Índice
O conduíte de PVC é um componente vital em instalações elétricas, oferecendo proteção e organização para sistemas de fiação elétrica. Entender as propriedades, tipos, métodos de instalação e aplicações do conduíte de PVC é essencial para garantir configurações elétricas seguras e eficientes em ambientes residenciais, comerciais e industriais.
Depois de ler este artigo, você saberá:
- O que é conduíte de PVC e tipos de conduíte
- Onde o conduíte de PVC pode ser usado
- Métodos e etapas de instalação de conduítes de PVC
- Como cortar e unir corretamente um conduíte de PVC
- O conduíte de PVC é adequado para aplicações de alta tensão?
- O conduíte de PVC pode ser dobrado e os métodos de dobra
- Qual é a diferença entre conduítes de PVC e UPVC
- Conduítes de PVC vs. Conduítes Metálicos
- Qual é a diferença entre tubo de PVC e conduíte de PVC?
- Conduíte de PVC vs. Conduíte estanque a líquidos
- Como escolher o conduíte de PVC certo para seu projeto
O que é conduíte de PVC?

Conduíte de PVC, abreviação de conduíte de cloreto de polivinila, é um tipo de sistema de tubulação projetado especificamente para instalações de fiação elétrica. Feitos de uma forma durável de plástico, os conduítes de PVC oferecem proteção para cabos elétricos contra danos físicos e elementos ambientais.
O PVC é um material não metálico que é leve e resistente à corrosão, o que o torna ideal para instalações internas e externas. Ele não conduz eletricidade, fornecendo uma camada adicional de isolamento para proteger os fios internos de riscos elétricos. Além disso, o PVC é flexível o suficiente para ser usado em uma variedade de situações em que os conduítes de metal tradicionais podem ser impraticáveis ou muito pesados.
Os conduítes de PVC vêm em vários tamanhos, espessuras e tipos, permitindo que sejam personalizados para projetos específicos, seja para aplicações residenciais, comerciais ou industriais. Eles são particularmente favorecidos em locais com altos níveis de umidade, como porões, paisagens externas ou instalações subterrâneas.
5 tipos de conduítes de PVC que você deve conhecer
Existem muitos tipos de conduítes no mercado. Aqui estão 5 tipos de conduítes da Ledes. Eles são os mais comumente usados que você deve conhecer:
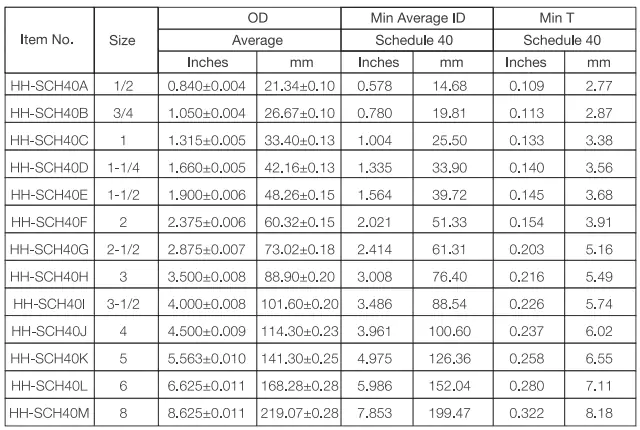
1. Conduíte e tubulação de PVC padrão UL
Conduíte de PVC padrão UL, Conduíte de PVC rígido Schedule 40 e Schedule 80 e Tubulação Elétrica Não Metálica ENT, três tipos principais.
Padrões: UL651, NEMA TC-2, ASTM D1784-20
Vantagens: Resistente à corrosão, resistente a impactos, resistente à luz solar, resistente ao fogo, fácil instalação.
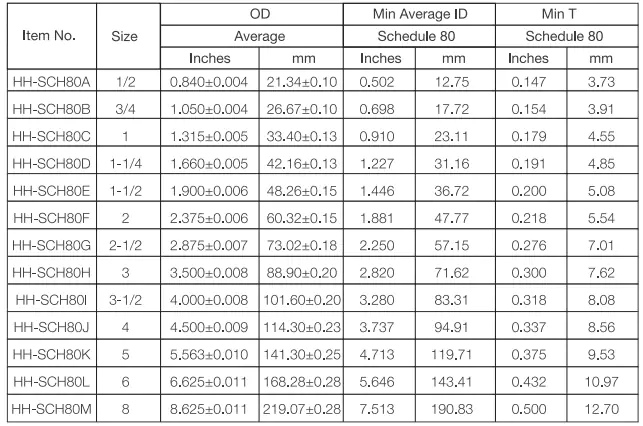
Padrões: UL651, NEMA TC-2, ASTM D1784-20
Vantagens: Resistente à corrosão, resistente a impactos, resistente ao fogo, alta resistência física, uso subterrâneo.
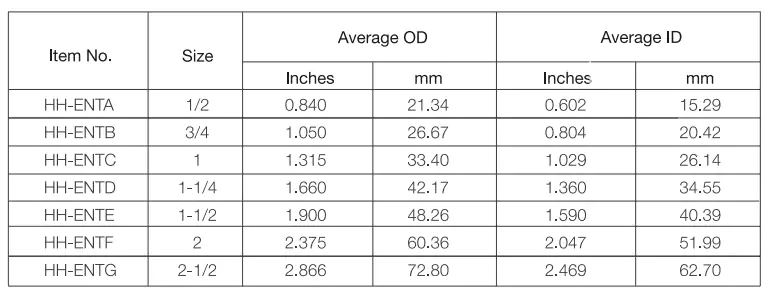
Padrões: UL1653
Vantagens: Resistente à corrosão, resistente a impactos, resistente à luz solar, resistente ao fogo, resistente à deflexão, leve, fácil de instalar.
2. Conduíte e tubulação de PVC padrão CSA
No Canadá, também existem três tipos de conduítes amplamente utilizados. Aqui estão as informações e os dados do produto da Ledes.
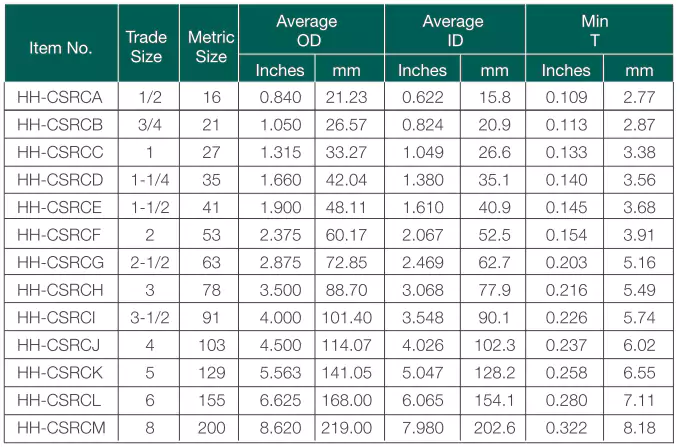
Padrões: CSA C22.2 Nº 211.2
Vantagens: Resistente à corrosão, resistente a impactos, resistente à luz solar, resistente ao fogo, fácil instalação.
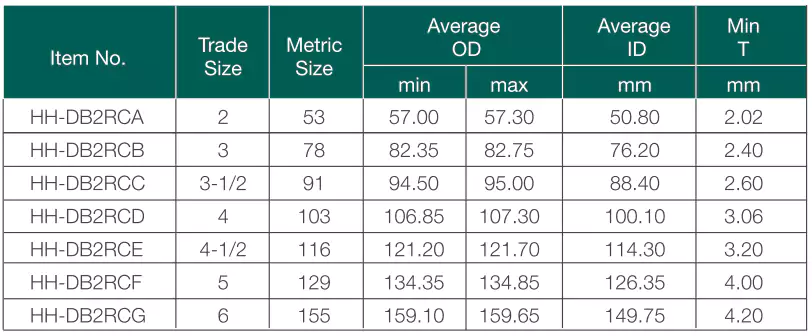
Padrões: CSA C22.2 No.211.1
Vantagens: Resistente à corrosão, resistente a impactos, resistente à luz solar, resistente ao fogo, estanque ao concreto, leve, enterramento direto.
