
Tabla de contenido
The Invisible Thread Binding the Modern World
Picture this: a team of scientists from three continents collaborating in real time to develop life-saving vaccines. A student in a rural village attends a virtual lecture from one of the world’s top universities. A family spread across multiple time zones comes together for a video call, celebrating a loved one’s milestone. These moments, so integral to our modern existence, are made possible by something we rarely think about – the vast and intricate web of telecommunications infrastructure and comms conduit that spans the globe.
At the heart of this infrastructure lies the conducto de comunicaciones, the physical channels that enable data to flow seamlessly between individuals, businesses, and nations. Whether buried beneath city streets, stretched across oceans, or threaded through towering buildings, these conduits are the unsung heroes of our hyper-connected age.
In this post, we will explore the transformative role of communication conduits in shaping how we live, work, and interact. From powering global business operations to bridging cultural divides and fostering innovation, telecom network infrastructure has redefined the possibilities of connection. We’ll uncover its importance in today’s society and examine how this infrastructure will continue to evolve to meet the demands of a rapidly digitizing world.
What Is a Communication Conduit?
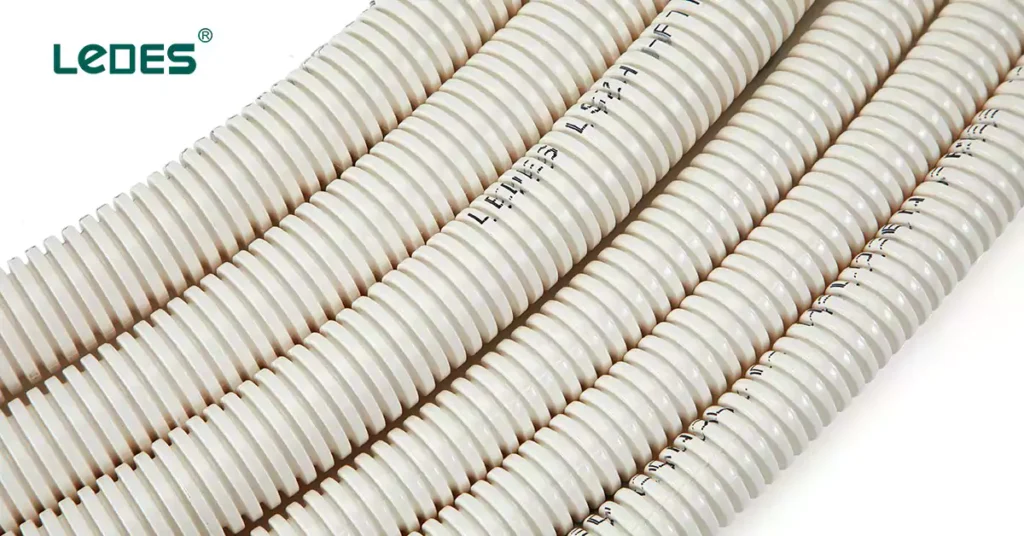

At its core, a communication conduit, often referred to as a comms conduit or telecommunications conduit, is a physical pathway used to house and protect the cables and wiring that transmit data across vast networks. These conduits are essential components of telecom network infrastructure, enabling the reliable and efficient flow of information. Typically constructed from durable materials like PVC, HDPE, or metal, communication conduits shield their contents from environmental elements, physical damage, and interference, ensuring the seamless transfer of data that modern life depends on.
Communication conduits are used across a range of applications, from urban fiber optic networks to rural broadband installations, and even in the deep-sea infrastructure that connects continents. These conduits can be buried underground, run along buildings, or even suspended on poles, forming the backbone of our telecommunications infrastructure.
To fully appreciate the role of communication conduits, it’s essential to understand the related industry terms and the key components that work in tandem to support global connectivity.
If you would like to learn more details, you can read our last post about the types and purposes of communication conduit.
5 Key Components of Telecommunications Infrastructure
Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables are the lifeblood of modern telecom networks. They use strands of glass or plastic fibers to transmit data as pulses of light, offering unparalleled speed and capacity compared to traditional copper cables.
Fiber optic cables are typically encased within communication conduits to protect them from physical damage, weather conditions, and electromagnetic interference. This combination of fiber optics and conduits forms the high-speed highways for data transmission.
Cell Towers
Cell towers serve as critical hubs for wireless communication. They transmit and receive radio signals to and from mobile devices, enabling voice calls, text messages, and mobile internet access.
These towers often rely on fiber optic cables running through communication conduits to connect them to the broader telecom network, ensuring high-speed data transfer between the tower and the core network.
Undersea Cables
Undersea cables are the hidden giants of global connectivity. Stretching across oceans and seas, these cables form the backbone of international telecommunications, carrying around 99% of all transoceanic internet data.
Protected by layers of armor and often laid within specialized conduits on the ocean floor, undersea cables connect countries and continents, enabling everything from video calls to e-commerce.
Satellites
While undersea cables dominate long-distance data transmission, satellites play a crucial role in areas where physical infrastructure is challenging to deploy, such as remote regions, mountainous terrains, and disaster-stricken zones.
Satellites rely on ground stations, connected through communication conduits, to receive and transmit data, creating a bridge between orbiting networks and terrestrial systems.
Routers
Routers are the traffic directors of telecom networks. They manage data flow between devices and networks, ensuring that information reaches its intended destination.
Positioned at key network nodes, routers connect to fiber optic cables housed in communication conduits, forming the critical intersections in data transmission pathways.
The Role of Communication Conduits in Telecom Infrastructure
Communication conduits serve as the protective channels for these components, ensuring their optimal functionality. By housing fiber optic cables, linking cell towers, and forming pathways for other network equipment, conduits enable the seamless operation of telecom systems. Their importance lies in their ability to adapt to diverse environments—be it urban, rural, or underwater—and provide the durability and scalability needed to support the increasing demands of digital connectivity.
As we move further into the digital age, the demand for robust and expansive telecom infrastructure will only grow, and communication conduits will remain a cornerstone of this evolution.
Exploring the Types and Uses of Communication Conduits
Communication conduits, or ducts, are the structural backbone of modern telecom infrastructure, facilitating the secure and efficient transfer of data across vast networks. Their designs and materials vary significantly depending on regional standards, environmental conditions, and intended applications. This section delves into the classifications and uses of communication conduits in three major regions—America, Canada, and Australia—highlighting their unique requirements, material preferences, and industry-specific applications.
