealed conduit wiring offers better protection against accidental damage, such as impact or tampering, compared to surface wiring methods. The wiring is shielded within the conduits, reducing the risk of electrical shock, fire hazards, or short circuits.
Concealed conduit wiring provides increased protection for electrical cables against environmental factors, such as moisture, dust, or pests. This improves the longevity and reliability of the electrical system, reducing the need for frequent maintenance or repairs.
Concealed conduit wiring minimizes electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) that can affect sensitive electronic devices. The conduits act as a barrier, shielding the cables from external sources of interference and ensuring better signal quality.
Concealed conduit wiring allows for more flexibility in determining the location of electrical outlets, switches, and fixtures. Modifications or additions to the electrical system can be made more easily since the conduits provide accessible pathways for future wiring changes.
Concealed conduit wiring requires more planning, labor, and expertise during the installation process compared to surface wiring methods. Routing conduits within walls, ceilings, or floors can be challenging, especially in existing structures, and may require additional construction work.
Concealed conduit wiring generally involves higher material and labor costs compared to surface wiring methods. The need for conduits, junction boxes, and associated hardware, along with the additional labor required for installation, can contribute to increased expenses.
Once the concealed conduit wiring is installed, accessing and troubleshooting the electrical system can be more challenging. Repairs or modifications may require opening walls, ceilings, or floors, which can be time-consuming, disruptive, and expensive.
While concealed conduit wiring offers flexibility in outlet placement, significant changes to the electrical system may still require modifications to the concealed conduits. This can be more complicated and costly compared to surface wiring methods, which allow for more straightforward modifications.
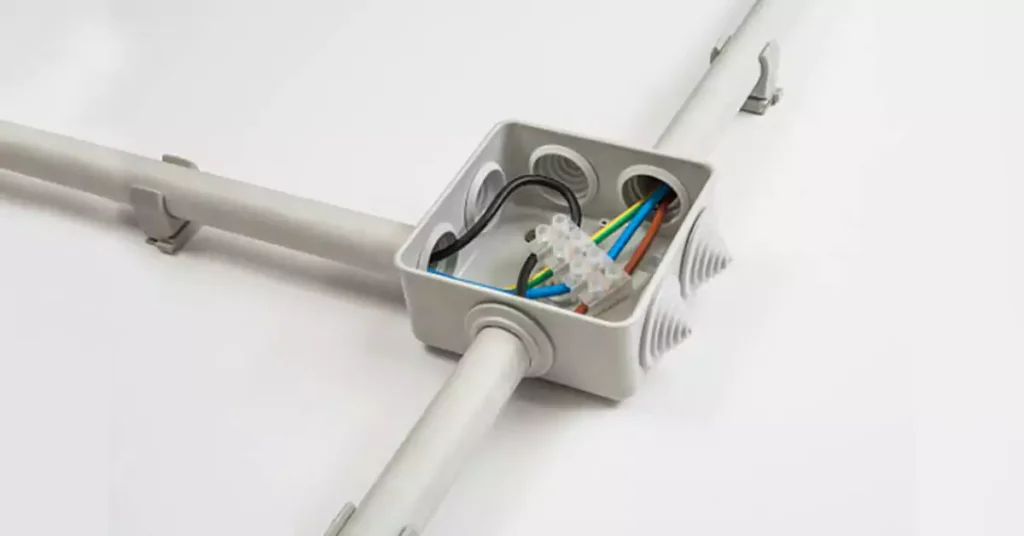

