목차
전기 도관 시스템 주거, 상업 및 산업 건물에서 안전하고 효율적인 배선의 중추 역할을 합니다. 신축 프로젝트이든 기존 건물 업그레이드이든, 전선 시스템은 전기 케이블을 보호하고 안전을 보장하는 데 필수적입니다. 이러한 시스템 내에서 중요하지만 종종 간과되는 구성 요소인 전선 본체가 핵심 역할을 합니다.
전기 설비에서 전선관은 전선관 내부의 배선을 보호하고 접근하는 데 필수적입니다. 전선관의 주요 기능은 전기 기술자가 전선관 시스템 내에서 방향이나 연결을 변경하여 전선 접합, 접합부 및 당김 지점을 위한 공간을 제공하는 것입니다. 전선관이 없으면 전기 시스템은 모서리나 굽은 곳을 돌아다닐 수 있는 유연성이 부족하고 전선을 유지 관리하거나 교체하기가 더 어려울 것입니다.
도관 본체는 또한 도관 내부의 전선이 물리적 손상, 환경적 위험 및 습기로부터 보호되도록 하는 보호 역할을 합니다. 이러한 보호는 단락이나 화재와 같은 문제를 방지하여 시스템의 수명과 안전성에 매우 중요합니다. 또한 도관 본체는 전기 기술자가 규정 준수 요구 사항을 충족하도록 돕고 설비가 확립된 안전 표준을 준수하도록 합니다.
실용성과 안전성을 모두 제공하는 전선관은 현대의 전기 설비에 없어서는 안 될 필수품이며, 특히 산업이나 상업 시설에서 사용되는 복잡한 배선 시스템에는 필수적입니다.
이 기사는 도관 본체에 대한 포괄적인 가이드 역할을 하며, 다양한 유형, 응용 분야 및 규정 준수를 분석합니다. 기사를 마칠 때까지 다음 사항을 확실히 이해하게 될 것입니다.
- 도관 본체 및 다양한 유형은 무엇입니까?
- 도관 본체의 이점
- 도관 본체에 대한 코드 및 표준
- 도관 본체 설치 방법
- 도관 본체의 응용 분야

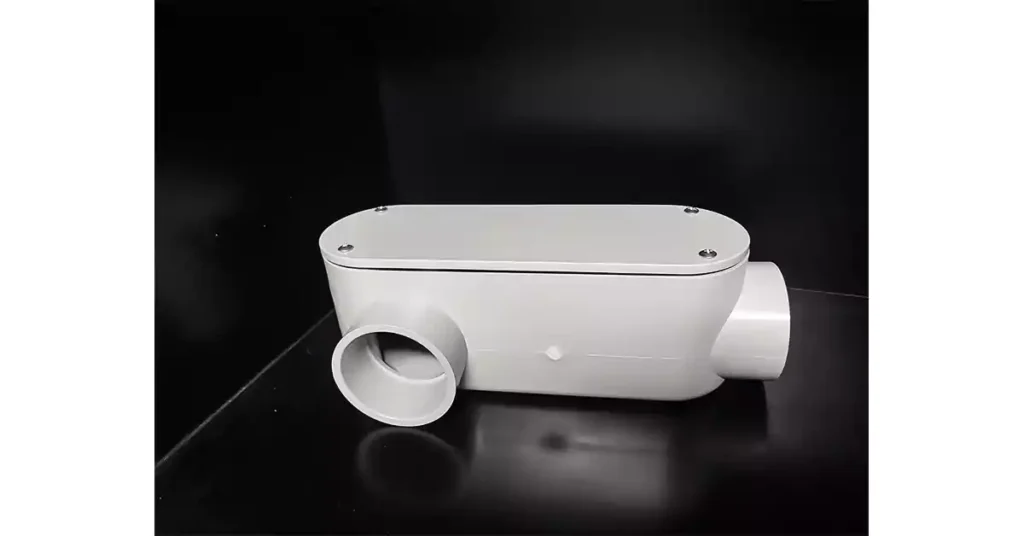
도관 본체는 도관 시스템에서 사용되는 전기 피팅의 한 유형으로, 방향을 바꾸고, 전선을 당기기 위한 접근 지점을 제공하고, 도관 섹션 간의 연결을 용이하게 하도록 설계되었습니다. 본질적으로 도관 런에 설치되는 상자 또는 인클로저로, 일반적으로 유지 관리 또는 수리를 위해 도관에 접근해야 하는 접합부, 모서리 또는 지점에 설치됩니다.
도관 본체는 설치 및 환경의 특정 요구 사항에 따라 알루미늄, 강철 및 플라스틱을 포함한 다양한 재료로 만들어집니다. 이러한 본체는 와이어 연결부를 수용하고, 와이어 스플라이스를 위한 공간을 제공하며, 시스템을 통한 전기 도체의 안전하고 효율적인 라우팅을 가능하게 합니다.
도관 본체는 스케줄 40 및 스케줄 80 강성 도관과 함께 가장 일반적으로 사용되는데, 이 둘은 모두 PVC(폴리염화비닐) 도관 유형입니다. 이러한 유형의 도관은 내구성, 부식 저항성 및 설치 용이성 때문에 선택됩니다.
도관 본체는 주로 다음과 같은 응용 분야에 사용됩니다.
- 방향의 변화: 도관 시스템에 회전이나 굽힘이 필요한 경우, 도관 본체는 한 섹션에서 다른 섹션으로의 원활한 전환을 허용합니다. 다양한 각도(예: 90°, 45°)의 굽힘을 수용할 수 있으며 전기 배선의 올바른 정렬을 유지하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
- 도관의 연결 섹션: 도관 본체는 두 개 이상의 도관 섹션이 만나는 연결 지점 역할을 합니다. 이러한 연결 지점은 시스템이 연속적이고 설치 전체에 걸쳐 전선을 안전하게 라우팅할 수 있도록 하는 데 필수적입니다.
- 와이어 접근 및 당김: 도관 본체의 주요 기능 중 하나는 전기 기술자가 전선을 당기거나, 검사하거나, 설치할 수 있는 접근 지점을 제공하는 것입니다. 이러한 본체는 전선을 길거나 복잡한 도관으로 당겨야 할 때 특히 유용하여 케이블을 탐색하고 설치하는 것이 더 쉬워집니다.
- 와이어 스플라이싱 및 종단: 도관 본체는 또한 전선 접합 및 종단을 허용하여 도관 시스템 내에서 전기 연결을 할 수 있습니다. 이는 전선을 연결해야 하는 시스템이나 추가 회로에 연결하기 위해 확장이 필요한 경우에 특히 유용합니다.
- 전기 연결을 위한 인클로저: 어떤 경우에는 도관 본체가 도관 런 내에서 작은 접합 상자 역할을 합니다. 이러한 인클로저는 전기 연결을 물리적 손상, 습기 및 오염 물질로부터 보호하여 시스템의 안전성과 수명을 보장합니다.
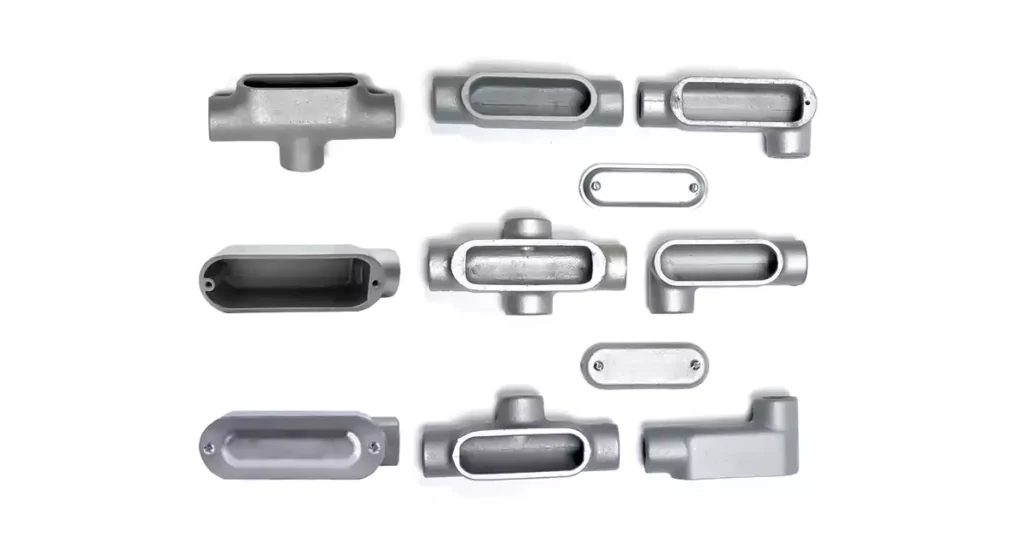
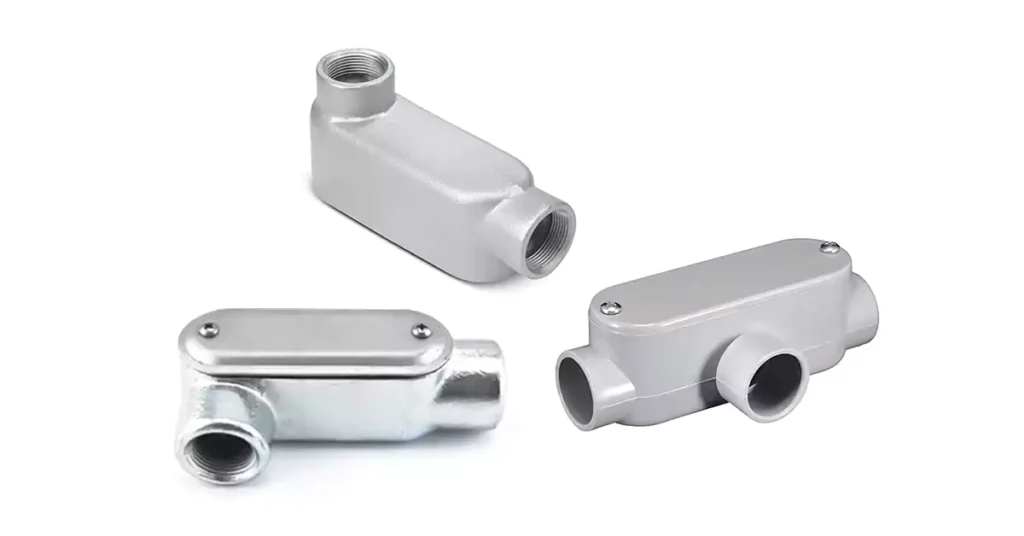
전선관 본체는 다양한 모양과 디자인으로 제공되며, 각각 전기 전선관 시스템의 특정 요구 사항을 충족하도록 맞춤 제작되었습니다. 이러한 피팅은 전선관의 방향을 변경하고, 배선을 위한 접근성을 제공하며, 전선 접합 또는 유지 관리를 허용하는 데 사용됩니다. 아래에서는 전기 설비에 일반적으로 사용되는 표준 유형의 전선관 본체와 대규모 시스템을 위해 설계된 보다 특수화된 유형을 다룹니다. 또한 전선관 본체와 접합 상자를 구별합니다. 이 두 구성 요소는 어떤 면에서는 비슷하지만 다른 용도로 사용됩니다.

