
목차
Direct burial conduit refers to a type of piping or conduit system that is designed and installed underground without the need for additional protection or encasement. It is commonly used for electrical, telecommunications, or data communication applications where cables or wires need to be routed underground.
직접 매설 도관은 일반적으로 고밀도 폴리에틸렌(HDPE) 또는 경질 PVC(폴리염화비닐)와 같은 내구성 있는 소재로 만들어지며, 이는 습기, 토양 산성도 및 기타 환경 요인으로부터 보호합니다. 도관은 부식, 충격 및 압착에 저항하도록 설계되어 수용된 케이블 또는 전선의 무결성을 보장합니다.
The “DB” in the name stands for “direct burial,” indicating its suitability for installation underground without requiring additional concrete encasement. This makes it a cost-effective and versatile option for various underground electrical applications.
There are several types of DB conduit available, each with its own specifications and advantages. Here are some of the most common used underground conduits in America and Canada.
Notes: Learn more about the details of the UL 651 standard requirement for PVC conduit in our last post if you are interested in this section.
DB60 conduit is a type of conduit specifically engineered to accommodate cables and wires in telecommunications and data networking applications. The “DB60” designation refers to its dimensions, with a standard size of 60mm in both height and width. However, it’s important to note that other sizes and variations may be available to suit specific installation requirements.
- 간편한 설치: 무거운 콘크리트 덮개와 작별하세요. DB60의 직접 매설 기능은 시간과 비용을 절약해 주며, 설치가 간편합니다.
- 뛰어난 강도: DB60은 지하 토양의 압력과 움직임에 따른 스트레스를 견딜 수 있도록 제작되어 케이블이 안전하게 고정됩니다.
- 비용 효율적인 선택: 기존 금속 도관과 비교해 DB60은 설치가 쉽고 무게가 가벼워 상당한 비용 절감 효과를 제공합니다.
전선관 유형 및 위치에 따른 최소 매설 깊이에 대한 일반 지침(특정 요구 사항에 대해서는 국가 전기 규정(NEC) 및 기타 산업 표준 참조):
- 주거 지역: 18인치(45cm)
- 상업 및 산업 지역: 24인치(60cm)
- 도로 교차로: 36인치(90cm)
DB100 conduit is a type of PVC (polyvinyl chloride) conduit specifically designed for direct burial. It’s mainly used to protect electrical cables underground without needing extra encasement like concrete. DB100 is a lighter-duty conduit compared to heavier options like DB120, and it’s commonly used for residential, light commercial, and communication cable applications.
비용 효율성:
DB100 is more affordable than heavier-rated conduits like DB120, making it a practical choice for projects that don’t require extreme mechanical strength.
Lightweight and Easy to Install:
Its thinner wall and lighter weight make DB100 easier to handle and faster to install, helping reduce labor time and costs.
Direct Burial Ready:
It’s manufactured specifically for underground installation without additional protection, simplifying trenching and cable laying.
Corrosion and Moisture Resistant:
Being PVC, DB100 doesn’t corrode like metal conduits and provides excellent resistance to moisture and many chemicals found in soil.
Smooth Interior:
The smooth inner surface reduces friction during cable pulling, helping prevent cable damage during installation.
While specific requirements can vary depending on local codes and project conditions, a common guideline is 18 to 24 inches (45–60 cm) from the top of the conduit to the ground surface for low-voltage and communication lines.
If installed under driveways, roadways, or where heavy equipment may cross, deeper burial (often 24 to 36 inches, sometimes with additional protection like concrete encasement) might be required.
DB120 conduit is a type of electrical conduit that is widely used for protecting and organizing electrical wires and cables. It is made from high-quality, durable materials such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or polyethylene (PE), which provide excellent resistance against corrosion, moisture, chemicals, and UV rays. The “DB120” designation refers to the specific schedule rating of the PVC, which indicates its wall thickness and strength.
- 내구성: DB120 도관은 부식, 화학물질, 풍화에 강하여 장기간 지하 사용에 이상적입니다.
- 충격 저항성: DB120 도관의 두꺼운 벽은 상당한 충격을 견딜 수 있어 내부의 전선이 손상되지 않도록 보호합니다.
- 경량: 콘크리트나 금속 도관에 비해 DB120은 훨씬 가벼워서 취급 및 설치가 더 쉽습니다.
- 유연성: DB120 도관은 다양한 길이와 직경으로 제공되므로 다양한 프로젝트 요구 사항에 쉽게 적응할 수 있습니다.
- Cost-effective: DB120 conduit is a relatively affordable option compared to other types of underground conduit.
- 주거 지역: 12인치(30cm)
- 상업 및 산업 지역: 18인치(45cm)
- 도로 교차로: 36인치(90cm)
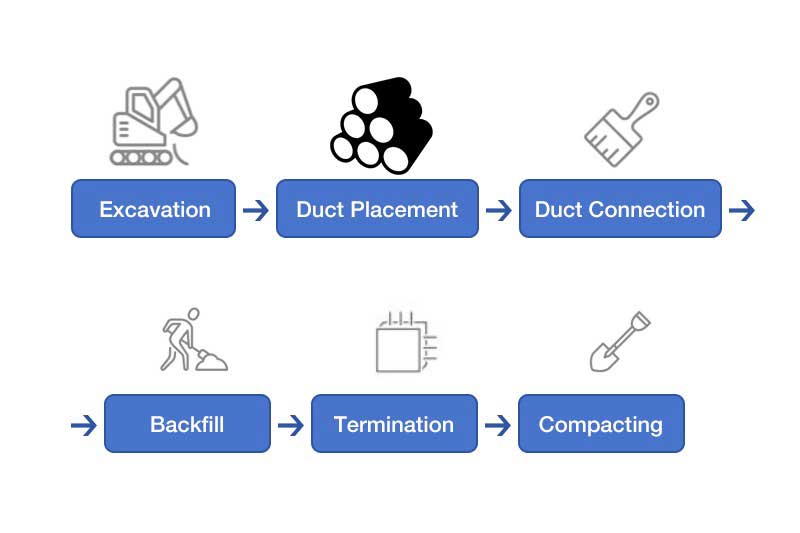
DB120 컨듀이트를 설치하는 것은 비교적 간단한 과정입니다. 기본 단계는 다음과 같습니다.