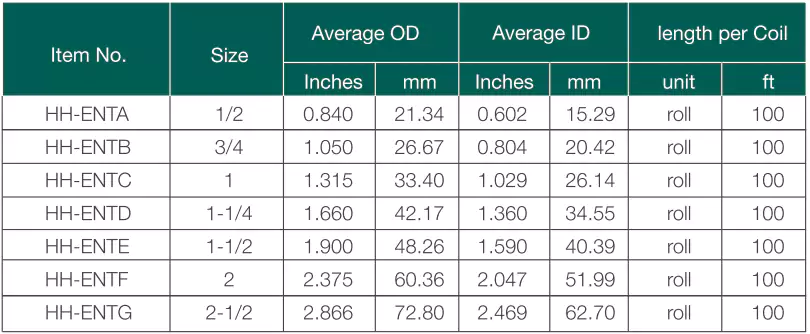
Padrões: CSA C22.2 No.211.1
Vantagens: Resistente à corrosão, resistente a impactos, resistente à luz solar, resistente ao fogo, resistente à deflexão, leve, fácil de instalar.
3. Conduíte de PVC padrão AS/NZS
Para o mercado australiano e neozelandês, a Ledes tem conduítes de PVC rígido para serviços médios e pesados, conduítes corrugados para serviços médios e pesados para diferentes necessidades e aplicações.
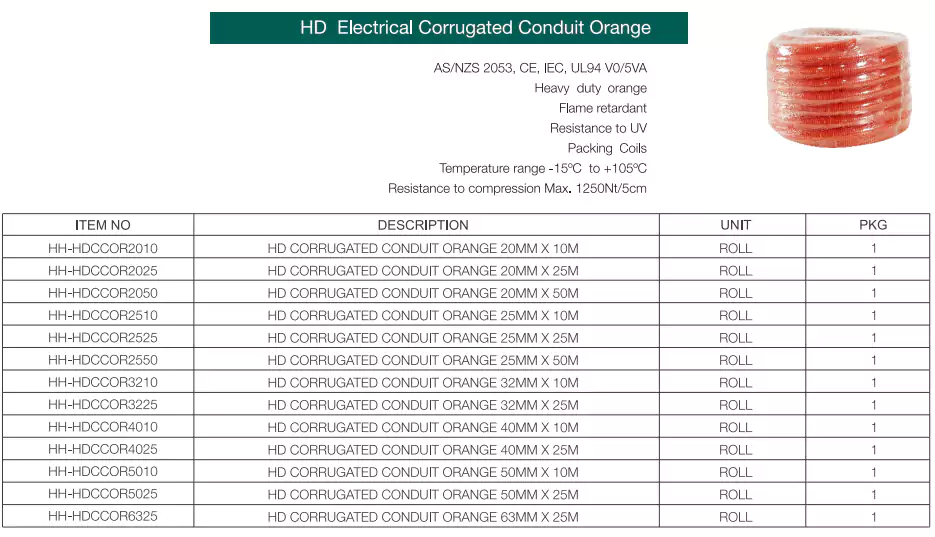
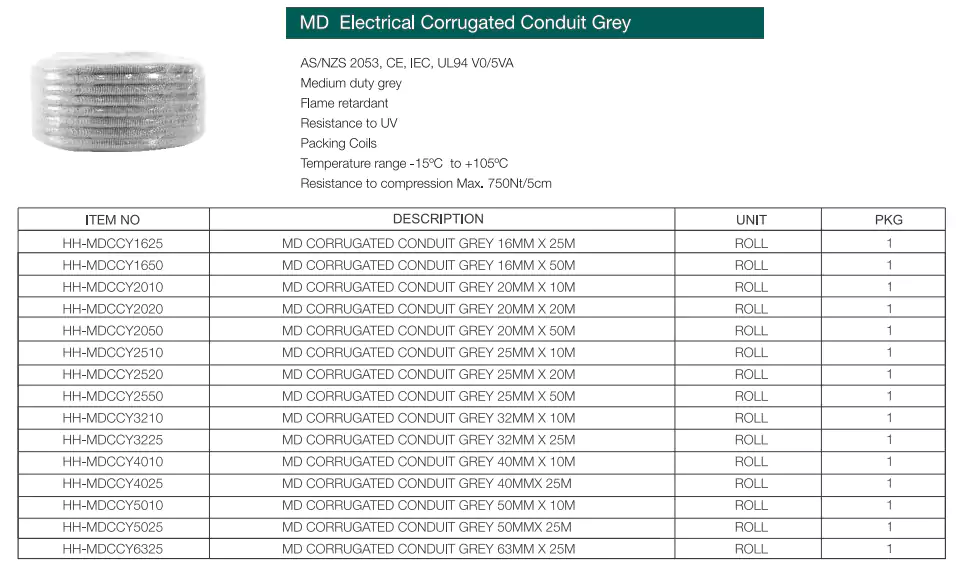
Padrões: Os conduítes corrugados HD&MD estão em conformidade com AS/NZS 2053.5, CE, IEC, UL94
Vantagens: Retardante de chamas, resistente a UV, alta resistência à compressão e ao impacto, leve, dobrável manualmente.
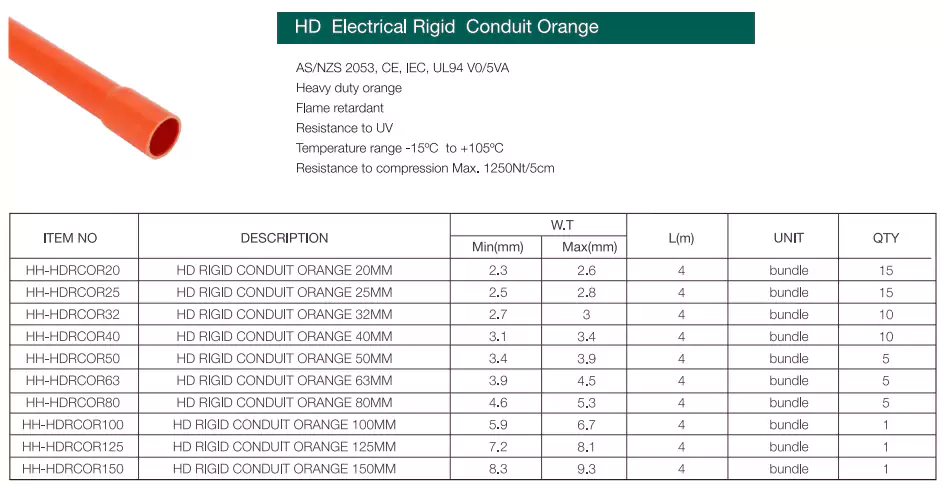
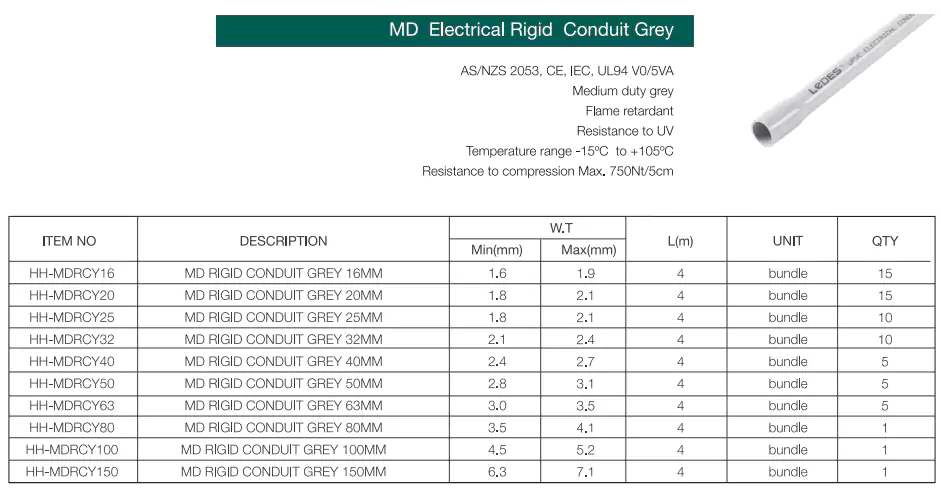
Padrões: Os conduítes rígidos de PVC HD&MD estão em conformidade com AS/NZS 2053.2, CE, IEC, UL94
Vantagens: Alta resistência física, retardante de chamas, resistente a UV
4. Conduíte Solar
O conduíte solar é um tipo de conduíte especialmente projetado para uso em aplicações externas, devido ao ambiente de instalação severo, os requisitos para a resistência física do conduíte e resistência a UV são muito altos. Aqui estão alguns tamanhos e tipos comuns fornecidos pela Ledes.
