Table des matières

Partagez cette image sur votre site
Aperçu
All information is explained based on UL 651 Eighth Edition, published on Oct 25, 2011, and all interpretation rights belong to UL.
Champ d'application
Conduits et raccords en PVC rigide extrudé de type EB et A, annexes 40 et 80. UL651 s'applique aux raccords associés, y compris les coudes, les raccords, les adaptateurs, les joints de dilatation, de déflexion et de déflexion et les raccords de tuyauterie rigides pour la construction. Cependant, le matériau UPVC doit répondre aux exigences pertinentes de la norme ASTM 1784.
Les normes pertinentes de l'UL 651 couvrent les normes pertinentes du NEC (National Electrical Code) et de la NFPA 70. Les conduits et raccords en PVC rigide Schedule 40 et 80 peuvent être utilisés pour la finition intérieure et extérieure ou pour une utilisation en extérieur. Ils doivent être protégés du soleil et des intempéries et peuvent être utilisés directement dans le béton.
Conduits et raccords en PVC rigide de série 40 et 80 peut être utilisé à 50°C (122°F) à 75°C (167°F)
Fonctionne bien et peut être utilisé pour les besoins de câblage à 90°C (194°F).
Dimensions Détails
Pour les matériaux recyclés propres ou les matériaux mélangés, les fabricants doivent s'assurer que les normes pertinentes sont respectées, telles que les normes UL746D et UL.
Ici, nous voulons exprimer notre point de vue. Même si, dans un souci de protection de l’environnement, l’utilisation de matériaux recyclés ou la production mixte peuvent réduire le gaspillage de matières premières, l’inconvénient est que cela entraîne une diminution des performances.
Il y aura alors une situation dans laquelle de nombreux produits sur le marché prétendront être certifiés par les normes UL pertinentes. En effet, ils disposent également de certificats de conformité. Mais en termes de performances, il y a bel et bien une baisse, comme la résistance à l'étirement.
Les conduits et raccords en PVC rigide Schedule 40 et 80 résistent aux influences corrosives courantes, notamment les vapeurs et brouillards d'acides alcalins, fluorhydriques et chromiques, ainsi que le décapage et la galvanoplastie, et répondent aux besoins des utilisateurs dans ces scénarios industriels.
Les conduits en PVC rigide Schedule 40 et 80 et les parois intérieures des raccords doivent être lisses et il ne devrait y avoir aucun risque de bavures endommageant les fils. De plus, il ne doit y avoir aucun éclat, cloque, fissure, écaillage, écaillage, farinage ou autre défaut sur la surface extérieure du tube.
Le corps du tuyau doit garder l'ordonnée verticale et ne comporter aucun filetage. Utilisez un micromètre ou une jauge à manchon conique pour mesurer, l'échelle doit être précise à 0,001 pouce ou 0,01 mm et l'écart de précision de la mesure ne doit pas dépasser ± 1%. Les dimensions mesurées doivent être conformes aux dimensions spécifiées pertinentes. Les données pertinentes incluent déjà la plage de tolérance. Les dimensions à respecter comprennent l’épaisseur extérieure, intérieure et de paroi. De plus, comme pour les accouplements, vous devez mesurer la longueur, la profondeur de la douille, etc.
Les exigences de taille pour les conduits en PVC rigide des séries 40 et 80 sont clairement décrites dans le tableau 4.1. D'une manière générale, la plage de tolérance du diamètre extérieur est de ±0,004 à ±0,011 pouce, tandis que le diamètre intérieur et l'épaisseur de paroi sont des valeurs minimales spécifiées pour garantir que les paramètres requis sont atteints.