LB 도관 본체는 도관 런에서 90도 회전을 하는 데 가장 일반적으로 사용되는 유형 중 하나이며, 와이어 풀링 및 스플라이싱을 위한 액세스도 제공합니다. 여기에는 들어오는 배선을 위한 하나와 나가는 배선을 위한 하나의 두 개의 도관 허브가 포함되어 있어 전기 기술자가 모서리를 따라 전선을 라우팅할 수 있습니다. LB 도관 본체의 액세스 지점은 본체 뒷면에 있어 벽이나 표면을 통해 전선을 라우팅하는 데 이상적입니다.
일반적인 사용: 특히 전선을 구조물 외부에서 내부로 설치해야 하는 경우, 도관의 방향을 90도 각도로 바꿔야 하는 상황에 이상적입니다.
LB와 유사하게 LL 도관 본체 또한 90도 회전을 형성하지만 배선은 오른쪽이 아닌 본체 왼쪽으로 나갑니다. 이 버전에는 두 개의 도관 허브가 포함되어 있습니다. 하나는 위쪽에서 와이어를 입력하기 위한 것이고 다른 하나는 왼쪽에서 와이어를 출력하기 위한 것입니다. LR 본체와 마찬가지로 LL 본체는 동일한 평면을 따라 배선을 재지정하는 데 유용합니다.
일반적인 사용: 일반적으로 90도 회전 후 배선을 왼쪽으로 연결해야 하는 설치에 사용됩니다.
그만큼 LR 도관 본체 또 다른 90도 엘보 피팅으로 전기 기술자가 도관 배선을 재지정할 수 있습니다. 이 버전은 두 개의 도관 허브를 특징으로 합니다. 하나는 전선 진입을 위한 상단, 다른 하나는 전선 출구를 위한 오른쪽에 있습니다. 이 설계는 평면을 변경하지 않고도 레이스웨이 방향을 조정할 수 있습니다.
일반적인 사용: 특히 좁은 공간이나 동일한 평면을 가로질러 배선을 연결할 때 도관에서 올바른 방향으로 배선을 연결해야 할 때 사용됩니다.
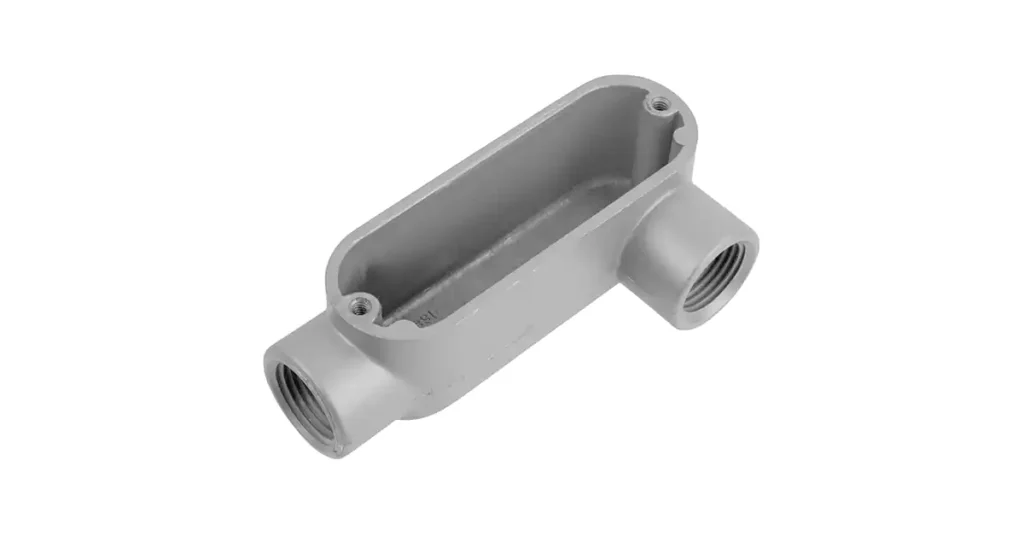
T형 도관 본체는 이 목록에서 두 개 이상의 허브를 특징으로 하는 최초의 도관 본체입니다. 하나의 도관 허브가 90도 각도로 향하고 다른 두 개가 서로 평행한 T자 모양의 접합부를 형성합니다. 이를 통해 전기 기술자는 두 개의 다른 위치에서 배선을 하나의 도관으로 병합하거나 하나의 도관에서 두 개의 별도 방향으로 분기할 수 있습니다.
일반적인 사용: 기존 시스템에 새로운 회로를 추가하는 등 배관 경로를 여러 방향으로 분할해야 하는 상황에서 일반적으로 사용됩니다.
C 콘듀이트 본체는 직선 스플라이스 본체 역할을 합니다. 배선 방향을 변경하지 않고 두 개의 콘듀이트 구간을 직선으로 연결합니다. 콘듀이트에 쉽게 접근할 수 있도록 분리형 플레이트로 설계되어 레이스웨이를 따라 서비스 가능한 지점을 제공합니다. 이 유형은 방향을 변경할 필요가 없는 콘듀이트 구간을 연결하는 데 이상적입니다.
일반적인 사용: 도관을 직선으로 연결하거나 확장해야 하는 시스템에서 사용되며, 경로를 따라 접근 지점을 제공합니다.
E 컨듀이트 본체는 본체 끝에 단일 액세스 지점이 있도록 설계되었습니다. 컨듀이트 런 끝에서 전선을 쉽게 넣거나 뺄 수 있습니다. E 컨듀이트 본체는 설계가 간단하지만 컨듀이트 섹션 끝에서 전선을 당기거나 유지 관리해야 하는 설치에 효과적입니다.
일반적인 사용: 일반적으로 직선 도관에 사용되며, 전선을 잡아당기거나 검사할 때 접근 지점이 하나만 필요합니다.
TB 도관 본체는 후면 액세스 포인트 외에도 상단 및 하단 액세스 포인트가 설계되었습니다. 이러한 추가적인 유연성 덕분에 여러 방향에서 전선을 잡아당기고 이어 붙이기가 더 쉬워져 좁은 공간이나 복잡한 전기 시스템에서 특히 유용합니다.
유지 보수, 검사 또는 여러 방향에서 전선을 잡아당길 때 여러 개의 접근 지점이 필요한 설치에 이상적입니다.
X 컨듀잇 바디는 T 바디와 비슷하지만 4개의 컨듀잇 허브가 특징입니다. 2개의 평행 세트가 교차 모양을 만듭니다. 이 구성을 통해 동일한 지점에서 여러 방향으로 배선을 들어오거나 나갈 수 있습니다. X 컨듀잇 바디는 여러 컨듀잇 런이 중앙 접합부에서 만나야 하는 경우 이상적인 솔루션으로, 복잡한 전기 시스템의 핵심 구성 요소입니다.
일반적인 사용: 일반적으로 여러 개의 도관이 중앙 지점에서 연결되거나 분기되어야 하는 대규모 상업 또는 산업용 전기 시스템에 사용됩니다.