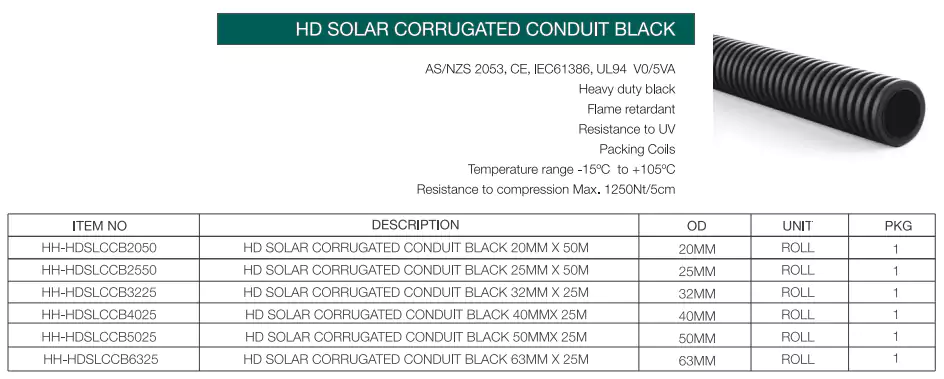
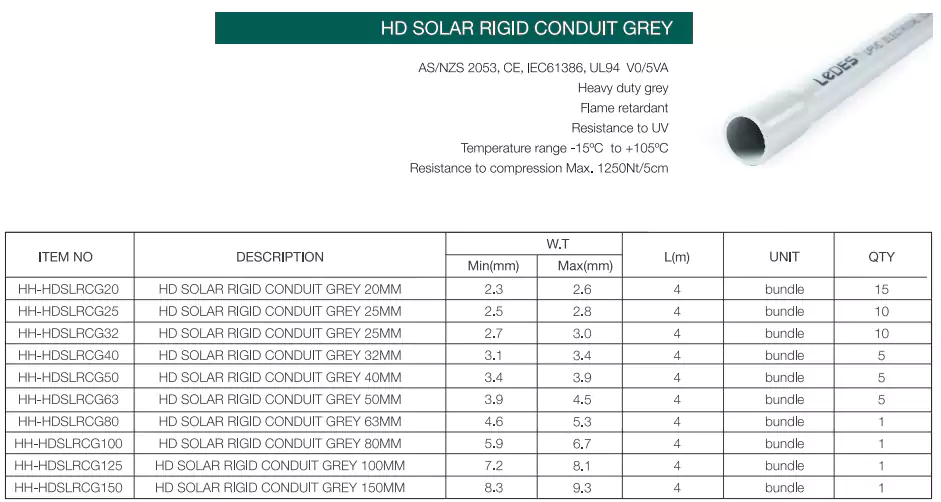
Padrões: AS/NZS 2053, CE, IEC
Vantagens: Resistente às intempéries, resistente aos raios UV, retardante de chamas, classificação V0/5VA, resistente à compressão e ao impacto.
O conduíte sem halogênio de baixa fumaça é um tipo especial de conduíte projetado para minimizar a liberação de gases tóxicos e fumaça em caso de incêndio. Com características principais de:
Sem halogênio:
Esses conduítes não contêm elementos de halogênio, como cloro, flúor, bromo ou iodo, que podem liberar gases tóxicos durante a combustão. Esse recurso aumenta a segurança em caso de incêndio.
Baixa emissão de fumaça:
Quando expostos a altas temperaturas ou chamas, os conduítes livres de halogênio produzem fumaça mínima. Isso reduz problemas de visibilidade durante um incêndio, permitindo evacuação mais segura e acesso mais fácil para resposta de emergência.
Excelente resistência ao fogo:
Projetados para suportar altas temperaturas, esses conduítes têm propriedades superiores de resistência ao fogo, tornando-os adequados para uso em diversas aplicações, incluindo edifícios públicos e instalações industriais.
Sem emissão de fumaça tóxica:
Em caso de incêndio, os conduítes sem halogênio emitem fumaça não tóxica, reduzindo significativamente o risco de inalação prejudicial para os ocupantes e socorristas.
Resistente a UV:
Esses conduítes são projetados para resistir à degradação causada pela luz ultravioleta (UV), tornando-os adequados para aplicações externas onde a exposição à luz solar é uma preocupação.
Resistência a temperaturas extremas:
Eles podem suportar temperaturas extremas de -45℃ a 150 ℃, tanto altas quanto baixas, garantindo desempenho confiável em uma variedade de condições ambientais.
Padrões: Normas de segurança IEC61386, ASTM, UL94
Aplicações: Hospitais, escolas, metrôs, lugares lotados.
Onde o conduíte de PVC pode ser usado?
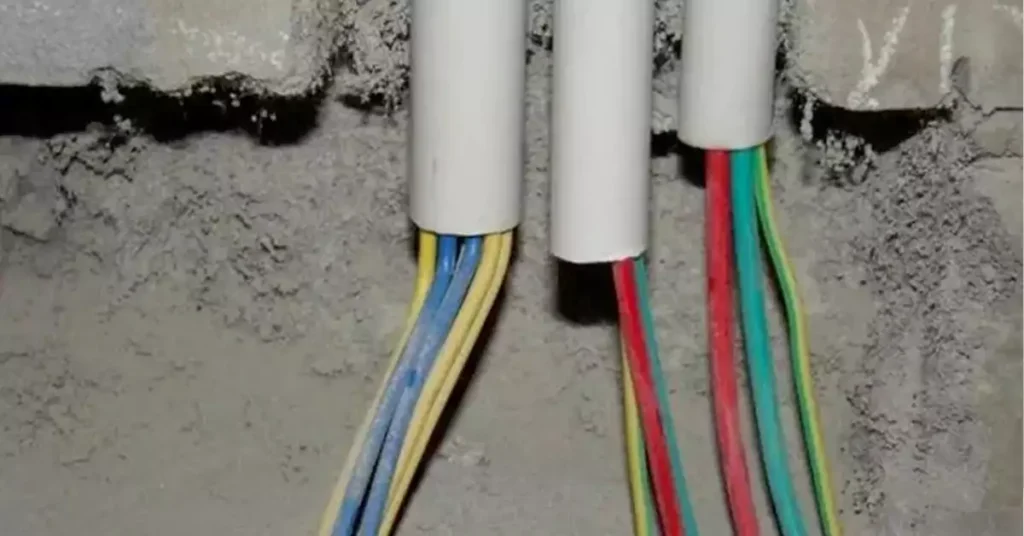

O conduíte de PVC é uma solução versátil para proteger a fiação elétrica e de comunicação em vários ambientes, tanto acima quanto abaixo do solo. Ele está em conformidade com as diretrizes do National Electrical Code (NEC), especificamente NEC 352, que rege seu uso em diferentes ambientes.
