Tabla de contenido
PVC conduit is a vital component in electrical installations, offering protection and organization for electrical wiring systems. Understanding the properties, types, installation methods, and applications of PVC conduit is essential for ensuring safe and efficient electrical setups in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
After reading this article, will know:
- What is PVC Conduit and Conduit Types
- Where Can PVC Conduit be Used
- Installation Methods and Steps of PVC Conduit
- How to Properly Cut and Join PVC Conduit
- Is PVC Conduit Suitable for High Voltage Applications
- Can PVC Conduit Be Bent and the Bending Methods
- What is the Difference Between PVC and UPVC Conduits
- PVC Conduits Vs Metallic Conduits
- What’s the difference between PVC pipe and PVC conduit
- PVC Conduit vs Liquid-tight Conduit
- How to Choose the Right PVC Conduit for Your Project
What is PVC Conduit?

PVC conduit, short for polyvinyl chloride conduit, is a type of piping system specifically designed for electrical wiring installations. Made from a durable form of plastic, PVC conduits offer protection for electrical cables against physical damage and environmental elements.
PVC is a non-metallic material that is both lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for both indoor and outdoor installations. It does not conduct electricity, providing an added layer of insulation to protect the wires inside from electrical hazards. Additionally, PVC is flexible enough to be used in a variety of situations where traditional metal conduits may be impractical or too heavy.
PVC conduits come in various sizes, thicknesses, and types, allowing them to be customized for specific projects, whether for residential, commercial, or industrial applications. They are particularly favored in locations with high moisture levels, such as basements, outdoor landscapes, or underground installations.
5 Types of PVC Conduit You Should Know About
There are many conduit types on the market, here are 5 conduit types from Ledes and they are the most commonly used conduit types you should know:
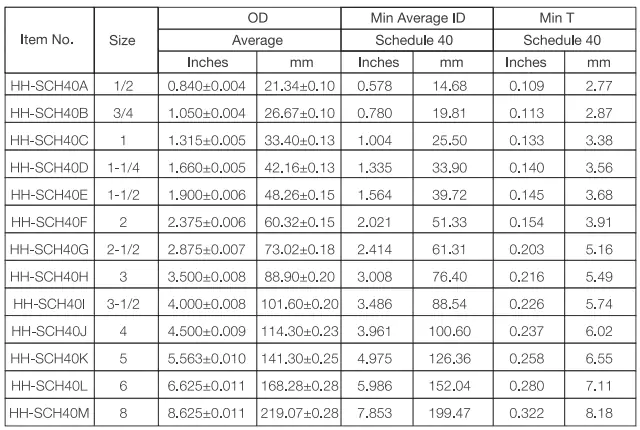
1. UL Standard PVC Conduit and Tubing
UL standard PVC conduit, Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 rigid PVC conduit, and Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing ENT, three main types.
Standards: UL651, NEMA TC-2, ASTM D1784-20
Ventajas: Corrosion resistant, impact resistant, sunlight resistant, fire resistant, easy of installation.
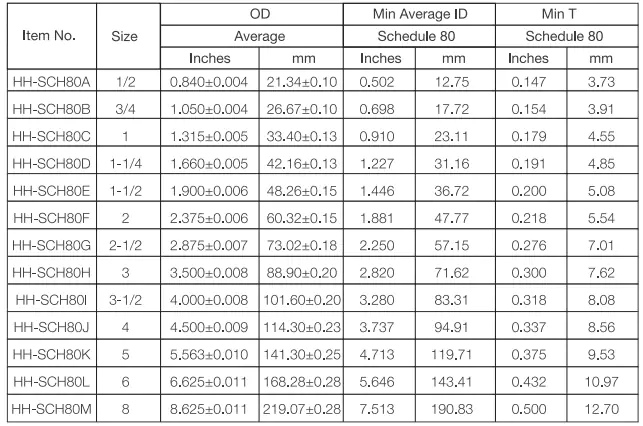
Standards: UL651, NEMA TC-2, ASTM D1784-20
Ventajas: Corrosion resistant, impact resistant, fire resistant, high physical strength, underground use.
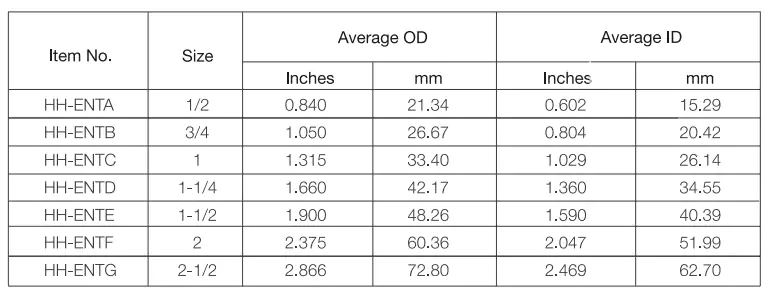
Standards: UL1653
Ventajas: Corrosion resistant, impact resistant, sunlight resistant, fire resistant, deflection resistant, lightweight, easy of installation.
2. CSA Standard PVC Conduit and Tubing
In Canada, there are also there widely used conduit types, here are the product information and data from Ledes.
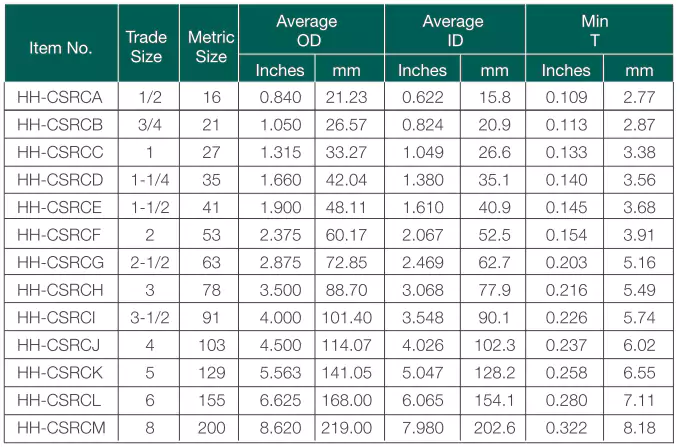
Standards: Norma CSA C22.2 N.º 211.2
Ventajas: Corrosion resistant, impact resistant, sunlight resistant, fire resistant, easy of installation.
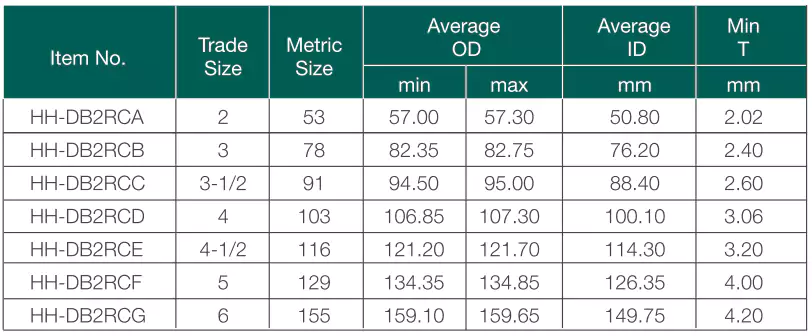
Standards: CSA C22.2 No.211.1
Ventajas: Corrosion resistant, impact resistant, sunlight resistant, fire resistant, concrete tight, lightweight, direct burial.
