Table of Contents

Share this Image On Your Site
Overview
All information is explained based on UL 651 Eighth Edition, published on Oct 25, 2011, and all interpretation rights belong to UL.
Scope of Application
Schedule 40 & 80, type EB and A extruded rigid PVC conduit and fittings. UL651 applies to related fittings, including elbows, couplings, adapters, expansion, expansion-deflection, deflection joints, and rigid pipe fittings for construction. However, the UPVC material must meet the relevant requirements of ASTM 1784.
The relevant standards of UL 651 have covered the relevant standards in NEC (National Electrical Code) and NFPA 70. Schedule 40 & 80 rigid PVC conduit and fitting can be used for interior and exterior finishing or outdoor use. They must be protected from sunlight and the effects of inclement weather and can be used directly in concrete.
Schedule 40 & 80 rigid PVC conduit and fitting can be used at 50°C (122°F) to 75°C (167°F)
Works fine and can be used for 90°C (194°F) wiring needs.
Dimensions Details
For clean recycled materials or mixed materials, manufacturers must ensure that relevant standards are met, such as UL746D and UL-related standards.
Here we want to express our views. Although for the sake of environmental protection, using recycled materials or mixed production can reduce the waste of raw materials, the disadvantage is that it leads to a decrease in performance.
Then there will be a situation where many products on the market claim to be certified by relevant UL standards. Indeed, they also have compliance certificates. But in terms of performance, there is indeed a decline, such as stretch resistance.
Schedule 40 & 80 rigid PVC conduit and fitting are resistant to common corrosive influences, including alkali, hydrofluoric, and chromic acid vapors and mist, as well as pickling and electroplating, and meet the needs of users in these industrial scenarios.
Schedule 40 & 80 rigid PVC conduit and fitting inner walls should be smooth, and there should be no risk of burrs causing damage to the wires. Also, there should be no chips, blisters, cracks, spalling, scaling, chalking, or other defects on the outer surface of the tube.
The pipe body must keep the ordinate vertical and have no threads. Use a micrometer or tapered sleeve gauge to measure, the scale needs to be accurate to 0.001 inches or 0.01mm, and the measurement accuracy deviation should not exceed ±1%. The measured dimensions need to conform to the relevant specified dimensions. The relevant data already includes the tolerance range. The dimensions to be met include outer, inner, and wall thickness. In addition, like couplings, you need to measure the length, socket depth, etc.
The size requirements for Schedule 40 & 80 rigid PVC conduit are clearly described in Table 4.1. Generally speaking, the tolerance range of OD is ±0.004 to ±0.011 inch, while ID and wall thickness are specified minimum values to ensure that the required parameters are achieved.
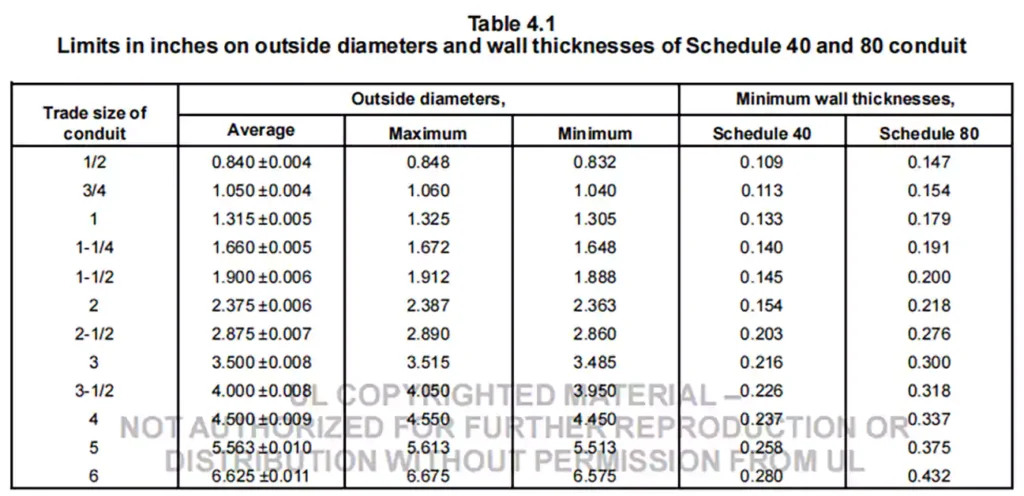
For Type A & EB, the basic method is similar. The difference is that in this version, the OD and wall thickness of Type EB, the official description is that “Additional requirements will be added as these sizes are determined to be acceptable.”