Os conduítes de PVC da Ledes têm sido usados em muitos projetos de grande porte, tanto para uso acima do solo quanto subterrâneo. Aqui estão alguns exemplos de projetos.
No projeto CHPE (Champlain Hudson Power Express) nos Estados Unidos, o conduíte de PVC desempenha um papel crucial no gerenciamento da fiação elétrica acima do solo. O projeto envolve sistemas elétricos extensivos que exigem soluções de fiação seguras e eficientes. O conduíte de PVC Schedule 40 é instalado em paredes, tetos e outras estruturas, fornecendo proteção robusta contra fatores ambientais e danos físicos. Sua capacidade de suportar a exposição à luz solar direta o torna adequado para instalações externas, garantindo a longevidade e a confiabilidade dos sistemas elétricos.
No projeto Melbourne Metro Tunnel na Austrália, o conduíte é utilizado para instalações subterrâneas. O projeto requer extensas valas e escavações para infraestrutura elétrica e de comunicação. Conduíte sem halogênio e com baixa emissão de fumaça protegendo a fiação contra umidade e danos relacionados ao solo. Esta aplicação é particularmente benéfica em ambientes urbanos onde o espaço é limitado e a instalação subterrânea é necessária para manter a acessibilidade e a segurança da superfície.
Onde o conduíte de PVC é permitido e NÃO permitido?
O National Electrical Code (NEC) descreve diretrizes específicas para onde o conduíte de PVC pode e não pode ser usado. Essas regras são essenciais para garantir a segurança e a conformidade em instalações elétricas.
Onde o conduíte de PVC é permitido
De acordo com a seção 352.10 do capítulo três da NEC, o conduíte de PVC pode ser usado nas seguintes situações:
1. Instalações subterrâneas
O conduíte de PVC é amplamente aprovado para uso subterrâneo devido à sua durabilidade, resistência à corrosão e proteção contra umidade. É comumente usado em:
- Enterro direto: Os conduítes de PVC podem ser enterrados diretamente no solo, protegendo a fiação elétrica do solo, da umidade e de possíveis danos.
- Bancos de dutos subterrâneos: Frequentemente usado em ambientes comerciais e industriais onde vários conduítes elétricos são agrupados para proteção.
2. Uso externo
- O NEC permite que o conduíte de PVC seja instalado ao ar livre, desde que seja classificado para resistência à luz solar. O PVC é frequentemente usado para:
- Paredes externas: Enquanto o conduíte de PVC for exposto à luz solar, ele deve ter proteção UV para evitar degradação.
- Aplicações expostas acima do solo: Em ambientes industriais e residenciais, conduítes de PVC são permitidos desde que atendam às especificações relevantes para o ambiente.
3. Locais molhados ou úmidos
- Como o PVC não é metálico e é resistente à água e à umidade, ele é ideal para locais molhados e úmidos, como:
- Porões: Áreas propensas à umidade podem se beneficiar das propriedades resistentes à corrosão dos conduítes de PVC.
- Áreas de lavagem industrial: Onde a exposição à água ou produtos químicos é frequente, o PVC oferece proteção duradoura para fiação elétrica.
4. Ambientes corrosivos
O conduíte de PVC é altamente resistente a produtos químicos, o que o torna adequado para ambientes onde a corrosão danificaria os conduítes de metal.
Onde o conduíte de PVC não é permitido
De acordo com a seção 352.12 do NEC, o conduíte de PVC agora é permitido nas seguintes situações:
1. Locais perigosos (classificados)
O conduíte de PVC não é permitido em locais perigosos (classificados), como áreas onde gases explosivos, vapores ou poeira combustível estão presentes, a menos que explicitamente permitido por outros artigos da NEC. Esses locais incluem:
- Refinarias de Petróleo
- Plantas Químicas
- Elevadores de grãos
Nesses ambientes, o PVC não oferece a proteção necessária contra riscos potenciais de incêndio ou explosão.
2. Suporte de Luminárias ou Equipamentos
É proibido que conduítes de PVC suportem luminárias (luminárias) ou outros equipamentos, a menos que sejam especificamente listados para tal uso (conforme descrito em NEC 352.10(H)). Isso significa que o PVC não pode ser usado como um elemento estrutural para suportar luminárias pesadas.
3. Áreas propensas a danos físicos
O conduíte de PVC não deve ser usado em áreas onde possa estar sujeito a danos físicos, a menos que seja especificamente identificado para tal uso. O PVC é menos resistente a impactos em comparação aos conduítes de metal, o que o torna inadequado para locais onde possa ser atingido ou esmagado, como:
- Áreas industriais de alto tráfego
- Zonas de Construção
4. Ambientes de alta temperatura
O conduíte de PVC não é permitido em ambientes onde a temperatura ambiente exceda 50°C (122°F), a menos que seja listado para uso em alta temperatura. O calor alto pode fazer com que o PVC deforme, perca sua integridade estrutural ou se torne um risco de incêndio. Tais ambientes incluem:
- Salas de caldeiras
- Áreas próximas a fornos industriais
5. Teatros e locais semelhantes
O conduíte de PVC é restrito para uso em teatros e locais similares, a menos que seja especificamente permitido pelas Seções 518.4 e 520.5 do NEC. Esses espaços podem ter requisitos exclusivos de segurança contra incêndio que o PVC não atende, como:
- Estágios de desempenho
- Cinemas
Entender onde os conduítes de PVC são permitidos e restritos de acordo com o NEC garante instalações seguras e em conformidade.
Instalando conduíte de PVC: um guia passo a passo
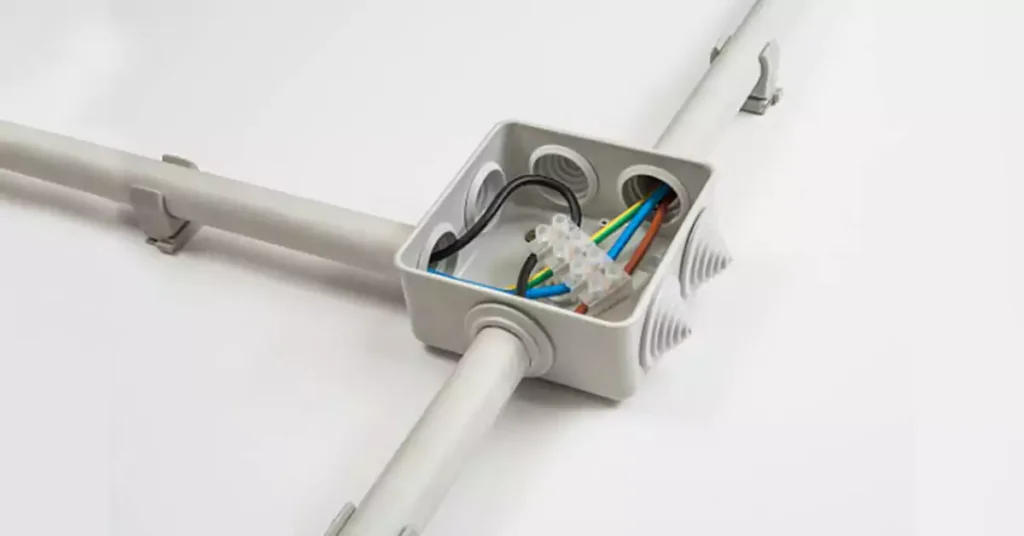

Já escrevemos um tutorial detalhado antes. Se você estiver interessado, você pode aprenda tudo sobre Instalação de Eletrodutos de PVC. A seguir estão as etapas gerais da instalação:
Etapa 1: planeje seu layout
Pesquise a área: Identifique o caminho para a passagem do seu conduíte, considerando onde suas caixas elétricas, tomadas ou interruptores ficarão localizados. Certifique-se de evitar áreas onde o conduíte de PVC não é permitido (por exemplo, espaços de plenum ou áreas de alto calor, conforme especificado pela NEC).
