
Índice
What’s different between Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC conduit? That’s a great question. Most posts will tell you the key is wall thickness. That’s right, but not all. We will list 7 points of difference in this post and let you fully understand the difference between the two. So, let’s get started.
Key Differences Between Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC Conduit
Material and Compliance
- Both Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC conduit are made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and meet applicable ASTM standards.
- They can undergo certification processes to meet safety standards and ensure quality.
Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC conduit are both manufactured using polyvinyl chloride (PVC), a material renowned for its excellent electrical insulation properties and resistance to corrosion. The manufacturing process ensures that the conduit meets the applicable ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) standards for PVC electrical conduit, ensuring the quality and reliability of the product.
In terms of market acceptance and compliance with safety standards, both Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC conduit can undergo certification processes to meet the necessary requirements. Certifications such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or ETL (Intertek) ensure that the conduits are rigorously tested and approved for their electrical performance, flame resistance, impact resistance, and other critical factors. These certifications provide assurance that the conduit complies with industry standards and regulations, instilling confidence in its suitability for electrical installations.
Types
- In addition to Schedule 40 and Schedule 80, there is also Schedule 20 PVC conduit available.
- Types A and EB are available, with Type A for indoor applications and Type EB for exposed or rugged environments.
Furthermore, it is worth noting that in addition to Schedule 40 and Schedule 80, there is also Schedule 20 PVC conduit available in the market. Schedule 20 conduit features a thinner wall compared to Schedule 40 and is primarily used in low-pressure applications where the primary function of the conduit is to protect the electrical wiring.
In accordance with the standards, PVC conduit is available in different types, such as Type A and Type EB. Type A refers to conduit with a smooth interior and is primarily used for above-ground applications. It is commonly employed in residential and commercial projects where the conduit is installed indoors and protected from harsh environmental conditions. On the other hand, Type EB indicates conduit with an embedded layer of elastomer for additional impact resistance. This type of conduit is often utilized in exposed or rugged environments where there is a higher risk of physical damage.
Espessura da parede
- Schedule 40 conduit has a thinner wall compared to Schedule 80.
- Schedule 80 conduit has a thicker wall, providing greater strength and durability.
