
Tabla de contenido
In modern electrical installations, conduit and trunking play a vital role in providing a safe and organized pathway for electrical wiring. These components not only protect the wiring from physical damage but also contribute to the overall efficiency and reliability of the electrical system. This article provides a comprehensive overview of conduit and trunking, highlighting their importance and applications in electrical installations.
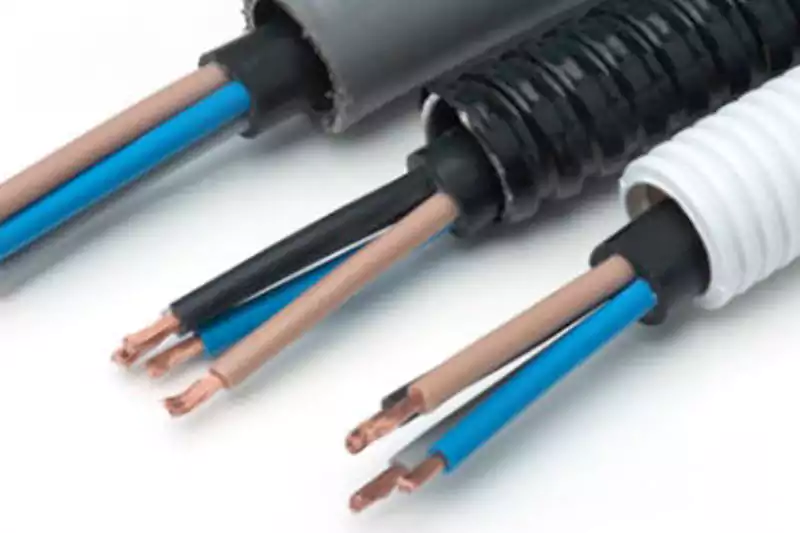

Conduit refers to a protective channel or tubing that encloses electrical cables, providing a shield against external elements and preventing accidental contact with the wires. It is available in various types, such as rigid conduit and flexible conduit. Rigid conduit, typically made of metal or PVC, offers higher mechanical strength and is commonly used in industrial settings. On the other hand, flexible conduit, usually made of PVC or metal-coated materials, provides flexibility and ease of installation in areas with tight bends or vibrations.
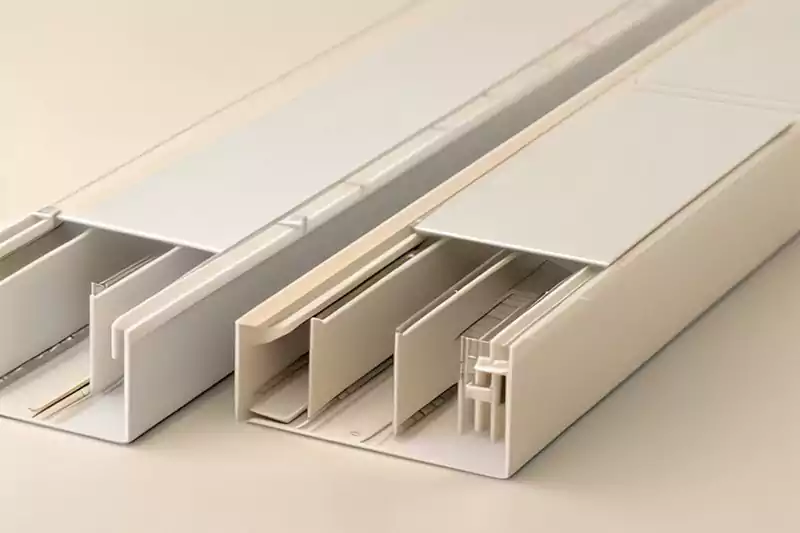

Trunking, also known as cable trunking or wireways, is a system of enclosed pathways that house electrical cables, allowing for organized routing and protection. It consists of a base and a cover, which can be easily opened for cable installation or maintenance. Trunking comes in different sizes and shapes, such as rectangular, square, or circular, to accommodate various cable sizes and quantities. It is commonly made of materials like PVC or metal, providing durability and electrical insulation.
Protection of Wiring: One of the primary purposes of conduit and trunking is to safeguard electrical wiring from physical damage, moisture, chemicals, and other external factors. By enclosing the cables within a protective housing, these components minimize the risk of accidents, such as short circuits or electrical shocks, ensuring the safety of individuals and the integrity of the electrical system.
Organization and Neatness: Conduit and trunking contribute to a well-organized and aesthetically pleasing electrical installation. They allow for the systematic routing of cables, preventing clutter and confusion. This organized approach simplifies future maintenance or troubleshooting activities, saving time and effort.
Cumplimiento de normas: Conduit and trunking play a crucial role in meeting electrical code requirements and industry standards. These standards specify the types, sizes, and installation methods of conduit and trunking, ensuring uniformity and consistency in electrical installations. Adhering to these standards is essential for regulatory compliance and ensuring the safety and reliability of the electrical system.
Flexibilidad y adaptabilidad: Conduit and trunking systems offer flexibility in accommodating changes or additions to the electrical system. They allow for easy re-routing or expansion of wiring without the need for extensive modifications. This flexibility makes conduit and trunking suitable for both residential and commercial applications, where modifications and upgrades are common.
Conduit is a protective channel or tubing that is used to enclose electrical cables, providing a secure pathway and insulation. Its primary purpose is to safeguard the electrical wiring from physical damage, moisture, and environmental factors. By containing and shielding the cables, conduit ensures the safety and longevity of the electrical system.
Conduit is available in various materials, each offering different characteristics and suitability for different applications. Common materials include:
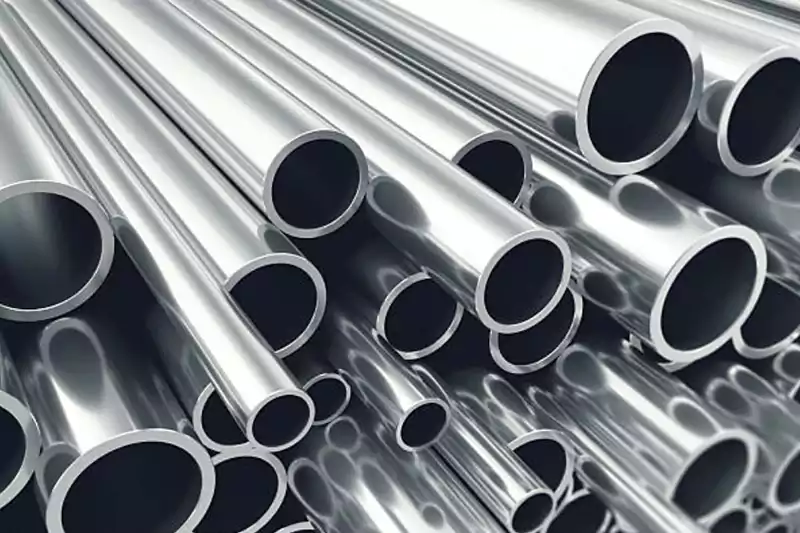