1. American Standard Communication Conduits

In the United States, communication conduits are classified by Direct Burial (DB) and Encased Burial (EB) standards, as well as by the materials used. These conduits play a critical role in protecting telecom cables in both underground and encased installations, offering solutions for diverse environmental and mechanical stress conditions.
EB (Encased Burial) Comms Conduit:
- EB20 and EB35 Duct are commonly used in projects where conduits are encased in concrete.
- EB20 has thinner walls and is used for lighter-duty applications.
- EB35 has thicker walls for high-stress environments, such as beneath roadways and heavily trafficked areas.
DB (Direct Burial) Comms Conduit:
- DB60 Duct: A medium-duty conduit used for shallow burial in residential or commercial applications.
- DB120 Duct: A heavy-duty conduit with thicker walls, suitable for deeper burial or under areas subject to heavy loads, such as highways.
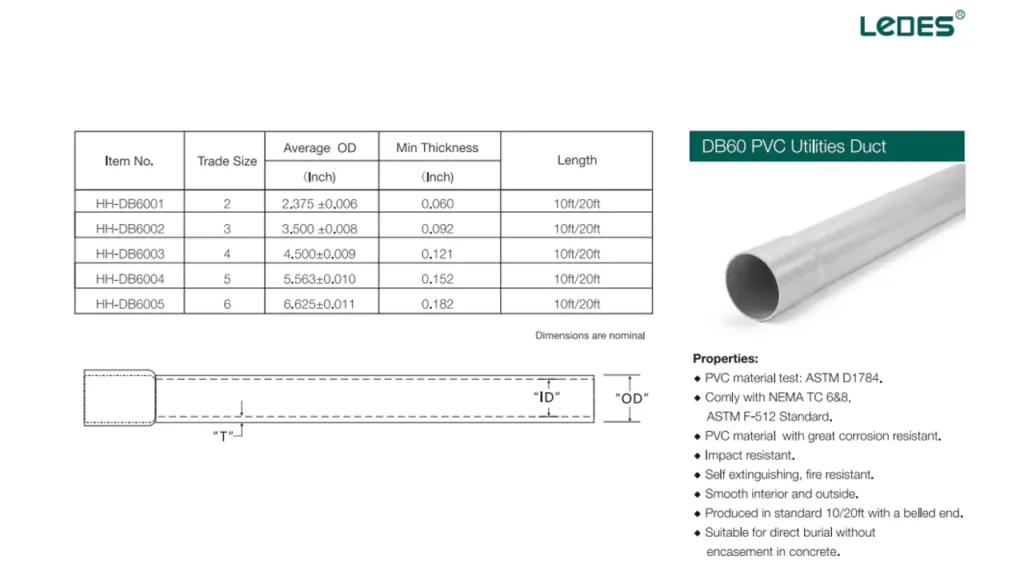
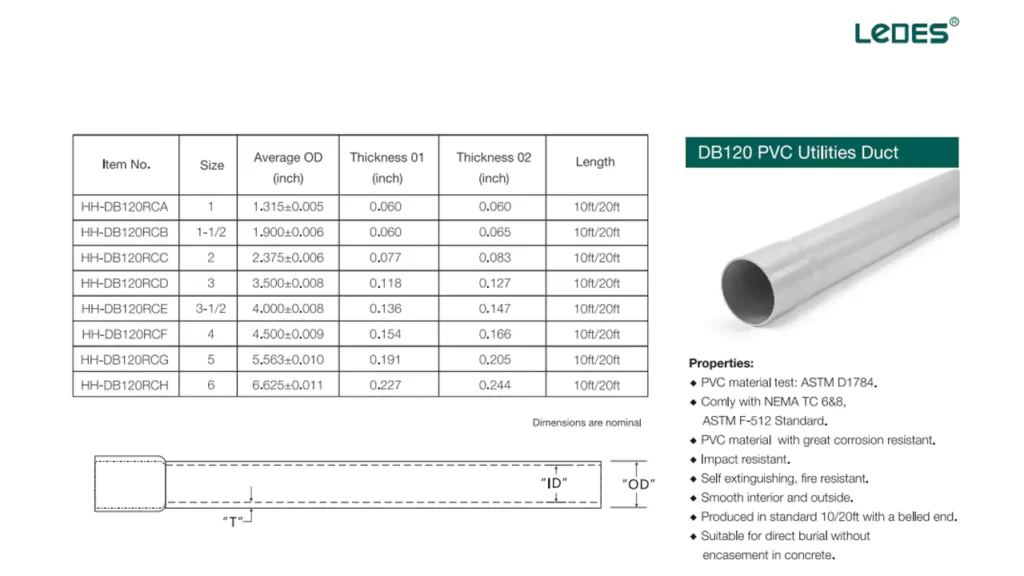
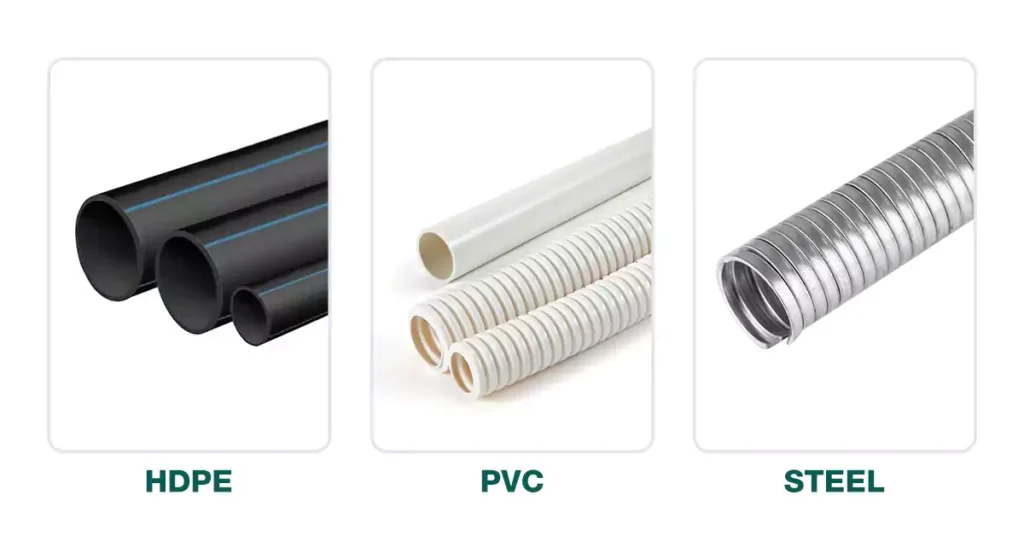
PVC Communication Conduit:
Widely used due to its resistance to corrosion and chemicals, cost-efficiency, and ease of installation.