For the quality requirements of accessories, UL651 also has some regulations, such as a smooth inner wall without burrs, which cannot affect the movement of wires. It does not allow debris, blisters, cracks, peeling, scaling, pulverization, or other defects.
UL 651 also specifies the maximum and minimum values of length, wall thickness, Socket diameter, and other parameters for all accessories to match rigid conduit. For example, for Coupling for Type EB and A conduit, under the condition of 1/2 to 6-inch trade size, the average tolerance of Inside diameter at the inner end of the socket is ±0.008 to ±0.014 inch, while the average tolerance of Inside diameter at the entrance to the socket is ±0.015 to ±0.023 inch, and the size requirements are specified in the relevant table.
There are also some special ones, which we will briefly list here. For example, in a threaded adapter suitable for threaded PVC wire and tube, the thread must be clear and clean, and the size needs to meet the requirements of ASME B1.20.1-1983. At the same time, the threaded port should have enough field and meet the bending test.
Because there are too many accessories, we will not list them here.
Performance and Testing
There are as many as 19 performance tests in UL651, which is the ultimate test for product performance. We pick the following items for some explanation,
- Tensile Strength
- Extrusion
- Water Absorption
- Resistance to Impact
- Resistance to Crushing
- Flame
- Sunlight Resistance
- Schedule 40 and 80 for use with 90°C wire
- Permanence of Printing
Tensile Strength
The primary goal of this test is to determine the tensile strength of both aged and unaged specimens of rigid PVC conduit. The aged specimens must retain at least 95% of the tensile strength of their unaged counterparts to meet compliance requirements.
Specimen Preparation
- Six specimens are cut from finished conduit, with specific dimensions based on the conduit type.
- Measurements, including wall thickness and diameter, are taken using precision micrometer calipers with a minimum accuracy of 0.0001 inches (0.001 mm).
- The conduit must be clean and at a controlled temperature of 23.0 ±2.0°C (73.4 ±3.6°F) before testing.
Test Procedure
- Aging Process: Three specimens are subjected to 168 hours in a circulating-air oven at 113.0 ±1.0°C (235.4 ±1.8°F), then cooled in still air.
- Tensile Testing:
- The six specimens (three aged and three unaged) are tested within 16 to 96 hours after aging.
- A metal plug is inserted to prevent crushing during testing.
- Each specimen is subjected to tensile force on a power-driven machine, with grips separating at a controlled rate of 1/2 ±1/8 inch (10.0 ±2.5 mm) per minute.
- The maximum load before failure is recorded.
Results & Evaluation
- Tensile strength is calculated by dividing the maximum load by the cross-sectional area.
- The average tensile strength of aged and unaged specimens is compared to ensure compliance with UL651 requirements:
Schedule 40 & 80: Minimum 5,000 psi (34.5 MN/m²).
Type A & EB: Minimum 4,000 psi (27.6 MN/m²).
- The aged specimens must maintain at least 95% of the unaged specimens’ tensile strength.
Extrusion
Simulate extruding PVC pipes using anhydrous acetone to observe and test for incomplete fusion. In general, whether there is a large area of peeling, cracking, and other problems after soaking, test whether the product meets the standard requirements. It is a great test for PVC catheters’ raw material quality and production process.
Water Absorption
UL651 requires that after the finished PVC conduit is soaked in distilled water for 24 hours, the water absorption rate shall not exceed 0.50% of its weight. It is very easy to understand. If we bury PVC pipes in the ground, they will inevitably be affected by the moisture in the soil. If the PVC conduit absorbs too much water and swells, it will cause the conduit junction to swell and deform, resulting in a poor seal, and the result is that the wires are not protected as they should be.