Conducto metálico rígido (RMC): Made of steel, RMC is known for its high mechanical strength and durability. It is commonly used in industrial and commercial applications where robust protection is required.
Tubería Metálica Eléctrica (EMT): EMT is made of galvanized steel or aluminum, providing a lightweight and cost-effective option. It is commonly used in residential and commercial applications.
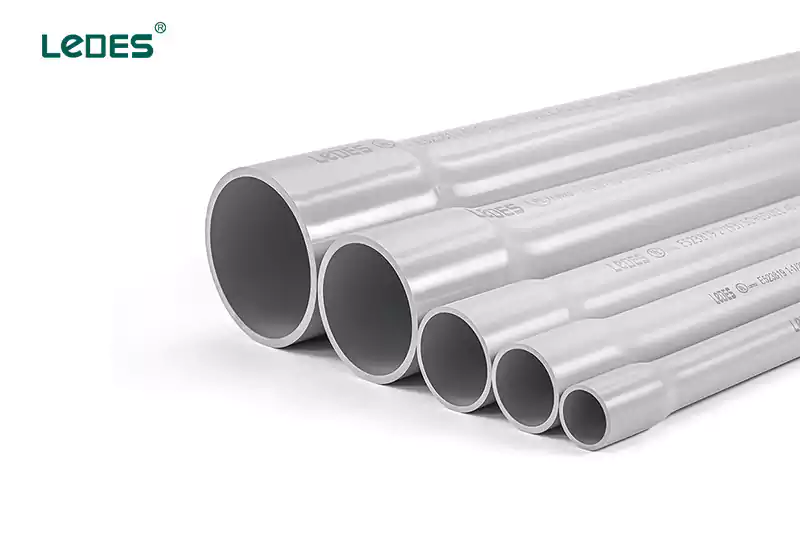

Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Conduit: Conducto de PVC is a popular choice due to its excellent corrosion resistance, affordability, and ease of installation. It is available in different schedules (thickness) and is commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
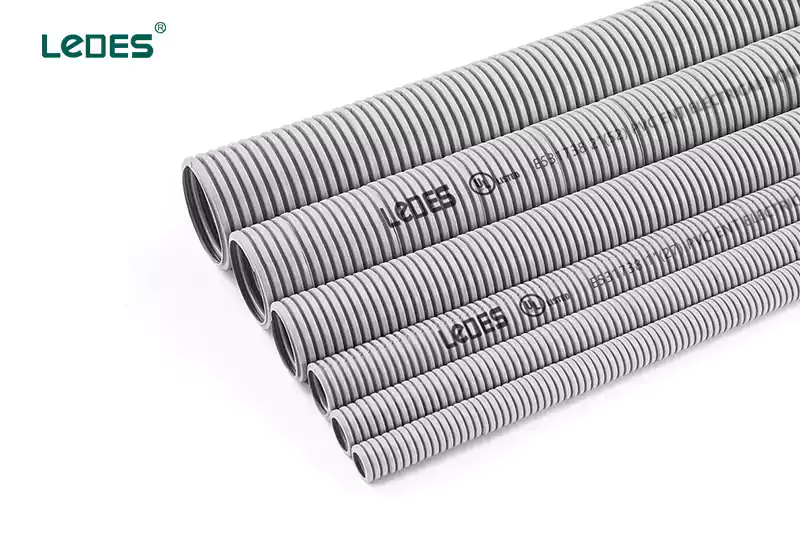