HDPE Communication Duct:
Flexible and impact-resistant, it is commonly used for long-distance fiber optic networks and trenchless installations.
Steel Communication Conduit:
Durable and highly protective, steel conduits are used in industrial or high-risk environments where maximum mechanical strength is required.

Comm Applications in the United States
Urban Infrastructure: EB ducts like EB35 are used in high-traffic areas where concrete encasement provides added protection.
Long-Distance Telecom Networks: HDPE conduits are preferred for flexible underground deployments, especially in trenchless applications.
Industrial Settings: Steel conduits are used where exposure to mechanical stress or potential damage is high.
2. Canadian Communication Conduits
In Canada, communication conduit standards are tailored to the country’s challenging environmental conditions, such as extreme cold and frost heave. The DB series dominates Canadian telecom conduit standards, providing reliable protection in both urban and remote applications.
DB2 conduit is a lighter-duty conduit used for shallow burial and residential applications.
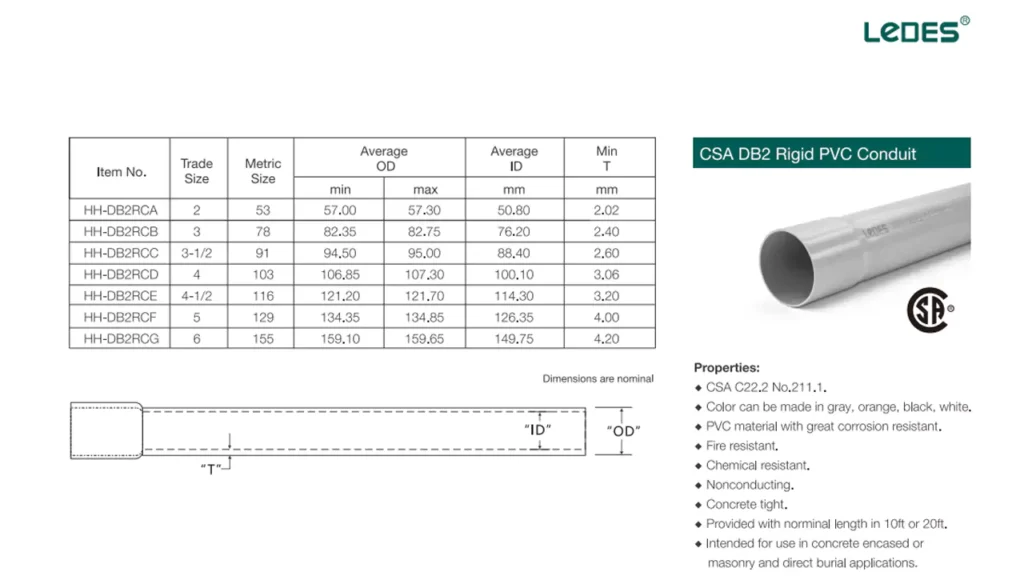
Steel Communication Conduits
Steel conduits are also used in Canada for environments requiring additional mechanical protection, particularly in industrial applications.
Common Applications in Canada
Underground Telecom Networks: DB-rated conduits like DB2 are used for direct burial to protect fiber optic and data cables.
Cold-Climate Installations: Conduits are engineered to resist frost heave and temperature fluctuations, ensuring durability in harsh conditions.
Industrial Environments: Steel conduits are used in heavy-duty or high-risk areas, ensuring maximum protection against physical damage.
3. Australian Communication Conduits
Australia’s vast geography and diverse environmental conditions, ranging from urban centers to remote deserts, require communication conduits that can withstand UV exposure, soil movement, and other challenges. Australian communication conduits adhere to AS/NZS standards, focusing on durability and adaptability.
PVC Comms Conduits
MD Communocation Conduit, including rigid conduit and conducto corrugado are widely used for their UV resistance and durability in outdoor and above-ground installations.