Medir o caminho: Meça o comprimento do conduíte necessário e marque as posições onde serão necessárias curvas, caixas e junções. Tenha em mente os requisitos da NEC para espaçamento entre suportes de conduíte e o posicionamento de caixas de junção.
Etapa 2: Corte o conduíte de PVC e rebarbe as bordas
Marque os pontos de corte: Use uma fita métrica e um marcador para medir e marcar o conduíte de PVC nos comprimentos necessários.
Corte o conduíte: Use um cortador de tubos de PVC para um corte limpo. Alternativamente, uma serra de arco de dentes finos pode ser usada.
Rebarbe as bordas: Após o corte, rebarbe as bordas do conduíte com uma faca utilitária ou lixa. Este passo é essencial para evitar que bordas afiadas danifiquem os fios elétricos durante a instalação.
Etapa 3: Use conduítes e caixas elétricas maiores
Escolha um conduíte maior: Para facilitar a instalação, especialmente ao passar vários fios, use um tamanho de conduíte maior do que o requisito mínimo da NEC. Isso reduzirá o atrito ao puxar os fios.
Selecione caixas elétricas apropriadas: Escolha caixas que forneçam espaço suficiente para conexões de fios, pois caixas apertadas podem levar ao superaquecimento. Certifique-se de que as caixas sejam classificadas para o local pretendido (por exemplo, caixas à prova de intempéries para uso externo).
Etapa 4: Dobre o conduíte ou use conexões para fazer curvas
Dobramento por calor (se necessário): Para curvas personalizadas, use uma pistola de ar quente para amolecer o conduíte de PVC e, em seguida, modele-o com cuidado. Segure a curva no lugar até que esfrie.
Cotovelos para giros: Se você não quiser dobrar o conduíte manualmente, use cotovelos de PVC para curvas de 90 graus ou outros ângulos.
Instalar caixas de junção para execuções complexas: Para trechos com múltiplas curvas ou para transição entre seções de conduíte, caixas de junção podem ser usadas para simplificar o roteamento do conduíte e fornecer pontos de acesso fáceis para a fiação.
Etapa 5: Aplique cimento de PVC (o conduíte de PVC não requer primer)
Aplicar cimento: Para unir seções de conduíte de PVC ou fixar o conduíte a conexões (cotovelos, acoplamentos), aplique cimento de PVC tanto na parte interna da conexão quanto na parte externa do conduíte.
Estabeleça conexões seguras: Empurre o conduíte para dentro do encaixe e gire levemente para garantir uma conexão forte e estanque. O conduíte de PVC geralmente não requer um primer como alguns outros sistemas de tubulação de PVC.
Etapa 6: Instalar caixas elétricas com conduíte de PVC
Conecte o conduíte às caixas: Fixe o conduíte de PVC às caixas elétricas usando encaixes apropriados. Certifique-se de que as caixas estejam firmemente montadas em paredes, tetos ou outras estruturas.
Caixas de vedação para áreas externas: Para instalações externas, use caixas elétricas à prova de intempéries e aplique selante ao redor dos pontos de entrada do conduíte para evitar a entrada de umidade.
Etapa 7: Use ganchos para apoiar o conduíte de PVC
Instalar suportes para conduítes: Fixe o conduíte de PVC em paredes, tetos ou ao longo de vigas usando ganchos ou cintas de conduíte. O NEC recomenda apoiar o conduíte de PVC em intervalos não maiores que 3 pés de distância.
Ancorar o conduíte: Use parafusos, âncoras ou outros fixadores para prender firmemente os ganchos de conduíte à estrutura. Certifique-se de que o conduíte não esteja cedendo e permaneça firmemente no lugar.
Etapa 8: Puxe os fios elétricos
Passe a fita de pesca pelo conduíte: Insira a fita de pesca em uma extremidade do conduíte e empurre-a até atingir a outra extremidade.
Fixe os fios à fita de pesca: Prenda os fios elétricos à fita isolante usando fita isolante.
Puxe os fios: Puxe delicadamente a fita de peixe pelo conduíte, trazendo os fios junto com ela. Tenha cuidado para não danificar o isolamento do fio.
Etapa 9: Instalar buchas de conduíte
Proteja as pontas dos fios: Nas extremidades do conduíte onde os fios saem, instale buchas de conduíte. Essas buchas protegem os fios de bordas afiadas nas extremidades do conduíte, prevenindo danos potenciais ao isolamento.
Buchas seguras no lugar: Certifique-se de que as buchas estejam devidamente instaladas e presas para proteger os fios quando eles saem do conduíte para caixas ou gabinetes elétricos.
Etapa 10: Teste o sistema
Verifique todas as conexões: Após instalar o conduíte e puxar os fios, verifique se todas as conexões do conduíte estão firmes e seguras. Certifique-se de que todos os encaixes, acoplamentos e caixas estejam devidamente selados.
Continuidade do teste: Use um multímetro para testar a continuidade da fiação e garantir que as conexões elétricas estejam funcionando corretamente antes de ligar o sistema.
Seguindo essas etapas detalhadas, você pode garantir uma instalação segura, eficiente e compatível de conduítes de PVC para seu projeto de fiação elétrica.
Como cortar e unir corretamente um conduíte de PVC?
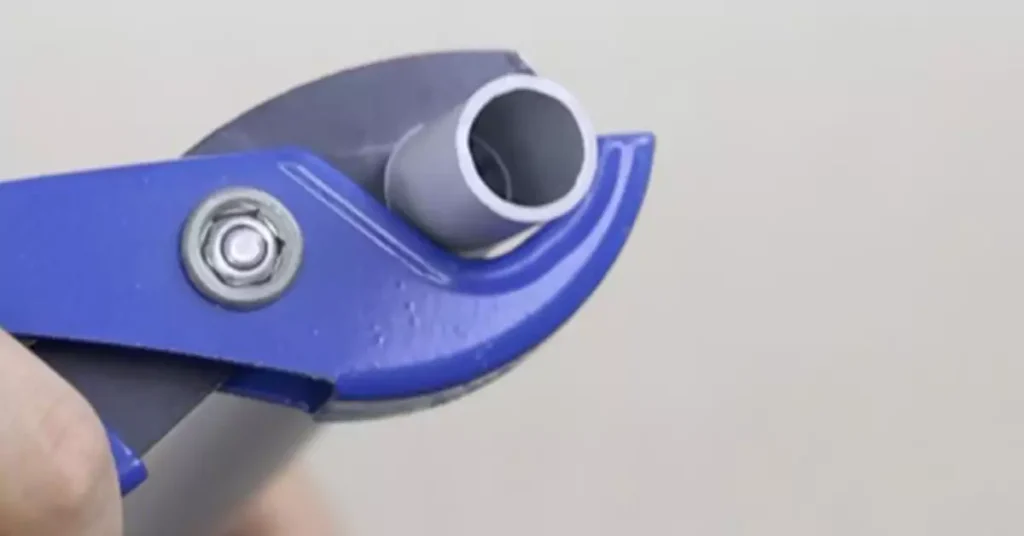

Cortar e unir conduítes de PVC corretamente é essencial para uma instalação elétrica limpa, eficiente e segura. Nesta seção, nós o guiaremos pelas melhores práticas para cortar conduítes de PVC e fazer juntas seguras usando cimento e conexões de PVC.