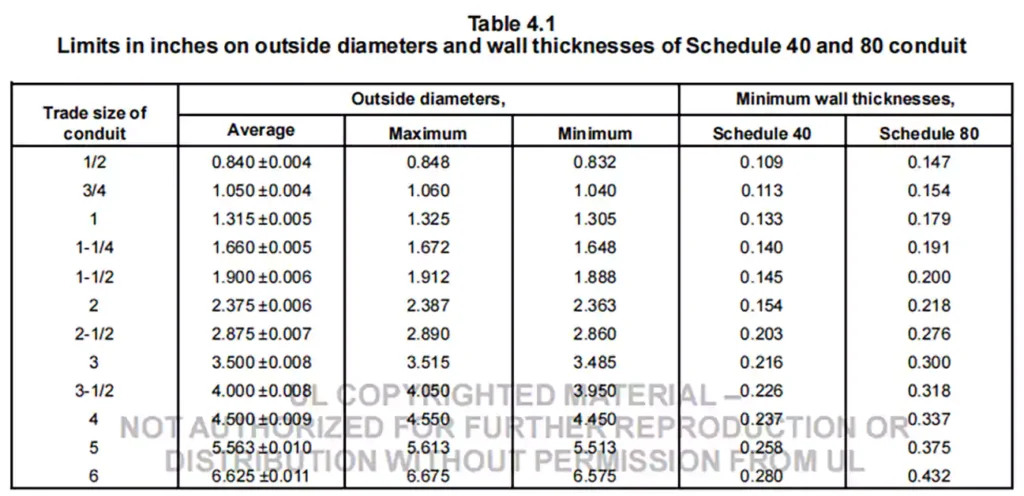
Pour les types A et EB, la méthode de base est similaire. La différence est que dans cette version, concernant le diamètre extérieur et l'épaisseur de paroi du type EB, la description officielle est que « des exigences supplémentaires seront ajoutées à mesure que ces tailles seront jugées acceptables ».
Pour les exigences de qualité des accessoires, UL651 a également certaines réglementations, comme une paroi intérieure lisse sans bavures, qui ne peut pas affecter le mouvement des fils. Il ne permet pas les débris, les cloques, les fissures, le pelage, la mise à l'échelle, la pulvérisation ou d'autres défauts.
UL 651 spécifie également les valeurs maximales et minimales de longueur, d'épaisseur de paroi, de diamètre de douille et d'autres paramètres pour tous les accessoires adaptés aux conduits rigides. Par exemple, pour les raccords pour conduits de type EB et A, dans des conditions de taille commerciale de 1/2 à 6 pouces, la tolérance moyenne du diamètre intérieur à l'extrémité intérieure de la douille est de ±0,008 à ±0,014 pouce, tandis que la tolérance moyenne du diamètre intérieur à l'extrémité intérieure de la douille est de ±0,008 à ±0,014 pouce, La tolérance du diamètre intérieur à l'entrée de la douille est de ±0,015 à ±0,023 pouce, et les exigences de taille sont spécifiées dans le tableau correspondant.
Il en existe également des spéciaux, que nous énumérerons brièvement ici. Par exemple, dans un adaptateur fileté adapté aux fils et tubes filetés en PVC, le filetage doit être clair et propre, et la taille doit répondre aux exigences de l'ASME B1.20.1-1983. Dans le même temps, le port fileté doit avoir suffisamment de champ et répondre au test de flexion.
Parce qu’il y a trop d’accessoires, nous ne les listerons pas ici.
Performances et tests
Il existe jusqu'à 19 tests de performances dans la norme UL651, qui constitue le test ultime pour les performances des produits. Nous sélectionnons les éléments suivants pour quelques explications,
- Résistance à la traction
- Extrusion
- Absorption de l'eau
- Résistance aux chocs
- Résistance à l'écrasement
- Flamme
- Résistance à la lumière du soleil
- Schedule 40 and 80 for use with 90°C wire
- Permanence de l'impression
Résistance à la traction
The primary goal of this test is to determine the tensile strength of both aged and unaged specimens of rigid PVC conduit. The aged specimens must retain at least 95% of the tensile strength of their unaged counterparts to meet compliance requirements.
Specimen Preparation
- Six specimens are cut from finished conduit, with specific dimensions based on the conduit type.