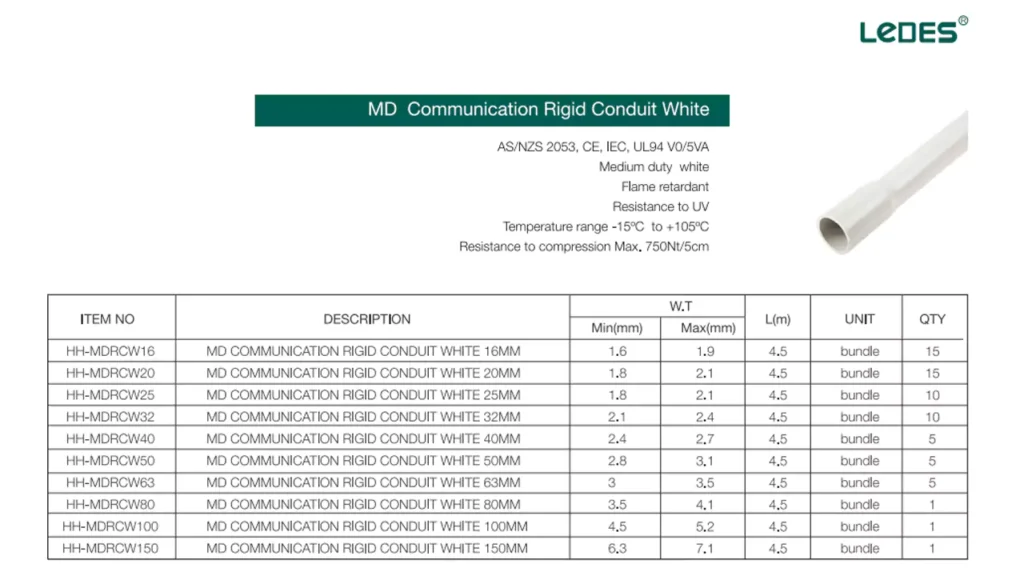
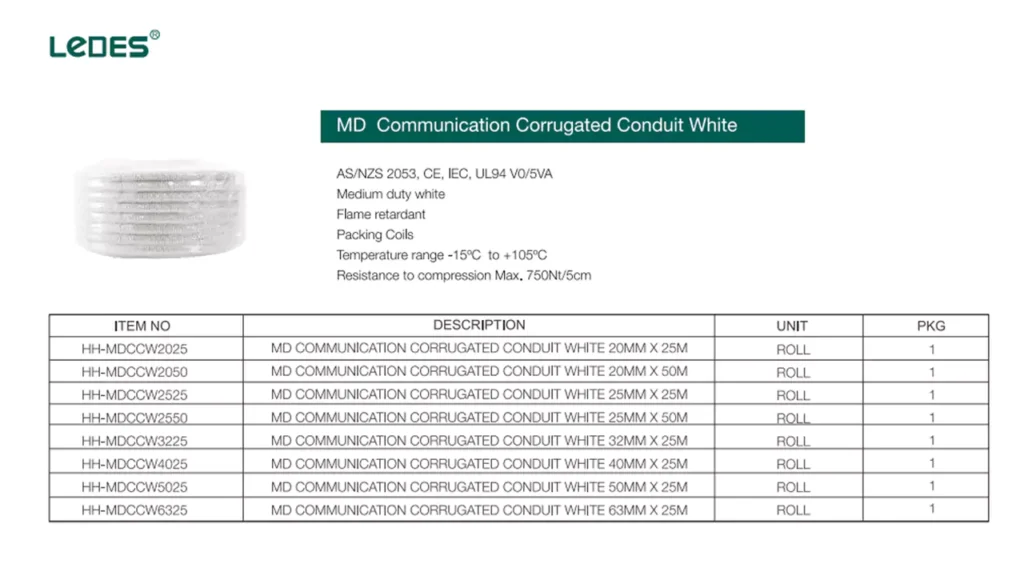
HDPE Comms Conduits
Used in underground installations, providing flexibility for trenchless methods and protection in shifting soils.
Steel Comms Conduits
Deployed in industrial settings or for projects requiring extreme mechanical protection.
Colores
In Australia, the color of communication conduits is often standardized to aid in identification during installation and maintenance. According to guidelines referenced in AS/NZS 2053 and AS 1345, different colors are associated with specific uses:
White: Data and telecommunications conduits.
Grey: Electrical conduits installed above ground.
Orange: Electrical conduits installed below ground.
These color codes simplify the identification of conduits in various environments, ensuring that the appropriate pipes are used for their intended purpose. For example, white conduits are explicitly used for data and telecom purposes, making it easier to distinguish them from electrical conduits in mixed-use installations.
While the AS/NZS 2053 standard does not explicitly mandate color specifications for electrical and communication conduits, other guidelines, such as AS 1345 and PIPA Guideline POP203, offer practical recommendations for color coding based on the location and type of installation.
Why Comms Conduit important in Telecom Infrastructure?
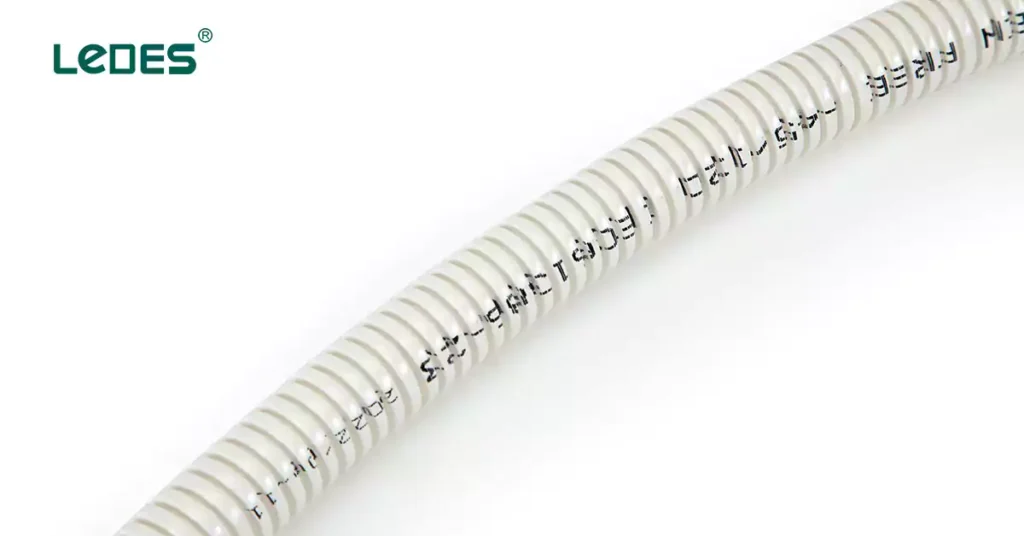

At their core, comms conduits serve a straightforward yet critical purpose: to protect and organize telecom cables. Whether they are buried underground, mounted above ground, or installed within buildings, these conduits shield cables from physical damage, environmental stress, and interference.
Without comms conduits, telecom infrastructure would face frequent failures, increased maintenance costs, and reduced efficiency. The reliability of high-speed internet, uninterrupted mobile services, and robust data centers depends significantly on the proper deployment of communication conduits.
The Role of Comms Conduits in Telecom Infrastructure
The comms conduits play important roles in telecom infrastructure running,
- Protection and Durability:
Conduits protect sensitive fiber optic cables, coaxial lines, and power cables from physical damage, moisture, and environmental wear. Whether buried underground, laid undersea, or installed in urban areas, conduits safeguard the integrity of telecom systems.
- Cable Management:
Efficient cable organization is essential for modern networks. Communication conduits streamline installations, allow for future upgrades, and minimize network disruptions during maintenance or repairs.
- Scalability and Growth:
Telecom networks must evolve to meet growing demands. Conduits enable easy expansion of networks by providing a structured system for adding or replacing cables.