One of the primary distinctions between Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC conduit lies in their wall thickness. In accordance with the UL 651 standard, the most significant difference between the two is the thickness of the conduit walls. Varying wall thicknesses can have implications for several factors, including performance and cost.
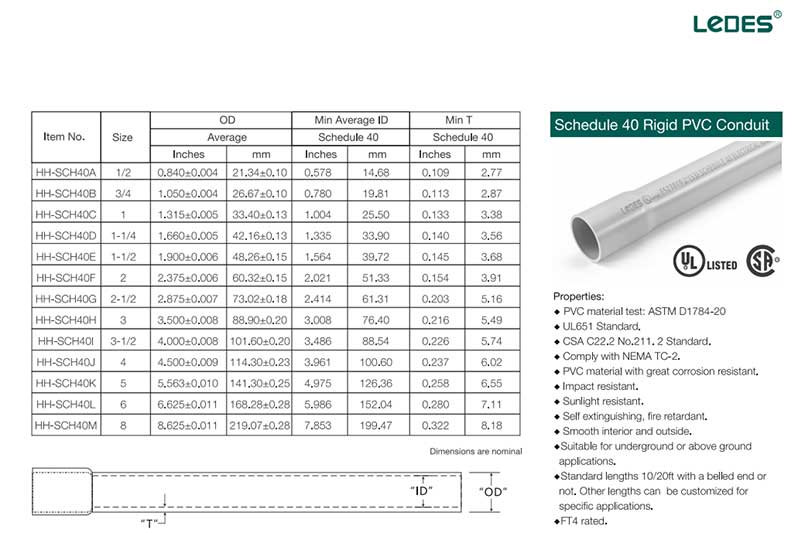
Schedule 40 PVC Electrical Conduit Dimensions
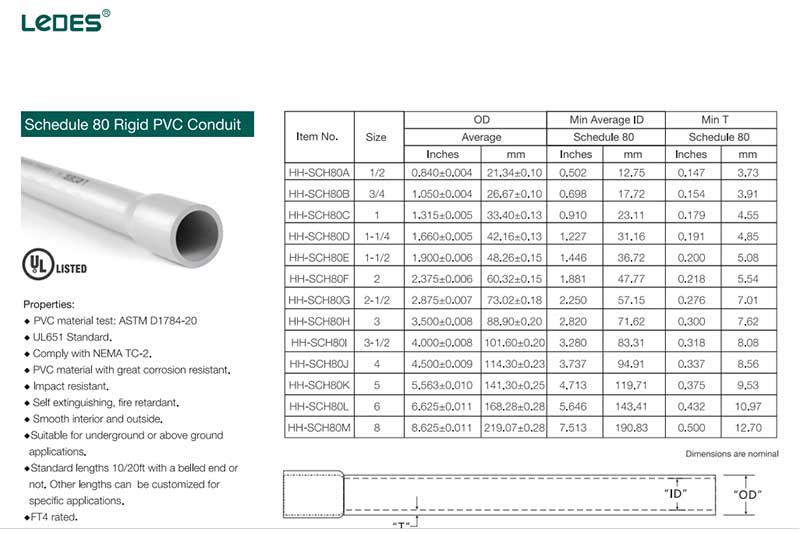
Schedule 80 PVC Electrical Conduit Dimensions
Conduíte de PVC Schedule 40 features a relatively thinner wall compared to Schedule 80. The thinner wall makes Schedule 40 conduit more lightweight and easier to handle during installation. It is a popular choice for applications where the conduit is not subjected to significant physical stress or harsh environmental conditions.
On the other hand, Conduíte de PVC Schedule 80 boasts a thicker wall, providing increased mechanical strength and durability. The added thickness enhances its ability to withstand external pressures, impacts, and other potentially damaging forces. Schedule 80 conduit is commonly used in applications where there is a higher likelihood of physical stress or exposure to harsh environments, such as outdoor installations or industrial settings.
The difference in wall thickness can also impact other factors, such as electrical performance and cost. Thicker walls in Schedule 80 conduit may offer improved electrical insulation properties, especially in situations where there is a need for enhanced protection against electrical interference or external factors. However, it’s important to note that specific performance characteristics and cost implications may vary depending on the manufacturer and the specific application requirements.
Understanding the distinctions in wall thickness between Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC conduit is essential for selecting the appropriate conduit for a particular electrical installation. Factors such as anticipated environmental conditions, mechanical stress, and budgetary considerations should be taken into account when deciding between the two options.
Performance Differences
- Schedule 80 conduit demonstrates enhanced durability and impact resistance compared to Schedule 40.
- UL 651 standard provides testing methods for impact resistance and resistance to crushing, showing Schedule 80’s superior physical performance.
In addition to the variation in wall thickness, Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC conduit also exhibit differences in performance characteristics. These differences can be observed through testing methods such as impact resistance and resistance to crushing, as outlined in the UL 651 standard. Comparing the values obtained from these tests clearly demonstrates that Schedule 80 conduit offers superior physical performance.
When it comes to impact resistance, Schedule 80 PVC conduit demonstrates enhanced durability compared to Schedule 40. Impact resistance testing evaluates the conduit’s ability to withstand external forces, such as accidental bumps or knocks. Due to its thicker wall, Schedule 80 conduit exhibits greater resistance to damage caused by impacts, making it a suitable choice for applications where there is a higher risk of physical stress.