- Measurements, including wall thickness and diameter, are taken using precision micrometer calipers with a minimum accuracy of 0.0001 inches (0.001 mm).
- The conduit must be clean and at a controlled temperature of 23.0 ±2.0°C (73.4 ±3.6°F) before testing.
Test Procedure
- Aging Process: Three specimens are subjected to 168 hours in a circulating-air oven at 113.0 ±1.0°C (235.4 ±1.8°F), then cooled in still air.
- Tensile Testing:
- The six specimens (three aged and three unaged) are tested within 16 to 96 hours after aging.
- A metal plug is inserted to prevent crushing during testing.
- Each specimen is subjected to tensile force on a power-driven machine, with grips separating at a controlled rate of 1/2 ±1/8 inch (10.0 ±2.5 mm) per minute.
- The maximum load before failure is recorded.
Results & Evaluation
- Tensile strength is calculated by dividing the maximum load by the cross-sectional area.
- The average tensile strength of aged and unaged specimens is compared to ensure compliance with UL651 requirements:
Schedule 40 & 80: Minimum 5,000 psi (34.5 MN/m²).
Type A & EB: Minimum 4,000 psi (27.6 MN/m²).
- The aged specimens must maintain at least 95% of the unaged specimens’ tensile strength.
Extrusion
Simulate extruding PVC pipes using anhydrous acetone to observe and test for incomplete fusion. In general, whether there is a large area of peeling, cracking, and other problems after soaking, test whether the product meets the standard requirements. It is a great test for PVC catheters’ raw material quality and production process.
Absorption de l'eau
La norme UL651 exige qu'une fois le produit fini Conduit en PVC est trempé dans de l'eau distillée pendant 24 heures, le taux d'absorption d'eau ne doit pas dépasser 0,50% de son poids. C'est très facile à comprendre. Si nous enterrons des tuyaux en PVC dans le sol, ils seront inévitablement affectés par l'humidité du sol. Si le conduit en PVC absorbe trop d'eau et gonfle, cela provoquera le gonflement et la déformation de la jonction du conduit, ce qui entraînera une mauvaise étanchéité et le résultat est que les fils ne sont pas protégés comme ils devraient l'être.
Résistance aux chocs
The Resistance to Impact Test outlined in UL 651 evaluates the ability of rigid PVC conduit to withstand physical impact without cracking or tearing beyond an acceptable limit. This test is crucial in assessing the durability and mechanical strength of conduit under real-world conditions, ensuring that it remains intact and functional even when subjected to sudden force or impact.
Specimen
- Ten 6-inch (150 mm) specimens are cut from finished lengths of each trade size of rigid PVC conduit.
- The specimens must be free from cracks, tears, or other imperfections before testing.
Conditionnement
- The specimens are conditioned in air at a temperature of 23.0 ±2.0°C (73.4 ±3.6°F) for at least 4 hours to ensure uniform testing conditions.
Impact Setup
- Each specimen is placed on a solid, flat, steel plate that is at least 1/2 inch (13 mm) thick and firmly anchored in a horizontal position.
Impact Mechanism
- UN steel weight, shaped as a solid, right-circular cylinder with a flat impact face and rounded edges, is dropped onto the specimen from a specified height.
- The impact conditions depend on the conduit type:
Schedule 40, Type A, and Type EB:
Poids: 20 livres (9,1 kg)
Cylinder diameter: 2 inches (51 mm)
Schedule 80:
Poids: 75 lbs (34 kg)
Cylinder diameter: 6 inches (150 mm)
- Le flat face of the weight strikes the center of the specimen across the diameter and along the longitudinal axis, ensuring a standardized impact force.
- A mechanism is in place to ensure the weight only strikes once per test.