- 참호를 파세요. 참호는 현지의 전기 및 통신선에 대한 매설 깊이 요건을 충족할 만큼 깊어야 합니다.
- 도관을 놓습니다. 도관을 도랑에 놓고 수평을 유지하며 이물질이 없는지 확인합니다.
- 도관 구간을 연결합니다. 용제 시멘트나 기계적 커플링을 사용하여 도관 구간을 연결합니다.
- 전선을 잡아당기세요. 전선이나 통신선을 도관을 통해 잡아당기세요.
- 참호를 다시 메웁니다. 참호를 흙으로 다시 메우고 압축하여 공기 주머니를 제거합니다.
DB120 도관은 다음을 포함한 다양한 응용 분야에 사용됩니다.
- 주거 및 상업용 지하 전기 배선
- 교통신호 및 가로등 시스템
- 통신 및 데이터 케이블

튼튼한 PVC(폴리염화비닐)로 제작된 이 도관은 콘크리트에 싸여 매장되도록 특별히 설계되었습니다. 즉, 지하 인프라의 필수적인 부분이 되어 민감한 전기 케이블을 매몰된 생명체의 혹독한 현실로부터 보호합니다.
- 뛰어난 강도: "EB"라는 명칭은 토양 이동과 우발적 충격의 압력을 견딜 수 있는 뛰어난 충격 저항성을 의미합니다. 전류가 중단 없이 흐르도록 하는 조용한 수호자라고 생각하세요.
- 뛰어난 내구성: 콘크리트로 둘러싸인 이 도관은 견고하고 안정적인 네트워크를 형성하여 지반 움직임으로 인한 손상 위험을 최소화하고 오래 지속되는 성능을 보장합니다.
- 경량: EB20/35 도관은 금속 제품에 비해 깃털처럼 가벼워 취급 및 설치가 쉽고 시간과 노동 비용을 절감할 수 있습니다.
- 호환성: 다양한 직경과 길이로 제공되는 이 도관은 소규모 주거 시설부터 대규모 상업 단지까지 다양한 프로젝트 요구 사항에 맞게 조정할 수 있습니다.
EB20/35 도관 설치는 간단한 과정을 따릅니다.
- 참호전: 현지 매몰 깊이 요건을 충족할 만큼 깊은 참호를 파서 내부의 전기 동맥을 충분히 보호합니다.
- 콘크리트 받침대: 도관을 지지하고 보호하는 덮개 역할을 할 튼튼한 콘크리트 바닥을 준비합니다.
- 기초 놓기: 도관 섹션을 조심스럽게 도랑에 놓고 올바른 정렬과 연결을 보장합니다.
- 힘의 결합: 용매 시멘트나 기계적 커플링을 사용하여 원활하고 누출 방지가 가능한 도관 네트워크를 만듭니다.
- 콘크리트 클로크: 준비된 콘크리트로 도관을 덮어 통합되고 침투할 수 없는 방패를 만듭니다.
DB2/ES2 conduit refers to a specific type of duct used for communication purposes. It is typically a nonmetallic duct designed to house and protect communication cables, such as fiber optic cables or Ethernet cables. Ledes DB2 duct is made of PVC, certifed by CSA C22.2 No.211.1, and is commonly used in various industries, including telecommunications, networking, and data centers, to provide a conduit for the efficient and organized installation of communication cables.

- 부식 방지: DB2/ES2 PVC 덕트는 높은 PVC 소재로 만들어졌으며, 비금속성이며 자연적으로 부식성 조건에 노출되어도 녹슬지 않습니다. 지하 세계에서 장기적인 성능을 보장하여 배선 시스템에 안전하고 신뢰할 수 있는 보호를 제공합니다.
- 경량: 가벼워서 취급 및 설치가 쉽고 시간과 노동 비용이 크게 절감됩니다.
- 직접 매설: 직접 매설 적용 분야이며 캐나다 전기 규정(CEC)에 따라 설치하는 경우 추가 보호가 필요하지 않습니다.
- 쉬운 전선 당김: DB2/ES2는 내부 표면이 매끄러워 긴 거리에서 전선과 케이블을 당길 때 마찰이 줄어듭니다.
DB2/ES2 PVC 덕트는 쇠톱으로 쉽게 절단할 수 있으며, 작은 크기의 경우 PVC 커터를 사용할 수 있습니다.
덕트나 피팅의 길이를 연결하려면 용매 시멘트만 있으면 됩니다. PVC 용매 시멘트는 조인트를 튼튼하고 누수 방지로 만들 수 있습니다. 취급이 간편하고 시간을 절약할 수 있습니다.
- 트렌치 바닥: 현지 매설 깊이 요건을 충족할 만큼 깊은 트렌치를 파서 내부의 전선을 보호합니다.
- 기초 놓기: DB2 덕트 섹션을 트렌치에 조심스럽게 놓고 용제 시멘트나 기계적 커플링을 사용하여 적절한 정렬과 연결을 보장합니다.
- 매립: 도관이 고정되면 흙으로 도랑을 매립하고 공기 주머니를 제거하기 위해 적절히 압축합니다.
DB 덕트를 묻어야 하는 깊이는 지역 규정, 특정 프로젝트 요구 사항 및 설치 유형을 포함한 다양한 요인에 따라 달라질 수 있습니다. 그러나 고려해야 할 몇 가지 일반적인 지침이 있습니다.
지역 규정: 해당 지역의 건축법규와 규정을 확인하세요. 종종 다양한 유형의 덕트와 유틸리티에 대한 최소 매설 깊이를 명시합니다.
환경적 요인: 서리 깊이, 토양 유형, 지반 조건과 같은 요인을 고려하십시오. 이러한 요인은 덕트의 안정성과 보호에 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다. 영하 기온이 있는 지역에서는 손상을 방지하기 위해 서리선 아래에 덕트를 묻는 것이 일반적입니다.
보호 및 접근성: 덕트는 굴착, 교통, 환경 요인과 같은 외부 요소로부터 적절한 보호를 제공하는 깊이에 매립되어야 합니다. 또한 필요한 경우 쉽게 유지 관리하고 접근할 수 있는 깊이에 매립되어야 합니다.