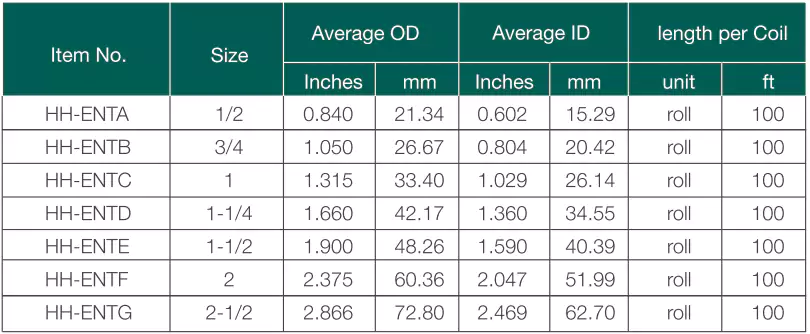
Standards: CSA C22.2 No.211.1
Ventajas: Corrosion resistant, impact resistant, sunlight resistant, fire resistant, deflection resistant, lightweight, easy of installation.
3. AS/NZS Standard PVC Conduit
For Australian and New Zealand market, Ledes has medium duty and heavy duty rigid PVC conduit, medium duty and heavy duty corrugated conduit for different needs and applications.
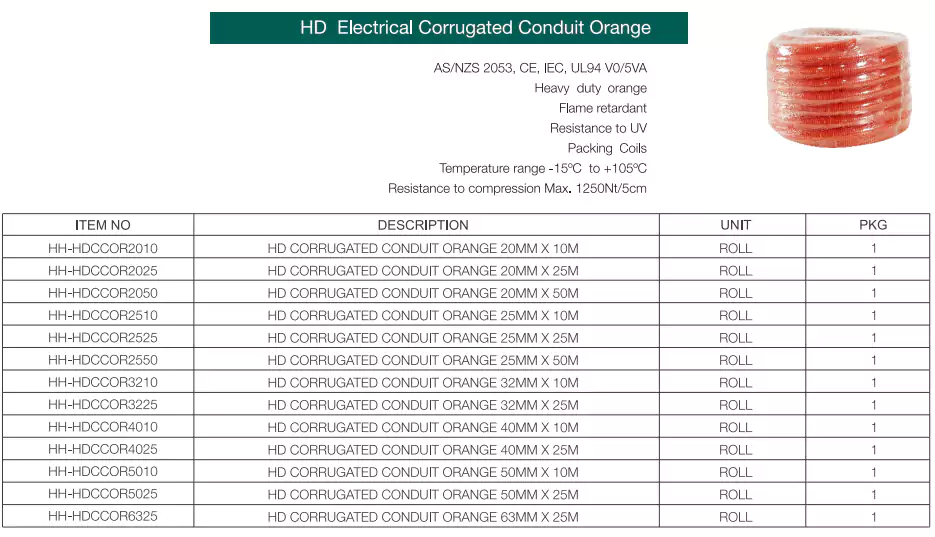
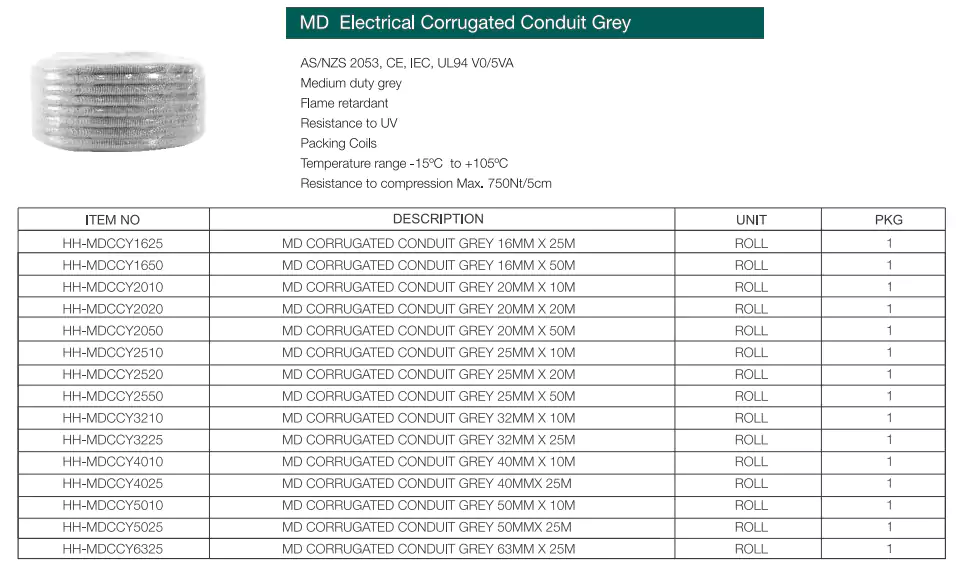
Standards: HD&MD corrugated conduits are comply to AS/NZS 2053.5, CE, IEC, UL94
Ventajas: Flame retardant, UV resistant, high compression and impact strength, lightweight, hand-bendable.