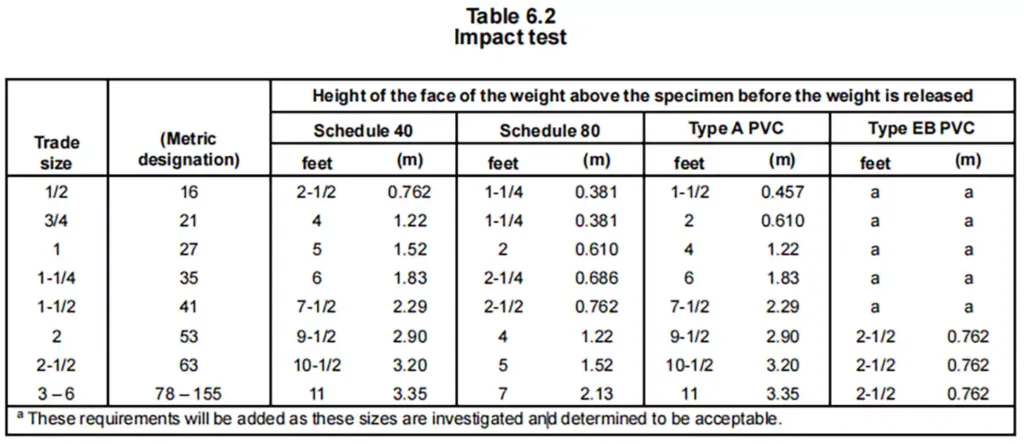
Pass/Fail Criteria
- The rigid PVC conduit fails the test if more than three out of ten specimens develop a crack or tear longer than 1/32 inch (0.8 mm) along the outer surface.
- If seven or more specimens remain intact or develop cracks/tears within the allowable limit, the conduit passes the test.
Résistance à l'écrasement
The Resistance to Crushing Test evaluates the ability of rigid PVC conduit to withstand external pressure without significant deformation or structural failure. This test ensures that the conduit maintains its integrity under compressive forces, which is essential for its performance in underground, encased, or exposed installations where it may be subjected to heavy loads.
By simulating real-world conditions, the test verifies that the conduit does not buckle or excessively deform under specified loads. A key criterion for passing the test is that the minor axis of the inner diameter must not be reduced to less than 70% of its original measurement before loading.
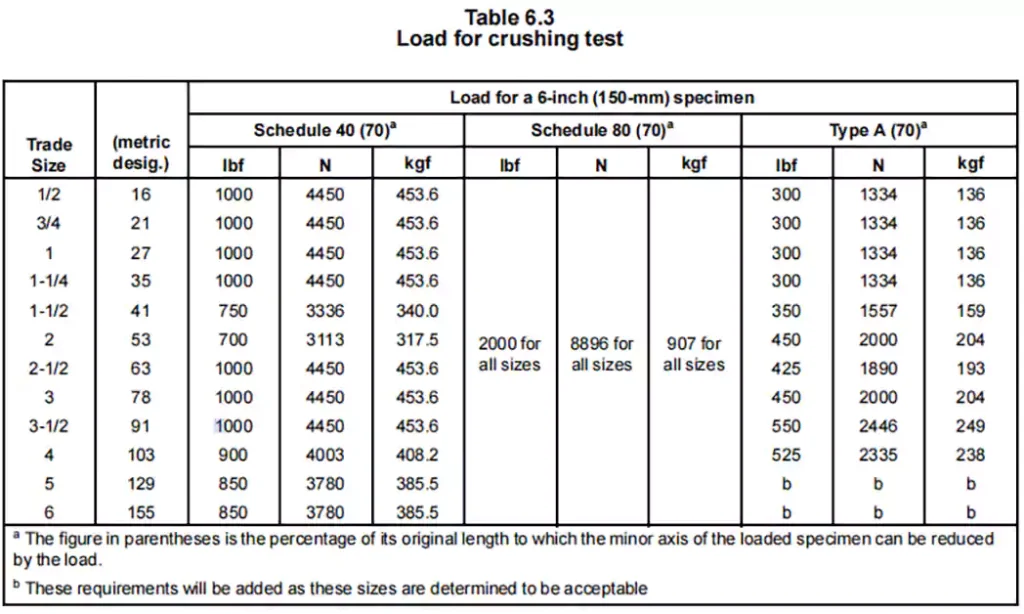
Ce test est différent du test de résistance aux chocs car le conduit PVC est encastré dans le sol ou dans le mur et est sous pression pendant une longue période. Ce test expérimente la capacité de compression du conduit en PVC sous l'action de la pression, qui l'affecte également. Facteurs de longévité.
