
목차
전기 설비 시스템에서 도관은 전기 배선을 보호하고 라우팅하는 데 중요한 역할을 하며 다양한 응용 분야에서 안전과 성능을 보장합니다. 사용 가능한 많은 유형의 도관 중에서 전기 비금속 튜빙(ENT)은 유연성과 사용 편의성으로 두드러집니다. ENT 튜빙은 가볍고 내구성이 뛰어나 주거, 상업, 심지어 산업 프로젝트에서도 인기 있는 선택이 되었습니다.
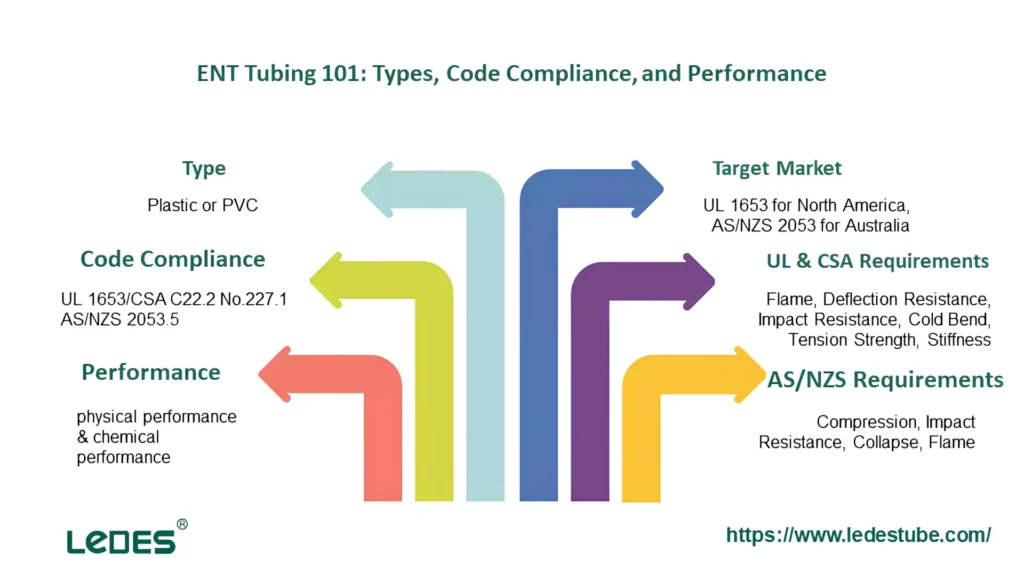
이 기사에서는 ENT 튜빙의 필수적인 측면을 탐구하여 정의, 주요 표준 및 성능 요구 사항을 포함한 포괄적인 개요를 제공합니다. 이 기사에서는 ENT 튜빙을 규제하는 UL 및 AS 표준을 살펴보고 이러한 표준을 비교하고 장단점을 검토하여 귀중한 지식을 제공합니다. 또한 ENT의 응용 프로그램, 설치 지침 및 피팅에 대해 알아보고 이러한 유형의 튜빙이 재생 에너지 및 자동차 도관 시스템과 같은 새로운 기술과 어떻게 통합되는지에 대한 통찰력을 얻을 수 있습니다. 마지막으로 이 기사에서는 해당 분야의 현재 추세와 미래 혁신에 대해 논의하여 현대 전기 인프라에서 ENT 튜빙의 역할을 철저히 이해할 수 있도록 합니다.
이 이미지를 귀하의 사이트에 공유하세요
전기 비금속 튜브(ENT) 는 주거 및 상업 분야에서 전선을 보호하고 배선하는 데 사용되는 유연하고 가벼운 도관입니다. 폴리염화비닐(PVC) 또는 기타 난연성 플라스틱으로 만들어진 ENT는 쉽게 구부릴 수 있도록 설계되었으며 충격, 습기 및 화학 물질 노출에 강합니다. ENT는 주로 단단한 도관이 설치하기 어렵거나 어려운 환경에서 사용되며 벽, 천장 및 바닥을 통해 전기 도체를 배선하기 위한 적응형 솔루션을 제공합니다.
다양한 국가와 지역에서 사용되는 많은 유형의 비금속 튜빙이 있습니다. 이 글에서는 주로 두 가지 표준 튜빙을 소개하고, 다양한 국가 및 국제 표준에 명시된 특정 안전 및 성능 기준 요구 사항을 알아보겠습니다.

이비인후과의 경우, 미국과 캐나다는 동일한 규격인 UL 1653/CSA C22.2 No.227.1을 공유합니다. 이 두 규격은 이비인후과 도관에 대한 동일한 요구사항을 공유하며, 일부 테스트만이 약간 다릅니다. 이 규격은 전기적 비금속 튜빙에 대한 안전 및 성능 요구사항을 설명합니다. UL 인증 ENT 건물 건설 시 안전한 사용을 보장하기 위한 설치 지침과 제한 사항을 명시한 국가 전기 규정(NEC) 제362조를 준수해야 합니다.
UL/CSA 표준 ENT 도관에 대해 자세히 알아보려면 다음 게시물을 읽어보세요. 미국 및 캐나다용 ENT 도관 가이드.