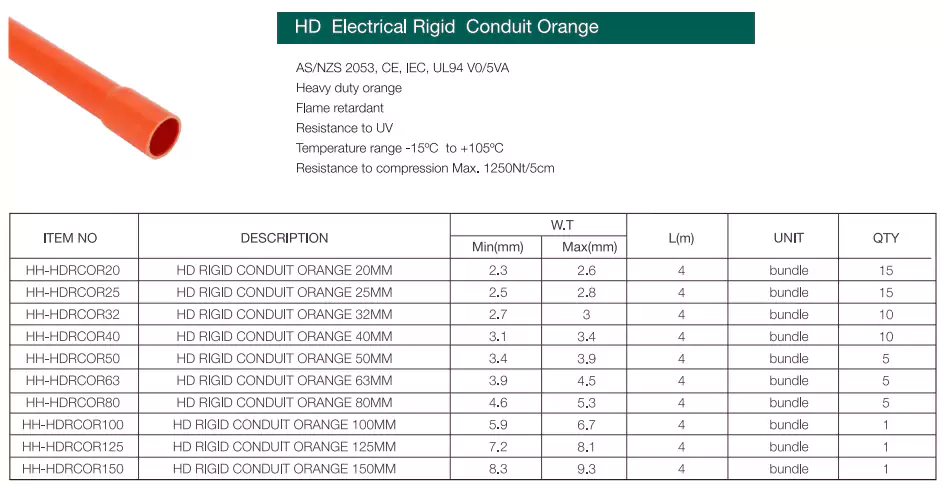
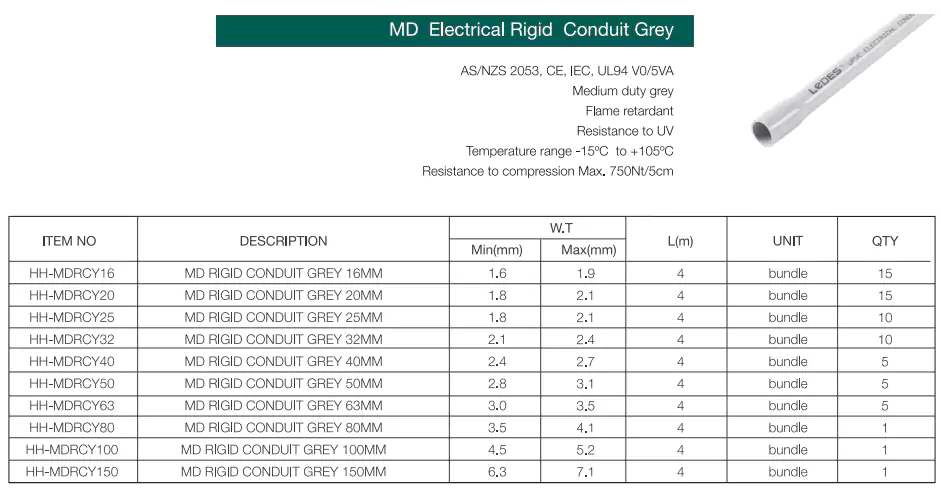
Standards: HD&MD rigid PVC conduits are comply to AS/NZS 2053.2, CE, IEC, UL94
Ventajas: High physical strength, flame retardant, UV resistant
4. Solar Conduit
Solar conduit is a type of conduit that specially designed for use in outdoor applications, due to the harsh installation environment, the requirements for conduit’s physical strength and resistance to UV are very high. Here are some common sizes and types provided by Ledes.
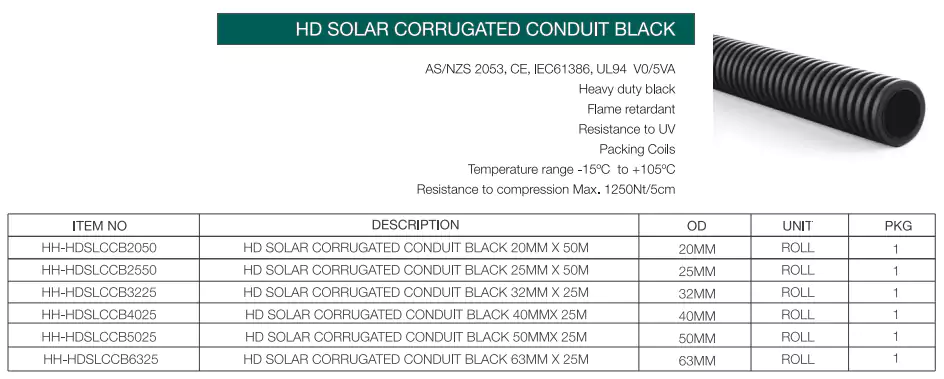
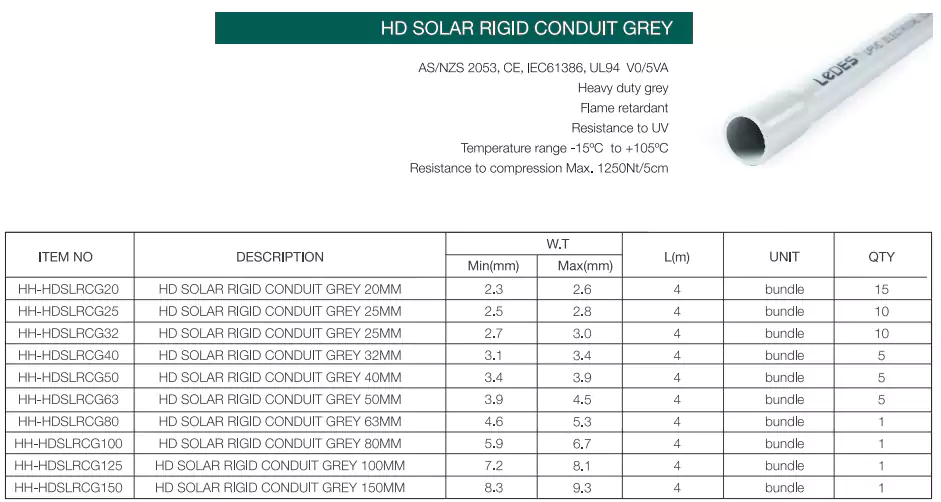
Standards: AS/NZS 2053, CE, IEC
Ventajas: Weather resistant, UV resistant, flame retardant V0/5VA rated, compression and impact resistant.
Low Smoke Halogen Free Conduit is special types of conduit that is designed to minimize the release of toxic gases and smoke in the event of a fire. With key features of:
Halogen-Free:
These conduits do not contain halogen elements such as chlorine, fluorine, bromine, or iodine, which can release toxic gases during combustion. This feature enhances safety in case of fire.
Low Smoke Emission:
When exposed to high temperatures or flames, halogen-free conduits produce minimal smoke. This reduces visibility issues during a fire, allowing for safer evacuation and easier access for emergency respond.
Excellent Fire Resistance:
Designed to withstand high temperatures, these conduits have superior fire resistance properties, making them suitable for use in various applications, including public buildings and industrial facilities.
No Toxic Smoke Emission:
In the event of a fire, halogen-free conduits emit non-toxic smoke, significantly reducing the risk of harmful inhalation for occupants and first respond.
UV Resistant:
These conduits are designed to resist degradation from ultraviolet (UV) light, making them suitable for outdoor applications where exposure to sunlight is a concern.
Extreme Temperature Resistance:
They can withstand extreme temperatures from -45℃ to 150 ℃, both high and low, ensuring reliable performance in a variety of environmental conditions.
Standards: IEC61386, ASTM, UL94
Aplicaciones: Hospitals, schools, subways, crowded places.
Where Can PVC Conduit be Used?