Flamme
The Flame Test in UL 651 evaluates the fire resistance of Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 rigid PVC conduit to ensure it does not sustain or spread flames in the event of a fire. This test is designed to confirm that the conduit self-extinguishes quickly and does not contribute to igniting nearby combustible materials.
During the test, the conduit is exposed to a 60-second flame application, repeated three times, with a 30-second interval between each exposure. The conduit must cease flaming within 5 seconds after each flame application and must not release flaming particles that could ignite surrounding materials. If the conduit fails to meet these criteria, it is considered unsuitable for applications where fire safety is a concern.
Ce test simule si les conduits en PVC des programmes 40 et 80 peuvent fournir une protection maximale lorsqu'ils sont menacés par un incendie. Si le conduit a un excellent retardateur de flamme, il peut garantir que les fils du conduit sont intacts lorsque la flamme nue est éteinte afin de ne pas provoquer un accident plus grave.
Résistance à la lumière du soleil
The Sunlight Resistance Test in UL 651 evaluates the ability of Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 rigid PVC conduit to withstand prolonged exposure to UV radiation without significant degradation. Since outdoor electrical installations often expose conduits to direct sunlight, this test ensures that the material maintains its mechanical integrity and impact resistance over time.
The test involves Izod impact strength measurements on notched specimens prepared from both unaged and UV-conditioned conduit samples. These samples are exposed to UV radiation for up to 1440 hours, after which their impact strength is tested according to ASTM D 256 standards. To pass the test, the conduit must retain an acceptable level of impact resistance as specified in UL 651.
This testing process ensures that rigid PVC conduits remain durable and reliable in outdoor applications, providing long-term performance and protection against environmental factors such as UV exposure and weathering.
Conduit for Use with 90°C Wire

Among UL651 requirements, one key specification is the ability to support 90°C-rated wire, which indicates the maximum operating temperature of the conductors inside the conduit.
What Does 90°C Wire Mean and Why It Matters?
The 90°C rating refers to the maximum temperature the wire’s insulation can withstand without degrading over time. UL 651-certified PVC conduit is typically rated for 75°C conductors, but many electrical specifications now demand 90°C-rated conduit to accommodate higher-temperature wiring without requiring system derating. This higher temperature tolerance ensures that the electrical system operates at full efficiency while maintaining safety and reliability.
To achieve a 90°C rating, PVC conduit must pass additional long-term testing beyond the standard requirements for 75°C conduit. The testing process outlined in UL 651 extends over 360 days, exposing the conduit to various environmental stresses, including prolonged high temperatures, to evaluate its resistance to thermal degradation, mechanical integrity, and overall performance.
Testing Requirements
The test involves accelerated aging by placing conduit specimens in a circulating-air oven at 80°C (176°F) for up to 360 days. At specific intervals, impact tests are conducted using a steel cylinder drop method to determine impact strength retention over time. A smooth degradation curve is plotted, and the conduit must maintain at least 50% of its initial impact strength after prolonged exposure.
This rigorous evaluation ensures that Schedule 40 and 80 PVC conduits remain reliable and structurally sound when used with high-temperature wiring, providing long-term safety and performance in demanding electrical applications.
How to Tell If the PVC Conduit is Listed to the 90°C Requirements?
Compliant 90°C-rated conduit must also include permanent markings that explicitly state “maximum 90°C wire” or “max 90°C wire”. Listing agencies such as UL, ETL require these markings to confirm the conduit meets the standard.