일반적인 지침으로 DB 덕트와 같은 비금속 통신 덕트는 종종 다음 깊이에 매설됩니다. 18~24인치 (45~60센티미터). 그러나 특정 프로젝트와 지역 규정을 잘 아는 지역 당국 및 전문가와 상의하여 해당 지역의 DB 덕트에 적합한 매몰 깊이를 결정하는 것이 중요합니다.

Before selecting a DB conduit for an underground project, it’s essential to understand the standards that govern its design, material, and performance. Standards ensure that conduits meet minimum safety, durability, and quality benchmarks – critical when infrastructure reliability is on the line.
In the United States, the main standards are:
- ASTM F512-19: Standard Specification for Smooth-Wall Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Conduit and Fittings for Underground Installation.
- NEMA TC 6 & 8: Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Plastic Utilities Duct for Underground Installers.
캐나다에서, the key standard is:
- CSA C22.2 No. 211.1: Rigid types EB1 and DB2/ES2 PVC conduit.
Pro Tips: Want to learn more about the details of the CSA CC22.2 standard? Click the link to read our last post.
One of the most important standards for underground electrical conduit in the United States is ASTM F512-19. This specification defines the material, construction, and performance requirements for smooth-wall poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) conduits and fittings used for underground installation of communication and electrical power cables.
The standard organizes conduits into five types, based on their stiffness and intended use:
Type EB-20 — Concrete encasement (lower stiffness)
Type EB-35 — Concrete encasement (higher stiffness)
Type DB-60 — Direct burial (lower stiffness)
Type DB-100 — Direct burial (higher stiffness)
Type DB-120 — Direct burial (very high stiffness)
EB types are mainly intended for installation within concrete encasement, while DB types are specifically built for burial directly in the soil, where higher strength and durability are essential.
To comply with ASTM F512-19, conduits must pass several critical tests that assess their durability and performance under underground conditions:
Conduits must be made from virgin or reworked PVC compound that meets detailed material properties such as strength, impact resistance, and chemical resistance.
The PVC material must meet specific cell classifications as defined in ASTM D1784, including:
- 12254
- 12164 (requiring a minimum tensile strength of 4000 psi or 28 MPa)
- 12264 (requiring a minimum tensile modulus of 500,000 psi)
Molded fittings must be made from PVC compounds with cell classifications of:
- 12234, or
- 13343,
also as defined under ASTM D1784.
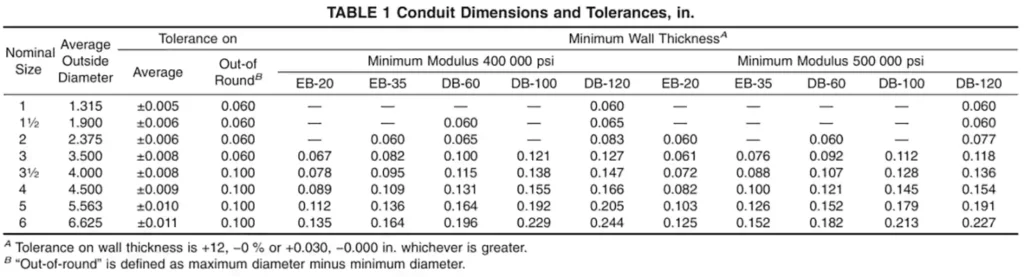
Outside diameters, wall thicknesses, and lengths must fall within tight tolerances to ensure consistent quality and compatibility with fittings.
Special dimensional requirements are defined separately for EB and DB types due to their different burial conditions.
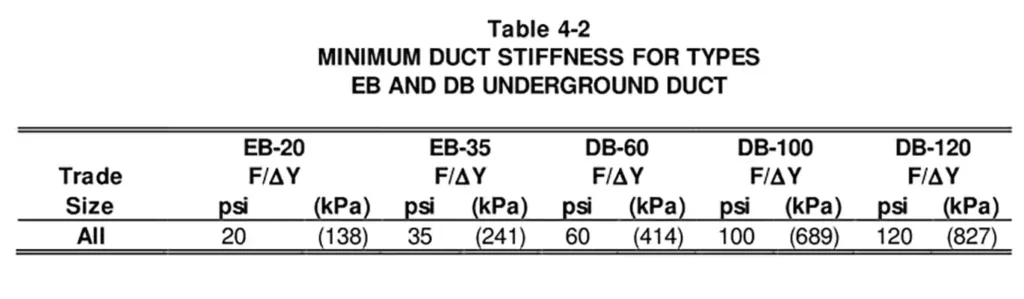
Pipe stiffness is a critical performance characteristic for underground conduits, particularly those intended for direct burial where soil loads and external pressures are a concern.
According to ASTM F512-19:
Minimum Pipe Stiffness Values are as follow:

시험 방법
The stiffness of the conduit is determined by a standardized parallel-plate loading test, following the procedures outlined in ASTM D2412. Here’s how the method works:
- A short length of pipe is placed horizontally between two rigid, parallel flat plates.
- The plates are brought together at a controlled rate of 0.50 ± 0.02 inches (12.5 ± 0.5 mm) per minute.
• During loading, load versus deflection (diameter change) data are recorded. - If cracking, crazing, delamination, or rupture occurs during the test, the corresponding load and deflection at the moment of failure are documented.