- Versatility in Application:
Whether made of PVC, HDPE, or steel, communication conduits are designed to meet diverse requirements. They can handle high-traffic urban environments, extreme weather conditions, or long-distance data transfers via undersea cables.
Industry Impact of Communication Conduits
Beyond their physical role, communication conduits influence the telecom industry in transformative ways.
- Supporting Business Growth:
For businesses, reliable telecom infrastructure is essential for operations. Conduits enable fast data transmission, facilitating secure e-commerce transactions, seamless video conferencing, and cloud-based services. They empower companies to adopt remote work models, access global talent pools, and enhance productivity.
- Driving Innovation in the Digital Economy:
Communication conduits underpin the digital economy, enabling online platforms, fintech services, and e-learning systems. By supporting fast and secure connectivity, conduits allow startups and enterprises to innovate, expand, and thrive in a highly competitive market.
- Fostering Global Connectivity:
Communication conduits bridge distances, allowing individuals and businesses to connect across the globe. This fosters economic collaboration, cultural exchange, and the sharing of ideas, driving social and economic progress.
- Addressing the Digital Divide:
In underserved areas, where connectivity is limited, conduits play a crucial role in bringing reliable internet and telecom services. Governments and private sectors use these conduits to expand networks, providing more people with access to education, jobs, and healthcare.
- Enabling Emerging Technologies:
Communication conduits are crucial for accommodating the infrastructure needs of 5G networks, smart cities, and the Internet of Things (IoT). These innovations rely on high-speed, low-latency connections, made possible by the protection and efficiency that conduits provide.
- Improving Network Security:
In a world where data breaches are a growing threat, conduits add a layer of physical protection to critical telecom lines. They guard against tampering, environmental hazards, and accidental damage, ensuring secure and reliable data transfer.
The Difference Between Power and Communication Conduits
While power conduits and communication conduits may appear similar in structure and materials, their purposes, designs, and requirements differ significantly. Both play crucial roles in modern infrastructure, but understanding their distinctions is essential for selecting the right solution for specific applications.
1. Purpose and Function
Power Conduits:
Power conduits are designed to house and protect electrical wiring that transmits electricity. They are primarily used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings to ensure safe and efficient electrical distribution. The Conducto Schedule 40 is a typical power conduit, for example.
Example Applications:
Suministro de energía a edificios, maquinaria y alumbrado público.
Sistemas eléctricos en fábricas y grandes instalaciones
Conductos de comunicación:
Los conductos de comunicación protegen los cables de bajo voltaje que se utilizan para transmitir datos, señales y comunicaciones. Estos conductos garantizan la integridad de los cables de fibra óptica, coaxiales o Ethernet en las redes de telecomunicaciones. Los conductos de comunicación típicos son los de tipo EB, DB (EE. UU. y Canadá) y los de PVC blanco de resistencia media (Australia).
Example Applications:
Redes de fibra óptica para internet de alta velocidad
Sistemas de telefonía, televisión y transmisión de datos
Cables de datos submarinos
2. Voltaje y tipos de señal

Power Conduits:
Los conductos eléctricos manejan cables eléctricos de alto voltaje, que generalmente transportan corriente alterna (CA) o corriente continua (CC). Estos voltajes varían desde los de baja potencia residencial (120-240 V) hasta los niveles industriales que superan los 10 kV.
Conductos de comunicación:
Los conductos de comunicación transportan señales de bajo voltaje o pulsos de datos ópticos, generalmente por debajo de los 60 V. Estas señales son más sensibles a las interferencias, por lo que es esencial contar con un blindaje y una separación adecuados.
3. Normas de diseño e instalación
Power Conduits:
Regido por códigos eléctricos como el Código Eléctrico Nacional (NEC) en los EE. UU.. y el Código Eléctrico Canadiense (CEC) en Canadá.
Debe cumplir con estándares de seguridad específicos de capacidad de voltaje, conexión a tierra y aislamiento.
Conductos de comunicación:
Regido por estándares de telecomunicaciones como ANSI/TIA o pautas específicas para cableado de fibra óptica y datos.
A menudo se instalan en vías separadas de los conductos de energía para reducir la interferencia electromagnética (EMI).
4. Separación y blindaje
Power Conduits:
Dado que transportan alto voltaje, los conductos de energía requieren aislamiento y deben colocarse a distancias seguras de equipos electrónicos sensibles para evitar riesgos eléctricos.
Conductos de comunicación:
Debido a que las señales de datos son sensibles a las interferencias, los conductos de comunicación suelen instalarse lejos de los conductos de alimentación. Se utilizan blindaje y conexión a tierra para reducir la interferencia electromagnética y mantener la calidad de la señal.
5. Aplicaciones típicas en la infraestructura moderna
Las aplicaciones comunes de los conductos de energía y comunicación son diferentes,
Diferentes aplicaciones entre conductos de energía y comunicación
Característica | Conductos de energía | Conductos de comunicación |
Propósito principal | Transmisión de energía eléctrica | Transmisión de datos y señales de comunicación |
Ubicaciones comunes | Edificios, fábricas, líneas eléctricas exteriores. | Centros de datos, torres de telecomunicaciones, cables submarinos |
Materiales | PVC, acero, aluminio | PVC, HDPE, polímeros compuestos |
Normas clave | Código nacional de la UE, CEC, IEC | ANSI/TIA, ISO/IEC para sistemas de telecomunicaciones |
Niveles de voltaje | De alta tensión | Señales de bajo voltaje o datos |
6. Importancia de mantenerlos separados
Para garantizar la seguridad y el rendimiento, los conductos de alimentación y comunicación se mantienen separados durante la instalación:
Preocupaciones de seguridad:
Los cables de alta tensión en conductos eléctricos pueden provocar riesgos eléctricos si no están aislados adecuadamente. La separación evita accidentes y fallos en los equipos.
Calidad de la señal:
Las líneas eléctricas pueden generar campos electromagnéticos que provocan interferencias con los cables de comunicación de bajo voltaje. Los conductos de comunicación dedicados mantienen la integridad de las señales de datos.
El cumplimiento del Código:
Los códigos eléctricos y de telecomunicaciones exigen distancias de separación y blindaje para garantizar el cumplimiento y la eficiencia operativa.