If a conduit does not have this mandatory marking, it is not compliant with the 90°C specification, regardless of manufacturer claims. Using non-compliant conduits in systems designed for 90°C conductors can lead to serious consequences, including failed inspections, system rejection, costly replacements, and legal liabilities.
Permanence de l'impression
Ce test nécessite que l'échantillon soit soumis à un test de vieillissement 168 heures à l'avance, trempé dans l'eau du robinet pendant 24 heures, puis frotté avec de l'huile IRM902 pour démarrer le test. Le test utilisera un simple dispositif automatique pour permettre à la bande d'entrer en contact avec la partie imprimée du cathéter à un cycle fixe, avec un mouvement de va-et-vient pour chaque cycle, pour un total de 50 cycles.
Après les tests ci-dessus, les caractères imprimés doivent être clairement visibles pour les produits qualifiés.
Étant donné que la plupart des fabricants gravent désormais au laser, ce test n’est pas trop sévère. Son objectif est principalement de conserver l’impression du cathéter, qui permet de retracer le fabricant, la date de production, etc.
Marquages

L’impression habituelle de tubes rigides en PVC doit inclure les éléments suivants :
1) Avec la mention « Conduit rigide en PVC » ;
2) Taille du commerce
3) Le nom du fabricant ou du propriétaire de la marque
4) Date de fabrication
5) Les informations ci-dessus doivent être imprimées au moins une fois tous les 10 pieds.
6) Comme indiqué dans le chapitre ci-dessus, l'impression est permanente
De plus, il existe des exigences détaillées pour les conduits en PVC des annexes 40 et 80. Par exemple, l'impression doit être mise à jour vers les conduits en PVC rigide Schedule 40 ou Schedule 80 pour ces deux conduits.
Certains sont adaptés aux fils à 90 °C (194 °F), il faut alors marquer le « fil à 90 °C maximum » sur l'impression. Il existe également des exigences particulières. Par exemple, si Conduit rigide de l'annexe 40 est uniquement adapté à une utilisation souterraine, alors « Utilisation souterraine uniquement » doit être imprimé.
Quant à l'impression des produits accessoires, la plupart d'entre eux étant réalisés par technologie de moulage par injection, elle ne doit être réalisée que lors de la conception du moule et doit répondre aux exigences permanentes. Le contenu imprimé est généralement le nom du fabricant ou de la marque et le modèle du produit. Semblable au conduit en PVC rigide Schedule 40 ou Schedule 80, s'il ne peut être utilisé que dans des scénarios limités, il doit être noté, comme enfoui dans le sol, ou s'il ne convient qu'aux fils à 90 °C.
Conduit Applications and Installation - NEC Article 352
NEC (National Electrical Code) has outlined the installation and usage requirements of PVC conduit, to ensure compliance with electrical safety standards. Article 352 of NEC specifies the key applications, limitations, and installation requirements, follow are some key information:
Applications for PVC Conduit:
Applications for PVC Conduit:
Uses Permitted | Uses Not Permitted |
Concealed installations within walls, floors, or ceilings | In hazardous (classified) locations unless specifically permitted |
Wet and dry locations | As a means of support for luminaries (light fixtures) |
Corrosive environments where metal conduits could deteriorate | Where subject to severe physical damage |
Underground installations, including direct burial | In areas where temperatures exceed 50°C (122°F) |
Exposed applications, provided the conduit is rated for sunlight resistance | Where it may be used as a grounding conductor |
Some Installation Considerations:
Conduit Fill: The number of conductors must comply with NEC Chapter 9.
Conduit Fill Size Chart for PVC Conduit
Nombre de conducteurs | Cross-Sectional Area (%) |
1 | 53 |
2 | 31 |
Plus de 2 | 40 |
Support Requirements: Must be secured within 3 feet (900mm) of terminations and supported per NEC Table 352.30.
Expansion Fittings: Required when thermal expansions is expected to exceed 1/4 inch (6mm).
Mise à la terre : PVC conduit does not provide an equipment grounding path; a separate grounding conductor is required.