Conducto metálico flexible (FMC): FMC consists of a spirally wound metal strip with a flexible PVC coating. It offers versatility and ease of installation in areas that require flexibility, such as tight bends or vibrations.
Liquid-tight Flexible Conduit (LFMC): LFMC is a flexible conduit with a liquid-resistant coating, making it suitable for areas where exposure to liquids or moisture is a concern.
Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing: Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing (ENT), made od PVC, also known as conducto flexible or plastic conduit, is a type of electrical conduit used to protect and route electrical wiring in buildings.
In the United States and Canada, the installation of conduit, particularly PVC conduit, must adhere to specific standards and regulations. The National Electrical Code (NEC) in the US and the Canadian Electrical Code (CEC) in Canada provide guidelines for conduit installation, covering aspects such as conduit sizing, routing, supports, and grounding requirements. These codes ensure uniformity, safety, and compliance with electrical regulations.
PVC Conduit is the most popular one on the market, and the most used PVC types such as rigid PVC conduit and nonmetallic tubing should complies to:
In the America: UL651, UL1653, NEMA TC-2
In Canada: CSA C22.2 No.211.2, CSA C22.2 No.227.1
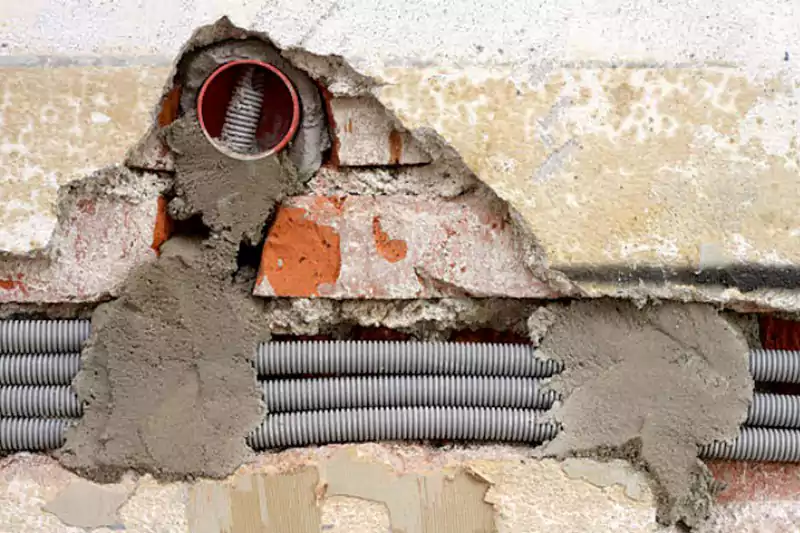

Conduit finds applications in various electrical installations, including:
Concealed wiring in walls, ceilings, and floors.
Wiring for lighting fixtures, outlets, and switches.
Outdoor electrical installations, such as landscape lighting.
Wiring for commercial buildings, offices, and retail spaces.
Industrial machinery and equipment wiring.
Hazardous locations, where conduit provides additional protection against flammable or explosive environments.
- Protection against physical damage, moisture, and environmental factors.
- Enhanced safety by reducing the risk of electrical shocks or short circuits.
- Organization and neatness, simplifying maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Flexibility for future modifications or upgrades to the electrical system.
- Compliance with electrical codes and regulations, ensuring safety and regulatory compliance.
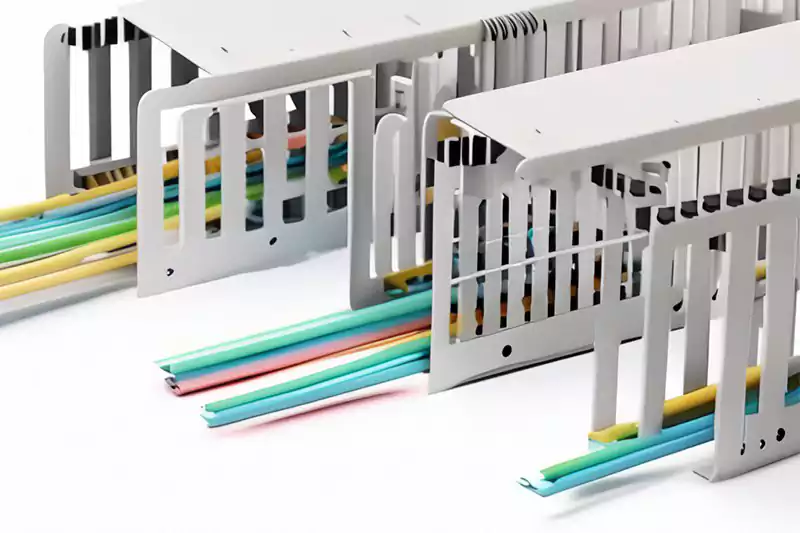
Trunking, also known as cable trunking or wireways, is a system of enclosed pathways that serves as a protective conduit for electrical cables. In most cases, it is rectangular or square in shape and has a lid that can be removed. Its primary purpose is to organize and route cables in a neat and efficient manner, ensuring easy installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting of the electrical system. Trunking plays a significant role in providing a safe and organized environment for cables, minimizing the risk of damage, tangling, or accidental contact.
Cable trunking, also known as cable ducting, is a type of trunking specifically designed for protecting and routing electrical cables. It is available in various sizes and materials, such as PVC, metal, or composite, to accommodate different cable capacities and environmental conditions. Cable trunking is commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings to create organized pathways for power, data, or communication cables.
Lighting trunking is specifically designed for the installation of lighting fixtures. It provides a convenient and organized solution for routing power and control cables to multiple lighting points. Lighting trunking often features pre-fabricated sections with integrated mounting options for light fittings, simplifying installation and maintenance. It is commonly used in commercial buildings, retail spaces, and large-scale lighting installations.
Bus-bar trunking (BBT) is a trunking system used for distributing electrical power in buildings and industrial facilities. It consists of a metal enclosure that houses multiple bus-bars, which are conductors used to transmit electric power. BBT offers a compact and efficient solution for power distribution, reducing the need for long cable runs and individual wiring. It is commonly used in applications where high power loads, such as lighting, machinery, or HVAC systems, need to be supplied.
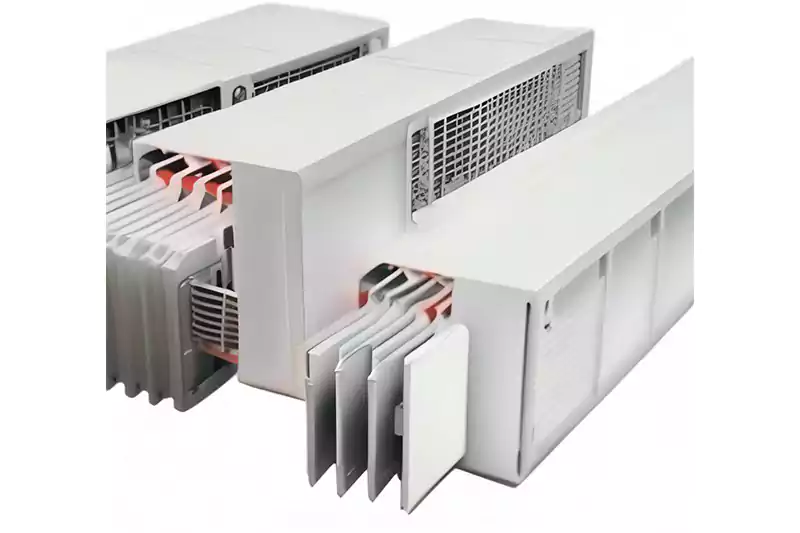