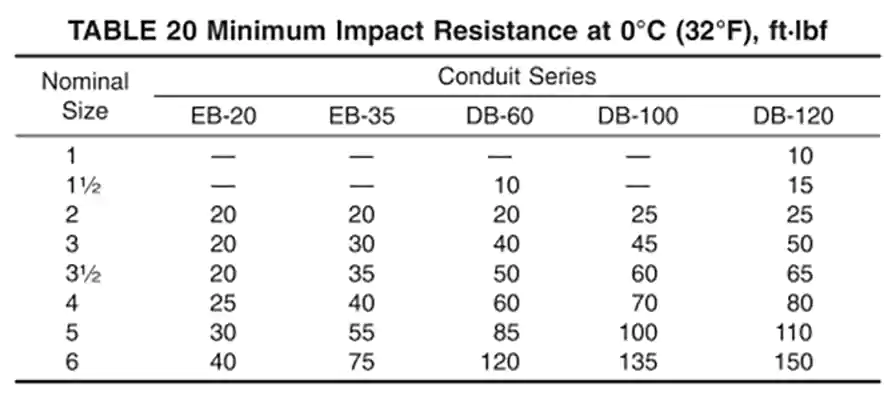
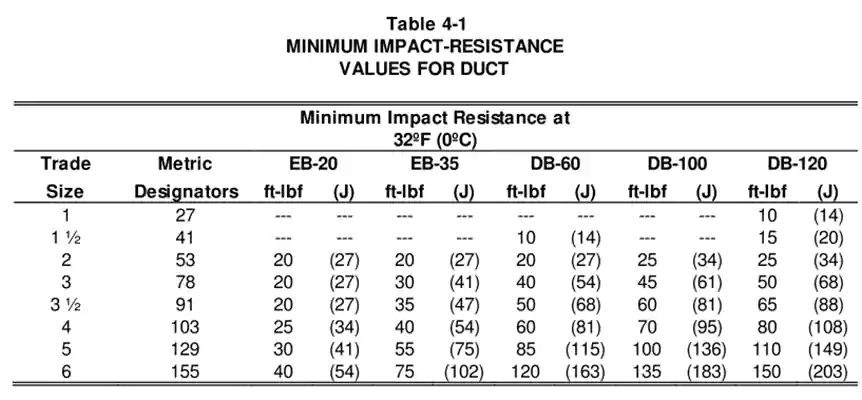
Impact resistance is another critical performance factor for underground PVC conduits. This is a quality control test that must be conducted at the time of manufacture to ensure consistent product reliability.
According to ASTM F512-19:
Minimum Requirements:
테스트 방법:
Impact testing is performed according to ASTM D2444, a 20-lb (9.1 kg) Tup B and a flat plate holder (Holder B) are used to apply the impact force.
온도 고려 사항:
If the test is performed at temperatures above 0°C (32°F), the specimen must be tested within 15 seconds after removal from the conditioning environment to maintain accuracy.
This impact test ensures that DB conduits can resist sudden, heavy loads without cracking or breaking, maintaining their structural integrity underground.
Ensuring a watertight connection between conduit sections is essential for underground installations, especially to prevent infiltration of moisture or soil into the electrical or communication pathways.
According to ASTM F512-19:
요구 사항:
Conduit joints must not leak when subjected to pressure testing.
테스트 방법:
- A section of conduit is cemented to a bell (socket) following the manufacturer’s instructions, or, if no instructions are available, by using the method described in ASTM Practice D2855.
- The assembled joint must stand undisturbed for at least 6 hours to allow the solvent cement to properly cure.
- After curing, the joint is subjected to an internal water pressure of at least 25 psi (170 kPa) and maintained at this pressure for at least 1 hour.
Passing Criteria:
During the test, no leakage of water is permitted.
Bond:
A probe or point of a knife blade is used to separate the concentric layers.
It shall not be possible to separate any two layers using a probe or the point of a knife blade in such a way that the layers come apart cleanly or that the probe or blade can move freely between them.
ASTM F512-19 requires conduit products to carry clear and standardized markings to ensure easy identification, traceability, and compliance with quality expectations. Key requirements include:
Manufacturer’s Name or Trademark
PVC Cell Classification
Nominal Size and Type of Conduit
Minimum Wall Thickness
Control or Code Number
Standard Designation must be marked:
“ASTM F512” for single extrusion conduit
“ASTM F512 COEX” for coextruded conduit
Marking Frequency: At intervals not exceeding 5 feet (1.5 meters) along the conduit length.
Additional markings are allowed if the manufacturer deems them useful.
In addition to ASTM standards, another important reference for underground PVC conduit manufacturing in North America is the NEMA TC 6 & 8 standard.
This standard is published by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) and plays a critical role in defining the performance and quality requirements for polyvinyl chloride (PVC) conduit used in both direct burial and concrete encasement applications.
Key Points and Testing Requirements:
Conduits and fittings must be made from high-quality PVC compounds that meet minimum performance standards for strength, chemical resistance, and durability. Similar as ASTM F512-19 requirements.
Precise tolerances are set for conduit diameter, wall thickness, and socket dimensions to ensure proper fit and function in the field.
Testing procedure and requirements are the same referenced in ASTM F512-19. Measurements are take at 5% vertical deflection of the conduit’s inside diameter.
The testing method and requirements are the same with ASTM F512-19, but NAME TC 6&8 explicitly warns that UV exposure reduces impact resistance; values only valid at time of manufacture.
Same requirements as ASTM F512-19.
Manufacturer’s Name or Trademark
Standard Size Designation and Type of Conduit
PVC Cell Classification
Standard designation
Marking Frequency: Markings must be repeated at uniform intervals and appear at least every 10 feet (3.05 meters).
Additional markings that manufacturer considers necessary.

In addition to ASTM and NEMA standards, CSA C22.2 No. 211.1 is an important specification covering polyvinyl chloride (PVC) conduit intended for underground installations in Canada. CSA (Canadian Standards Association) standards ensure products meet strict safety and performance requirements suitable for Canadian environments, including extreme cold.
This standard sets the materials, construction and performance requirements for:
- 강성 PVC 도관:
Type EB1: Intended for encasement in concrete or masonry.
Type DB2/ES2: Intended for direct burial in the ground or encasement in concrete or masonry.
- Associated Fittings:
Including straight couplings, 5° angle couplings, caps, plugs, bell-end terminators, bends, and adapters.
The conduit must be manufactured from PVC compounds that meet minimum requirements for physical and chemical properties such as tensile strength, impact resistance, and resistance to sunlight (for exposed sections). And have an ASTM D1784 cell classification of 12224.
The standards specifies the minimum wall thickness and outside diameters for different trade sizes. The requirements are different to ASTM and NEMA standards since they are different types and used in different regions.
This test verifies the toughness of the conduit material – especially under handling and installation conditions at both normal and cold temperatures.
테스트 방법:
A falling weight impacts the conduit placed on a specially prepared support bed.
Impact Energy and Temperatures
- At room temperature (23 °C): The impact energy applied must be 61 joules.
- At cold temperature (–18 °C): The impact energy applied must be 34 joules.