AS/NZS 2053.5 표준은 호주와 뉴질랜드에서 비금속 도관 및 피팅에 사용됩니다. UL1653의 ENT와 달리 다양한 요구 사항을 충족하기 위해 AS/NZS 표준 골판지 도관 다양한 응용 시나리오에 따라 여러 등급으로 구분됩니다. 가볍다, 보통, 무겁다, 등, 그리고 그들의 다양한 성능 강도도 다릅니다. 이 표준에는 열적 특성, 기계적 강도 및 환경 요인에 대한 저항성에 대한 요구 사항이 포함됩니다.
UL1653은 ENT에 대한 모든 치수 및 성능 요구 사항을 명시하고 있습니다. 알아야 할 가장 중요한 측면은 다음과 같습니다.
UL1653에는 화염 테스트가 2가지가 있는데, FT4 테스트는 선택 사항이지만 대부분의 사람들이 선호하는 테스트입니다. ENT도관 FT4테스트 통과. 다음은 이 두 가지 테스트에 대한 몇 가지 정보입니다.
- 수직 화염 시험(500W 버너): UL1653의 7.2절에서 수직 화염 시험은 제어된 조건에서 직접 화염에 노출되었을 때 도관의 성능을 평가합니다. 이 시험은 도관 샘플을 수직으로 배치하고 특정 기간 동안 바닥에 500와트 화염을 적용하여 수행합니다. 주요 목적은 소스를 제거한 후 화염이 자체적으로 꺼지는지 관찰하고 화염 확산이 지정된 한계를 초과하지 않는지 확인하는 것입니다.
- 케이블 트레이(FT4)의 화염 테스트: FT4 화염 시험은 조항 7.3에 명시되어 있으며, 시험 방법은 CSA C22.2. No.211.0에 따릅니다. 이 시험은 전선과 도관이 종종 밀접하게 그룹화되어 있는 케이블 트레이에서 발견되는 조건을 시뮬레이션합니다. 이 시험은 도관이 화재 노출 시 케이블과 도관 묶음에 화염이 퍼지는 것을 방지할 수 있는지 평가합니다. 설정에는 케이블 트레이 구성에 도관 샘플을 배치하고 더 어려운 조건에서 화염 확산을 시험하기 위해 상당한 화염원을 적용하는 것이 포함됩니다.
이 테스트의 요구 사항은 엄격합니다. 이 테스트는 튜빙이 일정 기간 동안 고강도 화염에 노출되었을 때 화염 확산을 견딜 수 있는지 여부를 결정하며, 자체 소화 및 제한된 탄화 길이에 대한 기준을 충족해야 합니다. FT4 테스트에 통과한다는 것은 ENT 튜빙이 여러 케이블과 도관이 있는 시나리오에서 신뢰할 수 있는 내화성을 제공하여 복잡한 전기 시스템에서 화재가 확대될 위험을 줄인다는 것을 의미합니다.
처짐 저항은 압축력 하에서 전기 비금속 튜빙(ENT)의 내구성과 기계적 안정성을 보장하는 중요한 매개변수입니다. UL 1653 표준의 조항 7.5는 ENT의 처짐 저항을 테스트하기 위한 구체적인 절차와 조건을 설명하여 튜빙이 상당한 변형이나 구조적 고장 없이 외부 하중을 견딜 수 있음을 보장합니다.
일반 요구 사항(조항 7.5.1):
- 검사를 위해 각 크기의 이비인후과용 튜빙에서 6개의 샘플을 채취해야 하며, 각 샘플은 150 ± 3mm(6 ± 1/8인치) 길이로 절단해야 합니다.
- 각 샘플은 거래 규모에 따라 다양한 특정 하중을 받습니다.
16(1/2) 무역 크기: 4448 N(1000 lbf)
21(3/4) 무역 크기: 3470 N(780 lbf)
27 (1) 무역 크기 : 3380 N (760 lbf)
35(1-1/4) 및 그 이상의 무역 크기: 1779 N(400 lbf)
- 캐나다 특정 요구 사항: 63(2-1/2) 거래 규모의 경우, 6개 샘플에 1334N(300lbf)의 하중을 가합니다. 이 요구 사항은 캐나다에만 적용되며 미국에는 적용되지 않습니다.
테스트 절차(조항 7.5.3)
처짐 저항성을 테스트하는 절차는 다음과 같습니다.
- 초기 측정: ENT 샘플의 내경을 측정하고 기록합니다.
- 위치: 압축기의 플레이트 사이에 샘플을 놓고, 내부 직경을 플레이트에 수직으로 맞춥니다.
- 로드 응용 프로그램: 무역 규모에 지정된 하중이 적용될 때까지 기계를 작동하세요.
- 부하 중 측정: 기계를 멈추고 내부 직경을 다시 측정한 후 직경 감소율을 계산합니다.
- 관찰: 시험 중 샘플에 좌굴 징후가 있는지 모니터링합니다.
- 사후 테스트 시험: 하중을 해제한 후 샘플을 제거하여 균열이나 손상이 있는지 검사합니다.
충격 저항성 전기 튜빙 특히 물리적 힘이나 환경 조건이 도관의 무결성에 도전할 수 있는 설비의 경우 필수적인 성능 특성입니다. UL 1653 표준은 ENT의 충격 저항성을 평가하기 위한 특정 테스트를 설명하여 상당한 손상 없이 기계적 응력을 견딜 수 있는지 확인합니다. 충격 테스트는 UL 1653의 조항 7.6에 자세히 설명되어 있으며, 샘플을 준비하고, 테스트하고, 평가하는 방법에 대한 명확한 지침을 제공합니다.