Resistance to Impact
The Resistance to Impact Test outlined in UL 651 evaluates the ability of rigid PVC conduit to withstand physical impact without cracking or tearing beyond an acceptable limit. This test is crucial in assessing the durability and mechanical strength of conduit under real-world conditions, ensuring that it remains intact and functional even when subjected to sudden force or impact.
Specimen
- Ten 6-inch (150 mm) specimens are cut from finished lengths of each trade size of rigid PVC conduit.
- The specimens must be free from cracks, tears, or other imperfections before testing.
Conditioning
- The specimens are conditioned in air at a temperature of 23.0 ±2.0°C (73.4 ±3.6°F) for at least 4 hours to ensure uniform testing conditions.
Impact Setup
- Each specimen is placed on a solid, flat, steel plate that is at least 1/2 inch (13 mm) thick and firmly anchored in a horizontal position.
Impact Mechanism
- A steel weight, shaped as a solid, right-circular cylinder with a flat impact face and rounded edges, is dropped onto the specimen from a specified height.
- The impact conditions depend on the conduit type:
Schedule 40, Type A, and Type EB:
Weight: 20 lbs (9.1 kg)
Cylinder diameter: 2 inches (51 mm)
Schedule 80:
Weight: 75 lbs (34 kg)
Cylinder diameter: 6 inches (150 mm)
- The flat face of the weight strikes the center of the specimen across the diameter and along the longitudinal axis, ensuring a standardized impact force.
- A mechanism is in place to ensure the weight only strikes once per test.
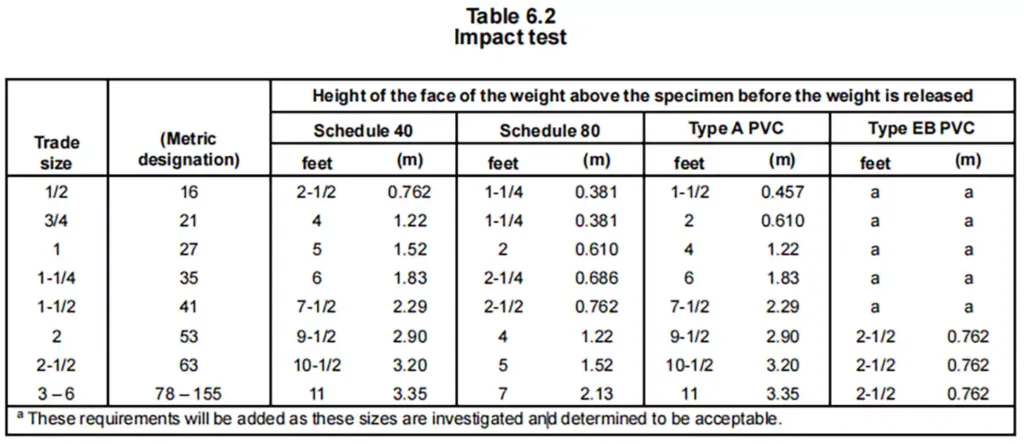
Pass/Fail Criteria
- The rigid PVC conduit fails the test if more than three out of ten specimens develop a crack or tear longer than 1/32 inch (0.8 mm) along the outer surface.
- If seven or more specimens remain intact or develop cracks/tears within the allowable limit, the conduit passes the test.
Resistance to Crushing
The Resistance to Crushing Test evaluates the ability of rigid PVC conduit to withstand external pressure without significant deformation or structural failure. This test ensures that the conduit maintains its integrity under compressive forces, which is essential for its performance in underground, encased, or exposed installations where it may be subjected to heavy loads.
By simulating real-world conditions, the test verifies that the conduit does not buckle or excessively deform under specified loads. A key criterion for passing the test is that the minor axis of the inner diameter must not be reduced to less than 70% of its original measurement before loading.