The crush resistance test evaluates the ability of PVC conduit to maintain its shape under compressive loading. This test ensures that the conduit can withstand burial or encasement pressures without permanent deformation.
테스트 절차:
- Test is performed at 23 ± 2°C (standard room temperature).
- Before loading, the vertical inside diameter of each specimen is measured and recorded.
- Each specimen is placed horizontally between two flat steel platens on a static load test bed (according to Figure 2 of CSA C22.2 No. 211.0).
The conduit is positioned so that the vertical axis (direction of measurement) is under compression. - A test mass of 90 kg, including the mass of the upper platen, is applied gradually onto the specimen. The load is maintained for 60 ± 5 seconds.
- After 60 seconds under load, remeasure the vertical inside diameter. And after 300 ± 20 seconds (5 minutes), measure the vertical inside diameter again to assess recovery.
Pass Criteria:
- During Load:
The average percentage decrease in vertical diameter shall not exceed:
12% for Type EB1 conduit
10% for Type DB2/ES2 conduit
- After Recovery:
The average percentage decrease shall not exceed 5% for both types.
The test method is same as ASTM and NEMA standards, which is performed in accordance with ASTM D2412.
요구 사항:
- Type EB1 conduit must have a minimum pipe stiffness of 200 kPa at 5% deflection.
- Type DB2/ES2 conduit must have a minimum pipe stiffness of 300 kPa at 5% deflection.
테스트 절차:
- Two pieces of conduit, each 1 ± 0.1 meters long, are solvent-cemented into a standard coupling.
- After assembly, the joint must be cured for 24 hours at room temperature to ensure proper bonding.
- The entire assembly is completely filled with water, ensuring no trapped air inside.
- A gauge pressure of 35 kPa (around 5 psi) is applied inside the filled assembly.
- The pressure must be maintained continuously for 4 hours.
승인 기준:
- Throughout the 4-hour period, the joint must withstand the pressure without any rupture or leakage.
- Visual inspection is performed after the test to ensure no signs of leaking or joint separation.
Bond Strength:
- Choose eight points spaced equally around the circumference (every 45 degrees approximately).
- At each valley point, use a sharp probe or knife point. Attempt to separate the inner and outer walls manually by prying or picking.
- The conduit cannot cleanly separate the inner and outer walls at any of the eight points.
The chemical resistance requirements ensure that rigid PVC conduits maintain their mechanical and physical properties when exposed to aggressive chemical environments.
About Test:
The conduits are immersed for 7 days in the selected chemical solutions.
After immersion, the specimens must not exhibit a mass change greater then 2%.
After removing the samples from the chemical solutions, the specimens are subjected to a tensile strength at a crosshead speed of 12.7 mm/min ± 25% within 1 hour.
The average tensile strength of the chemical-exposed specimens must not differ from the average tensile strength of the control (unexposed) specimens by more than 15%.
Manufacturer’s name, trademark
Conduit type, such as DB2/ES2 PVC Conduit
Trade size
The date of manufacture
Standard: CSA C22.2 No.211.1
Item | ASTM F512-19 | NEMA TC 6 및 8 | CSA C22.2 No.211.1 |
Region | U.S. | U.S. | 캐나다 |
Conduit Types | EB20, EB35, DB60, DB100, DB120 | EB20, EB35, DB60, DB100, DB120 | EB1, DB2/ES2 |
충격 저항성 | 20 ft-lbf at 0 °C | 20 ft-lbf at 0 °C | 61 J at 23 °C, 34 J at -18 °C |
Crush Resistance | Not specified | Not specified | 90 kg load for 60s, avg. Deformation: EB1≤12%, DB2≤10%, recovery≤5% |
단단함 | ASTM D2412: specify min. Stiffness for each conduit type at 5% deflection | Same as ASTM F512-19 | ASTM D2412: EB1≥200 kPa, DB2≥300 kPa at 5% deflection |
관절의 긴장감 | Water medium, 25 psi (172 kPa) pressure for 1 hour | Water medium, 25 psi (172 kPa) pressure for 1 hour | Water medium, 35 kPa (5 psi) pressure for 4 hours |
Bond Strength | No layer separation under probe or blade | Not specified | No clean separation allowed using knife at 8 points around circumference |
내화학성 | Not specified | Not specified | <2& mass change; tensile strength change <15% after 7-day immersion |
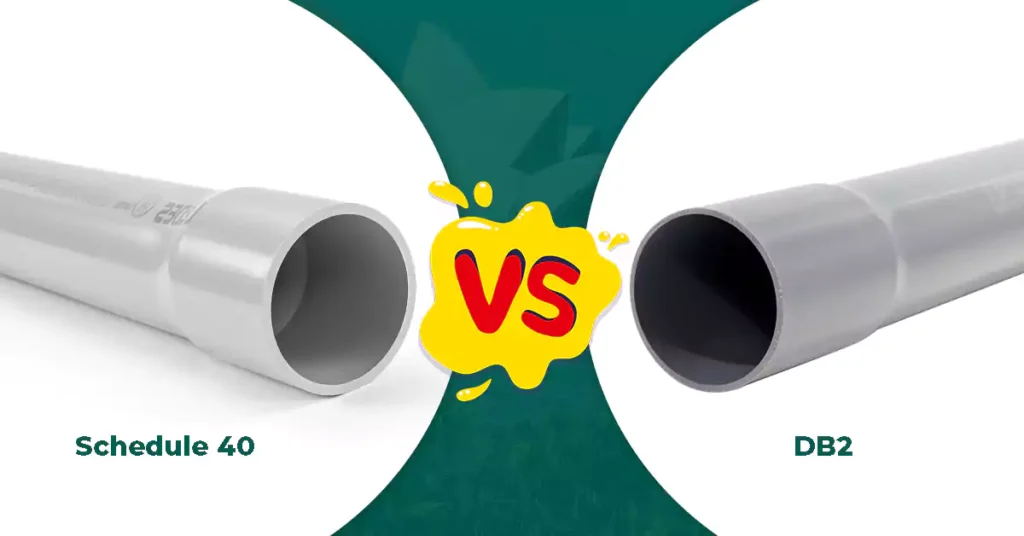

When selecting the right conduit for an electrical installation, one of the most important considerations is whether the conduit is intended for underground or above-ground applications. Two of the most common types are DB conduit (specifically DB2/ES2 for Canada or DB120 in the U.S.) and Schedule 40 PVC conduit.