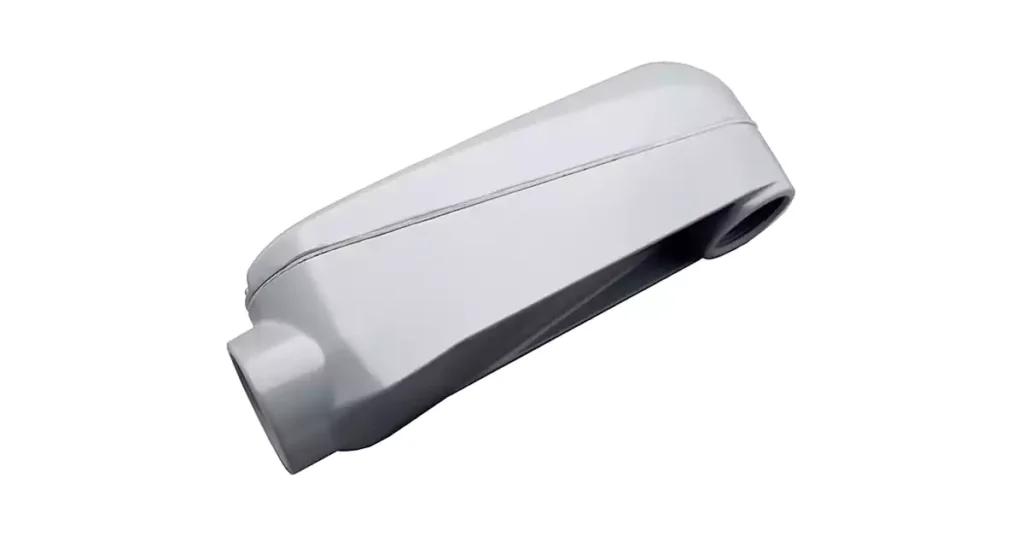

Mogul 콘듀이트 바디는 표준 콘듀이트 바디의 더 크고 견고한 버전입니다. 이 제품은 더 큰 콘듀이트 크기를 수용하도록 설계되었으며 일반적으로 콘듀이트 시스템이 대용량을 처리하는 산업용 애플리케이션이나 대규모 전기 설비에 사용됩니다. Mogul 콘듀이트 바디는 전기 배선을 관리하기 위해 더 크고 견고한 피팅이 필요한 상황에 이상적입니다.
일반적인 사용: 일반적으로 대형 전기 회로를 관리하기 위해 대형 도관 피팅이 필요한 산업용 또는 대용량 상업용 전기 시스템에 사용됩니다.
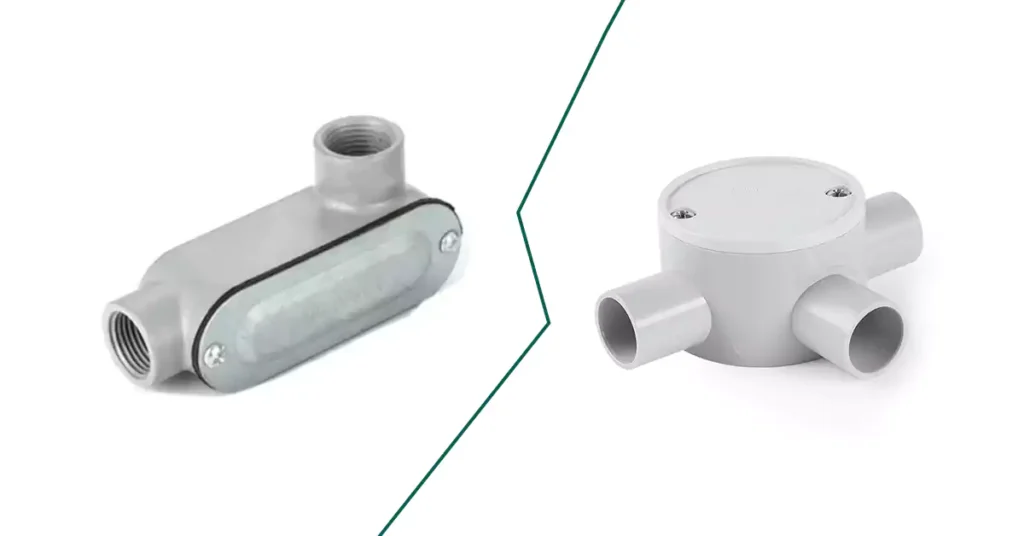

전선관 본체와 접속함은 둘 다 전기 설비에 필수적이지만, 그 용도가 다르고 사용 환경도 다릅니다.
특징 | 도관 본체 | 정션박스 |
목적 | 배관 시스템 내에서 접근성을 제공하고, 방향 변경을 허용하거나 배선을 연결합니다. | 전기 연결부, 접속부, 종단부를 보호합니다. |
주요 기능 | 전선의 방향을 바꾸고, 전선을 쉽게 잡아당기고, 이어붙이기 위한 접근 지점을 만듭니다. | 전기 연결부를 보호하고 둘러싸서 안전과 규정 준수를 보장합니다. |
위치 | 도관 시스템에 통합되어 있으며 경주로의 일부입니다. | 보호 및 접근성을 위해 도관 시스템 외부에 위치합니다. |
설계 | 일반적으로 도관 구간을 연결하기 위한 여러 개의 허브가 특징입니다. | 배선 연결을 위한 하나 이상의 진입/출구 지점이 있는 밀폐된 용기. |
장착 요구 사항 | 경주로의 일부이므로 개별적으로 지원할 필요가 없습니다. | 독립적으로 지지되어야 하며, 종종 표면에 장착됩니다. |
유형 | LB, LL, LR, C, T, X, TB, E 등 (다양한 기능에 따른 다양한 모양). | 정사각형, 직사각형, 둥글거나 타원형 모양의 상자로, 종종 덮개를 떼어낼 수 있다. |
접근 지점 | 도관 시스템 자체에서 직접 배선에 접근할 수 있습니다. | 유지관리나 검사를 위해 배선 연결에 대한 접근성을 제공합니다. |

도관 본체는 전기 시스템의 필수 구성 요소이며, 그 설계는 재료 구성, 내후성, 도관 유형과의 호환성 및 특정 응용 분야 요구 사항에 따라 다릅니다. 이 섹션에서는 다양한 재료 옵션, 장단점 및 도관 본체를 다양한 응용 분야에 적합하게 만드는 다양한 설계 기능을 살펴봅니다.
도관 본체는 여러 소재로 제조되며, 각각 환경 및 적용 요구 사항에 따라 뚜렷한 장점을 제공합니다. 가장 일반적으로 사용되는 네 가지 소재는 알루미늄, 강철, PVC 및 아연 도금 소재입니다.
알루미늄 도관 본체는 가볍고 부식에 강하며 내구성이 뛰어납니다. 도관 본체가 습기나 환경적 스트레스에 노출될 수 있는 응용 분야에서 널리 사용됩니다.
강철 도관 본체는 견고하며 충격이 심하거나 혹독한 환경에서 전기 배선에 대한 뛰어난 강도와 보호 기능을 제공합니다. 강철은 종종 추가적인 기계적 보호가 필요한 산업 또는 상업 시설에서 사용됩니다.
PVC 도관 본체는 내식성이 있는 플라스틱 소재로 만들어지며 저렴한 비금속 솔루션이 필요한 분야에 일반적으로 사용됩니다.
아연 도금(또는 아연 도금) 도관 본체는 일반적으로 강철로 만들어지지만 부식 저항성을 개선하기 위해 보호 아연 코팅이 되어 있습니다. 도관을 습기, 화학 물질 또는 기타 부식성 요소에 노출시킬 수 있는 환경에서 사용됩니다.
도관 본체의 주요 특징 중 하나는 요소에 노출되어도 견딜 수 있는 능력으로, 실내 및 실외 응용 분야에 모두 적합합니다. 다음은 다양한 재료의 내후성 및 내식성 특성에 대한 분석입니다.
- 알류미늄: 자연적으로 부식에 강하지만 시간이 지나면 산화될 수 있습니다. 습하거나 염분이 많은 환경에서도 잘 작동합니다.
- 강철: 튼튼하고 내구성이 있지만 아연 도금이나 코팅하지 않으면 녹이 슬기 쉽습니다. 산업 환경에 적합하지만 부식을 방지하기 위해 유지 관리가 필요합니다.
- 비닐: 우수한 내식성이며 습한 환경에 이상적입니다. 또한 비반응성이므로 화학 물질에 노출된 지역에 완벽합니다.
- 아연 도금 강철: 향상된 내식성을 제공하지만 아연 코팅이 손상되지 않도록 하려면 여전히 유지 관리가 필요합니다.
도관 본체의 재료를 선택할 때는 기상 조건, 습기 노출, 물리적 마모 및 파손 가능성을 고려해야 합니다.
도관 본체는 다양한 유형의 전기 도관과 호환되도록 설계되어 전체 도관 시스템에 원활하게 통합됩니다. 도관 본체와 함께 작동하는 일반적인 도관 유형은 다음과 같습니다.