일반 요구 사항:
- ENT 샘플은 온도의 통제된 조건에서 테스트되어야 합니다. -20 ± 1°C (-4 ± 1.8°F). 이러한 저온 요구 사항은 도관이 추운 환경에 노출될 수 있는 조건을 시뮬레이션하여 그러한 시나리오에서도 구조적 특성을 유지하도록 보장합니다.
- 충격 시험은 에너지 힘을 적용합니다. 2.7 줄(2.0 ft-lbf) 각 샘플을 검사하여 파손이나 변형에 대한 저항성을 평가합니다.
- 각 테스트 샘플은 세로축에 수직으로 절단해야 하며 필요한 길이는 1입니다.50 ± 6mm(6 ± 1/4인치) 시험을 표준화하기 위해.
- 검사한 샘플 10개 중 2개 이상에서 샘플 내부 또는 외부에 균열, 흠집 또는 파열이 발견되지 않아야 합니다.
ENT가 이런 엄격한 충격 시험을 통과할 수 있는 능력은 표준적인 응용 분야와 까다로운 응용 분야에서 모두 사용할 수 있음을 뒷받침하며, 기계적 응력을 유발할 수 있는 조건에서도 기능적이고 효과적임을 확인합니다.
저온 굽힘 시험은 전기 비금속 튜빙(ENT)이 저온에서 굽혀져 혹독한 환경 조건을 시뮬레이션할 때 유연성과 구조적 무결성을 유지할 수 있는지 확인하는 필수적인 평가입니다. 이를 통해 추운 기후에서 굽힘 응력에 노출되어도 도관이 균열, 깨짐 또는 파열되지 않습니다. UL 1653 표준은 조항 7.7에 따라 저온 굽힘 시험을 지정하여 이 시험을 수행하기 위한 절차와 요구 사항을 자세히 설명합니다.
조항 7.7 – 테스트 설명:
- 콜드 벤드 테스트는 ENT 튜빙의 각 트레이드 사이즈에 대한 6개의 샘플을 테스트해야 합니다. 이러한 샘플은 실제 저온 노출을 시뮬레이션하도록 조절되어야 합니다.
- 각 샘플은 ENT의 거래 규모에 따라 달라지는 지정된 반경을 가진 맨드릴 주위로 360° 구부러집니다. 맨드릴 반경 사양은 UL 1653의 표 2에 나열되어 있어 다양한 튜빙 크기에 대한 표준화된 테스트를 보장합니다.
- 굽힘 전에 샘플과 맨드렐은 모두 -20 ± 1°C(-4 ± 1.8°F)의 온도에서 4시간 동안 컨디셔닝됩니다. 이 컨디셔닝은 재료가 테스트 기간 내내 균일한 낮은 온도에 도달하고 유지되도록 보장합니다.
- 굽힘 공정은 샘플과 맨드렐이 여전히 낮은 온도에 있는 동안 수행되며, 이를 통해 테스트가 차가운 환경 조건에서 튜빙의 성능을 정확하게 반영하는지 확인할 수 있습니다.
테스트 요구 사항: 시험하는 동안 샘플은 손상을 일으키지 않고 맨드렐 주위로 매끄럽게 구부러져야 합니다. 구체적으로, 굽힘 과정 중 또는 굽힘 과정 후에 샘플에 균열, 칩 또는 파열이 없어야 합니다.

UL 1653의 조항 7.8에 명시된 인장 시험은 전기 비금속 튜빙(ENT)이 파손 없이 축 방향 힘을 견딜 수 있는지 평가합니다. 이 시험은 튜빙이 설치 중 또는 서비스 중에 발생할 수 있는 기계적 인장 응력을 구조적 무결성을 손상시키지 않고 견딜 수 있는지 확인합니다.
테스트 응용 프로그램:
- 더 작은 거래 크기인 16(1/2) 및 21(3/4)의 경우, 90kg(200lb)의 질량을 도관의 한쪽 끝에 부착하여 889N(200lbf)의 장력을 생성합니다. 반대쪽 끝을 당겨서 질량을 바닥에서 들어 올리고 하중을 1분 동안 유지합니다.
- 더 큰 규모의 거래 규모인 27(1) 이상의 경우 135kg(300lb)의 질량이 사용되어 1,334N(300lbf)의 인장력이 생성되고 1분의 유지 요구 사항은 동일합니다.
성과 기준
ENT 튜빙은 파손되거나 상당한 구조적 손상이 나타나지 않고 1분 동안 가해진 장력을 견뎌야 합니다. 이는 취급, 설치 또는 사용 중에 인장 응력을 처리할 수 있는 도관의 능력을 보여줍니다.
전기 비금속 튜빙(ENT)의 강성은 하중 하에서 변형에 저항하는 능력을 반영하는 중요한 특성입니다. 이 특성은 특히 토양 압력과 같은 외부 힘이 존재하는 지하 적용 분야에서 설치 시 도관이 구조적 무결성을 유지하는 데 필수적입니다. 강성 요구 사항은 특히 캐나다에서 중요하며 UL 1653의 조항 5.10에 설명되어 있습니다.