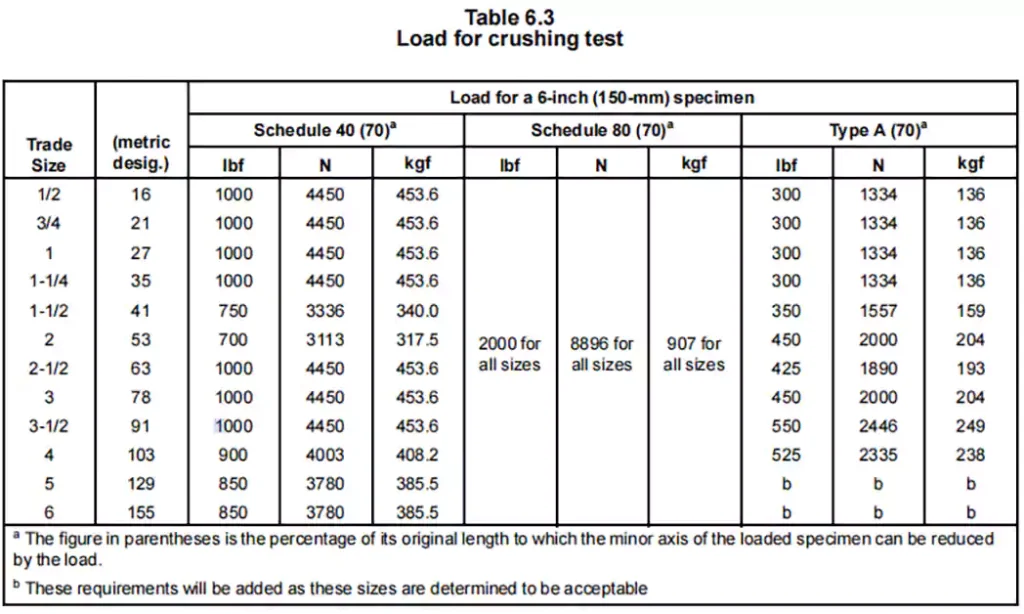
This test is different from the impact resistance test because the PVC conduit is embedded in the ground or the wall and is under pressure for a long time. This test experiments with the compressive capacity of the PVC conduit under the action of pressure, which also affects it. Factors of longevity.
Flame
The Flame Test in UL 651 evaluates the fire resistance of Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 rigid PVC conduit to ensure it does not sustain or spread flames in the event of a fire. This test is designed to confirm that the conduit self-extinguishes quickly and does not contribute to igniting nearby combustible materials.
During the test, the conduit is exposed to a 60-second flame application, repeated three times, with a 30-second interval between each exposure. The conduit must cease flaming within 5 seconds after each flame application and must not release flaming particles that could ignite surrounding materials. If the conduit fails to meet these criteria, it is considered unsuitable for applications where fire safety is a concern.
This test simulates whether the Schedule 40 & 80 PVC conduit can provide maximum protection when threatened by fire. If the conduit has excellent flame retardancy, it can ensure that the wires in the conduit are intact when the open flame is extinguished so as not to cause a more serious accident.
Sunlight Resistance
The Sunlight Resistance Test in UL 651 evaluates the ability of Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 rigid PVC conduit to withstand prolonged exposure to UV radiation without significant degradation. Since outdoor electrical installations often expose conduits to direct sunlight, this test ensures that the material maintains its mechanical integrity and impact resistance over time.
The test involves Izod impact strength measurements on notched specimens prepared from both unaged and UV-conditioned conduit samples. These samples are exposed to UV radiation for up to 1440 hours, after which their impact strength is tested according to ASTM D 256 standards. To pass the test, the conduit must retain an acceptable level of impact resistance as specified in UL 651.
This testing process ensures that rigid PVC conduits remain durable and reliable in outdoor applications, providing long-term performance and protection against environmental factors such as UV exposure and weathering.
Conduit for Use with 90°C Wire

Among UL651 requirements, one key specification is the ability to support 90°C-rated wire, which indicates the maximum operating temperature of the conductors inside the conduit.
What Does 90°C Wire Mean and Why It Matters?
The 90°C rating refers to the maximum temperature the wire’s insulation can withstand without degrading over time. UL 651-certified PVC conduit is typically rated for 75°C conductors, but many electrical specifications now demand 90°C-rated conduit to accommodate higher-temperature wiring without requiring system derating. This higher temperature tolerance ensures that the electrical system operates at full efficiency while maintaining safety and reliability.