Multi-compartment trunking features separate compartments or channels within a single enclosure. Each compartment is designed to accommodate different types of cables, such as power cables, data cables, or communication cables, while keeping them segregated. This design allows for the separation of various services within a single trunking system, providing a neat and organized solution while reducing the risk of interference or crosstalk between different types of cables. Multi-compartment trunking is commonly used in office buildings, data centers, and installations where multiple services need to be routed and managed efficiently.
In networking, trunking refers to the concept of link aggregation, where multiple physical network connections are combined to increase overall capacity and reliability. This technique allows for higher bandwidth and improved network performance. Trunking enables load balancing, where traffic is distributed across the aggregated links, and redundancy, ensuring uninterrupted network connectivity even if one link fails. It enhances network capacity and provides fault tolerance, making it particularly valuable in high-demand environments, such as data centers or enterprise networks.

Trunking technologies in both electrical and networking contexts often adhere to standards and protocols to ensure compatibility and interoperability. Some common standards and protocols include:
IEEE 802.3ad: This standard defines Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) for Ethernet trunking, enabling the dynamic creation and management of aggregated links.
Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP): VRRP is a network protocol that provides automatic failover and redundancy in routing by creating a virtual IP address that multiple routers can share.
IEEE 802.1Q: The IEEE 802.1Q standard, also known as VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) tagging, is a protocol used in computer networks to implement virtual LANs. It provides a method for identifying and separating different VLANs within a network infrastructure.
Trunking offers numerous benefits across different applications:
Gestión de cables: Trunking systems provide an organized and structured pathway for cables, minimizing the risk of tangling, damage, or accidental disconnection. This simplifies installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting processes.
Proteccion: Trunking shields cables from external elements, such as dust, moisture, or physical impact, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the electrical or network infrastructure.
Scalability: Trunking systems allow for easy expansion and modification of cables, accommodating future growth or changes in the system.
Seguridad y cumplimiento: Trunking ensures compliance with electrical codes and regulations, providing a safe environment for cables and reducing the risk of electrical hazards.
Efficiency: Trunking simplifies cable routing, saves installation time, and enhances system performance through link aggregation and load balancing in networking contexts.
Trunking systems provide efficient cable management, improved organization, and enhanced system performance, making them essential components in electrical and networking installations.
Conduit is a rigid or flexible tube-like structure made of materials such as metal or PVC.
It typically has a circular cross-section, although rectangular or square conduit is also available.
Conduit is designed to enclose and protect individual cables or wire runs.
It can be used for both exposed and concealed installations.
Trunking is an enclosed pathway system that consists of a series of interconnected sections or compartments. It’s usually rectangular or square in shape.
It can be made of materials like PVC, metal, or composite.
Trunking is designed to accommodate multiple cables and provide a pathway for their routing and protection.
Trunking is typically used for surface-mounted or overhead installations.
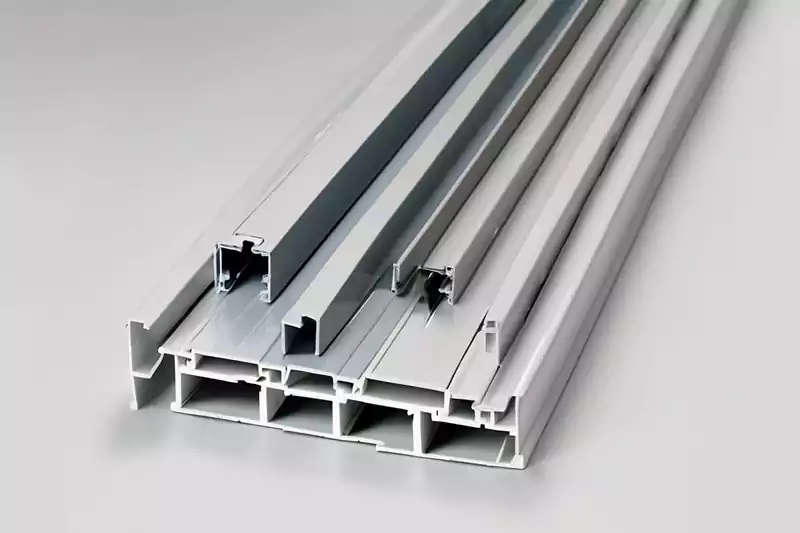