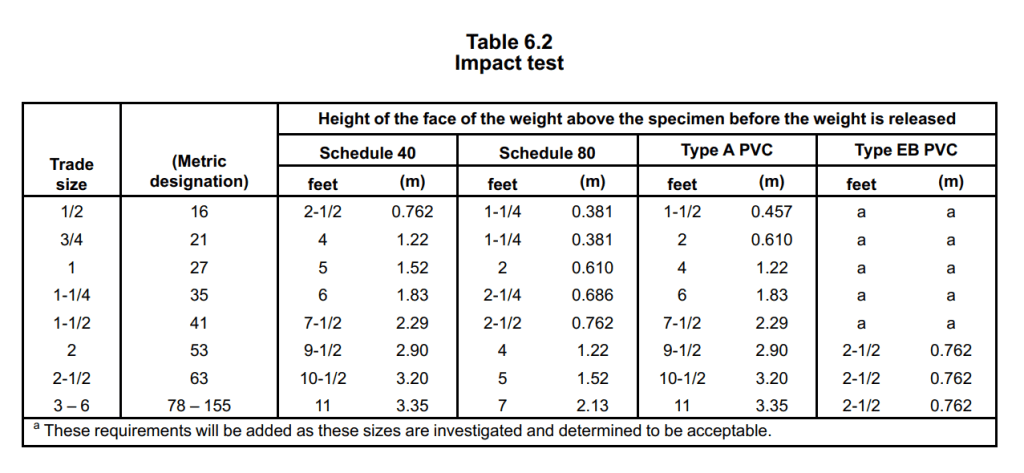
These data comes from the eighth edition of UL 651 STANDARD FOR SAFETY, and the ownership belongs to UL.
According to the UL 651 standard, the impact test for rigid PVC conduit is conducted as follows:
- Ten 6-inch (150-mm) specimens without cracks, tears, or imperfections are cut from finished lengths of each trade size of rigid PVC conduit.
- The specimens are conditioned in air at a temperature of 23.0 ±0°C (73.4 ±3.6°F) for a minimum of 4 hours before testing.
- The specimens are tested individually within 15 seconds after conditioning, while resting on a solid, flat steel plate that is at least 1/2 inch (13 mm) thick and firmly anchored with its upper surface horizontal.
- A protective cage surrounds the plates and specimens to reduce the risk of injury from broken conduit pieces.
- A steel weight, in the form of a solid, right-circular cylinder with a flat impact face having rounded edges, falls freely through a vertical guide from a specified height according to Table 6.2 in the UL 651 standard.
- For Schedule 40, Type A and EB rigid PVC conduit, the weight is 20 lbs (9.7 kg) with a cylinder diameter of 2 inches (51 mm). For Schedule 80 conduit, the weight is 75 lbs (34 kg) with a cylinder diameter of 6 inches (150 mm).
- The flat face of the weight strikes the center of the specimen across the diameter and along the longitudinal axis once, ensuring that the weight does not strike the specimen more than once.
- The rigid PVC conduit shall not exhibit cracks or tears longer than 1/32 inch (0.8 mm) along the outer surface in more than three out of the ten specimens.
According to the UL 651 standard, the crushing test for rigid PVC conduit is conducted as follows:
- Six-inch (150-mm) specimens of finished rigid PVC conduit are tested.
- The specimens should not flatten to the point of buckling under the load specified in Table 6.3.
- The minor axis measured inside each loaded specimen should not be less than 70% of the inside diameter of the specimen measured before loading.
- Three specimens are cut from finished lengths of each size of rigid PVC conduit.
- The specimens, testing machine, and surrounding air should be in thermal equilibrium at a temperature of 23.0 ±2.0°C (73.4 ±3.6°F) during the test.
- The inside diameter of each specimen is measured before testing.
- The specimens are individually tested between a pair of rigid, flat, steel plates that are at least 6 inches (150 mm) long, horizontal, and parallel to each other.
- One plate is moved towards the other at a rate of 1/2 ±1/8 inch (10.0 ±2.5 mm) per minute until the load specified in Table 6.1 is applied, as indicated on the testing machine’s dial.