Etapa 1: Escolha as ferramentas certas
Antes de começar a cortar e unir o conduíte de PVC, reúna as ferramentas necessárias:
Cortador de tubos de PVC: Um cortador de tubos de PVC com catraca proporciona cortes limpos e retos com o mínimo de esforço.
Serra: Se você não tiver um cortador de PVC, uma serra de dentes finos pode ser usada para cortar o conduíte, embora isso possa exigir mais tempo e esforço.
Ferramenta de rebarbação ou faca utilitária: Essas ferramentas ajudam a suavizar as arestas após o corte.
Fita métrica e marcador: Usado para medir e marcar o conduíte para corte.
Cimento PVC: Necessário para unir com segurança seções de conduítes e conexões.
Acoplamentos e conexões: Para conectar duas ou mais seções de conduíte ou para fixar conduíte em caixas elétricas.
Etapa 2: Meça e marque o conduíte
Medição precisa: Meça o comprimento necessário do conduíte usando uma fita métrica. Sempre meça duas vezes para garantir a precisão, especialmente se o conduíte passar por espaços apertados ou tiver que atender a dimensões específicas.
Marque o ponto de corte: Use um marcador permanente para marcar o ponto onde o conduíte será cortado. Desenhe uma linha ao redor de toda a circunferência para garantir um corte reto.
Etapa 3: Corte o conduíte de PVC
Usando um cortador de tubos de PVC: Abra as mandíbulas do cortador de tubos de PVC e posicione-as ao redor da linha marcada no conduíte. Aplique pressão uniforme ao apertar as alças para cortar o tubo. Esta ferramenta lhe dará um corte limpo e reto.
Usando uma serra: Se estiver usando uma serra, prenda o conduíte em um torno ou contra uma superfície estável para mantê-lo no lugar. Serre através do conduíte usando movimentos lentos e firmes, certificando-se de seguir a linha marcada para manter um corte reto.
Evite bordas irregulares: Certifique-se de que o corte seja suave e reto. Bordas irregulares ou irregulares podem dificultar a união do conduíte e podem danificar o isolamento do fio.
Etapa 4: rebarbe a borda cortada
Suavize a borda interna: Após o corte, o interior do conduíte terá rebarbas afiadas que podem danificar fios elétricos quando puxadas. Use uma ferramenta de rebarbação ou uma faca utilitária para alisar essas bordas ásperas.
Suavize a borda externa: Também é importante alisar a borda externa para garantir uma conexão limpa com acoplamentos e conexões.
Etapa 5: Aplicar Cimento PVC
Aplicar Cimento PVC: Ao contrário da tubulação de PVC usada para encanamento, o conduíte de PVC normalmente não requer um primer. Aplique cimento de PVC uniformemente ao redor da parte externa da extremidade do conduíte e da parte interna do encaixe. Certifique-se de usar cimento de PVC classificado especificamente para conduítes elétricos para garantir uma ligação segura e duradoura.
Empurre e gire: Imediatamente após aplicar o cimento, empurre o conduíte para dentro do encaixe e gire-o cerca de um quarto de volta para distribuir uniformemente o cimento. Segure o conduíte e o encaixe juntos por alguns segundos para permitir que o cimento seque.
Etapa 7: Deixe o cimento curar
Definir hora: Deixe o cimento curar de acordo com as instruções do fabricante. Geralmente, o cimento de PVC endurece em poucos minutos, mas pode levar até 24 horas para a junta curar completamente.
Verifique se há lacunas: Depois que o cimento estiver curado, inspecione as juntas para garantir que não haja lacunas ou conexões soltas. As juntas devem estar firmes, seguras e alinhadas corretamente.
O conduíte de PVC é adequado para aplicações de alta tensão?
Compreendendo as propriedades de alta tensão e PVC

Alta tensão normalmente se refere a sistemas elétricos operando em tensões acima de 1.000 volts CA ou 1.500 volts CC. O conduíte de PVC, feito de cloreto de polivinila, tem várias características que são benéficas e limitantes quando usado em tais aplicações:
Isolamento elétrico: O PVC é um material não condutor, o que o torna inerentemente resistente à corrente elétrica, o que pode ajudar a reduzir o risco de arco elétrico.
Retardante de chama: O conduíte de PVC tem propriedades retardantes de chamas, o que é um fator importante ao considerar ambientes de alta tensão, onde podem ocorrer acúmulo de calor e falhas elétricas.
Sensibilidade à temperatura: O PVC tem limitações em ambientes de alta temperatura (acima de 50 °C/122 °F) e pode amolecer ou deformar sob condições extremas, o que pode ser uma preocupação para sistemas de alta tensão onde a dissipação de calor é crítica.
Requisitos NEC para conduítes de PVC em aplicações de alta tensão
O National Electrical Code (NEC) fornece diretrizes rígidas sobre a instalação de conduítes elétricos, incluindo PVC, em aplicações de alta tensão. De acordo com o NEC Capítulo 3, Artigo 300, os sistemas de alta tensão têm padrões de instalação mais rígidos do que os sistemas de baixa tensão devido aos riscos potenciais associados ao aumento da corrente. Alguns pontos-chave incluem:
1. Artigo 352 do NEC:
Esta seção aborda o uso de conduítes de PVC rígido, mas para alta tensão, é necessário o cumprimento de certas condições:
Uso subterrâneo: O conduíte de PVC geralmente é permitido para aplicações subterrâneas de alta tensão, especialmente em situações de enterramento direto, onde o conduíte pode proteger os cabos contra umidade, movimentação do solo e corrosão.
Acima do solo: Embora o conduíte de PVC possa ser usado em sistemas de alta tensão acima do solo, ele deve ser listado para tal uso e atender a requisitos específicos, principalmente em relação à exposição à luz solar e altas temperaturas.
2. Isolamento e classificações de voltagem:
O Artigo 300 do NEC enfatiza a importância do isolamento e separação do condutor para instalações de alta tensão. Condutores classificados para alta tensão devem ter níveis de isolamento apropriados para evitar quebra, e o próprio conduíte de PVC deve ser aprovado para uso em alta tensão, especialmente se usado em conjunto com outros tipos de conduíte em sistemas mistos.
3. Preenchimento e redução de capacidade do conduíte:
Para aplicações de alta tensão, a NEC define limites rígidos para o preenchimento do conduíte e exige a redução da capacidade dos condutores para evitar o superaquecimento. Isso significa que o conduíte de PVC precisa ser dimensionado corretamente para evitar exceder a capacidade máxima de preenchimento, particularmente em instalações de alta tensão onde a dissipação de calor é crítica.
4. Expansão térmica:
Em longos trechos de conduíte de PVC, o NEC requer consideração de expansão e contração térmica. Sistemas de alta tensão geram mais calor, e a sensibilidade do PVC a mudanças de temperatura pode levar à expansão ou empenamento. Conexões de expansão podem ser necessárias para acomodar esse movimento e evitar danos ao conduíte ou aos cabos.
Quando o conduíte de PVC é adequado para alta tensão
O conduíte de PVC é adequado para certas aplicações de alta tensão, desde que a instalação atenda aos requisitos da NEC e trate das limitações do material. Aqui estão alguns cenários em que o conduíte de PVC é comumente usado para alta tensão:
1. Distribuição subterrânea de alta tensão:
O conduíte de PVC é frequentemente usado para distribuição subterrânea de alta tensão elétrica, particularmente em ambientes industriais, subestações ou linhas de serviços públicos. Sua resistência à umidade e corrosão o torna ideal para proteger cabos de alta tensão em aplicações enterradas.