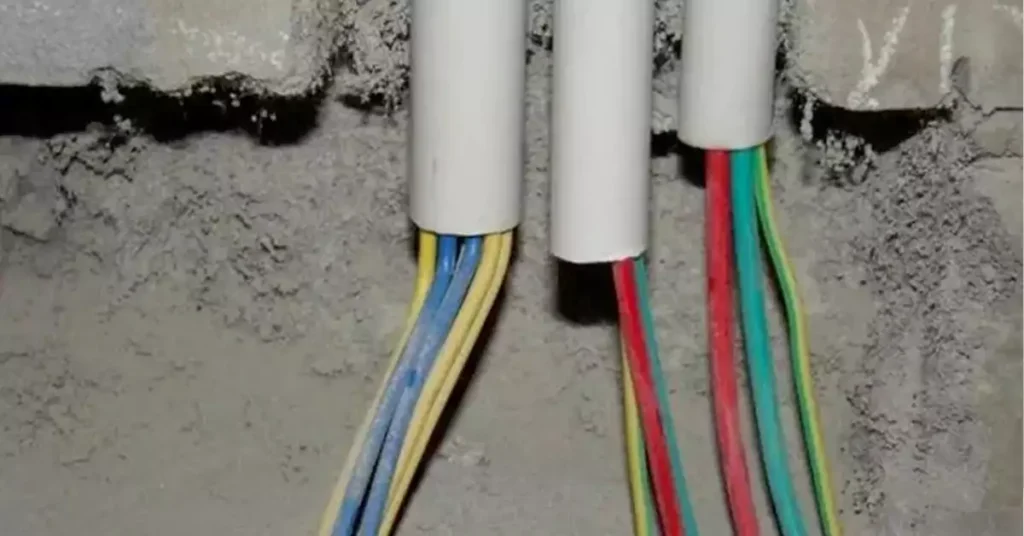

PVC conduit is a versatile solution for protecting electrical and communication wiring in various settings, both above and underground. It is compliant with the National Electrical Code (NEC) guidelines, specifically NEC 352, which governs its use in different environments.
Ledes’ PVC conduits have been used many large projects, for above ground and underground use, here are some of the project examples.
In the CHPE (Champlain Hudson Power Express) project in the United States, PVC conduit plays a crucial role in managing electrical wiring above ground. The project involves extensive electrical systems that require safe and efficient wiring solutions. Schedule 40 PVC conduit is installed in walls, ceilings, and other structures, providing robust protection against environmental factors and physical damage. Its ability to withstand exposure to direct sunlight makes it suitable for outdoor installations, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the electrical systems.
In the Melbourne Metro Tunnel project in Australia, conduit is utilized for underground installations. The project requires extensive trenching and excavation for electrical and communication infrastructure. Low smoke halogen free conduit safeguarding the wiring from moisture and soil-related damage. This application is particularly beneficial in urban environments where space is limited, and underground installation is necessary to maintain surface accessibility and safety.
Where is PVC Conduit Allowed and NOT Allowed?
The National Electrical Code (NEC) outlines specific guidelines for where PVC conduit can and cannot be used. These rules are essential for ensuring safety and compliance in electrical installations.
Where PVC Conduit is Allowed
According to 352.10 section in chapter three, NEC, PVC conduit can be used in the following situations:
1. Underground Installations
PVC conduit is widely approved for underground use because of its durability, corrosion resistance, and moisture protection. It is commonly used in:
- Direct Burial: PVC conduits can be buried directly in the ground, protecting electrical wiring from soil, moisture, and potential damage.
- Underground Duct Banks: Often used in commercial and industrial settings where multiple electrical conduits are grouped together for protection.
2. Outdoor Use
- The NEC allows PVC conduit to be installed outdoors, provided it is rated for sunlight resistance. PVC is often used for:
- Exterior Walls: As long as the PVC conduit is exposed to sunlight, it must be UV-rated to prevent degradation.
- Above Ground Exposed Applications: In industrial and residential settings, PVC conduits are allowed as long as they meet the relevant specifications for the environment.
3. Wet or Damp Locations
- Since PVC is non-metallic and resistant to water and moisture, it is ideal for wet and damp locations, such as:
- Basements: Areas prone to moisture can benefit from PVC conduit’s corrosion-resistant properties.
- Industrial Washdown Areas: Where exposure to water or chemicals is frequent, PVC offers long-lasting protection for electrical wiring.
4. Corrosive Environments
PVC conduit is highly resistant to chemicals, making it suitable for environments where corrosion would damage metal conduits.
Where PVC Conduit is Not Allowed
According to section 352.12 of the NEC, PVC conduit is now allowed in these situations:
1. Hazardous (Classified) Locations
PVC conduit is not allowed in hazardous (classified) locations, such as areas where explosive gases, vapors, or combustible dust are present, unless explicitly permitted by other NEC articles. These locations include:
- Petroleum Refineries
- Chemical Plants
- Grain Elevators
In these environments, PVC does not provide the necessary protection against potential fire or explosion hazards.
2. Support of Luminaires or Equipment
PVC conduit is prohibited from supporting luminaires (lighting fixtures) or other equipment unless they are specifically listed for such use (as described in NEC 352.10(H)). This means PVC cannot be used as a structural element to support heavy fixtures.
3. Areas Prone to Physical Damage
PVC conduit should not be used in areas where it may be subjected to physical damage, unless it is specifically identified for such use. PVC is less resistant to impact compared to metal conduits, which makes it unsuitable for locations where it could be struck or crushed, such as:
- High-Traffic Industrial Areas
- Construction Zones
4. High-Temperature Environments
PVC conduit is not permitted in environments where the ambient temperature exceeds 50°C (122°F), unless it is listed for high-temperature use. High heat can cause PVC to warp, lose its structural integrity, or become a fire hazard. Such environments include:
- Boiler Rooms
- Areas Near Industrial Ovens
5. Theaters and Similar Locations
PVC conduit is restricted from being used in theaters and similar locations, unless specifically permitted by NEC Sections 518.4 and 520.5. These spaces may have unique fire safety requirements that PVC does not meet, such as:
- Performance Stages
- Cinemas
Understanding where PVC conduit is allowed and restricted according to the NEC ensures safe, compliant installations.
Installing PVC Conduit: A Step-by-Step Guide
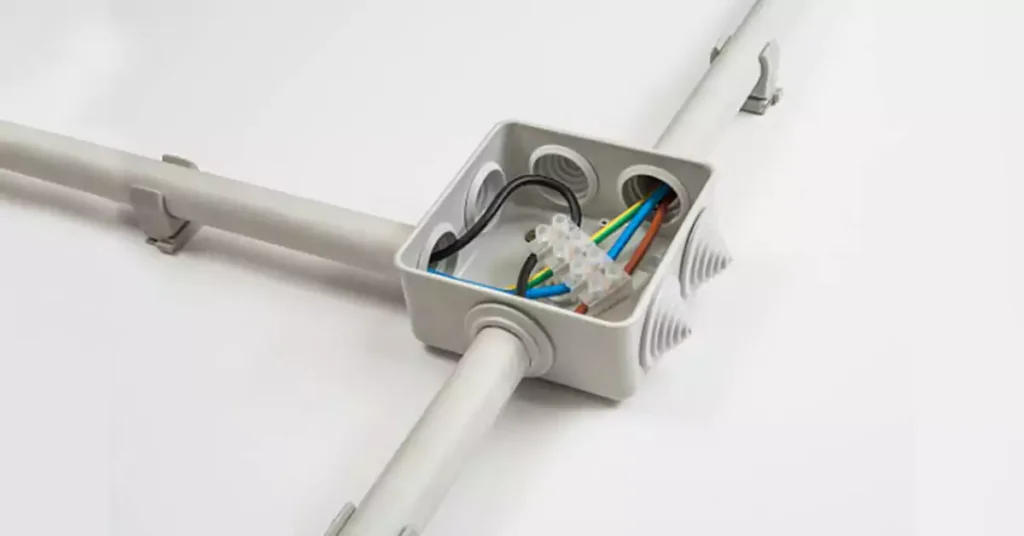

We have written a detailed tutorial before. If you are interested, you can learn everything about PVC Electrical Conduit Installation. The following are the general steps of installation:
Step 1: Plan Your Layout
Survey the Area: Identify the path for your conduit run, considering where your electrical boxes, outlets, or switches will be located. Make sure to avoid areas where PVC conduit is not allowed (e.g., plenum spaces or high-heat areas as specified by NEC).