- The rigid PVC conduit should not show any signs of pulling away from contact with either plate during or after the application of the load (buckling).
- The minor axis measured inside any flattened specimen should not be less than the specified percentage in Table 6.3 of the inside diameter of that specimen as measured before loading.
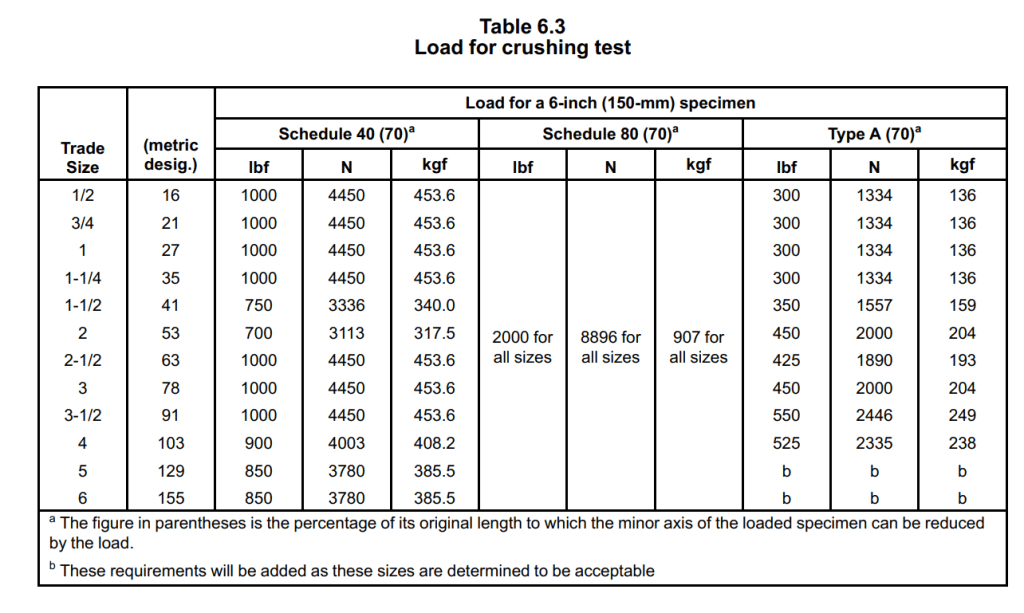
These data comes from the eighth edition of UL 651 STANDARD FOR SAFETY, and the ownership belongs to UL.
It’s worth noting that manufacturers of PVC conduit, like Ledes, continually invest in research and development to ensure that the increased wall thickness in Schedule 80 conduit is accompanied by consistent performance across all aspects. This commitment to product improvement ensures that the conduit meets and often exceeds the UL certification standards, as well as surpasses customer expectations.
For instance, Ledes’ Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC conduit series have been successfully deployed and utilized in prominent projects such as the CHPE and A.B Brown Station in the United States. These projects have demonstrated that Ledes’ conduit not only meets UL certification standards but also exceeds customer expectations in terms of overall performance and reliability.
By understanding the performance differences between Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC conduit, it becomes evident that the selection of the appropriate conduit should take into account the specific requirements of the electrical installation. Factors such as anticipated physical stress, environmental conditions, and industry standards should be carefully considered to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the conduit system.
Price Differences

- Schedule 80 conduit is generally more expensive due to its increased wall thickness and material requirements.
Based on the previous analysis and comparison, it can be concluded that Schedule 80 is generally more expensive than Schedule 40. This price difference is primarily due to the increased wall thickness and the higher material requirements associated with Schedule 80 conduit.
The thicker wall of Schedule 80 conduit requires more raw materials, which contributes to its higher manufacturing cost. Additionally, the production processes for Schedule 80 conduit may involve additional steps or specialized equipment to achieve the desired thickness, further adding to the overall cost.