- 강성 금속 도관(RMC): 이것은 산업 환경에서 사용되는 고성능 도관입니다. 도관 본체는 다음으로 만들어졌습니다. 강철 또는 알류미늄 RMC 시스템에 이상적입니다.
- 중간 금속 도관(IMC): RMC에 대한 더 얇은 대안, 강철 IMC 시스템에서는 도관 본체가 가장 많이 사용됩니다.
- PVC 도관: 비금속 도관 시스템의 경우 PVC 도관 본체 배관과의 호환성을 보장하고 습한 곳이나 지하 설치 시 부식으로부터 보호하는 데 사용됩니다.
도관 본체는 연결하려는 도관 유형과 일치해야 하므로 프로젝트에 적합한 유형을 선택할 때 호환성은 핵심 요소입니다.
도관 본체는 특정 애플리케이션의 요구 사항을 충족하기 위해 다양한 디자인으로 제공됩니다. 일부 디자인 변형은 다음과 같습니다.
- 사이즈: 도관 본체는 도관 직경에 맞게 다양한 크기로 제공되며 통과해야 하는 전선 수를 수용할 수 있습니다. 올바른 크기를 선택하면 전선을 당기고 유지 관리하기에 충분한 공간이 확보됩니다.
- 접근 지점: 많은 도관 본체에는 다음이 포함됩니다. removable covers 또는 multiple access points to facilitate wire pulling, splicing, and system inspections. The ability to open and close the body allows for ease of maintenance over time.
- Heavy-duty Options: For harsh environments, heavy-duty 강철 또는 zinc-coated conduit bodies may be used. These bodies are designed to withstand high-impact situations and offer enhanced durability.
Each type of conduit body is tailored to meet the needs of specific projects, offering versatility and flexibility in a variety of installations.

Conduit bodies must adhere to various regulatory standards to ensure they meet safety, durability, and performance requirements. In this section, we will discuss the NEC (National Electrical Code) requirements for conduit bodies, including the key codes that govern their use, UL (Underwriters Laboratories) Listing, and CSA (Canadian Standards Association) certifications. We will also cover best practices for installation to ensure compliance with these standards.
The National Electrical Code (NEC) is a set of regulations used in the United States to ensure safe electrical installations. Several specific NEC sections apply to the use of conduit bodies in electrical systems. These sections outline the necessary safety measures, proper installation practices, and performance criteria.
NEC 300.15 provides the general requirements for when a box, conduit body, or fitting is required in an electrical installation. These components are essential for providing proper access and protection for conductors at various points along the wiring system. The code outlines specific requirements for their use at outlet points, splice points, junction points, and other key locations.
General Requirement:
A box or conduit body must be installed at each outlet point, switch point, conductor splice point, conductor junction point, conductor termination point, wiring method transition point, or conductor pull point. This requirement applies when using conduit, tubing, Type AC cable, Type MC cable, Type MI cable, nonmetallic-sheathed cable, or other cables unless an exception is specifically permitted under 300.15(A) through (L).
Conduit bodies are essential components used to join, protect, and provide access to electrical conductors in various wiring installations. Under NEC Article 314, conduit bodies are classified as boxes or fittings that serve as junction points for wiring systems, enabling secure connections and ensuring accessibility for future maintenance or modification. The article provides comprehensive guidelines on the installation, sizing, and specific use cases for conduit bodies to maintain safety, efficiency, and code compliance in electrical systems.
Some key points introduced in Article 314:
Types of Conduit Bodies:
Conduit bodies come in various materials, including cast metal, sheet metal, and nonmetallic types. They serve as connection points between raceways and cables.
They must be designed and listed specifically for their intended use, ensuring safety and performance.
Volume Calculations:
Conduit bodies must be large enough to accommodate the number and size of conductors they enclose. The volume of a conduit body must meet the requirements set in 314.16(C), ensuring there is adequate space for all conductors.
Cross-sectional area: For most conduit bodies, the cross-sectional area must be at least twice the area of the largest conduit it is attached to, ensuring that conductors can be routed safely without overcrowding.
Installation and Use:
Conduit bodies are required to be securely supported in a rigid and stable manner. This ensures they can withstand environmental stresses and maintain structural integrity over time.
Short-radius conduit bodies, like elbows, which are intended to change the direction of the conduit system, are exempt from housing splices, taps, or devices.
Damp or Wet Locations: When installed in wet locations, conduit bodies must be designed to prevent moisture from accumulating inside. Drainage openings are allowed in such installations to prevent water ingress.
Conduit Bodies with Splices or Taps:
Only those conduit bodies marked by the manufacturer with their volume are permitted to contain splices, taps, or devices. These must comply with volume requirements and be sized appropriately to handle the electrical load.
Protection and Abrasion:
Conductors entering a conduit body must be protected from abrasion. Insulating bushings should be used where metal conduit bodies are installed with unprotected conductors.
Conduit bodies are also required to have adequate fittings and closures to prevent accidental contact with live conductors and to maintain the integrity of the wiring system.
Conduit Bodies for Larger Conductors:
For installations involving conductors larger than 6 AWG, the conduit body size must be calculated based on the conductors’ total cross-sectional area. This ensures enough space for proper conductor management and heat dissipation.
Maintenance and Accessibility:
Conduit bodies must remain accessible after installation for inspection, maintenance, and potential upgrades. This is essential for ensuring safety and allowing for any future modifications or repairs without significant disruption to the wiring system.
The Underwriters Laboratories (UL) is an independent safety certification organization that ensures electrical products meet established safety standards. Conduit bodies are typically UL Listed, which means they have passed rigorous testing and are deemed safe for use in electrical systems. The related UL standards for conduit bodies including UL514C and UL 514B.
UL514C sets forth the performance and testing requirements for conduit bodies. These standards are critical for ensuring that conduit bodies are safe, reliable, and durable in electrical systems. Some key performance tests and requirements under UL 514C include:
치수: UL 514C specifies the dimension requirements for conduit bodies, including their cross-sectional area requirements, inside volume etc.
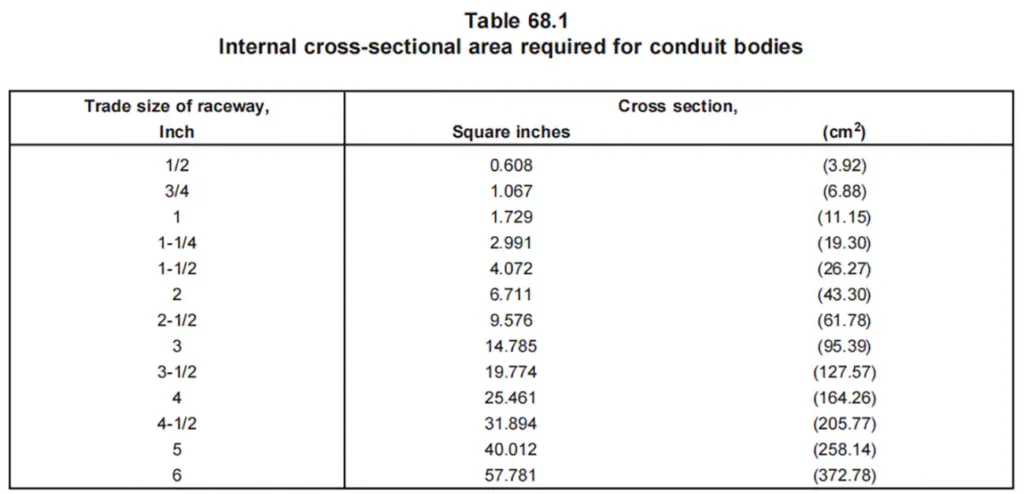
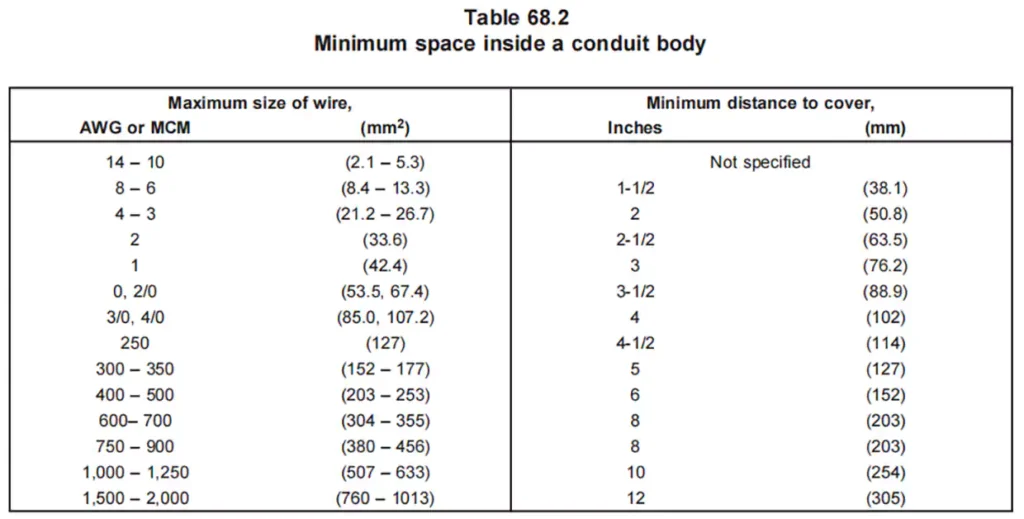
Temperature Endurance: Conduit bodies must withstand elevated temperatures, 92℃ as specified in the standard, without deformation, warping, cracking, or losing their structural integrity. UL 514C tests the ability of conduit bodies to handle extreme conditions, ensuring they perform reliably in both high and low-temperature environments.