요구 사항:
- 캐나다에서, ENT는 최소 파이프 강성을 충족해야 합니다. 5% 처짐에서 300kPa. 이 요구 사항은 ASTM D 2412에 따라 테스트됩니다. 이 표준 방법은 도관의 지정된 처짐을 유발하는 데 필요한 힘을 측정하여 플라스틱 파이프의 강성을 결정하는 데 사용됩니다.
- 미국에서, 이 강성 요구 사항은 적용되지 않습니다. 미국 애플리케이션에서 사용되는 ENT는 여전히 UL 1653 및 National Electrical Code(NEC)에 명시된 다른 성능 및 안전 기준을 충족해야 하지만 직접 매설에 대한 특정 강성 값은 의무화되지 않습니다.
압축 테스트는 튜빙이 구조적 무결성을 유지하면서 가해지는 기계적 압력을 견딜 수 있는지 확인하는 것입니다. 이는 전선에 대한 보호 기능을 손상시키지 않고 외부 하중을 견딜 수 있는 도관의 능력을 확인하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
테스트 요구 사항:
AS/NZS 2053.5 및 AS/NZS 2053.1에 따르면 골판지 유연 도관 다음 요구 사항을 준수해야 합니다.
- 일반 목표: 도관은 지정된 힘을 받았을 때 과도한 변형을 겪지 않음으로써 압축에 대한 저항성을 입증해야 합니다.
- 변형 한계: 이 시험을 통과하기 위한 중요한 요건은 도관의 초기 외경과 힘이 여전히 가해지는 동안 측정된 직경의 차이가 25%를 초과해서는 안 된다는 것입니다. 이렇게 하면 도관이 응력 하에서 적절한 기계적 특성을 유지하고 허용 가능한 한계를 넘어 변형되지 않습니다.
도관 | 압축력(N) |
매우 가볍다 | 125 |
빛 | 320 |
중간 | 750 |
무거운 | 1250 |
매우 무겁다 | 4000 |
AS/NZS 2053.1 표준은 비금속 골판지 도관이 구조적 무결성을 손상시키지 않고 기계적 충격을 견딜 수 있는 능력을 평가하는 구체적인 충격 시험 요구 사항을 설명합니다.
기구 및 시험편
조절 챔버: 도관의 최대 및 최소 서비스 온도를 ±2°C 허용 오차로 유지할 수 있는 두 개의 챔버. 이 챔버는 충격 테스트 전에 극한 온도 조건을 시뮬레이션하는 데 사용됩니다.
충격 시험 장치: 지정된 무게와 낙하 높이에 맞춰 설정된 망치와 강철판이 있는 받침대가 포함되어 있습니다.
스펀지 고무 패드: 장치 아래에 40mm 두께의 패드를 두어 충격을 흡수합니다.
테스트는 길이가 각각 200mm인 12개의 도관이나 실제 적용에 사용될 모든 구성 요소를 포함하는 12개의 조립된 피팅에 대해 수행됩니다.
충격 테스트 절차
- 챔버 1에서 최대 사용 온도에서 240시간 동안 시험편을 조절합니다.
- 시험편을 챔버 2로 옮기고, 최소 2시간 동안 또는 챔버의 기온과 일치할 때까지 최소 사용 온도에서 조절합니다.
- 시험편을 강철 베이스에 놓고 중간 강철 조각을 적용합니다.
- 지정된 무게와 높이의 망치를 떨어뜨려 충격을 시뮬레이션합니다.
테스트는 피팅의 가장 약한 부분을 대상으로 하지만, 소켓 입구에서 5mm 이내에서는 충격이 발생하지 않도록 합니다.
기계적 성질 | 망치의 무게 kg | 낙하 높이 mm |
매우 가볍다 | 0.5 | 100 ±1 |
빛 | 1.0 | 100 ±1 |
중간 | 2.0 | 100 ±1 |
무거운 | 2.0 | 300 ±1 |
매우 무겁다 | 6.8 | 300 ±1 |
Acceptance Criteria
At least 9 out of 12 test pieces must show no signs of cracking or disintegration when visually inspected with normal or corrected vision, without magnification.
Meeting these stringent criteria ensures that nonmetallic corrugated conduits provide consistent performance and durability, maintaining their protective qualities under mechanical stress.
The collapse test is a crucial evaluation in the AS/NZS 2053 series, which confirms that the metallic tubing can withstand environmental stress without compromising its internal diameter or structural form.
Test Procedure for Tubing Collapse
- Bend the Sample:
Carefully bend the ENT tube to 90° at room temperature using the specified bending device.
- Secure the Sample:
Attach the bent tube to a rigid support with four straps, as shown in the standard’s diagram.
Remove any tools used to bend the tube.
- Heat the Sample:
Place the support with the tube into a temperature-controlled chamber.
Keep the chamber at the highest temperature recommended by the manufacturer (±2°C) for 24 hours.
- Check the Sample:
Take the support with the tube out of the chamber.
Measure the inside diameter to ensure it meets the standard’s minimum requirement.
Acceptance Criteria
The ENT sample passes the collapse test if a gauge, as outlined in the relevant part of the AS/NZS 2053 series, can successfully pass through the conduit. This verifies that the tubing has maintained its shape and internal clearance, confirming its resilience under thermal stress.