While both are made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC), their designs, wall thicknesses, performance characteristics, and application scenarios differ significantly.
특징 | DB Conduit (DB2/ES2, DB120) | 스케줄 40 PVC 도관 |
Primary Use | Underground installations (direct burial or concrete encasement) | Above ground installations or embedded in walls/ floors |
Standard | CSA C22.2 No.211.1 (Canada), NEMA TC 6&8 (U.S.) | UL651, NEMA TC2 |
벽 두께 | Thinner than Schedule 40 | Thicker wall for higher mechanical protection |
Flexibility | More flexible for easier trench installation | More rigid |
Installation Method | Buried directly or encased in concrete | Surface-mounted or embedded in structures |
Crush Resistance | Designed for buried loads | Higher crush resistance due to thicker wall |
자외선 저항성 | Not always UV resistant (buried) | Typically UV resistant for outdoor exposure |
Impact resistant | 보통의 | Higher |
단단함 | 보통의 | Higher |
Cost | More cost-effective | More expensive |
Understanding their differences can better help you to choose the right conduit type for your project, whether to choose DB conduit or above ground use conduit.

Choosing the right underground conduit starts with understanding your installation environment and matching it with the appropriate conduit type and standard. In the U.S., popular underground conduit types include EB20, EB35, DB60, DB100, DB120, Schedule 40, and Schedule 80. Each has specific strengths designed for different applications.
For concrete encased underground installations, choose the EB types.
For light-duty direct burial underground installations, such as garden lighting or residential landscape wiring, DB60 or DB100 can offer a budget-friendly solution with adequate protection. However, for most utility-grade and code-compliant electrical work, DB120 is considered the standard. It offers a balance of crush resistance, flexibility, and durability, making it suitable for use under driveways, sidewalks, or landscaped areas.
If your project requires conduits to run both underground and above ground (e.g., from underground into a building or panel), you may need to use to Schedule 40 or even Schedule 80 conduit. These rigid PVC conduits can used both underground and above-ground, and are thicker-walled, provide better UV resistance and impact protection when exposed. However, Schedule 40/80 are generally more rigid and may be harder to install in tight bends or curved runs, unlike DB conduit, which is easier to work with in trench applications.
Not all suppliers are created equal. Beyond just selling conduit, a dependable supplier should provide verified compliance with standards like CSA C22.2 No. 211.1, ASTM F512, or NEMA TC6 & 8. Look for evidence of product testing, such as impact resistance, joint tightness, stiffness, and bond integrity. Ask for certifications or test reports when necessary.
It’s also beneficial to work with a supplier that offers a complete system—conduits along with compatible fittings, adapters, elbows, and accessories—to ensure ease of assembly and reduce compatibility issues. Consider the supplier’s track record in your industry, their availability of technical support, and their responsiveness to project-specific needs. Local warehousing, fast delivery, and customization options are also key indicators of a reliable partner.
Ultimately, the best supplier is one that not only delivers high-quality products but also stands behind them with technical knowledge, compliance documentation, and after-sales support. Making the right choice will help your underground installation go smoothly and perform reliably for years to come.
When choosing between direct burial (DB) conduit and above-ground conduit systems, understanding the full cost-benefit profile is essential.
Upfront Cost: DB conduit typically has a lower initial cost than above-ground use conduit, such as Schedule 40 rigid PVC conduit
Installation Costs: DB conduit is easier to install due it’s lighter weight, making the labor costs lower. While Schedule 40 is heavier and potentially increases the installation costs.
Long – Term Costs: While DB conduit is less expensive upfront, it may require more frequent maintenance or replacements due to lower durability. Schedule 40, with its greater durability, can lead to lower long-term maintenance and replacement costs.
Direct Burial (DB) conduit plays a vital role in today’s underground electrical infrastructure, offering a reliable, durable, and code-compliant solution for protecting cables in harsh below-ground environments. Whether used in residential power distribution, commercial utilities, or infrastructure projects like EV charging stations and data centers, DB conduit stands out for its moisture resistance, long-term performance, and ability to meet stringent testing standards such as CSA C22.2 No. 211.1, ASTM F512, and NEMA TC6 & 8.
In this guide, we’ve explored the key differences between DB conduit and above-ground options like Schedule 40, breaking down everything from crush resistance and joint integrity to bond strength, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness. We’ve also discussed how to choose the right type of conduit and the importance of selecting a trustworthy supplier to ensure both compliance and performance.
Ultimately, DB conduit offers more than just buried protection – it delivers peace of mind. For those planning underground installations where safety, longevity, and minimal maintenance are priorities, DB conduit is a forward-thinking and cost-efficient choice.
signed for direct burial and concrete encasement, are the ideal choice for underground electrical installations. For more product information, please 요청 양식을 보내주세요 또는 우리에게 직접 이메일을 보내주세요. Ledes의 전문가 팀이 귀하의 질문과 프로젝트 요구 사항을 도와드립니다.
도관 없이 직접 매설 케이블을 사용할 수 있나요?
Yes, you can use direct burial cables without a conduit—but only if the cable is specifically rated for direct burial use. These cables are designed with robust insulation and jackets that can withstand underground conditions, including moisture, soil pressure, and temperature changes.
However, using conduit, especially DB type conduit, can provide extra mechanical protection for cables against rocks, shifting soil, and accidental digging.
해외에서 직접 매장 제품을 조달하는 데에는 어떤 위험이 있습니까?
Sourcing direct burial (DB) conduit products internationally can offer cost advantages, but it also comes with notable risks. Here are the key concerns:
- Product Quality
Not all direct burial conduits can meet the industry safety and performance requirements, when selecting the conduit manufacturer, make sure their products comply with the required standards and provide relevant test reports or certifications. If the conduit can’t meet the requirements, can result in costly failure and pose safety risks.
- Lead Time and Logistics
Shipping products from overseas can lead to longer lead times, especially in peak construction seasons. Unpredictable customs delays or disruptions due to geopolitical issues or port congestion. And need to pay increased freight costs.