Código de conductos de comunicaciones y requisitos de instalación
Comprender los códigos y estándares para conductos de comunicación es esencial para garantizar el cumplimiento, la seguridad y el rendimiento óptimo en la infraestructura de telecomunicaciones. Estas regulaciones rigen todo, desde los materiales utilizados hasta las técnicas de instalación, lo que garantiza la protección y la eficiencia de la red de telecomunicaciones. Aquí, exploraremos los códigos y estándares clave para conductos de comunicación en Australia, Estados Unidos y Canadá, centrándonos en algunos de los más importantes, incluidos NEMA TC-10, NEC y otros estándares nacionales relevantes.
Conducto de comunicaciones de normas australianas

Las normas de Australia sobre conductos de comunicación se describen en varios documentos clave que brindan pautas para la construcción, instalación y uso de conductos en aplicaciones de telecomunicaciones y datos. Las normas australianas clave incluyen:
Normativa de la Unión Europea 2053: Esta norma cubre la instalación de cables de comunicación y proporciona especificaciones para sistemas de conductos de telecomunicaciones, garantizando su seguridad, durabilidad y funcionamiento eficaz. La serie AS/NZS 2053 incluye pautas sobre la instalación de sistemas de conductos tanto para interiores como para exteriores y define su compatibilidad con varios tipos de cables.
Norma AS/NZS 4296: Esta norma se ocupa de la instalación de cableado de telecomunicaciones y de la protección física de los cables, incluido el uso de conductos. Proporciona requisitos para las vías, los soportes y los sistemas de conductos para garantizar el funcionamiento seguro y la fiabilidad a largo plazo de las instalaciones de telecomunicaciones.
Norma AS/NZS 5033: Esta norma aborda principalmente la instalación de sistemas fotovoltaicos (solares), incluidos los requisitos para los cables de comunicación que pueden formar parte de los sistemas de energía solar. Los conductos utilizados en estas instalaciones deben cumplir con las normas de seguridad y compatibilidad con los sistemas eléctricos.
COMO 4702: Esta norma define los requisitos para los cables de comunicación utilizados en instalaciones de fibra óptica, incluida la protección de los conductos contra fuerzas externas. Garantiza que los cables estén adecuadamente protegidos contra daños mecánicos.
Conducto de comunicaciones según normas estadounidenses

En los Estados Unidos, los sistemas de conductos de telecomunicaciones están regulados por un conjunto integral de códigos y normas. Estas normas definen los requisitos físicos, las especificaciones de rendimiento y los métodos de instalación de los conductos de comunicación para garantizar la seguridad, la fiabilidad y la eficacia. Entre las normas clave se incluyen las siguientes:
NEMA TC-6 y TC-8: La Asociación Nacional de Fabricantes Eléctricos (NEMA) proporciona estas normas para conductos de telecomunicaciones. La NEMA TC-6 es para conductos no metálicos como PVC y HDPE, mientras que la NEMA TC-8 es para sistemas de conductos corrugados. Estas normas se centran en el material, el diseño y el rendimiento de los conductos utilizados en la industria de las telecomunicaciones.
NEMA TC-10: Esta norma, emitida por NEMA, se utiliza ampliamente en instalaciones de conductos para telecomunicaciones. NEMA TC-10 se centra en los sistemas de conductos subterráneos que necesitan proporcionar protección adicional para cables y equipos de comunicaciones. La norma cubre el diseño, la construcción y los métodos de prueba para conductos de comunicaciones, con énfasis en la reducción de interferencias electromagnéticas (EMI) y la protección mecánica. También aborda la resistencia al fuego y a la humedad, lo que garantiza que las instalaciones sean seguras y duraderas en el tiempo.
Normas UL (por ejemplo, UL 651A): Underwriters Laboratories (UL) ofrece certificaciones para conductos que cumplen con determinados criterios de seguridad y resistencia al fuego. Por ejemplo, UL 651A cubre los requisitos para conductos rígidos de HDPE utilizados en aplicaciones de telecomunicaciones, garantizando que el material y el diseño del conducto cumplan con los estándares de seguridad.
ASTM F-512: Esta norma ASTM especifica los requisitos para conductos eléctricos y de telecomunicaciones no metálicos, principalmente PVC y HDPE. Establece los criterios mínimos de desempeño, incluyendo resistencia mecánica, resistencia a factores ambientales y prácticas de instalación para un funcionamiento seguro y eficiente.
NEC (Código Eléctrico Nacional): El Capítulo 8 del NEC regula la instalación de cableado de telecomunicaciones y sistemas de conductos de comunicación. Incluye reglas para el tendido de conductos, la conexión a tierra, la unión y la separación de las líneas eléctricas para minimizar el riesgo de incendio o interferencia eléctrica. Este capítulo también define las medidas de seguridad necesarias para el cableado de telecomunicaciones en aplicaciones comerciales, industriales y residenciales.
EIA/TIA 569: La Electronics Industries Alliance (EIA) y la Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) proporcionan pautas para el diseño e instalación de vías y espacios de telecomunicaciones, incluidos conductos. TIA 569 Cubre tanto la instalación física como los factores ambientales que afectan el rendimiento de los conductos, garantizando que los sistemas de cableado de datos sean seguros y eficientes.
Conducto de comunicaciones según normas canadienses
En Canadá, los conductos de telecomunicaciones están regulados por una combinación de normas de la CSA y códigos nacionales que garantizan la seguridad y la funcionalidad. Las principales normas canadienses incluyen:
CSA C22.2 N.º 211.1: Esta norma define los requisitos de construcción y rendimiento para los conductos enterrados directamente que se utilizan para instalaciones de comunicaciones subterráneas. La norma CSA incluye especificaciones para conductos metálicos y no metálicos, abordando su capacidad para soportar tensiones ambientales y garantizando que proporcionen vías seguras para los cables de comunicación. Esta norma garantiza que los conductos cumplan con estrictos criterios de rendimiento para:
Composición del material Para resistir la corrosión química y la degradación.
Propiedades mecánicas como la resistencia al impacto y la resistencia al aplastamiento.
Tolerancia a la temperatura para extremos altos y bajos.