Measure the Path: Measure the length of the conduit needed and mark positions where bends, boxes, and junctions will be required. Keep in mind the NEC requirements for spacing between conduit supports and the positioning of junction boxes.
Step 2: Cut the PVC Conduit and Deburr the Edges
Mark the Cutting Points: Use a tape measure and marker to measure and mark the PVC conduit to the required lengths.
Cut the Conduit: Use a PVC pipe cutter for a clean cut. Alternatively, a fine-toothed hacksaw can be used.
Desbarbar los bordes: After cutting, deburr the edges of the conduit with a utility knife or sandpaper. This step is essential to prevent sharp edges from damaging the electrical wires during installation.
Step 3: Use Larger Conduit and Electrical Boxes
Choose Larger Conduit: For ease of installation, especially when running multiple wires, use a conduit size larger than the minimum NEC requirement. This will reduce friction when pulling wires.
Select Appropriate Electrical Boxes: Choose boxes that provide enough space for wire connections, as cramped boxes can lead to overheating. Make sure the boxes are rated for the intended location (e.g., weatherproof boxes for outdoor use).
Step 4: Bend the Conduit or Use Fittings for Turns
Heat Bending (If Necessary): For custom bends, use a heat gun to soften the PVC conduit, then gently shape it. Hold the bend in place until it cools.
Elbows for Turns: If you don’t want to bend the conduit manually, use PVC elbows for 90-degree or other angle turns.
Install Junction Boxes for Complex Runs: For runs with multiple bends or for transitioning between conduit sections, junction boxes can be used to simplify the routing of the conduit and provide easy access points for wiring.
Step 5: Apply PVC Cement (PVC Conduit Doesn’t Require Primer)
Apply Cement: To join sections of PVC conduit or attach the conduit to fittings (elbows, couplings), apply PVC cement to both the inside of the fitting and the outside of the conduit.
Make Secure Connections: Push the conduit into the fitting and twist slightly to ensure a strong, watertight connection. PVC conduit generally doesn’t require a primer like some other PVC piping systems do.
Step 6: Install Electrical Boxes with PVC Conduit
Connect Conduit to Boxes: Attach the PVC conduit to the electrical boxes using appropriate fittings. Make sure the boxes are securely mounted to walls, ceilings, or other structures.
Seal Outdoor Boxes: For outdoor installations, use weatherproof electrical boxes and apply sealant around the conduit entry points to prevent moisture ingress.
Step 7: Use Hangers to Support PVC Conduit
Install Conduit Hangers: Secure the PVC conduit to walls, ceilings, or along beams using conduit hangers or straps. The NEC recommends supporting PVC conduit at intervals no more than 3 feet apart.
Anchor the Conduit: Use screws, anchors, or other fasteners to firmly attach the conduit hangers to the structure. Ensure the conduit is not sagging and remains securely in place.
Step 8: Pull Electrical Wires
Feed Fish Tape Through the Conduit: Insert fish tape into one end of the conduit and push it through until it reaches the other end.
Attach Wires to Fish Tape: Secure the electrical wires to the fish tape using electrical tape.
Tirar de los cables: Gently pull the fish tape through the conduit, bringing the wires along with it. Be careful to avoid damaging the wire insulation.
Step 9: Install Conduit Bushings
Protect the Wire Ends: At the ends of the conduit where the wires exit, install conduit bushings. These bushings protect the wires from sharp edges at the conduit ends, preventing potential damage to the insulation.
Secure Bushings in Place: Ensure that the bushings are properly fitted and secured to protect the wires as they exit the conduit into electrical boxes or enclosures.
Step 10: Test the System
Check All Connections: After installing the conduit and pulling the wires, check that all conduit connections are tight and secure. Ensure all fittings, couplings, and boxes are properly sealed.
Test Continuity: Use a multimeter to test for continuity in the wiring and ensure that the electrical connections are working correctly before powering up the system.
By following these detailed steps, you can ensure a safe, efficient, and compliant installation of PVC conduit for your electrical wiring project.
How to Properly Cut and Join PVC Conduit?
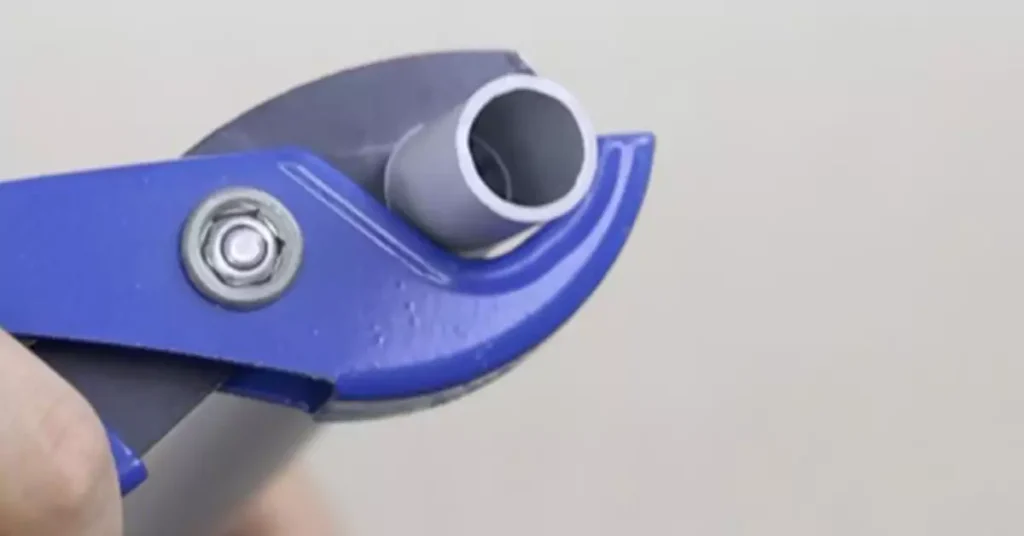

Cutting and joining PVC conduit correctly is essential for a clean, efficient, and safe electrical installation. In this section, we’ll guide you through the best practices for cutting PVC conduit and making secure joints using PVC cement and fittings.