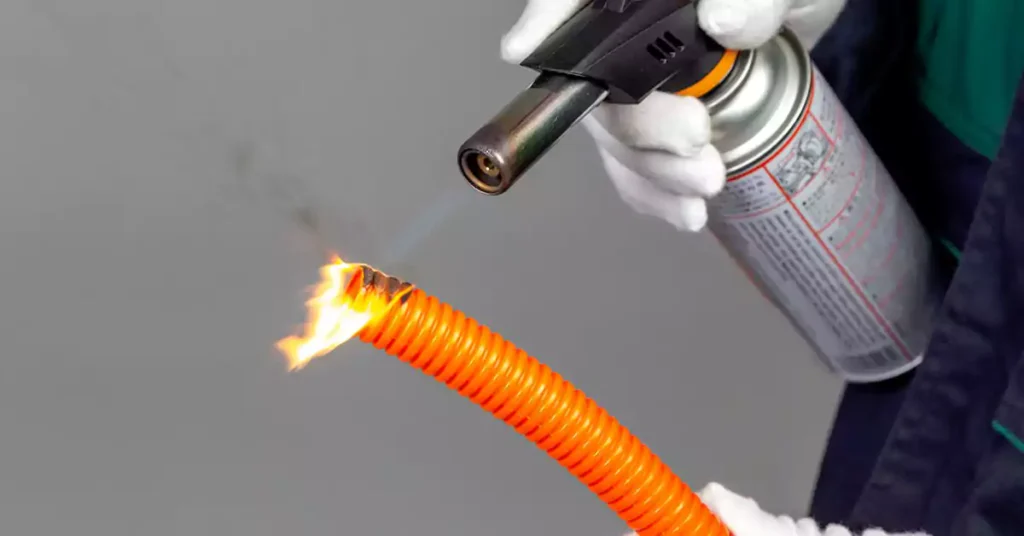

The corrugated conduit must demonstrate adequate resistance to flame propagation to be considered non-flame propagating as specified by AS/NZS 2053.5 and AS/NZS 2053.1. The flame resistance test involves the following key points:
Flame Application:
- A 1 kW flame is applied at a 45° angle to the sample, positioned 100 ±10 mm from the sample and aimed at a point 100 ±5 mm above the lower clamp.
- The flame is maintained for 60 ±1 seconds and then removed.
Test Criteria:
- The test is conducted on three samples.
- The sample passes if it does not ignite or if burning stops within 30 seconds after the flame is removed.
- The sample should show no charring or burning within 50 mm of the clamps.
- Ignition of the tissue paper beneath the sample indicates failure.
규정 준수:
To comply, the corrugated conduit samples must show no persistent combustion after flame removal and no charring close to the clamps. Presence of molten material does not constitute failure unless it results in burning or charring of the sample itself.
Two primary benchmarks used for flexible nonmetallic conduit comparison are the UL (Underwriters Laboratories) standard for electrical nonmetallic tubing (ENT) and AS/NZS 2053.5, which governs nonmetallic corrugated conduits used in Australia and New Zealand. Although both conduit types serve the same fundamental purpose of protecting electrical wiring, they are tailored to meet varying requirements in terms of dimensions, strength, and performance as stipulated by their respective standards.
When comparing UL standard electrical nonmetallic tubing and AS/NZS 2053.5 nonmetallic corrugated conduit, notable distinctions arise in areas such as:
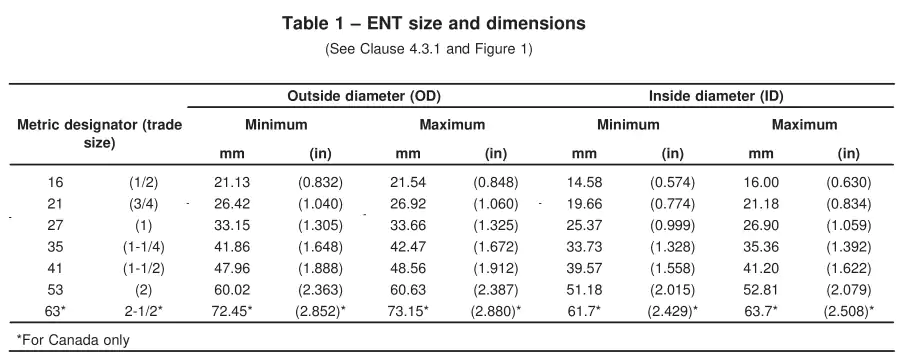
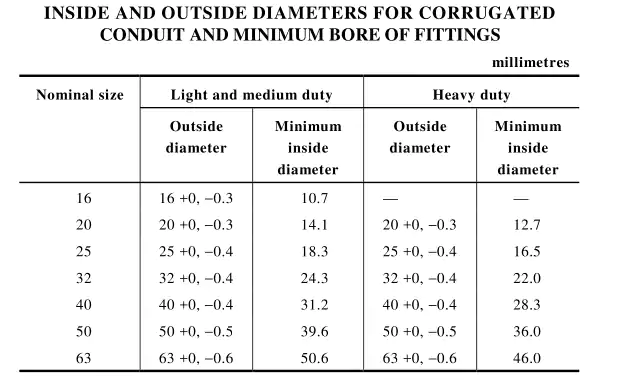
As you can see, even though they are made of the same material and have almost the same name, the size difference is huge. Even if the size is close, they are almost completely different when tolerances are taken into account.