Conduit installation involves threading individual cables through the conduit or pulling pre-wired cables.
It requires bending and cutting the conduit to fit the desired path.
Conduits may need to be secured with clamps or brackets.
Joining conduit sections often requires fittings, connectors, or couplings.
Trunking installation involves attaching trunking sections to walls, ceilings, or floors using brackets, clips, or screws.
Cables are laid or inserted into the trunking compartments.
Trunking often allows for easy access to cables through removable covers or access points.
Trunking sections can be connected or extended using compatible connectors or couplings.
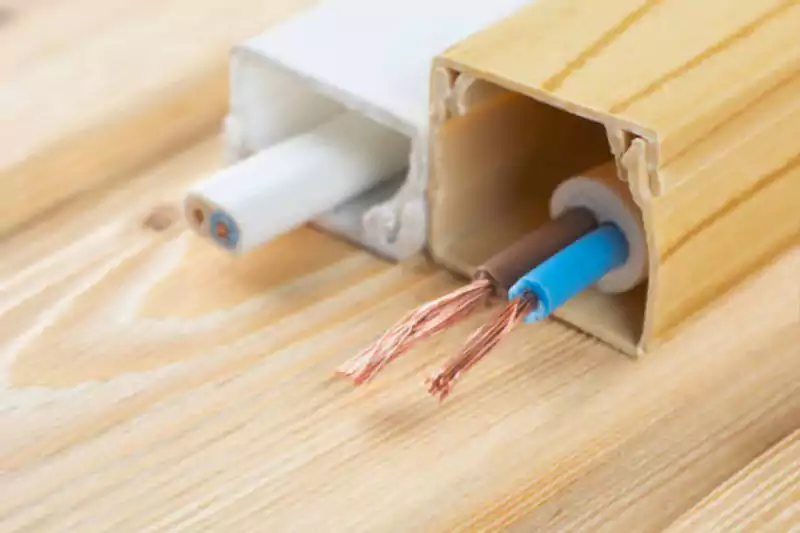

Conduit is commonly used in both residential and commercial settings.
It is suitable for installations where individual cable protection and segregation are required, such as electrical wiring, telecommunications, or data cabling.
Conduit is often used in concealed installations within walls, floors, or ceilings.
Trunking is widely used in commercial, industrial, and institutional settings.
It is ideal for installations that involve multiple cables or wire runs, such as power distribution, data centers, or audio/video installations.
Trunking is commonly used for surface-mounted installations where cable routing needs to be visible and easily accessible.
Conduit can be more expensive due to the cost of materials, fittings, and labor-intensive installation.
The cost may vary depending on the conduit type (rigid, flexible) and material (metal, PVC).
Trunking is often more cost-effective compared to conduit, especially for installations with multiple cables.
The cost may vary based on the trunking material, size, and complexity of the installation.
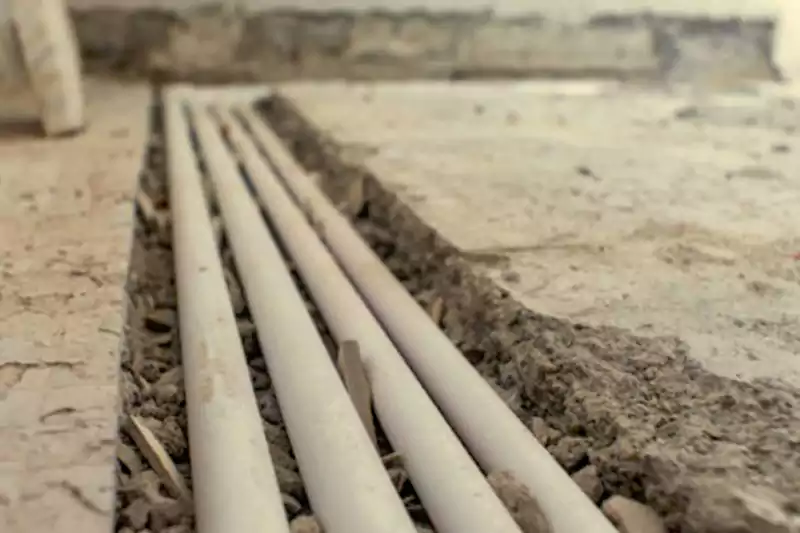