Composition du matériau : Must be made from non-plasticized PVC, resistant to moisture, chemicals, impact, and fire, and UV-resistant for above ground use.
Your Reliable Electrical Solution – Ledes

Ledes is a trusted manufacturer in high-quality electrical conduit solutions, committed to delivering safe, durable, and high-performance products that meet industry standards. Our extensive range of UL-listed PVC conduits and fittings ensures compliance with the UL standard, offering superior reliability for a variety of electrical applications.
Ledes provides UL-listed PVC conduits and fittings that for use with the conduits, including:
- Conduit en PVC de catégorie 40 – A versatile, lightweight option suitable for general-purpose electrical installations, both aboveground and underground.
- Conduit en PVC de la série 80 – Features a thicker wall for enhanced impact resistance, ideal for high-traffic or demanding environments.
- Elbows – Available in 45°, 90°, and other custom angles of standard elbows and special radius elbows, these elbows allow smooth directional changes in conduit runs without compromising wiring integrity.
- Accouplements – Essential for joining conduit sections, ensuring a seamless and secure connection for continuous wiring runs.
- Adaptateurs – Including Male Terminal Adapters and Female Adapters, enabling smooth transitions between different conduit types, boxes, or enclosures.
- Pipe Straps – Strong and reliable conduit supports that securely fasten Schedule 40 and 80 conduits to walls, ceilings, or other structures.
- Gang Boxes – Designed for secure mounting of electrical devices and wiring connections.
- Conduit Bodies – Ideal for providing pull points, splicing spaces, and directional changes, available in multiple styles such as Type LB, LL, LR, T, and C to suit different installation needs.
Trusted by Major Infrastructure Projects
Champlain Hudson Power Express (CHPE) Project

The Champlain Hudson Power Express (CHPE) is a landmark high-voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission project, spanning 339 miles from Quebec, Canada, to New York City. This project is critical for:
- Delivering clean, renewable hydroelectric power to New York.
- Reducing carbon emissions and enhancing grid reliability.
- Creating thousands of jobs and modernizing the region’s energy infrastructure.
For this massive underground and underwater transmission line, Ledes’ UL-listed PVC conduits and fittings were selected due to their superior durability, corrosion resistance, and electrical safety. Our Schedule 40 and 80 PVC conduits provide secure cable protection over long distances, ensuring efficient energy transmission while withstanding underground conditions.
A.B. Brown Power Station Project

The A.B. Brown Generating Station is a 700-megawatt (MW) power plant located along the Ohio River in Indiana, just southwest of Evansville. This facility, owned by CenterPoint Energy (formerly Vectren), consists of:
- Two coal-fired units, each with a 265.2 MW nameplate capacity, primarily using bituminous coal with the capability to substitute natural gas.
- Two gas turbine units, each providing 88.2 MW of capacity for additional power generation.
As part of CenterPoint Energy’s modernization plan, there are ongoing infrastructure improvements and grid enhancements to support future energy needs. The company previously announced plans to retire the coal-fired units and transition to natural gas-powered generation, pending approval from the Indiana Utility Regulatory Commission.
To ensure a secure and reliable electrical system, Ledes’ UL-listed PVC conduits and fittings were selected for various electrical installations and upgrades within the A.B. Brown facility.
Pourquoi choisir Ledes ?
Homologué UL – Ensuring compliance with safety and performance standards.
Durable & Corrosion-Resistant – Made from high-quality PVC for long-lasting performance in harsh environments.
Installation facile – Lightweight and designed for quick assembly.
Versatile Applications – Suitable for residential, commercial, and industrial electrical installations.
Ledes is proud to be a supplier for critical infrastructure projects that shape the future of energy. Our innovative, high-performance conduit solutions ensure safe and efficient electrical installations in the most demanding environments.