2. Ambientes úmidos e corrosivos:
Em ambientes onde o conduíte pode ser exposto à água ou produtos químicos, o PVC oferece excelente resistência à corrosão em comparação aos conduítes de metal. Isso o torna adequado para instalações de alta tensão industriais ou externas, como estações de tratamento de águas residuais ou regiões costeiras.
3. Instalações solares e eólicas de alta tensão:
O conduíte de PVC é frequentemente usado em sistemas de energia renovável, como parques solares ou eólicos, onde cabos de alta tensão devem ser protegidos no subsolo ou em ambientes expostos aos elementos.
Quando o conduíte de PVC não é adequado para alta tensão
Apesar de suas vantagens, o conduíte de PVC não é adequado para todas as aplicações de alta tensão, particularmente em situações que excedem suas limitações físicas ou químicas:
Aplicações de alta temperatura
Locais perigosos
Áreas com alto estresse físico
O conduíte de PVC pode ser dobrado?
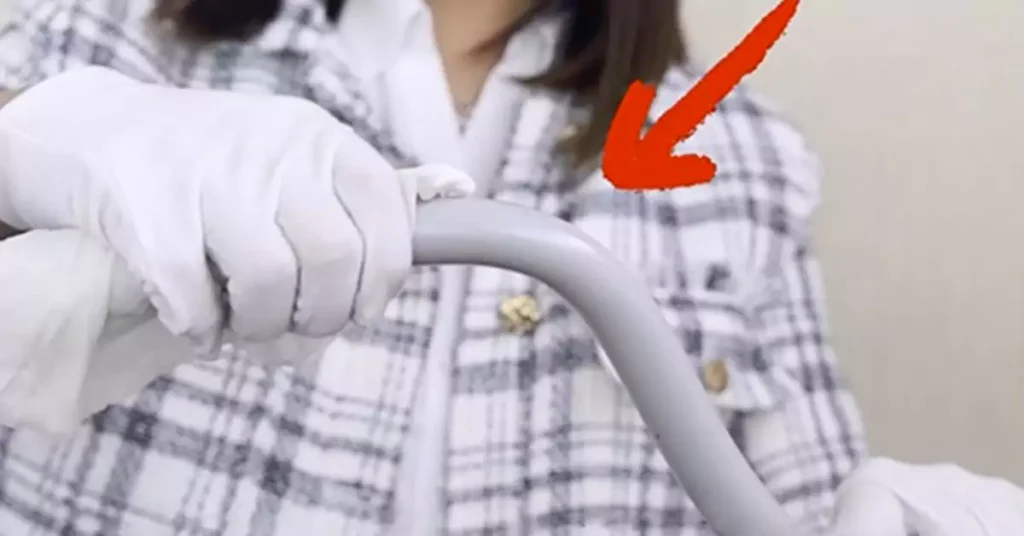

Sim, o conduíte de PVC pode ser dobrado para acomodar vários ângulos e mudanças de direção durante a instalação. Existem dois métodos comuns para dobrar conduítes de PVC: usando uma pistola de ar quente ou um dobrador de conduítes com um elemento de aquecimento projetado para PVC.
Método 1: Usando uma pistola de ar quente
- Prepare o conduíte: Meça e marque onde a dobra precisa ocorrer. Prenda o conduíte no lugar para evitar movimento durante a dobra.
- Aqueça o conduíte: Use uma pistola de ar quente para aplicar calor uniforme ao longo da seção do conduíte que você deseja dobrar. Mova a pistola de ar quente para frente e para trás para evitar concentrar calor em um ponto, o que pode fazer o PVC borbulhar ou queimar. Aqueça o PVC até que ele se torne flexível, normalmente em torno de 180°F (82°C).
- Dobre o conduíte: Assim que o PVC estiver flexível, dobre-o suavemente com a mão até o ângulo desejado. Você pode usar um gabarito ou forma de dobra para manter uma curva uniforme. Segure a dobra no lugar até que o PVC esfrie e endureça.
- Resfrie e verifique a curva: Depois que o conduíte esfriar (o que geralmente leva alguns minutos), verifique se a curva está lisa e se o interior não está dobrado ou obstruído, pois isso pode danificar os fios ou violar os requisitos do código.
Método 2: Usando um dobrador de conduíte de PVC
- Use um dobrador aquecido: Dobradores especiais de conduíte de PVC estão disponíveis para aquecer o conduíte uniformemente e permitir curvas precisas. Esses dobradores têm um elemento de aquecimento para amolecer o PVC e guias integradas para dobrar em ângulos exatos.
- Dobre o conduíte: Após o conduíte ser aquecido, use o dobrador para criar a curva desejada. Este método garante dobras consistentes, especialmente para projetos maiores com múltiplas dobras em ângulos diferentes.
Dicas de segurança para dobrar conduítes de PVC
Evite o superaquecimento: Aplicar muito calor ou segurar a pistola de ar quente muito perto pode fazer com que o PVC forme bolhas ou queime. Mantenha a pistola de ar quente em movimento e mantenha uma distância segura para distribuir o calor uniformemente.
Use luvas e equipamentos de segurança: O PVC aquecido pode ficar muito quente, então é essencial usar luvas resistentes ao calor ao manusear o conduíte. Além disso, garanta que você esteja trabalhando em uma área bem ventilada, pois o PVC aquecido pode liberar vapores.
Prevenir torções: Sempre dobre o conduíte lentamente e uniformemente para evitar torções. Um conduíte torcido pode danificar os fios elétricos ou reduzir o espaço interno, dificultando a passagem dos cabos.
Verifique se há deformação: Após a curvatura ser concluída, inspecione o conduíte para garantir que ele não tenha achatado ou deformado excessivamente. O diâmetro interno deve permanecer desobstruído para cumprir com os códigos elétricos.
Considere expansão e contração: O PVC pode expandir ou contrair devido a mudanças de temperatura, então leve isso em consideração ao planejar curvas, especialmente para longos percursos de conduíte. Usar conexões de expansão pode ajudar a evitar problemas.
Qual é a diferença entre conduítes de PVC e UPVC?
Os conduítes de PVC (Policloreto de Vinila) e UPVC (Policloreto de Vinila Não Plastificado) são amplamente usados para instalações elétricas, mas diferem em termos de flexibilidade, resistência e aplicação. Aqui está uma análise das principais diferenças:
Características | Conduíte de PVC | Conduíte UPVC |
Resistência e durabilidade | Menos resistente a impactos, adequado para uso mais leve | Alta resistência ao impacto, durável para ambientes difíceis |
Resistência térmica | Menor resistência a altas temperaturas | Maior resistência ao calor, adequado para ambientes quentes |
Resistência química |
Bom, mas inferior ao UPVC | Excelente, mais resistente a produtos químicos e corrosão |
Aplicações típicas | Fiação interna, residencial, comercial leve | Instalações externas, industriais e subterrâneas |
Custo | Menor custo, mais acessível para uso geral | Custo mais alto devido à maior durabilidade e resistência |
Conduítes de PVC vs. Conduítes Metálicos
Quando se trata de instalações elétricas, a escolha do material do conduíte é crucial para garantir segurança, durabilidade e conformidade com as regulamentações locais. Dois tipos comuns de conduítes são os de PVC (cloreto de polivinila) e os metálicos (como EMT, RMC e IMC). Cada tipo tem suas vantagens e desvantagens, tornando-os adequados para diferentes aplicações.