Flame Retardant: Require the conduit box do not support combustion for more than 5 seconds after the third application of the flame, and there should be no flame drops, and the box should not be completely consumed.
기계적 강도: Conduit bodies are subject to mechanical stress testing to ensure they can resist physical impacts, vibrations, and other mechanical stresses typically encountered in electrical systems. Including the tensile test, impact test.
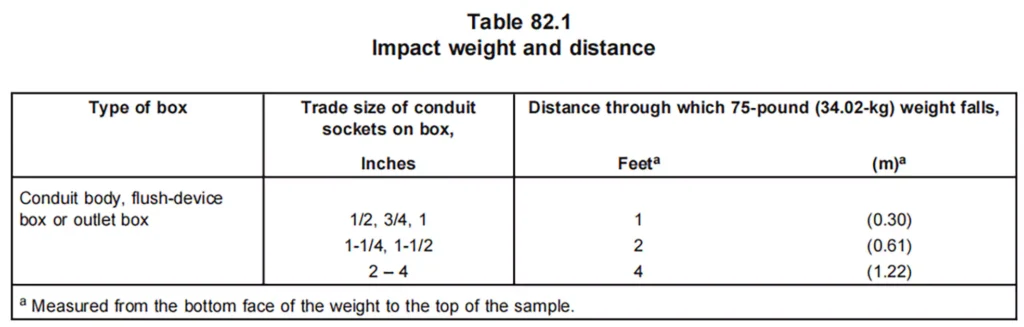
부식 저항성: UL 514C requires that conduit bodies meet specific corrosion resistance standards, particularly for those used in wet or harsh environments. This ensures that the conduit body will not degrade or compromise the integrity of the wiring.
Electrical Insulation and Conductivity: For non-metallic conduit bodies, UL 514C verifies that the material is non-conductive, preventing any risk of electrical shorts or shocks. For metallic bodies, they must be properly insulated or grounded as necessary.
Protection Against Environmental Elements: Conduit bodies used in outdoor or harsh environments must be tested for weatherproofing and resistance to elements like moisture, dust, and chemicals. This ensures that electrical systems remain safe even in challenging environments.
UL 514B is the Underwriters Laboratories standard that outlines the construction, performance, and safety requirements for conduit bodies, ensuring they are safe for use in electrical installations. This standard applies to all conduit bodies used to connect raceways and cables, including those intended for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. Below is an overview of the key requirements outlined in UL 514B regarding dimensions, construction materials, and performance standards. It covers aspects like:
Dimensions of Conduit Bodies:
UL 514B specifies precise dimensional criteria to ensure conduit bodies are suitable for housing conductors and maintaining their intended function.
Construction and Material Requirements:
The materials and construction methods used in the manufacturing of conduit bodies are crucial for their durability, performance, and safety. UL 514B specifies the following requirements for construction:
Performance Requirements:
UL 514B ensures that conduit bodies meet stringent performance standards to guarantee electrical safety, durability, and overall functionality. These include:
Physical Strength:
충격 저항성: Conduit bodies must be able to withstand physical impact without cracking or failing. This is particularly important in environments subject to mechanical stresses.
Compression Strength: The material must be strong enough to resist deformation when subject to compression, ensuring the conduit body maintains its shape under load and does not collapse or become deformed under normal conditions.
전기 안전:
전기 절연: For nonmetallic conduit bodies, the materials must be electrically insulating to prevent inadvertent short circuits or shock hazards. Metal conduit bodies, on the other hand, must be properly bonded and grounded to ensure that they do not carry stray electrical current that could pose a shock risk.
Moisture and Corrosion Resistance: UL 514B requires that conduit bodies have sufficient protection against moisture and corrosion, particularly when used in damp or wet environments. This includes proper sealing and the use of corrosion-resistant materials to maintain electrical safety over time.
In Canada, the Canadian Standards Association (CSA) establishes safety standards for electrical products. Conduit bodies sold in Canada must comply with CSA C22.2 No. 85, which provides the requirements for fittings for electrical conduit and tubing. Some key requirements under CSA C22.2 No. 85 include:
Similar to UL standards, CSA requires that conduit bodies meet specific material composition and design criteria to ensure they are suitable for safe and reliable use in electrical systems.
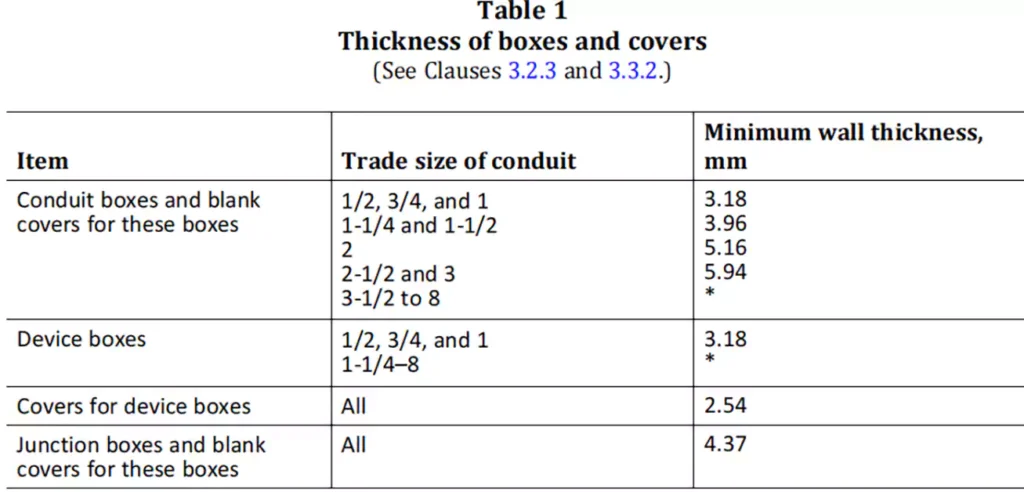
CSA C22.2 No. 85 sets specific dimensional criteria to ensure that conduit bodies have adequate space for wiring and can accommodate the conductors within raceways without risking overcrowding or improper installation.
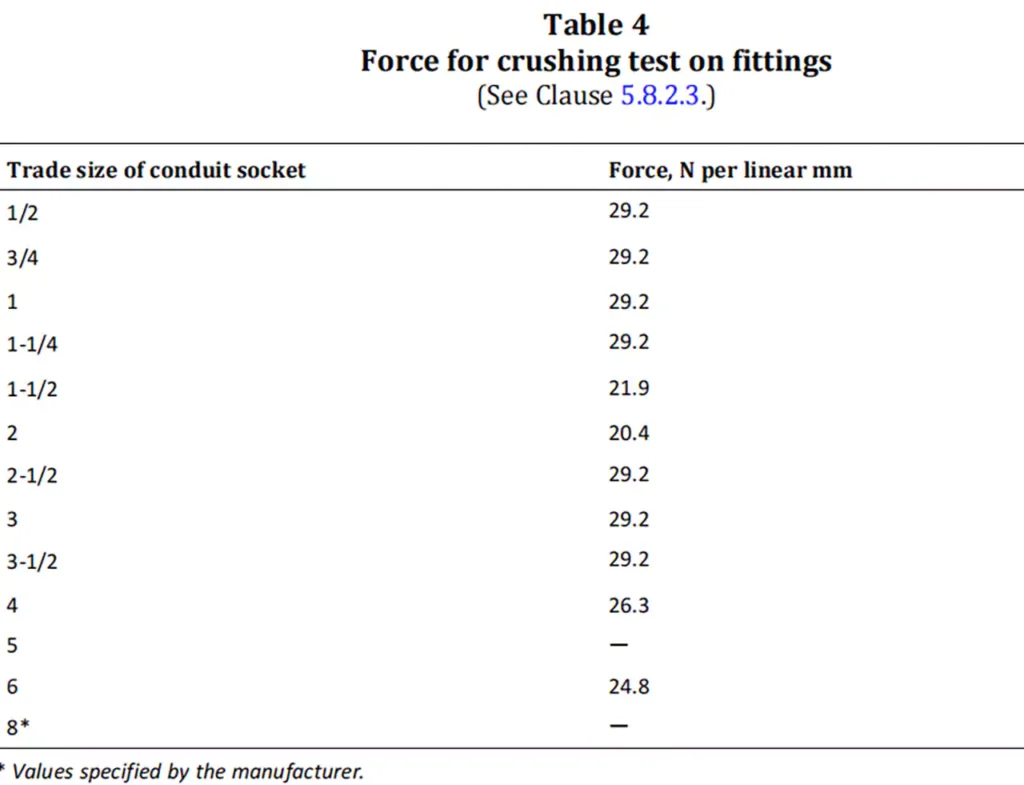
CSA C22.2 No. 85 outlines various physical and environmental performance requirements to ensure that conduit bodies can operate reliably under harsh conditions. These include resistance to heat, flame, impact at -34 Degree Celsius., and crushing.