Moreover, the increased weight of Schedule 80 conduit, resulting from its thicker wall, can lead to higher transportation and handling costs during installation. The additional weight requires more effort and resources for shipping, handling, and lifting, which can incur added expenses.
As a result, many projects opt for Schedule 40 conduit because it offers a cost-effective solution while still meeting the necessary requirements. Schedule 40 conduit is widely used in various applications where the increased strength and durability of Schedule 80 may not be essential.
However, it is important to note that the selection of conduit type should consider the specific needs and requirements of the project. If your project has special considerations or demands, it is advisable to consult with us to obtain more detailed information and guidance.
Ultimately, balancing the performance requirements with the associated costs is crucial in making an informed decision about which schedule of PVC conduit is most suitable for your specific application.
Installation of Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 Conduit

- Both types of conduit have identical dimensions and can use the same fittings for connections.
- Proper installation practices should be followed according to relevant local codes and guidelines.
Since UL and related standards have defined that Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 conduits have identical dimensions, it means that they can use the same fittings for connections. However, it is important to adhere to the relevant standards of each country during the installation process.
In the United States, the National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines for the proper installation of PVC conduit. These guidelines include instructions for cleaning the conduit, making connections, and ensuring overall electrical safety.
Here are 8 tips for the installation of both Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 conduit:
- Planning and Design: Determine the appropriate conduit size and route for the electrical installation. Consider factors such as the number and size of conductors, environmental conditions, and any specific requirements for the project.
- Cutting and Reaming: Use appropriate tools to cut conduit sections to the desired lengths. After cutting, remove any burrs or sharp edges using a reaming tool or file to ensure a smooth and clean surface for proper fittings and connections.
- Cleaning: Thoroughly clean the inside of the conduit using a suitable solvent or cleaner to remove any debris, dirt, or moisture that may hinder the installation or affect the electrical performance.
- Fittings and Connections: Select fittings that are compatible with the chosen conduit type (Schedule 40 or Schedule 80). Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for making secure and watertight connections, such as using solvent cement or mechanical connectors.
- Proper Support: Install conduit supports at appropriate intervals to ensure proper alignment and to prevent sagging or excessive stress on the conduit. Follow local building codes and regulations regarding support spacing and attachment methods.
- Dobrando: If necessary, use proper bending techniques and tools to create bends in the conduit. Avoid excessive bending, as it can weaken the conduit and affect its overall performance.
- Grounding: Follow the NEC or relevant local codes for grounding requirements. Properly bond and ground the conduit system to ensure electrical safety.
- Sealing and Protection: Use appropriate sealing methods, such as PVC-compatible sealants or gaskets, at entry points to protect against moisture ingress. Install conduit in locations where it is adequately protected from physical damage, such as impact or exposure to harsh elements.
Always consult and adhere to the specific guidelines and regulations provided by the relevant authorities and standards organizations in your country or region. Proper installation practices are crucial for maintaining the integrity and safety of the electrical conduit system.
Aplicações
- Schedule 40 conduit is suitable for residential, commercial, and light industrial applications, as well as indoor installations and low-traffic areas.
- Schedule 80 conduit is preferred for heavy industrial facilities, chemical plants, outdoor and underground installations, hazardous locations, and mechanical rooms.
Where is Schedule 40 PVC Conduit Used
Schedule 40 PVC conduit safely protects and routes electrical wiring in walls, floors, ceilings, and even direct burial applications, meeting NEC 352 standards for residential, commercial, and industrial use.
- Residential Buildings: Schedule 40 conduit is commonly used in residential construction for electrical wiring installations. It is suitable for typical residential environments where the risk of physical damage or extreme conditions is relatively low.
- Edifícios comerciais: In non-demanding areas of commercial structures, such as offices, retail stores, or small businesses, Schedule 40 conduit is often used. It provides adequate protection for electrical wiring without the need for the enhanced strength of Schedule 80.