Características | Conduítes de PVC | Eletrodutos Metálicos |
Material | Plástico (cloreto de polivinila) | Metal (Aço, Alumínio) |
Peso | Leve | Mais pesado |
Custo | Geralmente menor custo | Custo tipicamente mais alto |
Resistência à corrosão | Excelente resistência | Suscetível à corrosão |
Flexibilidade | Mais flexível e fácil de instalar | Rígido, menos flexível |
Resistência ao fogo | Bom, mas não à prova de fogo | Melhor resistência ao fogo |
Condutividade elétrica | Não condutivo | Condutor |
Resistência ao impacto | Moderado | Alto |
Resistência UV | Limitado (pode degradar-se ao ar livre) | Excelente |
Aplicativo | Uso interno, locais úmidos | Uso interno e externo, aplicações industriais |
Qual é a diferença entre tubo de PVC e conduíte de PVC?
Nós comparamos as diferenças entre tubos de encanamento de PVC e conduítes de PVC em detalhes. Para detalhes, consulte o artigo A diferença entre PVC para encanamento e PVC para conduíte elétrico. Aqui estão algumas diferenças importantes entre eles.
Características | Tubo de PVC | Conduíte de PVC |
Uso primário | Encanamento e drenagem | Proteção de fiação elétrica |
Composição do material | PVC padrão | PVC rígido com aditivos para maior resistência |
Espessura da parede | Paredes mais finas, mais leves | Paredes mais grossas, mais pesadas |
Classificação de temperatura | Tolerância à temperatura mais baixa | Maior tolerância à temperatura |
Classificação de pressão da água | Requisitos de alta pressão | Nenhum requisito específico |
Padrões de Aprovação | Varia de acordo com a aplicação | Deve atender aos códigos elétricos |
Custo | Geralmente menos caro | Geralmente mais caro |
Por que o conduíte de PVC é mais caro que o tubo de PVC?
Composição do material: O conduíte de PVC é fabricado com aditivos adicionais para aumentar sua durabilidade e resistência a estressores ambientais. Isso leva a um custo de material mais alto.
Espessura da parede: As paredes mais espessas dos conduítes de PVC proporcionam maior proteção à fiação elétrica, o que aumenta os custos de fabricação.
Padrões e testes: Os conduítes de PVC devem atender a códigos e padrões elétricos rigorosos, que exigem testes adicionais e garantia de qualidade durante a produção, contribuindo para custos mais altos.
Demanda de mercado: A demanda por conduítes elétricos em aplicações industriais e de construção pode aumentar os preços em comparação aos tubos de PVC para encanamento padrão.
Custos de instalação: Embora não seja um custo direto do conduíte em si, o processo de instalação também pode contribuir para as despesas gerais, dada a necessidade de conexões especializadas e adesão às normas de segurança.
Como fabricante, achamos que o maior fator que afeta o preço do tubo de PVC e do conduíte de PVC é o preço das matérias-primas e aditivos de PVC. Não há muita diferença entre os dois em essência, mas a aplicação é diferente.
Conduíte de PVC vs. Conduíte estanque a líquidos
Dois tipos comuns de conduíte são o conduíte de PVC (cloreto de polivinila) e o conduíte estanque a líquidos. Cada um tem suas próprias características, vantagens e aplicações.
Conduíte de PVC: Este é um tipo de conduíte rígido feito de cloreto de polivinila, um plástico leve e durável. É comumente usado em aplicações residenciais e comerciais para proteger fiação elétrica. O conduíte de PVC é resistente à umidade, produtos químicos e corrosão, tornando-o adequado para várias condições ambientais.
Conduíte estanque a líquidos: Este conduíte é projetado para fornecer um invólucro flexível e estanque para fiação elétrica. Ele é tipicamente feito de PVC flexível ou metal com uma vedação estanque, permitindo que seja usado em locais molhados ou úmidos. O conduíte estanque é ideal para aplicações onde ocorre movimento ou vibração, pois pode dobrar sem quebrar.
Recurso | Conduíte de PVC | Conduíte estanque a líquidos |
Material | PVC rígido | PVC flexível ou metal |
Flexibilidade | Rígido | Flexível |
Resistência à água | Bom (não adequado para água parada) | Excelente (à prova d'água) |
Instalação | Requer cola ou acessórios | Pode ser instalado sem cola |
Aplicações | Interior e exterior (áreas não molhadas) | Locais molhados ou úmidos, áreas de máquinas |
Custo | Geralmente mais baixo | Maior devido à flexibilidade e vedação |
Durabilidade | Resistente a produtos químicos e corrosão | Altamente durável, resistente à umidade |
Classificação de temperatura | Moderado, normalmente até 60°C (140°F) | Classificações de temperatura mais altas disponíveis |
Como escolher o conduíte de PVC certo para seu projeto?

Escolher o conduíte de PVC certo para seu projeto envolve várias considerações para garantir segurança, conformidade e eficiência. Aqui estão os principais fatores a serem lembrados:
1. Entenda os tipos de conduítes de PVC
Conduíte de PVC rígido: Durável e adequado para instalações subterrâneas ou expostas.
Eletroduto de PVC flexível: Ideal para aplicações que exigem flexão ou movimento.
Anexo 40 vs. Anexo 80: O Schedule 80 é mais espesso e robusto, adequado para ambientes mais adversos.
2. Considere o meio ambiente
Interno vs. Externo: Conduítes externos devem ser resistentes a UV. Aplicações internas podem ter requisitos diferentes.
Exposição à umidade e produtos químicos: Use conduítes adequados para locais úmidos ou resistentes a produtos químicos, se necessário.
3. Verifique os requisitos de tamanho
Diâmetro: Escolha um tamanho de conduíte que acomode o número e o tamanho dos fios que você planeja passar. Use as diretrizes do NEC (National Electrical Code) para capacidade de preenchimento.
Comprimento: Certifique-se de que o comprimento do conduíte seja suficiente para sua instalação, sem juntas excessivas.
4. Revise os códigos e padrões elétricos
Familiarize-se com os códigos de construção locais e o NEC para garantir a conformidade com os regulamentos de segurança.
5. Avalie as condições de instalação
Curvas e voltas: Considere quantas curvas sua instalação exigirá. Conduítes flexíveis podem ser melhores para espaços apertados.
Suporte e montagem: Certifique-se de ter os suportes necessários para a instalação do seu conduíte.
6. Avalie o custo e a disponibilidade
Compare os custos de diferentes tipos e marcas de conduíte de PVC. Certifique-se de que o produto esteja prontamente disponível em sua área.
7. Consulte profissionais
Caso não tenha certeza, consultar um eletricista ou um profissional pode fornecer informações específicas sobre as necessidades do seu projeto.
Conclusão
Em resumo, o conduíte de PVC é um componente essencial em aplicações elétricas e de construção, oferecendo uma combinação de durabilidade, flexibilidade e custo-benefício. Sua resistência à umidade, produtos químicos e corrosão o torna uma escolha ideal para instalações internas e externas. Seja você um empreiteiro profissional ou um entusiasta do faça você mesmo, entender os vários tipos de conduíte de PVC e suas aplicações pode aumentar a segurança e a eficiência de seus projetos.
Ao considerar fatores como métodos de instalação, códigos de construção locais e condições ambientais, você pode tomar decisões informadas que maximizem os benefícios do uso de conduíte de PVC. À medida que a demanda por sistemas elétricos sustentáveis e confiáveis continua a crescer, o conduíte de PVC continua sendo uma solução prática que atende às necessidades modernas, ao mesmo tempo em que garante a conformidade com os padrões da indústria. Adotar esse material versátil não apenas melhora a longevidade de suas instalações, mas também contribui para uma infraestrutura elétrica mais segura e organizada.