Step 1: Choose the Right Tools
Before you start cutting and joining PVC conduit, gather the necessary tools:
PVC Pipe Cutter: A ratcheting PVC pipe cutter provides clean, straight cuts with minimal effort.
Sierra: If you don’t have a PVC cutter, a fine-toothed hacksaw can be used to cut the conduit, though it may require more time and effort.
Deburring Tool or Utility Knife: These tools help smooth the rough edges after cutting.
Tape Measure and Marker: Used to measure and mark the conduit for cutting.
PVC Cement: Required to securely join conduit sections and fittings.
Couplings and Fittings: For connecting two or more sections of conduit, or for attaching conduit to electrical boxes.
Step 2: Measure and Mark the Conduit
Accurate Measurement: Measure the required length of the conduit using a tape measure. Always measure twice to ensure accuracy, especially if the conduit will run through tight spaces or has to meet specific dimensions.
Mark the Cut Point: Use a permanent marker to mark the point where the conduit will be cut. Draw a line around the entire circumference to ensure a straight cut.
Step 3: Cut the PVC Conduit
Using a PVC Pipe Cutter: Open the jaws of the PVC pipe cutter and position them around the marked line on the conduit. Apply even pressure as you squeeze the handles to cut through the pipe. This tool will give you a clean and straight cut.
Using a Hacksaw: If using a hacksaw, secure the conduit in a vice or against a stable surface to hold it in place. Saw through the conduit using slow, steady strokes, making sure to follow the marked line to maintain a straight cut.
Avoid Jagged Edges: Ensure the cut is smooth and straight. Jagged or uneven edges can make joining the conduit difficult and may damage the wire insulation.
Step 4: Deburr the Cut Edge
Smooth the Inside Edge: After cutting, the inside of the conduit will have sharp burrs that could potentially damage electrical wires when pulled through. Use a deburring tool or a utility knife to smooth out these rough edges.
Smooth the Outside Edge: It’s also important to smooth the outside edge to ensure a clean connection with couplings and fittings.
Step 5: Apply PVC Cement
Apply PVC Cement: Unlike PVC piping used for plumbing, PVC conduit typically doesn’t require a primer. Apply PVC cement evenly around the outside of the conduit end and the inside of the fitting. Be sure to use PVC cement specifically rated for electrical conduit to ensure a secure, long-lasting bond.
Push and Twist: Immediately after applying the cement, push the conduit into the fitting and twist it about a quarter turn to evenly distribute the cement. Hold the conduit and fitting together for a few seconds to allow the cement to set.
Step 7: Allow the Cement to Cure
Set Time: Allow the cement to cure according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Generally, PVC cement will set within a few minutes, but it may take up to 24 hours for the joint to fully cure.
Check for Gaps: Once the cement is cured, inspect the joints to ensure there are no gaps or loose connections. The joints should be tight, secure, and properly aligned.
Is PVC Conduit Suitable for High Voltage Applications?
Understanding High Voltage and PVC Properties

High voltage typically refers to electrical systems operating at voltages above 1,000 volts AC or 1,500 volts DC. PVC conduit, made from polyvinyl chloride, has several characteristics that are both beneficial and limiting when used in such applications:
Aislamiento eléctrico: PVC is a non-conductive material, making it inherently resistant to electrical current, which can help reduce the risk of electrical arcing.
Flame Retardancy: PVC conduit has flame-retardant properties, which is an important factor when considering high voltage environments where heat buildup and electrical faults may occur.
Temperature Sensitivity: PVC has limitations in high-temperature environments (above 50°C/122°F) and can soften or warp under extreme conditions, which can be a concern for high voltage systems where heat dissipation is critical.
NEC Requirements for PVC Conduit in High Voltage Applications
The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides strict guidelines regarding the installation of electrical conduits, including PVC, in high voltage applications. According to NEC Chapter 3, Article 300, high voltage systems have stricter installation standards than low voltage systems due to the potential hazards associated with increased current. Some key points include:
1. NEC Article 352:
This section covers the use of rigid PVC conduit, but for high voltage, compliance with certain conditions is required:
Underground Use: PVC conduit is often permitted for underground high voltage applications, especially in direct burial situations, where the conduit can protect cables from moisture, soil movement, and corrosion.
Above Ground: While PVC conduit can be used for high voltage systems above ground, it must be listed for such use and meet specific requirements, particularly regarding exposure to sunlight and high temperatures.
2. Insulation and Voltage Ratings:
NEC Article 300 emphasizes the importance of conductor insulation and separation for high voltage installations. Conductors rated for high voltage must have appropriate insulation levels to prevent breakdown, and PVC conduit itself must be approved for high voltage use, especially if used in conjunction with other conduit types in mixed systems.
3. Conduit Fill and Derating:
For high voltage applications, NEC sets strict limits on conduit fill and requires derating of the conductors to prevent overheating. This means that PVC conduit needs to be sized properly to avoid exceeding the maximum fill capacity, particularly in high voltage installations where heat dissipation is critical.
4. Thermal Expansion:
In long runs of PVC conduit, the NEC requires consideration of thermal expansion and contraction. High voltage systems generate more heat, and PVC’s sensitivity to temperature changes can lead to expansion or warping. Expansion fittings may be required to accommodate this movement and prevent damage to the conduit or cables.
When PVC Conduit is Suitable for High Voltage
PVC conduit is suitable for certain high voltage applications, provided that the installation meets NEC requirements and addresses the limitations of the material. Here are some scenarios where PVC conduit is commonly used for high voltage:
1. Underground High Voltage Distribution:
PVC conduit is frequently used for underground high voltage electrical distribution, particularly in industrial settings, substations, or utility lines. Its resistance to moisture and corrosion makes it ideal for protecting high voltage cables in buried applications.
2. Wet and Corrosive Environments:
In environments where the conduit might be exposed to water or chemicals, PVC offers excellent resistance to corrosion compared to metal conduits. This makes it suitable for outdoor or industrial high voltage installations, such as wastewater treatment facilities or coastal regions.
3. High Voltage Solar and Wind Installations:
PVC conduit is often used in renewable energy systems, such as solar or wind farms, where high voltage cables must be protected underground or in environments exposed to the elements.
When PVC Conduit is Not Suitable for High Voltage
Despite its advantages, PVC conduit is not suitable for all high voltage applications, particularly in situations that exceed its physical or chemical limitations:
High Temperature Applications
Hazardous Locations
Areas with High Physical Stress
Can PVC Conduit Be Bent?