Concealed conduit wiring finds extensive use in various types of buildings and facilities due to its benefits of enhanced aesthetics, safety, and durability. The following are common applications of concealed conduit wiring:
Concealed conduit wiring is commonly used in single-family homes for the entire electrical system. It provides a clean and uncluttered appearance, allowing homeowners to maintain the desired interior design without visible wiring.
In apartment complexes, condominiums, or townhouses, concealed conduit wiring is employed to ensure safety and uniformity throughout the building. It allows for efficient distribution of electrical power to individual units while reducing the risk of accidental damage or tampering.
When renovating or remodeling residential properties, concealed conduit wiring is often preferred to update the electrical system without compromising the aesthetics. It allows for the installation of new outlets, switches, and fixtures while minimizing visible wiring.
Concealed conduit wiring is widely used in office buildings to provide a neat and professional appearance. It accommodates the electrical requirements of various workstations, conference rooms, and common areas while ensuring a safe and reliable power supply.
Concealed conduit wiring is employed in retail spaces to power lighting, display units, point-of-sale systems, and other electrical devices. It helps maintain a clean and visually appealing environment for customers while ensuring electrical safety.
Concealed conduit wiring is commonly utilized in restaurants, hotels, and other hospitality establishments. It enables efficient distribution of power for kitchen equipment, lighting, HVAC systems, and guest amenities while maintaining a visually pleasing ambiance.
Concealed conduit wiring is essential in industrial facilities to power heavy machinery, production lines, and control systems. It provides a safe and organized electrical infrastructure in challenging environments, such as factories or assembly lines.
Concealed conduit wiring is employed in large-scale storage facilities to support lighting, conveyor systems, material handling equipment, and other electrical needs. It ensures efficient and reliable power distribution throughout the facility.
Concealed conduit wiring is utilized in scientific and research facilities to power specialized equipment, data collection systems, and experimental setups. It allows for the safe and organized routing of electrical cables to support complex research activities.
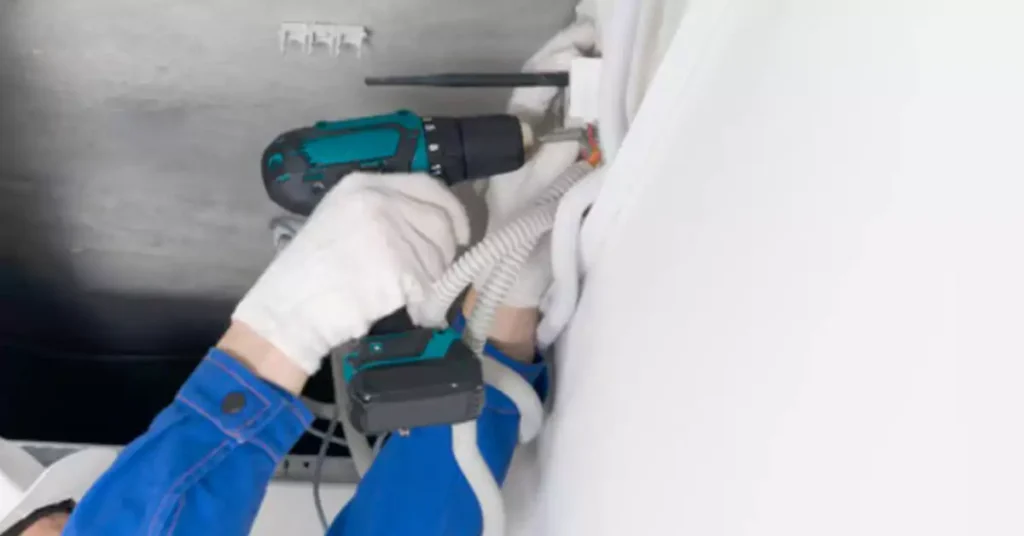

Proper maintenance and timely troubleshooting are essential for ensuring the safety, functionality, and longevity of concealed conduit wiring installations.
Conduct visual inspections of concealed conduit wiring to identify any visible signs of damage, wear, or loose connections. Look for indications such as frayed or exposed wires, discolored or melted insulation, or signs of moisture or pest infestation near the conduits.
Perform periodic electrical testing using appropriate equipment to check the continuity, insulation resistance, and grounding of the concealed conduit wiring system. This helps identify potential faults or electrical issues that may not be visible during visual inspections.
Ensure that the conduits and junction boxes are kept clean and free from dust, debris, or any other obstructions. Regularly remove any accumulated debris or dust that may impede the proper functioning of the electrical system.
Check and tighten all electrical connections, including junction box terminals, switches, outlets, and grounding connections. Loose connections can lead to electrical arcing, overheating, or intermittent power supply issues.
Verify the integrity of any protective measures, such as conduit covers, guards, or insulation. Replace damaged or deteriorated covers or guards promptly to prevent accidental contact or damage to the wiring.
If damaged wiring is identified, such as frayed or exposed wires, it should be repaired promptly. Cut out the damaged portion of the wire and install a junction box or wire splice connector to join the sections securely. Ensure proper insulation and protection of the repaired area.
Faulty outlets, switches, or light fixtures should be replaced with new ones of the appropriate type and rating. Follow manufacturer instructions and electrical codes when replacing components, and ensure that all connections are secure and properly grounded.
If modifications or extensions are required in the concealed conduit wiring system, consult with a qualified electrician or electrical professional. They can provide guidance on the appropriate procedures, conduit sizing, and necessary permits to ensure compliance with electrical codes.

In conclusion, concealed conduit wiring offers aesthetic appeal, safety, and durability benefits, making it a popular choice in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. It provides a clean and uncluttered appearance, protects against accidental damage, and enhances the longevity of the electrical system.
Considering the advantages, disadvantages, maintenance practices, and troubleshooting guidelines of concealed conduit wiring allows individuals and organizations to make informed decisions about its suitability for their specific applications. Prioritizing safety, compliance, and regular maintenance will contribute to a reliable and efficient electrical system within buildings and facilities.
Any questions, don’t hesitate to contact us for professional advice.