Crush and Impact Resistance:
UL ENT: Outlines rigorous testing for crush resistance with specific load thresholds to ensure the conduit can withstand pressure without permanent deformation.
AS/NZS 2053.5 Flexible: Employs impact tests suitable for conduits used in diverse settings, with particular attention to temperature resilience and recovery after compression.
Aspects | UL1653 | AS/NZS 2053 |
Test Temperature | -20 ± 1°C (-4 ± 1.8°F) | Max and min service temperatures |
Sample | 150 ± 6 mm length, cut perpendicularly | 200 mm length, 12 samples |
Impact Energy Force | 2.7 줄(2.0 ft-lbf) | Variable (0.5 kg to 6.8 kg hammer) |
Conditioning Time | Minimum 4 hours | 240 hours at max temperature, 2+ hours at min temperature |
Number of Samples | 10 samples | 12 samples |
Acceptance Criteria | Max 2 out of 10 can show damage | At least 9 out of 12 must pass |
Inspection Method | Visual, without magnification | Visual, without magnification |
UL ENT: Includes tests such as the UL 94 flame retardancy test to ensure that the tubing meets fire safety regulations.
AS/NZS 2053.5: Specifies testing for fire resistance, focusing on self-extinguishing properties to minimize the risk of flame propagation.
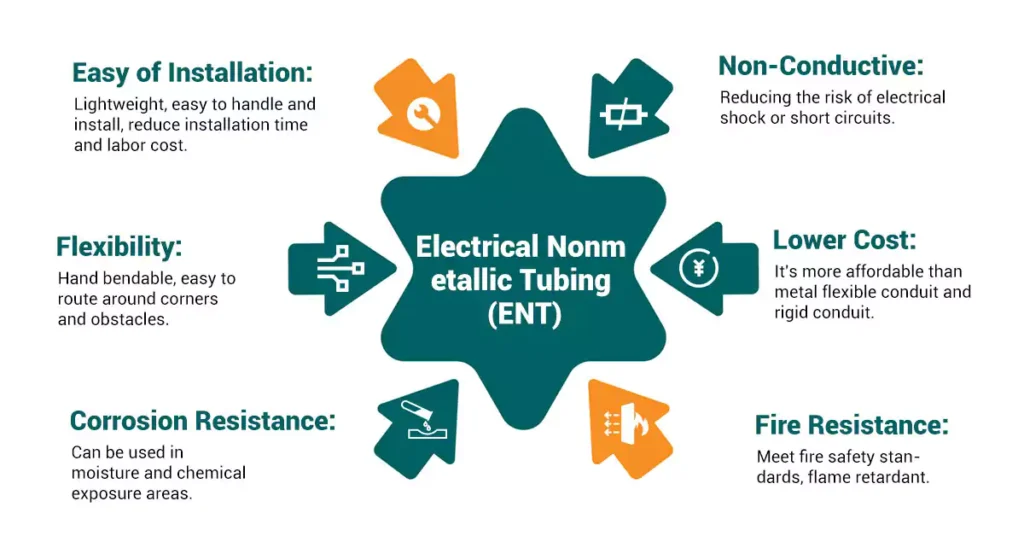
Lightweight and Easy to Install:
ENT is significantly lighter than metallic conduits, making it easy to handle and install. This can reduce labor costs and installation time, especially in large-scale projects.
- 유연성:
Its inherent flexibility allows ENT to be routed around obstacles without the need for complex fittings or jointing, simplifying the installation process and reducing material costs.
- 부식 저항성:
ENT is highly resistant to corrosion, making it an excellent choice for environments prone to moisture or chemical exposure, such as basements and coastal areas.
- Non-Conductive Properties:
As a non-metallic conduit, ENT does not conduct electricity, providing a safer option by reducing the risk of electrical shock or short circuits in case of wire damage.
- Lower Cost:
ENT is generally more affordable than rigid metal conduit (RMC) or intermediate metal conduit (IMC), making it an economical solution for standard electrical installations.
- 내화성:
ENT can meet fire safety standards when properly rated, providing flame-retardant properties that enhance safety in case of a fire.
Lower Mechanical Strength:
ENT is not as robust as metallic conduits, making it less suitable for applications where high mechanical strength is required, such as in areas with potential for heavy impact or compression.
- Limited Temperature Tolerance:
ENT may have reduced performance at high or low temperatures. It can become brittle in extremely cold environments or warp under intense heat unless specifically designed for such conditions.
- UV Sensitivity:
ENT may degrade over time when exposed to direct sunlight unless treated with UV stabilizers. This limits its use in outdoor installations without additional protective measures.
- Not Suitable for Certain Environments:
In some high-stress or industrial applications where fire hazards or exposure to chemicals that can degrade plastic exist, ENT might not meet the necessary safety and durability standards.
- Support and Installation Requirements:
ENT must be properly supported throughout its length to prevent sagging or damage over time. This can add to the installation complexity, especially when long runs are needed.
Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing offers a flexible, cost-effective, and corrosion-resistant solution for many electrical installation needs. However, it is essential to consider its limitations, particularly in terms of mechanical strength and environmental exposure, to ensure its suitability for a given application. Understanding these pros and cons helps in making informed decisions about when and where to use ENT in electrical projects.
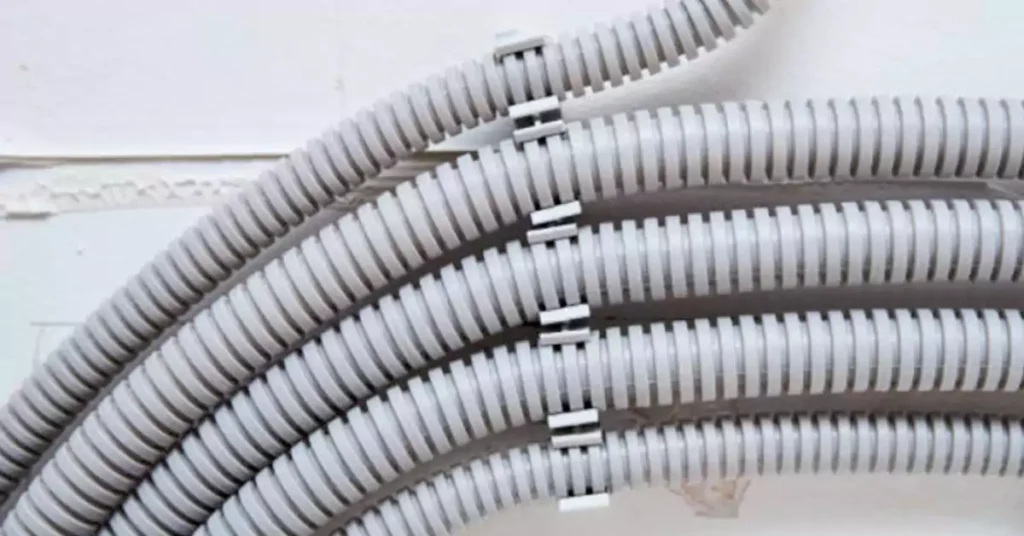

Installing electrical nonmetallic tubing requires careful planning and execution to ensure proper protection and functionality of electrical wiring. The National Electrical Conduit (NEC) has outlined the guidelines of installations for ENT, the process is generally straightforward, involving a series of preparatory and installation steps. Here are the general installation steps:
There are 8 steps to install the ENT tubing:
- Plan the Installation Path: Identify and mark the route for the conduit.
- Cut the Tubing: Measure and cut ENT to the desired length using a conduit cutter or fine-toothed saw.
- Deburr the Ends: Smooth any rough edges at the cut ends to prevent damage to the wiring.
- Connect Fittings and Couplings: Attach fittings to connect ENT segments and ensure a secure connection.
- Position and Secure the ENT: Place the tubing along the planned path and secure it with clamps or brackets at regular intervals.
- Pull the Wires : Use a fish tape to pull the wires through the ENT, ensuring no sharp bends or kinks.
- Connect to Electrical Boxes: Securely connect the ENT to electrical boxes and enclosures.
- Inspect and Finalize Installation: Conduct a final inspection to check for proper support, secure fittings, and compliance with electrical codes.
There are 6 things you need to know before installation:
Support and Spacing: Ensure that ENT is supported at regular intervals, typically no more than 3 feet apart, to prevent sagging or stress on the tubing.
Avoid Sharp Bends: Avoid excessive bending of the tubing, which can restrict wire movement and cause damage. Use fittings designed for turns when necessary.
온도 고려 사항: Do not install ENT in temperatures below its rated minimum or in areas where it will be exposed to extreme heat without proper thermal protection.
UV Exposure: For outdoor installations, confirm that the tubing is rated for UV exposure or take additional protective measures such as placing it under a cover.
Secure Fittings Properly: Use approved fittings and connectors to secure ENT to electrical boxes or junctions. Improperly attached fittings can lead to conduit disconnection and electrical hazards.
Verify Code Compliance: Always ensure that the installation meets local electrical code requirements, which may specify additional guidelines for conduit placement, wire capacity, and connection methods.
By following these installation steps and precautions, electricians and installers can achieve a secure and reliable ENT installation that meets safety and performance standards.

There are 6 tips for buying electrical nonmetallic tubing,
- Understand the Application:
Indoor or Outdoor Use: Make sure the ENT is rated for the environment where it will be installed, such as dry, wet, or outdoor spaces.
Wire Capacity: Choose the right size based on how many wires need to be protected.
- Check the Material and Ratings:
Quality of Plastic: Look for ENT made of strong, durable plastic that can resist fire and chemicals.
Standards Compliance: Make sure the product meets industry standards like UL (U.S.) or AS/NZS (Australia/New Zealand).
- Consider Flexibility and Installation:
Pick ENT that is flexible enough to go around obstacles but still sturdy.
Ensure it’s easy to cut and work with using standard tools.
- Look for Durability:
Impact Resistance: Choose tubing that won’t easily crack or dent.
UV Protection: For outdoor use, make sure it’s protected against sun damage.
- Balance Cost and Quality:
Don’t just go for the cheapest option. Higher-quality ENT often lasts longer and performs better, which can save money over time.