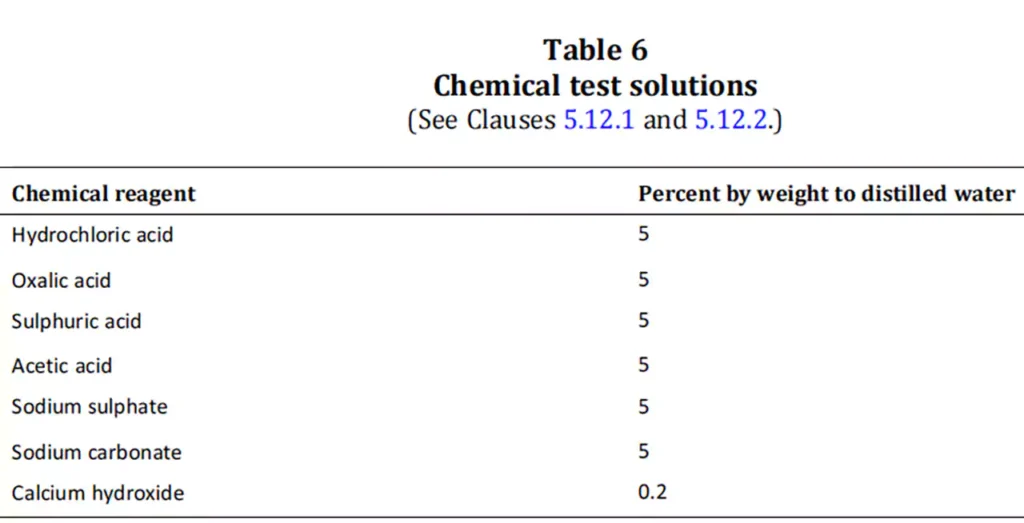
부식 저항성: Conduit bodies, especially those used in outdoor or industrial applications, must be resistant to corrosion caused by exposure to moisture, chemicals, and pollutants. This is especially true for metallic conduit bodies, which must be treated or coated with corrosion-resistant materials to prevent rusting and deterioration.
화학 물질 노출: Nonmetallic conduit bodies must also exhibit resistance to common industrial chemicals, oils, and solvents that may be encountered in some electrical installations, ensuring they do not degrade or lose their structural integrity.
Conduit bodies must be clearly marked with manufacturer information, material type, voltage ratings, and CSA certification. Durable labeling ensures that conduit bodies are used properly and meet safety regulations.
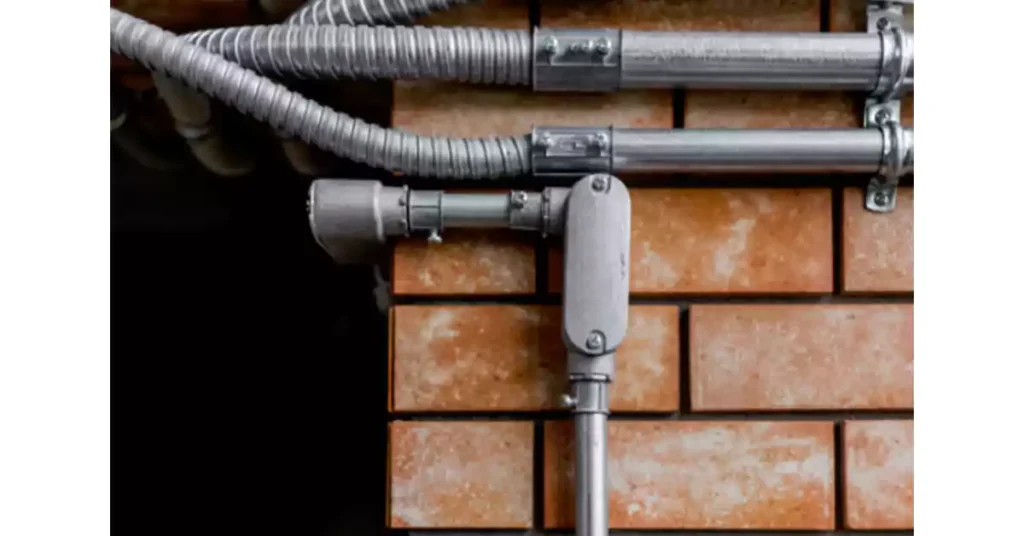
Conduit bodies are essential components used in various electrical installations to protect and organize wiring. Their versatility makes them suitable for a wide range of applications in both residential and industrial environments. Below are some common uses for conduit bodies:
In homes, conduit bodies are used for:
배선 연결: They provide a secure space for connecting and joining electrical wires. This ensures that wiring is well-organized and accessible for future maintenance.
보호: They help protect electrical wiring from physical damage and environmental factors like moisture and heat, especially in areas like basements or kitchens.
분기 회로: Conduit bodies allow electrical systems to branch out and power multiple circuits, such as outlets, lights, and appliances.
In businesses and factories, conduit bodies are used in:
Control Panels: They house wiring connections and provide easy access to electrical systems, ensuring smooth operations in industrial settings.
Heavy-Duty Systems: They protect wiring from physical damage in environments that involve high mechanical stress, such as factories and warehouses.
Automation Systems: Conduit bodies help route electrical wiring safely to machinery, robots, and automated equipment.
In areas with exposure to moisture, conduit bodies are designed to meet specific standards for wet and damp locations:
야외 설비: Conduit bodies used outdoors—such as for street lighting, signage, or landscape lighting—are built to prevent moisture ingress and protect wiring from weather-related damage.
Damp Environments: In places like basements, parking garages, or laundry rooms, conduit bodies prevent moisture from affecting the wiring, reducing the risk of short circuits or deterioration of the electrical system.
습한 장소: In locations directly exposed to water, like outdoor swimming pools, fountains, or marine environments, special conduit bodies rated for wet locations provide full protection against moisture, ensuring the safety of electrical systems.
In data centers and telecommunications systems, conduit bodies are used to:
Manage Cables: They keep cables organized and protected while ensuring the safe routing of electrical wiring within the infrastructure of sensitive equipment.
Provide Safety: Conduit bodies help to prevent electrical interference, protect wiring from external elements, and ensure that the electrical systems continue to function smoothly without risk to critical data and communication systems.
In environments with a higher risk of fire or explosion, such as chemical plants or oil refineries, conduit bodies are designed to:
Explosion-Proof: Explosion-proof conduit bodies prevent the risk of sparks or electrical arcs from igniting flammable gases or vapors, providing safety in volatile environments.
부식 저항성: In areas where the electrical system is exposed to harsh chemicals or corrosive elements, conduit bodies are made from corrosion-resistant materials, ensuring they maintain their protective function
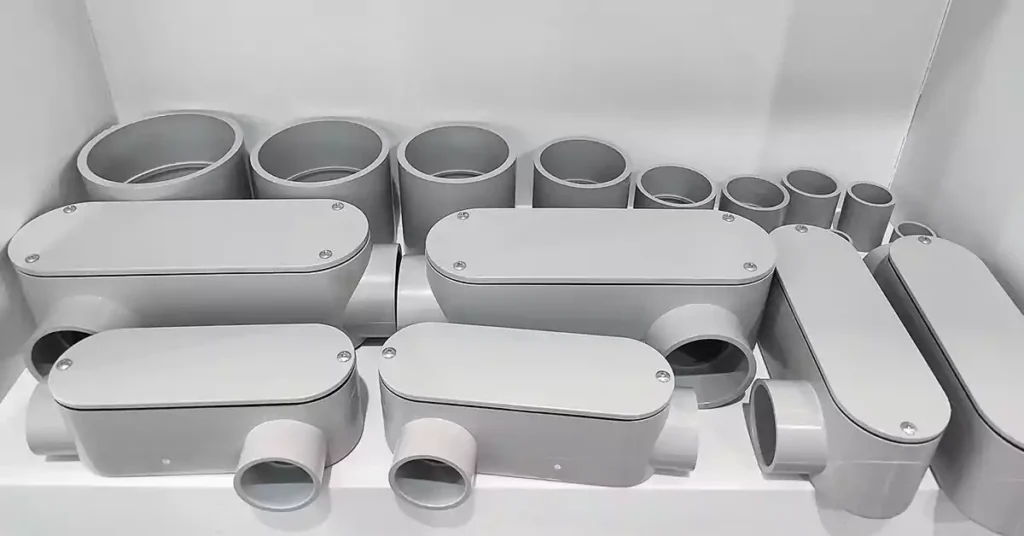

Conduit bodies are not just functional components; they offer a wide range of benefits that enhance the performance, safety, and longevity of electrical installations. Below are some key advantages of using conduit bodies in electrical systems:
One of the primary benefits of conduit bodies is the flexibility they provide in designing and modifying electrical conduit systems.