To achieve a 90°C rating, PVC conduit must pass additional long-term testing beyond the standard requirements for 75°C conduit. The testing process outlined in UL 651 extends over 360 days, exposing the conduit to various environmental stresses, including prolonged high temperatures, to evaluate its resistance to thermal degradation, mechanical integrity, and overall performance.
Testing Requirements
The test involves accelerated aging by placing conduit specimens in a circulating-air oven at 80°C (176°F) for up to 360 days. At specific intervals, impact tests are conducted using a steel cylinder drop method to determine impact strength retention over time. A smooth degradation curve is plotted, and the conduit must maintain at least 50% of its initial impact strength after prolonged exposure.
This rigorous evaluation ensures that Schedule 40 and 80 PVC conduits remain reliable and structurally sound when used with high-temperature wiring, providing long-term safety and performance in demanding electrical applications.
How to Tell If the PVC Conduit is Listed to the 90°C Requirements?
Compliant 90°C-rated conduit must also include permanent markings that explicitly state “maximum 90°C wire” or “max 90°C wire”. Listing agencies such as UL, ETL require these markings to confirm the conduit meets the standard.
If a conduit does not have this mandatory marking, it is not compliant with the 90°C specification, regardless of manufacturer claims. Using non-compliant conduits in systems designed for 90°C conductors can lead to serious consequences, including failed inspections, system rejection, costly replacements, and legal liabilities.
Permanence of Printing
This test requires the sample to be subjected to an aging test for 168 hours in advance, soaked in tap water for 24 hours, and then rubbed with IRM902 oil to start the test. The test will use a simple automatic device to allow the tape to contact the printed part of the catheter at a fixed cycle, with a back-and-forth motion for each cycle, for a total of 50 cycles.
After the tests above, the printed characters should be clearly visible for qualified products.
Since most manufacturers are now laser engraving, this test is not too harsh. Its purpose is mainly to retain catheter printing, which can trace the manufacturer, production date, etc.
Markings

The usual PVC rigid tube printing needs to include the following:
1) With the words’ Rigid PVC conduit’;
2) Trade size
3) The name of the manufacturer or brand owner
4) Production date
5) The information above needs to be printed at least once every 10ft.
6) As stated in the chapter above, printing is permanent
In addition, there are some detailed requirements for Schedule 40 & 80 PVC conduit. For example, the printing should be updated to Schedule 40 or Schedule 80 Rigid PVC conduit for these two conduits.
Some are suitable for 90°C (194°F) wires, then the “maximum 90°C wire” should be marked on the printing. There are also some special requirements. For example, if Schedule 40 rigid conduit is only suitable for underground use, then “Underground Use Only” should be printed.
As for the printing of accessory products, because most of them are produced by injection molding technology, it only needs to be done during the mold design, and it needs to meet the permanent requirements. The printed content is generally the manufacturer’s or brand’s name and the product model. Similar to Schedule 40 or Schedule 80 Rigid PVC conduit, if it can only be used in limited scenarios, it needs to be noted, such as buried in the ground, or it is only suitable for 90°C wires.
Conduit Applications and Installation - NEC Article 352
NEC (National Electrical Code) has outlined the installation and usage requirements of PVC conduit, to ensure compliance with electrical safety standards. Article 352 of NEC specifies the key applications, limitations, and installation requirements, follow are some key information:
Applications for PVC Conduit:
Applications for PVC Conduit:
Uses Permitted | Uses Not Permitted |
Concealed installations within walls, floors, or ceilings | In hazardous (classified) locations unless specifically permitted |
Wet and dry locations | As a means of support for luminaries (light fixtures) |
Corrosive environments where metal conduits could deteriorate | Where subject to severe physical damage |
Underground installations, including direct burial | In areas where temperatures exceed 50°C (122°F) |
Exposed applications, provided the conduit is rated for sunlight resistance | Where it may be used as a grounding conductor |
Some Installation Considerations:
Conduit Fill: The number of conductors must comply with NEC Chapter 9.