- Check Compatibility:
Make sure the ENT can be used with standard fittings and connectors.
The future of Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing (ENT) is set to expand into areas that support sustainability and smart technologies. Here are some key trends:
- Renewable Energy Systems
ENT is expected to play a bigger role in renewable energy installations, such as solar and wind power systems. These setups often require flexible, non-corrosive conduits that can withstand various weather conditions. ENT’s lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties make it ideal for routing cables in solar farms and wind turbine installations, contributing to cleaner energy infrastructure.
- Green Building Construction
As construction shifts towards greener practices, ENT will be increasingly used in eco-friendly buildings. Sustainable buildings aim to reduce environmental impact and improve energy efficiency, and ENT fits well in these designs due to its recyclable material options and lower overall environmental footprint compared to metal conduits.
- Smart Homes and IoT Integration
ENT is likely to see more use in smart home systems where extensive wiring is needed for sensors, automation controls, and IoT devices. Its flexibility and ease of installation make it a practical choice for accommodating complex wiring setups in homes that incorporate smart technologies.
- Electric Vehicle (EV) Infrastructure
With the growth of electric vehicle charging stations, ENT can serve as a conduit solution for routing power and data cables. Its adaptability and durability help support both indoor and outdoor charging stations, facilitating the expansion of EV infrastructure that is crucial for sustainable transportation.
- Smart Grids and Power Management Systems
ENT’s role may expand in the development of smart grids, which require extensive wiring for data communication and power distribution. These systems rely on real-time data to optimize energy use and improve reliability. ENT’s potential integration with monitoring technologies could help improve the efficiency and manageability of such smart power systems.

The use of Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing (ENT) and other conduits in the electric vehicle (EV) and automotive industries is a rapidly growing area, as these industries adopt more advanced electrical systems. Here’s a closer look at how ENT and similar conduits are being used and their future potential:
- Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Infrastructure
With the increase in electric vehicle adoption, EV charging stations are becoming more widespread, requiring robust and flexible conduit solutions. ENT and other conduits are used for:
케이블 보호: ENT is ideal for protecting charging cables from physical damage and environmental factors. The tubing ensures the safe routing of cables from the power supply to the charging point.
Outdoor Durability: ENT’s weather-resistant qualities make it suitable for both indoor and outdoor installations, as charging stations often need to withstand harsh environmental conditions such as rain, snow, and UV exposure.
Data and Power Cable Management: For advanced charging stations with smart capabilities (e.g., energy monitoring, payment systems), ENT can protect both the power and data cables that are required for the system to function efficiently.
- Electric Vehicle Wiring Systems
Electric vehicles require extensive electrical wiring for various systems, including the battery management system, motors, charging systems, and sensors. Conduits like ENT are used to:
Cable Routing: ENT is used to route wires in the car’s body, ensuring that sensitive wiring is protected from physical stress, moisture, and temperature fluctuations.
유연성: The flexibility of ENT allows it to be installed in tight spaces within EVs, such as around motors, batteries, and other critical components. This flexibility helps streamline the assembly process and ensure safety.
Thermal Protection: ENT’s resistance to heat makes it suitable for managing the heat generated by power cables or components in high-performance EVs.
- Automotive Manufacturing
In the automotive industry, conduit systems are essential for organizing and protecting cables that power vehicle electronics. ENT and other conduits help in:
Protection During Manufacturing: ENT protects wiring from potential damage during the manufacturing process, including paint application, mechanical assembly, and other stages.
Flexible Wiring: For complex wiring systems in modern vehicles, ENT’s flexibility allows it to be easily routed through different sections of the vehicle, providing protection against abrasion, cuts, and environmental exposure.
- Battery Storage Systems
As more companies develop energy storage systems for EVs and other renewable energy projects, ENT can play a role in ensuring that the battery systems are properly wired and shielded. ENT is used to route electrical wiring from the batteries to various components, ensuring that these systems remain safe, reliable, and efficient.
- Smart Vehicles and Autonomous Cars
With the development of smart vehicles and autonomous driving technology, the need for reliable and durable electrical systems has skyrocketed. ENT plays a role in:
Data Cable Protection: Autonomous vehicles rely heavily on sensors, cameras, and other connected systems that generate vast amounts of data. ENT can protect the data cables that carry signals from these systems to the vehicle’s central processing units.
Low-Voltage Wiring: As vehicles become more automated and include systems for driver assistance, comfort, and entertainment, ENT is used to protect low-voltage wiring that powers these systems.
Understanding the fundamentals of Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing (ENT) is essential for industry professionals seeking reliable, flexible, and efficient solutions for electrical installations. ENT tubing serves a critical role in both residential and commercial applications due to its lightweight nature, ease of installation, and adaptability.
In this overview, we explored the main types of ENT, their respective uses, and the performance attributes that make them suitable for various environments. Compliance with codes such as UL 1653 and AS/NZS 2053 underscores the importance of meeting stringent safety and performance standards, ensuring that ENT remains a dependable choice even under challenging conditions.
Staying informed on the latest standards and advancements ensures that electrical professionals can leverage the full benefits of ENT tubing, optimizing both safety and efficiency in their projects. And evaluate the project needs before you choose the tubing types, making sure you choose the right one and comply with your local codes.