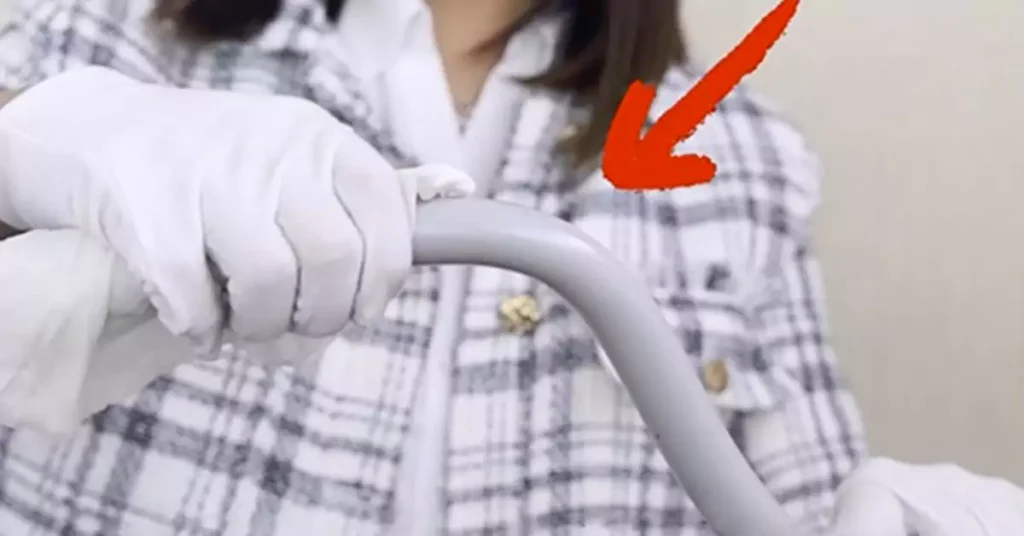

Yes, PVC conduit can be bent to accommodate various angles and changes in direction during installation. There are two common methods to bend PVC conduit: using a heat gun or a conduit bender with a heating element designed for PVC.
Method 1: Using a Heat Gun
- Prepare el conducto: Measure and mark where the bend needs to occur. Secure the conduit in place to prevent movement during bending.
- Heat the Conduit: Utilice una pistola de calor para aplicar calor de manera uniforme a lo largo de la sección del conducto que desea doblar. Mueva la pistola de calor hacia adelante y hacia atrás para evitar concentrar el calor en un solo punto, lo que podría provocar que el PVC forme burbujas o se queme. Caliente el PVC hasta que se vuelva flexible, generalmente a unos 180 °F (82 °C).
- Doblar el conducto: Una vez que el PVC esté flexible, dóblelo suavemente con la mano hasta obtener el ángulo deseado. Puede utilizar una plantilla o un molde para doblar para mantener una curva uniforme. Mantenga la curva en su lugar hasta que el PVC se enfríe y se endurezca.
- Enfriar y comprobar la curvatura: Una vez que el conducto se haya enfriado (lo que generalmente demora unos minutos), verifique que la curva sea suave y asegúrese de que el interior no esté doblado ni obstruido, ya que esto podría dañar los cables o violar los requisitos del código.
Método 2: Utilizar una dobladora de conductos de PVC
- Utilice una dobladora calentada: Existen dobladoras especiales para conductos de PVC que calientan el conducto de manera uniforme y permiten realizar curvas precisas. Estas dobladoras tienen un elemento calefactor para ablandar el PVC y guías integradas para realizar curvas en ángulos exactos.
- Doblar el conducto: Una vez calentado el conducto, utilice la dobladora para crear la curva deseada. Este método garantiza curvas uniformes, especialmente para proyectos más grandes con múltiples curvas en diferentes ángulos.
Consejos de seguridad para doblar conductos de PVC
Evite el sobrecalentamiento: Aplicar demasiado calor o sostener la pistola de calor demasiado cerca puede provocar que el PVC se ampolle o se queme. Mantenga la pistola de calor en movimiento y a una distancia segura para distribuir el calor de manera uniforme.
Utilice guantes y equipo de seguridad: El PVC calentado puede calentarse mucho, por lo que es fundamental usar guantes resistentes al calor al manipular el conducto. Además, asegúrese de trabajar en un área bien ventilada, ya que el PVC calentado puede liberar vapores.
Prevenir torceduras: Siempre doble el conducto de manera lenta y uniforme para evitar que se doble. Un conducto doblado puede dañar los cables eléctricos o reducir el espacio interno, lo que dificulta el paso de los cables.
Comprobar si hay deformación: Una vez que se haya completado la curva, inspeccione el conducto para asegurarse de que no se haya aplanado ni deformado excesivamente. El diámetro interior debe permanecer sin obstrucciones para cumplir con los códigos eléctricos.
Considere la expansión y la contracción: El PVC puede expandirse o contraerse debido a los cambios de temperatura, por lo que debe tener esto en cuenta al planificar las curvas, especialmente para conductos largos. El uso de accesorios de expansión puede ayudar a prevenir problemas.
¿Cuál es la diferencia entre los conductos de PVC y UPVC?
Los conductos de PVC (cloruro de polivinilo) y UPVC (cloruro de polivinilo no plastificado) se utilizan ampliamente en instalaciones eléctricas, pero difieren en términos de flexibilidad, resistencia y aplicación. A continuación, se detallan las diferencias clave:
Características | Conducto de PVC | Conducto de UPVC |
Resistencia y durabilidad | Menos resistente a los impactos, adecuado para un uso más ligero. | Alta resistencia al impacto, durable para entornos difíciles. |
Resistencia térmica | Menor resistencia a altas temperaturas. | Mayor resistencia al calor, adecuado para entornos cálidos. |
Resistencia química |
Bueno, pero inferior al UPVC | Excelente, más resistente a los químicos y la corrosión. |
Aplicaciones típicas | Cableado interior, residencial, comercial ligero | Instalaciones exteriores, industriales, subterráneas |
Costo | Menor costo, más asequible para uso general. | Mayor costo debido a una mayor durabilidad y resistencia. |
PVC Conduits Vs Metallic Conduits
En lo que respecta a las instalaciones eléctricas, la elección del material de los conductos es crucial para garantizar la seguridad, la durabilidad y el cumplimiento de las normativas locales. Dos tipos comunes de conductos son los conductos de PVC (cloruro de polivinilo) y los conductos metálicos (como EMT, RMC e IMC). Cada tipo tiene sus ventajas y desventajas, lo que los hace adecuados para diferentes aplicaciones.
Características | Conductos de PVC | Conductos Metálicos |
Material | Plástico (cloruro de polivinilo) | Metal (acero, aluminio) |
Peso | Ligero | Más pesado |
Costo | Generalmente de menor costo | Generalmente, el costo es más alto |
Resistencia a la corrosión | Excelente resistencia | Susceptible a la corrosión |
Flexibilidad | Más flexible y fácil de instalar. | Rígido, menos flexible |
Resistencia al fuego | Bueno, pero no ignífugo. | Mejor resistencia al fuego |
Conductividad eléctrica | No conductor | Conductivo |
Resistencia al impacto | Moderado | Alto |
Resistencia a los rayos UV | Limitado (puede degradarse al aire libre) | Excelente |
Solicitud | Uso en interiores, lugares húmedos. | Uso interior y exterior, aplicaciones industriales. |
¿Cuál es la diferencia entre una tubería de PVC y un conducto de PVC?