Conduit provides limited access to cables once installed, requiring disassembly or cutting for modifications or repairs.
Maintenance or troubleshooting may involve more effort and time due to the enclosed nature of conduit.
Trunking offers easy access to cables through removable covers or access points, simplifying maintenance, modifications, and troubleshooting.
Trunking allows for easier reconfiguration or addition of cables without disrupting the entire system.
Conduit provides better protection against physical damage, moisture, and environmental hazards.
It offers improved fire resistance due to the materials used, such as metal conduit offering higher fire-rated properties.
Trunking also provides cable protection but may offer less resistance to physical damage compared to conduit.
Fire resistance may vary depending on the trunking material used.
It’s important to consider specific project requirements, regulations, and budget when choosing between conduit and trunking. Factors such as cable quantity, installation location, accessibility needs, and fire safety requirements will influence the decision-making process. Consulting with electrical professionals or conducting a thorough analysis of the project’s needs will ensure the appropriate choice between conduit and trunking.
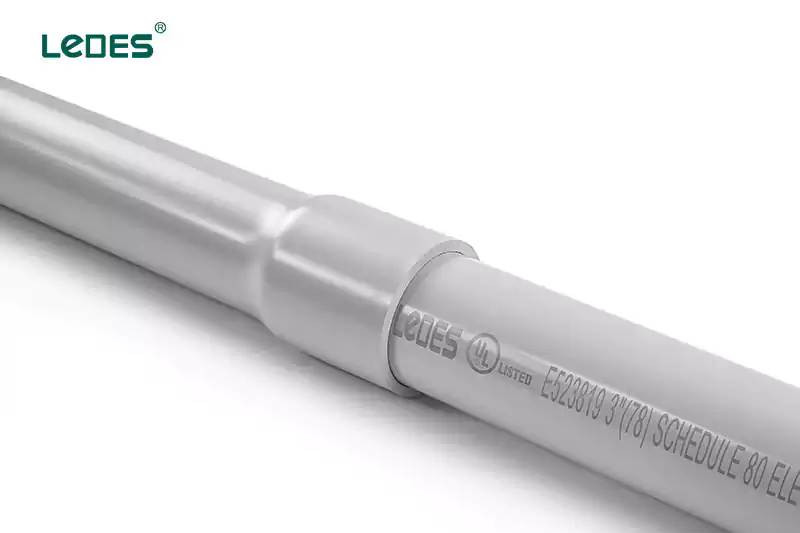