팁: Plan procurement schedules in advance and ensure suppliers have reliable logistics partners. Always factor in buffer stock for urgent needs.
- Communication Barriers and After-Sales Support
Cross-time zone collaboration and language differences can lead to misinterpretations or delays in communication. Technical requirements may not be fully understood, and important issues might not be addressed in a timely manner. This can become especially problematic during installation or in the event of product failure, where quick access to technical support or replacement parts is critical. In some cases, after-sales service from international suppliers may be slow, unresponsive, or not aligned with local expectations.
팁: Choose suppliers with bilingual technical teams, clear communication channels, and a local or regional support network. Always confirm their responsiveness and support capabilities before committing to large-scale procurement.
직접 매설 설비에 대한 환경적 고려사항이 있습니까?
Yes. Direct burial conduit systems must be designed with environmental factors in mind to ensure long-term reliability and safety. One of the primary concerns is soil composition—certain soils can be highly acidic or alkaline, which may degrade materials over time. In addition, microbial activity in the soil can contribute to corrosion, particularly in metallic components.
To mitigate these risks, conduits used for direct burial—such as PVC DB2 or HDPE conduit—are typically engineered to resist chemical attack and biological degradation. These materials are non-reactive, corrosion-resistant, and well-suited for harsh subsurface environments.
직접 매장 제품을 구매할 때 어떤 인증을 찾아야 합니까?
In the United States and Canada, products are expected to meet standards set by organizations like UL (Underwriters Laboratories), CSA (Canadian Standards Association), ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials), and NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association). These certifications confirm that the conduit has been rigorously tested for factors such as structural integrity, stiffness, chemical resistance, and joint tightness—qualities especially important in underground environments where long-term durability is critical.
For example, CSA C22.2 No. 211.1 covers direct burial PVC conduit in Canada, including DB2 and EB1 types, and mandates performance under various physical and chemical tests. Similarly, ASTM F512 addresses the requirements for coextruded pipe, such as uniform bond strength and resistance to layer separation. Products certified under UL standards may also carry additional marks for fire resistance or impact performance. Ensuring that your direct burial conduit carries these recognized certifications helps protect your installation from failure, reduces liability, and guarantees that you’re using a product suited for its intended underground application.
지중 케이블의 단점은 무엇입니까?
지하 케이블은 여러 가지 장점을 제공하지만, 사용과 관련된 몇 가지 단점도 있습니다. 지하 케이블의 몇 가지 일반적인 단점은 다음과 같습니다.
- 더 높은 설치 비용: 지하 케이블의 주요 단점 중 하나는 가공 케이블에 비해 설치 비용이 더 높다는 것입니다. 케이블을 지하에 놓으려면 굴착, 도랑 파기 및 특수 장비가 필요합니다. 이러한 추가 비용으로 인해 초기 설치 비용이 상당히 더 많이 들 수 있으며, 특히 복잡한 지리적 특징이 있는 지역이나 광범위한 지하 인프라가 이미 있는 도시 환경에서는 더욱 그렇습니다.
- 유지 관리 및 수리 난이도 증가: 지하 케이블의 유지관리 및 수리는 가공 케이블에 비해 더 어렵고 시간이 많이 걸립니다. 지하 케이블의 결함을 찾으려면 특수 장비와 전문 지식이 필요하며, 지하에 묻힌 케이블에 접근하는 것은 번거로울 수 있습니다. 결함 탐지 및 수리의 어려움으로 인해 가동 중지 시간이 길어지고 유지관리 비용이 높아질 수 있습니다.
- 제한된 접근성: 지하 케이블은 유지 관리 및 수리에 덜 접근 가능합니다. 인구가 밀집된 지역이나 도시 환경에서는 건물, 도로 및 기타 인프라가 있기 때문에 지하 케이블에 접근하는 것이 특히 어려울 수 있습니다. 이러한 제한된 접근성으로 인해 유지 관리 및 수리 작업 중에 지연 및 중단이 발생하여 비용이 더욱 증가하고 서비스 제공자와 고객에게 불편을 끼칠 수 있습니다.
도관 없이 지하 케이블을 매설할 경우 어떤 위험이 있습니까?

도관 없이 지하 케이블을 매설하면 여러 가지 위험과 단점이 발생할 수 있습니다. 지하 케이블 설치에 도관을 사용하지 않는 것과 관련된 잠재적 위험은 다음과 같습니다.
- 물리적 손상: 도관 보호가 없으면 지하 케이블은 바위, 나무 뿌리, 건설 활동 또는 우발적인 파기와 같은 외부 요인으로 인한 물리적 손상에 더 취약합니다. 보호 장벽이 없으면 케이블이 더 노출되고 잠재적인 충격이나 압축에 취약해져 케이블 절연 손상이나 도체 파손이 발생할 수 있습니다.
- 습기 및 물 침투: 지하 환경은 습기와 물이 침투하기 쉽습니다. 도관이 없으면 케이블 시스템으로 물이 스며들어 절연 저하, 단락, 도체 또는 커넥터 부식이 발생할 위험이 더 큽니다. 습기가 침투하면 케이블의 성능과 수명에 상당한 영향을 미쳐 서비스 중단과 비용이 많이 드는 수리가 발생할 수 있습니다.
- 화학 물질 노출: 지하 위치에는 케이블 무결성과 성능에 부정적인 영향을 미칠 수 있는 화학 물질이나 물질이 포함될 수 있습니다. 도관이 없으면 케이블은 토양 오염 물질, 산업 활동 또는 우발적 유출로 인한 잠재적 화학 물질 노출에 더 많이 노출됩니다. 화학 상호 작용으로 인해 케이블 저하, 절연 파괴 및 전반적인 시스템 오류가 발생할 수 있습니다.
- 케이블 교체 또는 업그레이드의 어려움: 도관이 없으면 지하 케이블을 교체하거나 업그레이드하는 것이 더 어려워집니다. 전용 경로가 없으면 새 케이블을 제거하고 설치하거나 기존 인프라를 수정하기 어려울 수 있습니다. 이러한 제한으로 인해 향후 케이블 교체 또는 시스템 업그레이드와 관련된 복잡성, 시간 및 비용이 증가할 수 있습니다.