Multiple Entry Points: Conduit bodies offer various openings and configurations, allowing for easy access points at different locations within a system. This flexibility makes it easier to change or expand electrical systems without the need to completely redesign the layout.
Complex Routing: They enable complex wiring configurations, such as sharp bends, branches, or 90-degree turns, without compromising the integrity or performance of the system. This is especially important in spaces with limited access or where the wiring must follow specific paths.
Adaptability: Conduit bodies are available in many sizes and shapes, allowing them to be used in a wide variety of installations, from small residential systems to large commercial and industrial setups.
Conduit bodies serve as access points for wiring connections, which simplifies the maintenance, inspection, and modification of electrical systems.
Easy Maintenance: Because they are designed for easy access, conduit bodies make it much simpler to perform electrical maintenance. Technicians can easily access splices, taps, or connections housed within the conduit body without disassembling large portions of the conduit system.
Convenient Modifications: If the electrical system needs to be updated or expanded, conduit bodies provide a convenient place for adding or modifying circuits without the need to disrupt the entire installation.
Safe Access: They also provide safe and organized access to wiring, which can be important for troubleshooting or repairs, reducing the risk of accidental damage to the wiring or the system as a whole.
Conduit bodies play a crucial role in protecting electrical connections and ensuring the overall safety of the electrical system.
Shielding from Physical Damage: By enclosing wiring connections, conduit bodies protect them from external forces such as physical impacts, abrasion, or crushing. This is particularly important in environments where cables are at risk of being damaged by equipment, machinery, or everyday wear and tear.
Moisture and Dust Protection: In wet or damp environments, conduit bodies can be designed to prevent moisture or dust from entering the electrical connections, helping to maintain the integrity of the system and reducing the risk of electrical faults or failures.
향상된 안전성: Conduit bodies help maintain safe electrical systems by ensuring that connections are properly protected from environmental hazards. This contributes to reducing the risk of short circuits, sparks, and potential fire hazards.
Electrical cables and wires are often subjected to mechanical stresses, especially in systems with sharp bends or high traffic areas. Conduit bodies help alleviate this stress, contributing to the longevity of the wiring system.
Preventing Physical Stress: By providing a smooth path for cables and offering space for changes in direction, conduit bodies reduce the risk of kinks, tight bends, or other forms of mechanical stress on the wires. This helps prevent the potential for insulation damage and reduces the risk of wire breakage.
Minimizing Wear and Tear: Conduit bodies can also prevent direct contact between the cables and surfaces that might cause abrasion, further protecting the wiring and extending its service life.
Reducing Tension on Wires: They allow for smoother transitions and more room for wiring within the system, ensuring that wires do not experience undue tension, which can lead to failure or degradation of the cable insulation.
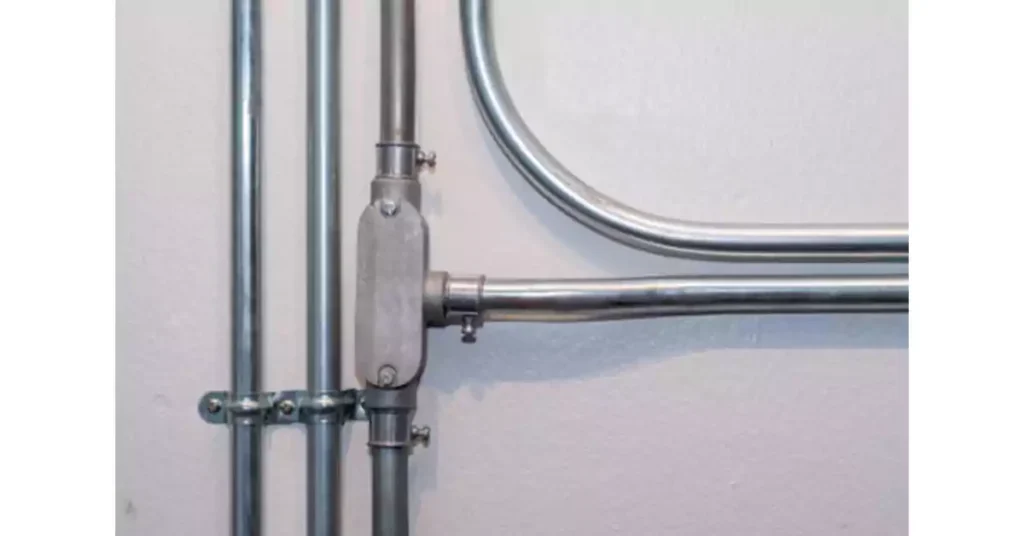

Installing conduit bodies correctly is essential for ensuring a safe and reliable electrical system. Proper installation not only helps maintain code compliance but also ensures the system operates efficiently and minimizes the risks of electrical faults or failures. This section provides a step-by-step guide to installing conduit bodies, highlights the tools needed, and emphasizes key considerations based on relevant codes of such as International Residential Code and NEC.
Before starting the installation, ensure you have the following tools:
- Measuring Tape: For accurately measuring distances and ensuring conduit bodies are placed in the right location.
- Screwdriver: To secure screws and fasteners in place.
- Wire Strippers: To prepare the conductors before they enter the conduit body.
- Hacksaw or Pipe Cutter: For cutting conduits to the required length.
- Conduit Bender: To bend the conduit to fit the installation layout if required.
- Drill: To create holes for mounting the conduit body if needed.
- Level: To ensure the conduit body is correctly aligned.
- Conduit Wrenches: For tightening connections securely.
Measure and cut the conduit to the required lengths using a hacksaw or pipe cutter. Make sure the conduit ends are clean and free from burrs.
Strip the insulation from the conductors carefully, ensuring the exposed wires are ready for connection.
Select the appropriate location for the conduit body. Ensure that the position complies with NEC Code Section 314.17 for access and clearance, allowing space for wiring and other connections.
Mount the conduit body securely, using a level to ensure it is aligned correctly. Make sure it is placed at an accessible location for future maintenance.
Connect the conduit to the conduit body by threading the conduit into the appropriate entry points on the conduit body. Use a conduit wrench to tighten the connections and ensure they are secure.
If using any fittings or bushings, ensure they are installed correctly to avoid damage to the conductors (NEC 300.4(G)).
Insert the prepared conductors into the conduit body, ensuring they pass through any openings smoothly and without damage. According to NEC, conductors entering the conduit body should be protected from abrasion. Use insulating fittings or bushings where necessary.
If there are unused openings in the conduit body, close them with approved plugs or covers as to prevent any exposure to moisture or dust, which could compromise the safety of the installation.
Secure the cover or device to the conduit body, ensuring it is tightly fastened using appropriate screws. Follow manufacturer instructions for any specific sealing requirements.
Use non-corrosive, weather-resistant materials if installing in wet or damp environments.
Once the conduit body and conductors are installed and secured, test the system for continuity and proper operation. Inspect all connections for tightness, ensuring that no part of the system is loose or improperly mounted.
- Tighten Connections Properly: Always ensure that threaded connections between the conduit and the conduit body are tightened securely. Over-tightening can damage threads, while under-tightening can lead to leaks or faults in the system.
- Use Insulated Fittings: To protect the conductors from abrasion when entering the conduit body, use insulated fittings (per NEC 300.4(G)) where appropriate.
- Seal Unused Openings: Unused openings must be sealed using proper plugs or covers to prevent entry of moisture, dust, or debris. Ensure that these covers are properly secured.
- Waterproofing in Wet Locations: In wet or damp environments, be sure to use waterproof conduit bodies and ensure all connections are sealed with a gasket or other weatherproof material.
- Ensure Proper Grounding: Make sure that any metal conduit bodies are properly grounded as per the grounding requirements of the NEC (Section 250).
- Incorrect Placement: Ensure that the conduit body is installed in a location that allows easy access for future maintenance and modification. Avoid placing the conduit body where it is difficult to reach or in locations with poor ventilation.
- Not Sealing Unused Openings: Leaving unused openings in the conduit body open can lead to moisture ingress, which could result in short circuits or corrosion over time.
- Failure to Follow Code: Make sure the installation adheres to the local code, including requirements like those outlined in NEC for securing, sealing, and mounting conduit bodies. Not complying with these can result in unsafe installations or costly repairs.
- Improper Support: Make sure the conduit body is properly supported, especially when mounted in areas with high vibration or movement. According to NEC, all enclosures should be securely mounted to prevent accidental dislodging.