- Planificación: Determine el tamaño, el tipo (rígido o flexible) y el material del conducto según la aplicación y los códigos eléctricos locales.
- Planificación de ruta: Trace la ruta del conducto deseado, teniendo en cuenta los obstáculos, las curvas y los puntos de acceso necesarios.
- Calificación: Utilice un lápiz o marcador para marcar la trayectoria del conducto en las paredes, pisos o techos.
Montaje: Instale abrazaderas o soportes para conductos a intervalos regulares a lo largo de la ruta marcada para asegurar el conducto.
- Corte y doblado: Corte las secciones de conducto a la longitud necesaria con una sierra para metales o un cortador de conductos. Utilice una dobladora de conductos para crear curvas donde sea necesario.
- Enhebrar o tirar: Pase cables individuales a través del conducto o utilice cables precableados y páselos a través de las secciones del conducto.
- Unión: Utilice accesorios, conectores o acoplamientos adecuados para unir secciones de conductos de forma segura.
- Toma de tierra: Asegúrese de que el sistema de conductos tenga una conexión a tierra adecuada conectando cables de conexión a tierra a cada sección del conducto y al sistema de conexión a tierra.
- Fijación y sujeción: Asegure el sistema de conductos firmemente en su lugar usando abrazaderas, correas o sujetadores.
- Pruebas: Realice las pruebas necesarias para garantizar una instalación adecuada, como pruebas de continuidad, resistencia de aislamiento o caída de tensión.
- Cubierta: Instale cubiertas o accesorios para conductos para proteger los extremos expuestos del conducto y garantizar la seguridad.
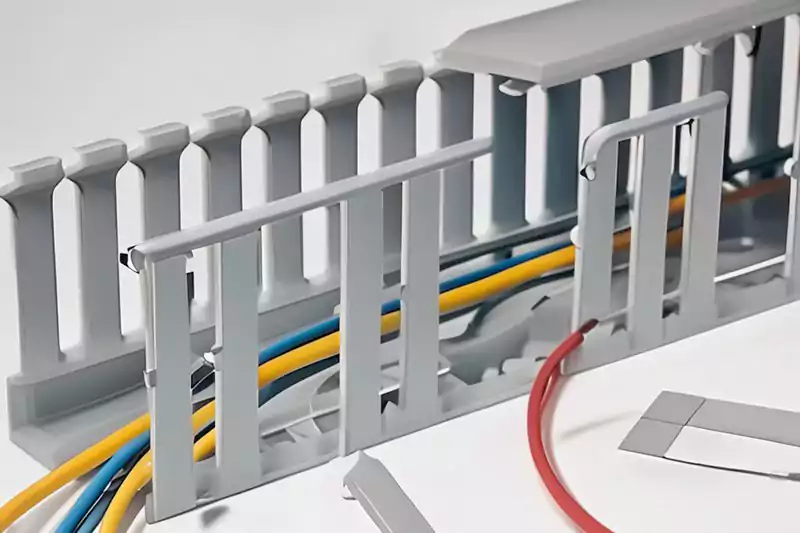
- Planificación: Determine el tamaño, el material y la configuración del canal en función de la cantidad y los tipos de cables que se van a acomodar.
- Planificación de rutas:Decida la ruta del cableado, teniendo en cuenta la accesibilidad, la gestión de cables y la estética.
- Montaje: Coloque soportes de canaletas, clips o tornillos en las paredes, techos o pisos a intervalos adecuados a lo largo del camino planificado.
- Corte: Corte las secciones de canaletas a las longitudes deseadas utilizando las herramientas de corte adecuadas, siguiendo las pautas del fabricante.
- Unión: Conecte las secciones del canal entre sí mediante conectores o acoplamientos compatibles.
- Colocación del cable: Coloque o inserte los cables en los compartimentos de la canaleta, asegurando una adecuada organización y segregación.
- Cubierta: Instalar tapas de canaletas o puntos de acceso, facilitando el acceso a los cables y asegurando al mismo tiempo su protección.
- Fijación: Asegure el sistema de canaletas firmemente en su lugar usando los sujetadores o clips provistos.
- Pruebas: Realice las pruebas necesarias, como comprobaciones de continuidad o integridad del cable, para garantizar una instalación adecuada.
- Etiquetado: Etiquete las secciones o compartimentos de los conductos para facilitar las actividades de identificación y mantenimiento.
- Inspecciones regulares: Realice inspecciones rutinarias del sistema de conductos o canaletas para identificar cualquier signo de daño, desgaste o conexiones sueltas. Revise si hay corrosión, abolladuras o impactos físicos.
- Limpieza: Mantenga el sistema de conductos o canaletas limpio, eliminando cualquier polvo, residuo u obstrucción que pueda acumularse con el tiempo.
- Gestión de cables: Asegúrese de que los cables estén correctamente organizados y asegurados dentro del conducto o sistema de canalización, evitando doblarlos, torcerlos o tensarlos excesivamente.
- Reparación y reemplazo: Repare o reemplace rápidamente secciones de conductos o canaletas, accesorios o cubiertas dañados para mantener la integridad del sistema.
- Protección contra la humedad: Tome medidas para evitar la entrada de agua o humedad en el sistema de conductos o canaletas, como sellar los puntos de entrada o usar juntas impermeables.
- Integridad de la puesta a tierra: Inspeccione y mantenga periódicamente las conexiones a tierra adecuadas dentro del conducto o sistema de canalización para garantizar la seguridad eléctrica.
- Etiquetado y documentación: Mantenga el etiquetado preciso de los cables y documente cualquier cambio o adición al sistema de conductos o canalizaciones para futuras referencias y fines de resolución de problemas.
- Cumplimiento de Códigos y Normas: Asegúrese de que las prácticas de instalación y mantenimiento cumplan con los códigos eléctricos, las reglamentaciones y los estándares de la industria pertinentes.
El mantenimiento regular y el cumplimiento de los procedimientos de instalación adecuados ayudarán a garantizar la longevidad, la seguridad y el rendimiento de los sistemas de conductos y canaletas.
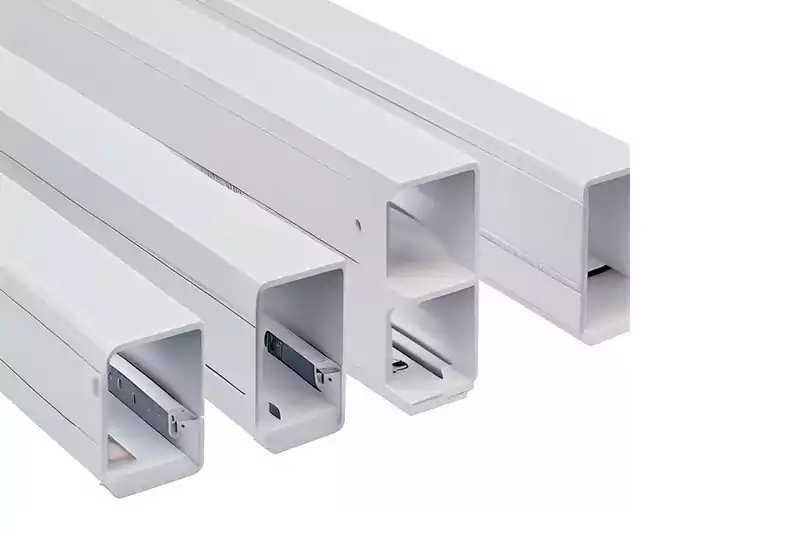

Los conductos se utilizan comúnmente en ambientes exteriores y húmedos, ofreciendo protección contra la humedad y los productos químicos. Son ideales para instalaciones que podrían sufrir modificaciones y se pueden modificar o retirar fácilmente. También son eficaces para minimizar las interferencias electromagnéticas al utilizar sistemas de conductos metálicos.
Las canalizaciones se utilizan a menudo para la distribución de energía en edificios, equipos y patios de maniobras donde se utilizan múltiples cables eléctricos. Son excelentes para la gestión de cables, facilitando su acceso y organización. Los sistemas de canalizaciones son adecuados para aplicaciones que requieren una alta distribución de corriente y donde la estética es importante.