Conduit Fill Size Chart for PVC Conduit
Number of Conductors | Cross-Sectional Area (%) |
1 | 53 |
2 | 31 |
Over 2 | 40 |
Support Requirements: Must be secured within 3 feet (900mm) of terminations and supported per NEC Table 352.30.
Expansion Fittings: Required when thermal expansions is expected to exceed 1/4 inch (6mm).
Grounding: PVC conduit does not provide an equipment grounding path; a separate grounding conductor is required.
Material Composition: Must be made from non-plasticized PVC, resistant to moisture, chemicals, impact, and fire, and UV-resistant for above ground use.
Your Reliable Electrical Solution – Ledes

Ledes is a trusted manufacturer in high-quality electrical conduit solutions, committed to delivering safe, durable, and high-performance products that meet industry standards. Our extensive range of UL-listed PVC conduits and fittings ensures compliance with the UL standard, offering superior reliability for a variety of electrical applications.
Ledes provides UL-listed PVC conduits and fittings that for use with the conduits, including:
- Schedule 40 PVC Conduit – A versatile, lightweight option suitable for general-purpose electrical installations, both aboveground and underground.
- Schedule 80 PVC Conduit – Features a thicker wall for enhanced impact resistance, ideal for high-traffic or demanding environments.
- Elbows – Available in 45°, 90°, and other custom angles of standard elbows and special radius elbows, these elbows allow smooth directional changes in conduit runs without compromising wiring integrity.
- Couplings – Essential for joining conduit sections, ensuring a seamless and secure connection for continuous wiring runs.
- Adapters – Including Male Terminal Adapters and Female Adapters, enabling smooth transitions between different conduit types, boxes, or enclosures.
- Pipe Straps – Strong and reliable conduit supports that securely fasten Schedule 40 and 80 conduits to walls, ceilings, or other structures.
- Gang Boxes – Designed for secure mounting of electrical devices and wiring connections.
- Conduit Bodies – Ideal for providing pull points, splicing spaces, and directional changes, available in multiple styles such as Type LB, LL, LR, T, and C to suit different installation needs.
Trusted by Major Infrastructure Projects
Champlain Hudson Power Express (CHPE) Project

The Champlain Hudson Power Express (CHPE) is a landmark high-voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission project, spanning 339 miles from Quebec, Canada, to New York City. This project is critical for:
- Delivering clean, renewable hydroelectric power to New York.
- Reducing carbon emissions and enhancing grid reliability.
- Creating thousands of jobs and modernizing the region’s energy infrastructure.
For this massive underground and underwater transmission line, Ledes’ UL-listed PVC conduits and fittings were selected due to their superior durability, corrosion resistance, and electrical safety. Our Schedule 40 and 80 PVC conduits provide secure cable protection over long distances, ensuring efficient energy transmission while withstanding underground conditions.
A.B. Brown Power Station Project

The A.B. Brown Generating Station is a 700-megawatt (MW) power plant located along the Ohio River in Indiana, just southwest of Evansville. This facility, owned by CenterPoint Energy (formerly Vectren), consists of:
- Two coal-fired units, each with a 265.2 MW nameplate capacity, primarily using bituminous coal with the capability to substitute natural gas.
- Two gas turbine units, each providing 88.2 MW of capacity for additional power generation.
As part of CenterPoint Energy’s modernization plan, there are ongoing infrastructure improvements and grid enhancements to support future energy needs. The company previously announced plans to retire the coal-fired units and transition to natural gas-powered generation, pending approval from the Indiana Utility Regulatory Commission.
To ensure a secure and reliable electrical system, Ledes’ UL-listed PVC conduits and fittings were selected for various electrical installations and upgrades within the A.B. Brown facility.
Why Choose Ledes?
UL Listed – Ensuring compliance with safety and performance standards.
Durable & Corrosion-Resistant – Made from high-quality PVC for long-lasting performance in harsh environments.
Easy Installation – Lightweight and designed for quick assembly.
Versatile Applications – Suitable for residential, commercial, and industrial electrical installations.