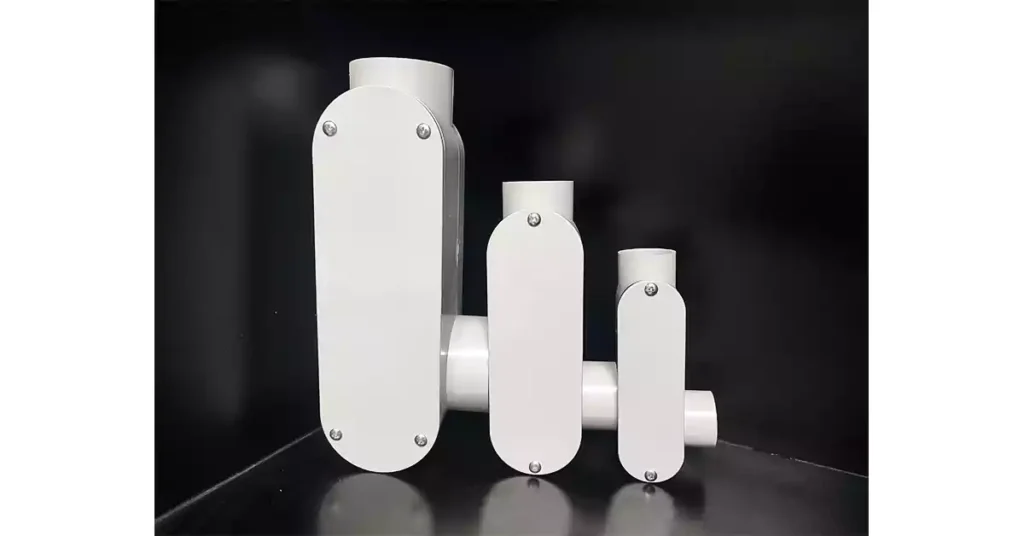

Choosing the right conduit body is crucial for ensuring the safety, efficiency, and longevity of your electrical installations. With a variety of options available, it’s important to consider the specific requirements of your project, including environmental factors, installation conditions, and compliance with relevant standards. This guide will help you navigate the selection process and make an informed purchase decision.
Conduit bodies come in different sizes, often referred to as “trade sizes,” which relate to the diameter of the conduit. You need to pick a size that suits the number of conductors (wires) you will be using, as well as any future wiring that might need to pass through. If the conduit body is too small, it could lead to crowded wires that are difficult to manage. If it’s too large, it may be unnecessary and take up too much space.
The material of the conduit body affects its durability and ability to handle environmental factors.
The environment where the conduit body will be installed is crucial. For indoor use, plastic or aluminum is often sufficient. However, for outdoor use or areas exposed to moisture, heat, or chemicals, you’ll need a more rugged material like aluminum or steel. Make sure the conduit body is sealed properly to prevent water or dust from entering.
Ensure the conduit body matches the size and type of conduit you’re using. Conduit bodies come in different styles (like LB, T, LL) and sizes, so check that the trade size of the conduit body matches your conduit, and that the style works with your wiring layout.
Choosing a conduit body from a reputable manufacturer ensures you’re getting a high-quality, durable product that meets safety standards. Trusted brands typically offer better customer service, warranties, and ensure that their products meet important certifications like UL or CSA.
Proper maintenance of conduit bodies is essential to ensure the continued safety and functionality of your electrical system. Regular inspections and prompt attention to any signs of wear or damage can help you avoid costly repairs and potential electrical hazards. In this section, we’ll explore some key tips for maintaining your conduit bodies and troubleshooting common issues.
Routine inspections are crucial to ensure that your conduit bodies remain in good condition. Here’s how to go about it:
- Visual Inspection: Start with a visual check to spot any obvious signs of damage or wear. Look for cracks, dents, or deformations in the conduit body. Check the cover and sealing gaskets for any signs of looseness, rust, or corrosion.
- Cleanliness: Make sure that the conduit body is free from debris, dirt, or any other buildup that could block openings or impede airflow. Dust or dirt can build up over time, which might also affect the performance of the seals or cause overheating.
- Secure Connections: Ensure that all fasteners are tight and that the conduit body is securely mounted. Loose connections or poorly sealed conduit bodies can lead to moisture intrusion, which could damage the wiring inside.
- Check for Ingress: Examine the conduit body for any signs of water, dust, or other contaminants entering. This is especially important for outdoor or wet-location installations. Look for moisture buildup inside the body or at the conduit entry points, as this could indicate a compromised seal.
Identifying wear and damage early can save you from more serious problems down the line. Here are some common signs to look for:
물리적 손상: Look for cracks, splits, or other physical damage to the conduit body. These can weaken the structure and compromise its protective function. Impact damage is particularly common in outdoor installations, so be sure to check for any visible dents or deformations.
부식: In wet or outdoor environments, metal conduit bodies can corrode over time. If you notice rust, pitting, or any signs of oxidation, this can lead to structural weaknesses and potential failure. Corrosion can also affect the electrical grounding of the system.
Loosening or Displacement: If the conduit body cover or fittings are loose or have become misaligned, this can lead to improper sealing, exposing the internal wiring to environmental factors. Tighten any loose screws and ensure that all components are properly aligned.
Moisture or Debris Inside: If you find water, rust, or other debris inside the conduit body, it could indicate that the seal is no longer intact. Moisture is especially concerning as it can lead to short circuits or corrosion of the internal wiring.
When a conduit body shows signs of wear, you may be faced with the decision to repair or replace it. Here are some considerations to guide your decision:
Minor Damage: If the damage is minor (such as a loose cover or a small crack), a simple repair might be sufficient. Tighten any loose fasteners or replace worn seals, gaskets, or screws. For cracks or damage in plastic conduit bodies, you might be able to apply a sealant or patch if the damage is not severe.
Corrosion or Major Damage: If the conduit body is significantly corroded or structurally compromised (such as severe cracking or rusting), it is often best to replace it entirely. Corrosion can weaken the integrity of the conduit body, making it a safety hazard. A replacement ensures that your electrical system remains secure and fully functional.
Old or Outdated Conduit Bodies: If your conduit body is outdated or no longer complies with current electrical codes, it might be worth replacing it with a newer model that meets modern standards. This is particularly true if the conduit body has been in place for a long time and shows signs of aging, such as brittle materials or outdated fittings.
비용 고려 사항: While repairs might seem more cost-effective in the short term, it’s important to evaluate the long-term cost. In some cases, replacing a conduit body with a newer, more durable model may be a more cost-effective solution in the long run, as it will likely last longer and require fewer repairs.
야외 사용을 위해 전선관을 어떻게 밀봉하나요?
Sealing conduit bodies for outdoor use is essential to protect electrical connections from moisture, dust, and other environmental elements. Here’s how to properly seal them:
- Use Weatherproof Gaskets: When installing conduit bodies outdoors, ensure that the cover and the body are equipped with a weatherproof gasket or sealant. This will help prevent water and dirt from entering the body.
- Apply Silicone Sealant: For additional protection, you can apply silicone or polyurethane sealant around the edges of the conduit body cover before securing it. This creates a more airtight and waterproof seal.
- Use Approved Outdoor-Rated Fittings: When using conduit bodies outdoors, it’s crucial to use components specifically rated for outdoor use, such as weather-resistant covers and corrosion-resistant fittings.
- Check Seals Regularly: Over time, seals and gaskets may wear out, so it’s important to inspect and replace them periodically to ensure a continued waterproof barrier.
도관 본체는 무엇에 사용되나요?
Conduit bodies serve several functions in electrical systems:
- Junction Points: They act as connection points where different sections of conduit come together. Conduit bodies provide a safe, accessible location for splicing or joining electrical wires and cables.
- Wiring Access: They provide access to the wiring within the conduit system for future maintenance or troubleshooting. This allows electricians to work on the wiring without needing to dismantle large sections of the conduit system.
- Cornering and Bending: Conduit bodies, such as the LB, LR, and LL types, allow for smooth direction changes in the conduit system, helping to run wires around corners and bends.
- 보호: They offer additional protection to wiring from external elements and damage by enclosing the wires in a safe, secure box.
모서리 주위에 배관을 어떻게 설치하나요?
Running a conduit around corners requires either using pre-made fittings or bending the conduit manually. Here’s how to do it:
- Use Conduit Bodies: The most common method to run conduit around corners is by using a conduit body, such as the LB, LR, or LL models, which are designed for this purpose. These conduit bodies have built-in angles that allow for smooth changes in direction without the need for bends.
- Use Elbows or 90-Degree Bends: If you’re not using a conduit body, you can use elbows or pre-formed 90-degree bends. These fittings are installed directly into the conduit system to turn the conduit at the desired angle. Ensure that the bend radius meets the requirements for the type of conduit you’re using to prevent damage to the wire inside.
- Manual Bending: For metal conduit (such as EMT or RMC), you can use a conduit bender to create a custom bend around a corner. However, be mindful of the conduit’s minimum bend radius to prevent damaging the conduit or wiring.
In this article, we’ve explored the essential role that conduit bodies play in electrical systems, offering both functional and safety benefits. Conduit bodies are critical for providing accessible junction points, simplifying wiring layouts, protecting electrical connections, and ensuring smooth transitions in conduit systems. Whether you’re working with an LB, LR, or LL type, each conduit body is designed to meet specific needs while adhering to safety codes like NEC and CSA standards.
Understanding the types of conduit bodies, their applications, and the importance of code compliance ensures that your installations are both efficient and safe. Regular maintenance and correct installation will keep your electrical systems functioning smoothly and compliant with industry regulations.
If you’re ready to enhance your electrical systems with high-quality conduit bodies, contact us today or explore our wide selection of conduit bodies and fittings that meet the highest industry standards. Let us help you create safe, reliable, and efficient electrical systems with the right conduit solutions!