- Light Industrial Facilities: Certain light industrial applications, such as workshops or small-scale manufacturing facilities, where the risk of impact or extreme conditions is minimal, can benefit from the cost-effectiveness of Schedule 40 conduit.
- Indoor Installations: Schedule 40 conduit is commonly used for indoor electrical installations, including wiring in walls, ceilings, and floors, where it provides protection against physical damage and helps organize and route electrical wires efficiently.
- Low-Traffic Areas: Locations with minimal foot traffic, such as storage rooms or utility closets, where the conduit is less likely to be exposed to accidental impacts, may utilize Schedule 40 conduit due to its lower cost and sufficient protection capabilities.
What is Schedule 80 Conduit Used for
Schedule 80 conduit safely protects and routes electrical wiring in walls, floors, ceilings, and even direct burial applications, meeting NEC 352 standards for residential, commercial, and industrial use.
- Heavy Industrial Facilities: Schedule 80 conduit is often used in heavy industrial environments where there is a higher risk of impact, chemical exposure, extreme temperatures, or greater mechanical stress. It provides superior protection for electrical wiring in these demanding settings.
- Chemical Plants and Processing Facilities: Environments with corrosive substances or chemicals necessitate the use of Schedule 80 conduit to withstand the potential corrosive effects and provide robust protection for electrical systems.
- Outdoor and Underground Installations: Schedule 80 conduit is preferred for outdoor and underground applications where the conduit may be exposed to UV radiation, moisture, soil pressure, or potential damage from excavation activities. It offers enhanced durability and resistance to external forces.
- Locais perigosos: Areas classified as hazardous, such as oil refineries, petrochemical plants, or facilities with flammable gases or dust, require the added strength and durability of Schedule 80 conduit to ensure the safety of electrical systems.
- Mechanical Rooms and Equipment: Schedule 80 conduit is suitable for housing electrical wiring in areas with heavy mechanical equipment, such as generators, pumps, or industrial machinery, where vibrations and mechanical stress are present.
5 Thing You Need To Know Before Purchasing Electrical Conduit

- Reliable Brand Supplier: Choosing a reliable brand supplier is crucial when purchasing electrical conduit. A reputable brand like Ledes, for example, has a track record of delivering high-quality products and solutions. Known for it’s commitment to excellence and innovation, Ledes offers a comprehensive range of electrical conduit systems designed to meet industry standards and ensure reliable electrical installations.
- Compliance with Local Construction Standards: It is essential to ensure that the electrical conduit you purchase complies with the local construction standards and codes. For example, in the United States, the National Electrical Code (NEC) sets the standards for electrical installations. The conduit you choose should meet the NEC requirements to ensure safety and compliance with local regulations.
- Services Provided by the Supplier: In addition to the product itself, consider the services provided by the supplier. This includes factors such as transportation, delivery, and after-sales support. A reliable supplier will offer efficient transportation options, ensuring that the conduit reaches your site in a timely manner. They should also have a responsive customer service team that can address any inquiries or issues you may have after the purchase.
- Product Quality and Durability: Evaluate the quality and durability of the electrical conduit being offered. Look for products that have undergone rigorous testing, such as flame resistance and extreme temperature tests. High-quality conduit will ensure long-lasting performance, reducing the need for frequent replacements and maintenance.
- Compatibility and Versatility: Consider the compatibility and versatility of the electrical conduit system. It should be able to accommodate various types of wiring and be suitable for different applications. Choosing a conduit system with a wide range of fittings and accessories will provide flexibility in installation and meet the specific requirements of your project.
Overall, electrical conduit is an important part in electrical systems, Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC Conduits are the two most widely used conduit types in the market, they share the same functions and properties, but differ in performance details, dimensions, and applications. When choosing these two types, consider your special project needs and requirements to choose the right one.
Contato
É isso. Sinta-se à vontade para entrar em contato conosco se tiver alguma dúvida. Você pode simplesmente send email to us.