La eficiencia de canalización se refiere a la eficacia y el uso de los sistemas de canalización para gestionar y distribuir eficazmente los cables. Mide la eficacia con la que el sistema de canalización optimiza el espacio y los recursos disponibles, manteniendo al mismo tiempo una gestión eficaz de los cables.
A continuación se presentan algunos factores que contribuyen a la eficiencia del trunking:
Capacidad del cable: La eficiencia de las canalizaciones depende de la capacidad del sistema para acomodar la cantidad y el tamaño de cables necesarios para una aplicación específica. Un sistema de canalizaciones bien diseñado debe tener la capacidad suficiente para gestionar las necesidades de cableado actuales y futuras sin sobrecarga ni congestión excesiva.
Organización del cable: Los sistemas de canalización eficientes garantizan la correcta organización y agrupación de los cables. Esto incluye el uso de accesorios adecuados para la gestión de cables, como bridas, clips o bandejas, para organizar y dirigir los cables de forma ordenada dentro de la canalización. Unos cables bien organizados minimizan el riesgo de enredos, torceduras u obstrucciones, lo que facilita el mantenimiento y la resolución de problemas.
Utilización del espacio: La eficiencia de las canalizaciones también depende de la eficacia con la que se utiliza el espacio disponible. Un sistema de canalizaciones bien diseñado maximiza el uso del espacio disponible, considerando factores como el radio de curvatura de los cables, los requisitos de ventilación y el acceso para mantenimiento. El uso eficiente del espacio garantiza que el sistema de canalizaciones pueda alojar los cables necesarios sin desperdicios ni sobrecargas innecesarias.
Escalabilidad y expansión futura: La eficiencia de la canalización incluye la capacidad del sistema para escalar y adaptarse a futuras ampliaciones o modificaciones de cables. Un sistema de canalización flexible se adapta fácilmente a las necesidades cambiantes, lo que permite la integración fluida de nuevos cables o la eliminación de los obsoletos. Esta escalabilidad minimiza las interrupciones y la necesidad de realizar modificaciones importantes en el futuro.
Accesibilidad y mantenimiento: Un sistema de canalización eficiente facilita el acceso a los cables, lo que permite realizar tareas de mantenimiento, reparaciones o modificaciones de forma rápida y sencilla. Los sistemas de canalización con cubiertas extraíbles o puntos de acceso simplifican la instalación y extracción de cables, lo que reduce el tiempo de inactividad y minimiza las interrupciones en la red o la infraestructura general.
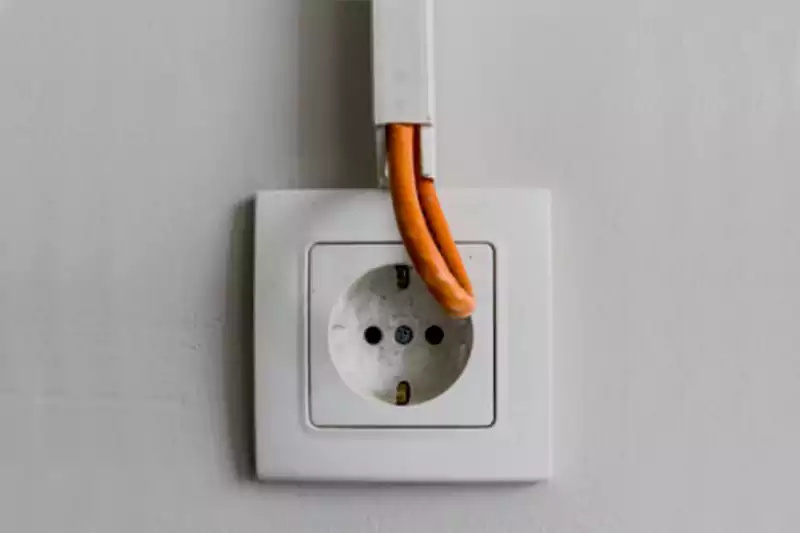

La elección entre bandejas portacables y conductos como diseño de sistema de cableado depende de diversos factores y de los requisitos específicos del proyecto. Ambos sistemas tienen sus ventajas y consideraciones. Las bandejas portacables suelen ser más adecuadas para gestionar grandes volúmenes de cable, ya que ofrecen flexibilidad y rentabilidad. Por otro lado, los conductos ofrecen una protección superior para los cables, blindaje EMI y cumplimiento de ciertas normativas. En algunos casos, se puede utilizar una combinación de sistemas de bandejas portacables y conductos, aprovechando las ventajas de cada sistema para las diferentes secciones de la instalación. Se recomienda consultar con electricistas profesionales y considerar los requisitos y limitaciones específicos del proyecto antes de tomar una decisión.
Los sistemas de conductos y canalizaciones desempeñan un papel fundamental en la gestión de cables eléctricos, ya que proporcionan protección, organización y enrutamiento. Este artículo abordó los puntos clave de estos sistemas. Los conductos encierran y protegen los cables, mientras que los sistemas de canalizaciones facilitan la limpieza y la identificación. Ambos contribuyen a la seguridad al minimizar los riesgos eléctricos. Las opciones de conductos incluyen conductos metálicos rígidos, metálicos intermedios y flexibles, cada uno con aplicaciones específicas. Los sistemas de canalizaciones suelen estar hechos de PVC o metal. Al elegir entre conductos y canalizaciones, se deben considerar los niveles de protección requeridos, los factores ambientales, la facilidad de instalación, el costo y el cumplimiento de la normativa. Se recomienda encarecidamente consultar con electricistas o ingenieros para una correcta selección e instalación del sistema. Los profesionales garantizan el cumplimiento de las normas y regulaciones de seguridad, lo que resulta en una infraestructura eléctrica confiable y segura.
Si tiene más preguntas sobre cables o sistemas de cableado, Ledes está aquí para ayudarle a resolver los problemas de cableado. Envíanos un correo electrónico o Envíe un formulario completo en cualquier momento.