Inflamabilidad para reducir los riesgos en entornos propensos a incendios.
Código Eléctrico Canadiense (CEC):
La CEC establece las normas fundamentales para el diseño, instalación y mantenimiento de sistemas eléctricos y de comunicación. Entre sus numerosas secciones, Sección 12 (Métodos de cableado) y Sección 60 (Sistemas de comunicación eléctrica) Proporcionan una guía fundamental para las instalaciones de conductos de comunicación, garantizando la seguridad, la confiabilidad y el cumplimiento normativo. En conjunto, estas secciones ofrecen un marco integral para proteger los cables de comunicación y permitir la conectividad moderna.
- Sección 12 – Métodos de cableado: La Sección 12 del CEC está dedicada a los métodos de cableado y cubre la instalación de conductores, cables y canalizaciones en diversas aplicaciones. Hace hincapié en la versatilidad y la seguridad, y ofrece reglas detalladas para todo, desde cableado expuesto en exteriores de edificios hasta canalizaciones especializadas como conductos. El objetivo general de la Sección 12 es garantizar que los sistemas de cableado sean duraderos, eficientes y adaptables a las necesidades futuras.
En lo que respecta a los conductos de comunicación, la Sección 12 destaca:
Requisitos materiales: Los conductos deben cumplir altos estándares de durabilidad, con especial atención a la resistencia al estrés ambiental y mecánico.
Compatibilidad con cables: Los conductos del tamaño adecuado son esenciales para alojar los cables de forma segura, lo que permite una instalación sin problemas y futuras actualizaciones.
Separación y enrutamiento: Asegura que los conductos de comunicación estén instalados con una separación adecuada del cableado eléctrico para minimizar la interferencia electromagnética (EMI).
Esta sección subraya que las canalizaciones eléctricas, incluidos los conductos rígidos y flexibles, no son simplemente vías de protección sino componentes integrales de una infraestructura eléctrica segura y eficiente.
- Artículo 60 – Sistemas de comunicación eléctrica: La Sección 60 se centra exclusivamente en los sistemas de comunicación y aborda los desafíos particulares del tendido y la protección de los cables utilizados para datos, voz y señalización. Con la creciente dependencia de una conectividad rápida y confiable en entornos residenciales, comerciales e industriales, esta sección garantiza que los conductos de comunicación cumplan con las demandas modernas de rendimiento y seguridad.
Los aspectos clave de la Sección 60 incluyen:
Protección personalizada: Los conductos de comunicación deben proteger los cables contra daños físicos, exposición ambiental e interferencias de señal.
Adaptabilidad para tecnologías emergentes: Al reconocer el crecimiento de los sistemas de Internet de alta velocidad y de la IoT, la Sección 60 garantiza que los conductos de comunicación sean adecuados para aplicaciones avanzadas.
Cumplimiento de las normas de instalación: Desde instalaciones subterráneas hasta aéreas, esta sección garantiza que los conductos mantengan un rendimiento y una seguridad a largo plazo en diversas condiciones ambientales.
El artículo 60 se basa en los principios del artículo 12 y los aplica específicamente a los sistemas de comunicación. Garantiza que estos sistemas no solo sean funcionales, sino que también estén preparados para el futuro y en consonancia con la creciente demanda de infraestructura digital de Canadá.
¿Conducto o cable enterrado directo para sistemas de fibra óptica?
A la hora de instalar sistemas de fibra óptica, la elección entre cables enterrados y conductos implica tener en cuenta factores como la protección, la escalabilidad, la instalación y los requisitos de mantenimiento. Cada método tiene sus ventajas, pero los conductos ofrecen ventajas notables en términos de longevidad, flexibilidad y menor complejidad operativa.
Instalación y mantenimiento
Los cables de fibra enterrados directamente suelen requerir una armadura metálica para protección física y detección, así como conexión a tierra y unión para protegerse contra peligros eléctricos. Estos pasos pueden agregar complejidad, tiempo y costo al proceso de instalación. Además, cuando llega el momento de terminar el cable, quitar la armadura presenta más desafíos.
Por el contrario, los conductos eliminan la necesidad de blindaje metálico y los requisitos de conexión a tierra asociados. Los conductos proporcionan una vía de protección permanente para los cables de fibra, lo que simplifica el proceso general de instalación. El mantenimiento también se vuelve más manejable, ya que los técnicos pueden acceder fácilmente al conducto para reparar o reemplazar cables dañados sin alterar el entorno circundante.
Durabilidad y mitigación de riesgos
El riesgo de daños a los cables de comunicación durante la construcción o las alteraciones del suelo es significativo, especialmente en zonas urbanas o de mucho tráfico. Los conductos actúan como una barrera protectora robusta, que protege los cables de las agresiones ambientales, como la humedad, los desplazamientos del suelo y las fuerzas mecánicas externas, incluidos los golpes accidentales durante la excavación.
Los cables enterrados directamente, aunque están equipados con cubiertas exteriores duraderas, son inherentemente más vulnerables a estos riesgos. Reparar estos cables no solo es costoso, sino que también requiere tiempo, en particular cuando las interrupciones del servicio dan lugar a sanciones en virtud de los acuerdos de nivel de servicio. Los conductos mitigan estos riesgos al separar físicamente los cables de los peligros potenciales, lo que ofrece tranquilidad en instalaciones de alto riesgo.
Escalabilidad y preparación para el futuro
Una de las ventajas más importantes de los sistemas de conductos es su escalabilidad inherente. La instalación de conductos crea una vía protegida que puede dar cabida a cables de fibra adicionales a medida que aumenta la demanda de la red. Esta flexibilidad elimina la necesidad de excavaciones repetidas o nuevos permisos, lo que ahorra tiempo y recursos. Los conductos también permiten la posibilidad de alquilar capacidad sobrante a otros proveedores de servicios, lo que ofrece un flujo de ingresos secundario para los operadores.
En cambio, para actualizar una red de fibra enterrada directamente es necesario reabrir zanjas y tender cables nuevos, un proceso costoso y que requiere mucho tiempo. A medida que tecnologías como 5G y Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) impulsan la necesidad de un mayor ancho de banda, los sistemas de conductos brindan la adaptabilidad necesaria para satisfacer las demandas cambiantes de manera eficiente.