Hemos comparado en detalle las diferencias entre las tuberías de plomería de PVC y los conductos de PVC. Para obtener más información, consulte el artículo La diferencia entre el PVC para plomería y el PVC para conductos eléctricos. A continuación se presentan algunas diferencias clave entre ellos.
Características | Tubo de PVC | Conducto de PVC |
Uso principal | Plomería y drenaje | Protección del cableado eléctrico |
Composición del material | PVC estándar | PVC rígido con aditivos para mayor resistencia. |
Espesor de la pared | Paredes más delgadas, más livianas. | Paredes más gruesas, más pesadas. |
Clasificación de temperatura | Tolerancia a temperaturas más bajas | Mayor tolerancia a la temperatura |
Clasificación de presión de agua | Requisitos de alta presión | No hay requisitos específicos |
Normas de aprobación | Varía según la aplicación | Debe cumplir con los códigos eléctricos. |
Costo | Generalmente menos costoso | Generalmente más caro |
¿Por qué el conducto de PVC es más caro que la tubería de PVC?
Composición del material: Los conductos de PVC se fabrican con aditivos adicionales para mejorar su durabilidad y resistencia a los factores ambientales estresantes, lo que genera un mayor costo del material.
Espesor de la pared: Las paredes más gruesas del conducto de PVC proporcionan una mayor protección al cableado eléctrico, lo que aumenta los costos de fabricación.
Normas y pruebas: Los conductos de PVC deben cumplir con estrictos códigos y estándares eléctricos, que requieren pruebas adicionales y garantía de calidad durante la producción, lo que contribuye a aumentar los costos.
Demanda del mercado: La demanda de conductos eléctricos en la construcción y aplicaciones industriales puede aumentar los precios en comparación con las tuberías de PVC de plomería estándar.
Costos de instalación: Si bien no es un costo directo del conducto en sí, el proceso de instalación también puede contribuir a los gastos generales, dada la necesidad de accesorios especializados y el cumplimiento de las normas de seguridad.
Como fabricantes, creemos que el factor más importante que afecta el precio de las tuberías y conductos de PVC es el precio de las materias primas y los aditivos de PVC. En esencia, no hay mucha diferencia entre ambos, pero la aplicación es diferente.
PVC Conduit vs Liquid-tight Conduit
Los dos tipos más comunes de conductos son los de PVC (cloruro de polivinilo) y los herméticos. Cada uno tiene sus propias características, ventajas y aplicaciones.
Conducto de PVC: Se trata de un tipo de conducto rígido fabricado con cloruro de polivinilo, un plástico ligero y duradero. Se utiliza habitualmente en aplicaciones residenciales y comerciales para proteger el cableado eléctrico. El conducto de PVC es resistente a la humedad, a los productos químicos y a la corrosión, lo que lo hace adecuado para diversas condiciones ambientales.
Conducto estanco al líquido: Este conducto está diseñado para proporcionar un recinto flexible y hermético para el cableado eléctrico. Generalmente está hecho de PVC flexible o metal con un sello hermético, lo que permite su uso en lugares húmedos o mojados. El conducto hermético es ideal para aplicaciones en las que se produce movimiento o vibración, ya que se puede doblar sin romperse.
Característica | Conducto de PVC | Conducto estanco a líquidos |
Material | PVC rígido | PVC flexible o metal |
Flexibilidad | Rígido | Flexible |
Resistencia al agua | Bueno (no apto para agua estancada) | Excelente (hermético) |
Instalación | Requiere pegamento o accesorios. | Se puede instalar sin pegamento. |
Aplicaciones | Interior y exterior (áreas no húmedas) | Lugares húmedos o mojados, áreas de maquinaria. |
Costo | Generalmente más bajo | Mayor flexibilidad y estanqueidad. |
Durabilidad | Resistente a productos químicos y corrosión. | Altamente duradero, resistente a la humedad. |
Clasificación de temperatura | Moderado, normalmente hasta 60 °C (140 °F) | Clasificaciones de temperatura más altas disponibles |
¿Cómo elegir el conducto de PVC adecuado para su proyecto?

Elegir el conducto de PVC adecuado para su proyecto implica tener en cuenta varios factores para garantizar la seguridad, el cumplimiento normativo y la eficiencia. Estos son los factores clave que debe tener en cuenta:
1. Comprenda los tipos de conductos de PVC
Conducto de PVC rígido: Durable y adecuado para instalaciones subterráneas o expuestas.
Conducto de PVC flexible: Ideal para aplicaciones que requieren flexión o movimiento.
Anexo 40 vs. Anexo 80: El Schedule 80 es más grueso y más robusto, adecuado para entornos más hostiles.
2. Considere el medio ambiente
Interior vs. Exterior: Los conductos para exteriores deben ser resistentes a los rayos UV. Las aplicaciones en interiores pueden tener requisitos diferentes.
Humedad y exposición a sustancias químicas: Utilice conductos aptos para lugares húmedos o resistentes a productos químicos si es necesario.
3. Verifique los requisitos de tamaño
Diámetro: Elija un tamaño de conducto que se adapte a la cantidad y el tamaño de los cables que planea instalar. Use las pautas del NEC (Código Eléctrico Nacional) para determinar la capacidad de llenado.
Longitud: Asegúrese de tener suficiente longitud de conducto para su instalación sin juntas excesivas.
4. Review Electrical Codes and Standards
Familiarize yourself with local building codes and the NEC to ensure compliance with safety regulations.
5. Assess Installation Conditions
Bends and Turns: Consider how many bends your installation will require. Flexible conduits might be better for tight spaces.
Support and Mounting: Ensure you have the necessary supports for your conduit installation.
6. Evaluate Cost and Availability
Compare the costs of different types and brands of PVC conduit. Ensure the product is readily available in your area.
7. Consult with Professionals
If unsure, consulting with an electrician or a professional can provide insights specific to your project needs.
Conclusión
In summary, PVC conduit is an essential component in electrical and construction applications, offering a combination of durability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Its resistance to moisture, chemicals, and corrosion makes it an ideal choice for both indoor and outdoor installations. Whether you’re a professional contractor or a DIY enthusiast, understanding the various types of PVC conduit and their applications can enhance the safety and efficiency of your projects.
By considering factors such as installation methods, local building codes, and environmental conditions, you can make informed decisions that maximize the benefits of using PVC conduit. As the demand for sustainable and reliable electrical systems continues to grow, PVC conduit remains a practical solution that meets modern needs while ensuring compliance with industry standards. Embracing this versatile material not only improves the longevity of your installations but also contributes to a safer and more organized electrical infrastructure.