- 케이블 식별 및 구성 부족: Conduit은 케이블에 대한 체계적이고 조직적인 경로를 제공하여 식별 및 관리를 더 쉽게 합니다. Conduit이 없으면 케이블이 엉키거나 무질서해질 수 있으며, 유지 관리, 수리 또는 확장을 위해 특정 케이블을 찾기가 더 어려워질 수 있습니다. 이로 인해 문제 해결 또는 시스템 업그레이드 중에 다운타임이 증가하고 비효율성이 발생할 수 있습니다.
직접 매설 케이블에 도관이 필요한가요?
직접 매설 케이블은 설치에 도관이 필요하지 않습니다. 추가 보호 없이 땅에 직접 매설되도록 특별히 설계되었습니다. 이 케이블은 습기, 온도 변화 및 물리적 손상에 대한 저항성을 제공하는 절연 및 재킷을 갖추고 있습니다. 그러나 지역 전기 코드 및 규정에는 특정 요구 사항이 있을 수 있으므로 이를 참조하는 것이 중요합니다.
직접 매설 케이블은 도관 없이 설치할 수 있지만, 도관을 사용하면 프로젝트의 특정 요구 사항에 따라 추가적인 이점이 있을 수 있습니다. 도관은 추가적인 물리적 보호를 제공하고 케이블 교체 또는 유지 관리를 더 쉽게 만들 수 있습니다. 또한 까다로운 환경 조건이나 케이블 위치를 찾는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다. 그러나 도관을 설치하면 프로젝트에 비용과 복잡성이 추가됩니다.
궁극적으로 직접 매설 케이블이 있는 도관을 사용하기로 결정하는 것은 토양 조건, 프로젝트 요구 사항 및 지역 규정과 같은 요인에 따라 달라집니다. 이러한 측면을 평가하고 전문 전기 기술자와 상담하면 특정 상황에 가장 적합한 접근 방식을 결정하는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다.
직접 매설에 가장 적합한 도관은 무엇입니까?
직접 매설에 가장 적합한 도관은 내구성, 안정성, 입증된 성능으로 인해 일반적으로 PVC(폴리염화비닐)로 권장됩니다. PVC 도관은 지하 설치에 광범위하게 사용되고 테스트되었습니다. 다음과 같은 여러 가지 장점을 제공합니다.
견고성: PVC 도관은 강도와 외부 압력 및 충격을 견뎌내는 능력으로 유명합니다. 암석, 토양 이동 또는 기타 잠재적 위험으로부터 케이블을 물리적으로 손상시키지 않도록 안정적으로 보호합니다.
습기 저항성: PVC는 습기와 물의 침투에 매우 강해 지하 응용 분야에 이상적인 선택입니다. 케이블에 물이 닿는 것을 방지하여 절연 저하나 단락을 일으킬 수 있습니다.
사이즈 옵션: PVC 도관은 다양한 크기로 제공되므로 다양한 케이블 직경이나 단일 도관 내의 여러 케이블을 수용하는 데 유연성이 있습니다. 이러한 다재다능함 덕분에 PVC 도관은 광범위한 직접 매설 케이블 설치에 적합합니다.
비용 효율성: PVC 도관은 일반적으로 금속 도관과 같은 다른 옵션에 비해 비용 효율적입니다. 구매 및 설치 비용이 저렴하여 프로젝트의 전체 비용 절감에 기여합니다.
또한, 유리섬유 강화 플라스틱(FRP) 도관은 직접 매설 적용을 위한 또 다른 옵션입니다. FRP 도관은 뛰어난 내구성, 내식성 및 높은 인장 강도를 제공합니다. 비전도성으로 알려져 있어 전기 접지가 문제가 되는 설치에 적합합니다. FRP 도관은 특히 부식성 환경이나 수분 함량이 높은 지역에서 유용합니다.
PVC 도관은 직접 매설에 적합합니까?
NEC 코드 352.10 허용 용도에 따르면 PVC 도관은 직접 매설 및 콘크리트로 둘러싼 지하 매설에 적합합니다. 즉, PVC 도관은 NEC 섹션 300.5 및 305.15에 명시된 요구 사항을 준수하는 한 추가 보호 없이도 땅에 직접 매설할 수 있습니다. 이 섹션은 직접 매설 시나리오를 포함한 지하 응용 분야에서 도관을 설치하기 위한 지침을 제공합니다. 따라서 PVC 도관은 NEC 규정에 따라 직접 매설 설치에 적합한 옵션으로 간주됩니다.
전선은 얼마나 깊이 매설해야 합니까?
전선을 매설해야 하는 깊이는 전선의 종류, 지역 건축법규, 규정을 포함한 여러 요인에 따라 달라질 수 있습니다. 다음은 몇 가지 일반적인 지침입니다.
- 주거용 전력선: 대부분 주거용 애플리케이션에서 서비스 진입 케이블이나 지하 피더와 같은 전기 회선은 일반적으로 18~24인치(45~60cm) 깊이에 매설됩니다. 그러나 지역 규정에 따라 더 깊은 매설 깊이가 필요할 수 있으므로 해당 지역의 특정 규정을 참조하는 것이 필수적입니다.
- 상업 및 산업용 전력선: 상업 또는 산업 설비의 경우 전선의 매설 깊이는 주거 환경보다 더 큰 경우가 많습니다. 깊이는 전선의 종류, 전압 및 지역 규정에 따라 24~36인치(60~90cm) 또는 그 이상일 수 있습니다.
- 직접 매설 케이블: 도관 없이 지하 설치용으로 설계된 직접 매설 케이블은 일반적으로 제조업체에서 지정한 특정 매설 깊이 요구 사항이 있습니다. 케이블의 적절한 설치 및 성능을 보장하려면 제조업체의 지침을 따르는 것이 중요합니다.
- 기타 요소: 매몰 깊이 외에도 토양 유형, 환경 조건 및 기타 공공 시설의 존재와 같은 요소를 고려하는 것이 중요합니다. 일부 지역 규정은 외부 요인이나 향후 굴착으로 인한 손상으로부터 전선을 보호하기 위해 추가 깊이 또는 여유 공간 요구 사항을 요구할 수 있습니다.