Ledes is proud to be a supplier for critical infrastructure projects that shape the future of energy. Our innovative, high-performance conduit solutions ensure safe and efficient electrical installations in the most demanding environments.
UL vs. CSA Standard PVC Conduits

UL (Underwriters Laboratories) and CSA (Canadian Standards Association) are two leading organizations establishing safety and performance benchmarks for electrical conduits. Their standards ensure products meet rigorous requirements for durability, fire resistance, and environmental adaptability, with distinct regional and technical emphases.
- UL Standards: Primarily recognized in the United States, UL standards focus on ensuring that electrical products, including PVC conduits, are safe to use within the U.S. infrastructure. The UL standard for PVC conduit (e.g., UL 651) addresses fire safety, impact resistance, temperature ratings, and more.
- CSA Standards: These are focused on ensuring that products are safe for use within Canada. CSA standards often align with international guidelines but may have specific adjustments to reflect local safety and regulatory needs. CSA C22.2 No. 211.2 is the standard for PVC conduit in Canada, outlining similar requirements to UL but tailored for Canadian safety regulations.
Performance Requirements for UL and CSA
Performance Requirements UL651 and CSA C22.2:
Aspects | UL651 | CSA C22.2 No.211.2 |
Temperature | Use at 50° C(122°F) or lower ambient temperatures; Use with 75° C (or maybe 90° C) wiring. | Use at a continuous operating temperature of 75° C.
|
Impact Resistance | Test at 23.0 ±2.0° C, with 20lbs (9.1 kg) weight for Schedule 40. | Test at –34 ± 2 °C, with 12 J impact energy for rigid conduit.
|
Tensile Strength | 5,000 psi for Schedule 40 conduit | Not specified |
Resistant to Crushing | Detail required in section 6.9 | Not specified |
Compression | Not specified | No cracks and decrease no more than 25% when subjected to certain forces. |
Flame | 3 times of 60-seconds flame application, no more than 5s flame after each application. No flaming drops. | Not burn than 30 seconds, no flaming or glowing particles. |
Sunlight Resistance | Same requirements with CSA | Same requirements with UL |
Code Compliance
- National Electrical Code (NEC): UL-certified PVC conduits are recognized for compliance with the U.S. National Electrical Code (NEC), which is the standard governing electrical installations across the United States.
- Canadian Electrical Code (CEC): CSA-certified PVC conduits are recognized for compliance with the Canadian Electrical Code (CEC), ensuring that products meet the specific safety and installation standards for electrical systems in Canada.
Marking and Labeling
- UL Mark: PVC conduit that is UL-listed typically displays the UL mark, which indicates that it meets the specific UL safety standards and is approved for use in the United States.
- CSA Mark: Similarly, PVC conduit that meets CSA standards is marked with the CSA logo, indicating that it is compliant with Canadian requirements.
Both UL and CSA standards are crucial for ensuring that PVC conduits meet the necessary safety, performance, and regulatory requirements in their respective regions. While there are similarities in the testing protocols and requirements, the key difference lies in their geographic applicability and specific regulations. For projects in the United States, UL-listed PVC conduit is the ideal choice, while CSA-certified conduit is essential for Canadian installations.
Conclusion
As we’ve explored throughout this guide, UL 651 PVC conduit plays a crucial role in modern electrical installations by offering a combination of durability, fire resistance, corrosion resistance, and compliance with NEC requirements. Its classification into Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 allows for flexibility in different applications, ensuring that electricians and contractors can choose the right type based on mechanical protection needs and environmental conditions.
Whether you’re working on an underground installation, a commercial building, or an industrial facility, using UL 651-compliant PVC conduit ensures that your electrical system meets safety standards and performs reliably over time. By selecting certified conduit from reputable manufacturers, you can guarantee long-term performance while ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
As the demand for sustainable, cost-effective, and reliable electrical solutions continues to grow, UL 651 PVC conduit remains a key component in safe and efficient wiring infrastructure. Now that you have a thorough understanding of UL 651, you can confidently choose the right conduit for your next project.
If you have any questions or are interested in our UL product series, you can contact us by email or even What’s app, and we will generally reply to you within 1 business day.