UL vs. CSA Standard PVC Conduits

UL (Underwriters Laboratories) and CSA (Canadian Standards Association) are two leading organizations establishing safety and performance benchmarks for electrical conduits. Their standards ensure products meet rigorous requirements for durability, fire resistance, and environmental adaptability, with distinct regional and technical emphases.
- UL Standards: Primarily recognized in the United States, UL standards focus on ensuring that electrical products, including PVC conduits, are safe to use within the U.S. infrastructure. The UL standard for PVC conduit (e.g., UL 651) addresses fire safety, impact resistance, temperature ratings, and more.
- CSA Standards: These are focused on ensuring that products are safe for use within Canada. CSA standards often align with international guidelines but may have specific adjustments to reflect local safety and regulatory needs. CSA C22.2 No. 211.2 is the standard for PVC conduit in Canada, outlining similar requirements to UL but tailored for Canadian safety regulations.
Performance Requirements for UL and CSA
Performance Requirements UL651 and CSA C22.2:
Aspects | UL651 | CSA C22.2 No 211.2 |
Température | Use at 50° C(122°F) or lower ambient temperatures; Use with 75° C (or maybe 90° C) wiring. | Use at a continuous operating temperature of 75° C.
|
Résistance aux chocs | Test at 23.0 ±2.0° C, with 20lbs (9.1 kg) weight for Schedule 40. | Test at –34 ± 2 °C, with 12 J impact energy for rigid conduit.
|
Résistance à la traction | 5,000 psi for Schedule 40 conduit | Non spécifié |
Resistant to Crushing | Detail required in section 6.9 | Non spécifié |
Compression | Non spécifié | No cracks and decrease no more than 25% when subjected to certain forces. |
Flamme | 3 times of 60-seconds flame application, no more than 5s flame after each application. No flaming drops. | Not burn than 30 seconds, no flaming or glowing particles. |
Résistance à la lumière du soleil | Same requirements with CSA | Same requirements with UL |
Conformité au code
- Code national de l'électricité (NEC): UL-certified PVC conduits are recognized for compliance with the U.S. National Electrical Code (NEC), which is the standard governing electrical installations across the United States.
- Code canadien de l'électricité (CCE): CSA-certified PVC conduits are recognized for compliance with the Canadian Electrical Code (CEC), ensuring that products meet the specific safety and installation standards for electrical systems in Canada.
Marking and Labeling
- UL Mark: PVC conduit that is UL-listed typically displays the UL mark, which indicates that it meets the specific UL safety standards and is approved for use in the United States.
- CSA Mark: Similarly, PVC conduit that meets CSA standards is marked with the CSA logo, indicating that it is compliant with Canadian requirements.
Both UL and CSA standards are crucial for ensuring that PVC conduits meet the necessary safety, performance, and regulatory requirements in their respective regions. While there are similarities in the testing protocols and requirements, the key difference lies in their geographic applicability and specific regulations. For projects in the United States, UL-listed PVC conduit is the ideal choice, while CSA-certified conduit is essential for Canadian installations.
Conclusion
As we’ve explored throughout this guide, UL 651 PVC conduit plays a crucial role in modern electrical installations by offering a combination of durability, fire resistance, corrosion resistance, and compliance with NEC requirements. Its classification into Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 allows for flexibility in different applications, ensuring that electricians and contractors can choose the right type based on mechanical protection needs and environmental conditions.
Whether you’re working on an underground installation, a commercial building, or an industrial facility, using UL 651-compliant PVC conduit ensures that your electrical system meets safety standards and performs reliably over time. By selecting certified conduit from reputable manufacturers, you can guarantee long-term performance while ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
As the demand for sustainable, cost-effective, and reliable electrical solutions continues to grow, UL 651 PVC conduit remains a key component in safe and efficient wiring infrastructure. Now that you have a thorough understanding of UL 651, you can confidently choose the right conduit for your next project.
Si vous avez des questions ou êtes intéressé par notre série de produits UL, vous pouvez contactez-nous par email ou même What’s app, et nous vous répondrons généralement dans un délai d'un jour ouvrable.