Enfoques innovadores: soluciones de conductos compactos
Los avances en la tecnología de conductos, como los sistemas de microconductos, han mejorado aún más el atractivo de su uso. Los microconductos son conductos de diámetro más pequeño diseñados para optimizar el espacio y permitir múltiples vías de fibra dentro de una única estructura protectora. Estos sistemas ofrecen:
Optimización del espacio: más cables en un espacio más pequeño, ideal para redes urbanas densas.
Facilidad de enrutamiento: instalación simplificada para aplicaciones distribuidas como backhaul 5G.
Actualizaciones rentables: la capacidad de agregar o reemplazar cables sin alterar la infraestructura general.
Conducto frente a cable enterrado directamente
Aspecto | Conducto | Cable enterrado directamente |
Instalación | Estructurado y optimizado | Simpler initial setup but with added steps |
Protección | High level of mechanical and environmental safety | Moderate, relying on cable construction |
Repair Accessibility | Accessible without excavation | Requires trenching for repairs |
Scalability | Future-ready, supporting additional capacity | Limited and costly to upgrade |
Environmental Conditions | Ideal for unstable or high-risk areas | Suitable for stable, low-risk environments |
Costo | Higher upfront cost; lower long-term expenses | Lower initial cost; higher maintenance and repair costs |
Installation Requirements and Considerations
The installation of communication conduit systems must adhere to various requirements that ensure both safety and reliable performance. Here are the primary considerations and installation guidelines drawn from NEC, ASTM, and other standards:
Material Compatibility: The conduit must be compatible with the type of cable being used, ensuring protection against physical damage, moisture, and electromagnetic interference.
Separation from Power Lines: In many codes, such as the NEC Chapter 8, conduits carrying communication cables must be installed separately from high-voltage power lines to reduce the risk of electrical hazards and signal interference.
Conexión a tierra y unión: Communication conduit systems must be properly grounded and bonded to avoid electrical shock hazards and to ensure signal integrity.
Temperature and Environmental Resistance: Communication conduits must be able to withstand environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations, moisture, and UV exposure. This is particularly important in outdoor or underground installations, as per standards like NEMA TC-10.
Resistencia al fuego: Conduits must meet specific fire-resistance standards, such as those outlined in UL 651A and other relevant fire codes, to prevent the spread of fire and protect telecom infrastructure.
The Evolution of the Comms Conduit

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
The telecom industry has always been in a state of constant evolution, adapting to the increasing demand for faster, more reliable connections and the emergence of new technologies. As the backbone of global communications, communication conduits have undergone significant transformations to meet the ever-growing needs of both consumers and businesses. From the early days of copper wire and basic protection systems to today’s advanced fiber optic networks and smart conduits, the evolution of the comms conduit is closely tied to the technological advances shaping the world.
Rising Demands: A New Era for Connectivity
The demand for faster internet speeds, low-latency communication, and the ability to handle massive amounts of data is at an all-time high. This is due in part to the expansion of 5G networks, which promise to revolutionize connectivity. With ultra-fast speeds and minimal delay, 5G technology is expected to support cutting-edge applications such as autonomous vehicles, virtual reality, and real-time data analytics. As these technologies require more advanced communication systems, the role of comms conduit systems in enabling them becomes even more critical.
Similarly, the expansion of fiber optic networks continues to provide the bandwidth needed for applications like seamless cloud computing, streaming, and the proliferation of the Internet of Things (IoT). Fiber optic cables, which use light to transmit data, require specialized conduits that protect the delicate fibers while maintaining high performance. Over time, fiber optic conduits have evolved to offer enhanced durability, flexibility, and easy installation, helping telecom networks keep pace with the demand for high-speed data transfer.
New Frontiers: Expanding the Reach of Connectivity
One of the most promising developments in the telecom world is the rise of satellite internet solutions. These networks are bridging the digital divide by providing internet access to remote and underserved areas. Through the use of advanced satellite technology, communication conduits are extending their reach far beyond urban centers, ensuring that even the most geographically isolated communities can benefit from reliable internet connections. This is particularly important for rural areas and developing nations, where traditional cable-based infrastructure may be cost-prohibitive or impractical.
Smart Conduits: The Future of Telecom Infrastructure
The future of communication conduits goes beyond physical protection to include smart technology. Smart conduits integrate sensors and monitoring systems that can detect issues such as cable damage, temperature fluctuations, or moisture ingress in real time. This allows telecom companies to proactively maintain their networks, preventing outages and minimizing downtime. As telecom systems become more complex and interconnected, the role of smart conduits in maintaining the integrity of the network becomes increasingly important.
These innovations not only improve the efficiency and longevity of telecom infrastructure but also align with the growing demand for sustainability. The push for environmentally friendly materials is driving the development of more sustainable conduits made from recycled plastics or biodegradable materials. As the world becomes more conscious of its environmental impact, the materials used in telecom conduit systems are evolving to reflect these concerns.
A Connected Future
The evolution of the comms conduit is a testament to the rapidly changing telecom landscape. From simple protective tubes to advanced systems capable of supporting cutting-edge technologies like 5G, fiber optics, and satellite internet, communication conduits are more critical than ever. As we move toward a future where information flows seamlessly across the globe, the role of these conduits will only grow, ensuring that our networks remain fast, reliable, and capable of supporting the innovations of tomorrow
Conclusión
The comms conduit plays a crucial role in our modern world, providing the connections that make everything from video calls to online shopping possible. Although it’s often hidden, it is essential to the way we communicate, do business, and innovate. This network of communication conduits is what connects people, powers economies, and helps new technologies thrive.
We’ve discussed how communication conduits come in different types, like fiber optic cables, HDPE ducts, and steel conduits, each serving specific needs. These conduits ensure fast, reliable connections that support the growth of industries, especially with the rise of 5G networks and satellite internet bringing connectivity to remote areas.
Looking to the future, advancements in smart conduits and sustainable materials will continue to improve telecom infrastructure, enabling new technologies like IoT and AI. As these systems grow, it’s important that everyone has access to the benefits they bring.
We’d love to hear your thoughts on the future of comms conduits and how they might impact your life. And if you have any questions or requirements for communication conduit, contact us at any time.



