Table of Contents
In the world of construction and infrastructure, PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) pipes play a pivotal role. They are widely used for various applications due to their durability, affordability, and versatility. However, within the realm of PVC pipes, there are two distinct types that often cause confusion among users: plumbing PVC and electrical conduit PVC. While they may appear similar at first glance, and many people mistakenly assume that these two types of PVC pipes are interchangeable, but this misconception can have significant consequences. It is crucial to recognize that plumbing PVC and electrical conduit PVC are designed for entirely different applications and possess distinct characteristics that make them suitable for specific purposes. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive understanding of plumbing PVC and electrical conduit PVC, shedding light on their differences and ensuring that users can make informed decisions when selecting the appropriate type for their specific needs.
What is Plumbing PVC Pipe?
Plumbing PVC, also known as PVC-U (Unplasticized Polyvinyl Chloride), is a type of PVC pipe specifically designed for use in plumbing systems. Unlike flexible PVC used in other applications, plumbing PVC is rigid and durable, capable of withstanding high water pressures and temperature variations commonly encountered in plumbing systems.
Plumbing PVC pipes are made from a combination of PVC resin, stabilizers, and other additives to enhance their strength and durability. The absence of plasticizers in plumbing PVC gives it a rigid and non-flexible nature, making it ideal for plumbing applications.
What is PVC Pipe Used for in Plumbing?

- Potable Water Supply: PVC pipes are widely used for carrying potable water in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. They are suitable for both cold and hot water supply lines. PVC pipes are resistant to corrosion, scale, and chemical reactions, making them a reliable choice for delivering clean and safe drinking water.
- Drainage and Waste Systems: PVC pipes are extensively used for drainage and waste systems in buildings. They efficiently transport wastewater and sewage from fixtures, such as sinks, toilets, showers, and washing machines, to the main sewer or septic system. PVC pipes have smooth interiors that facilitate the flow of waste and prevent clogs.
- Ventilation Systems: PVC pipes are commonly employed for ventilation systems in plumbing. Vent pipes are used to remove sewer gases and odors from the plumbing system, ensuring proper air circulation and preventing unpleasant smells in the building. PVC pipes are lightweight, easy to install, and resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for venting applications.
- Irrigation Systems: PVC pipes are widely utilized in irrigation systems for agricultural, residential, and commercial purposes. They are used to distribute water to fields, gardens, and landscaping areas. PVC pipes have excellent resistance to chemicals and UV rays, making them suitable for outdoor applications where exposure to sunlight and soil chemicals is common.
- Industrial Plumbing Applications: PVC pipes are utilized in various industrial plumbing applications, such as chemical processing plants, factories, and manufacturing facilities. They are used for transporting fluids, acids, alkalis, and other chemicals in industrial processes. PVC pipes offer chemical resistance and can handle a range of temperatures, making them suitable for diverse industrial plumbing needs.
What is the Feature of Plumbing PVC Pipe?

Plumbing PVC pipes possess several key features and specifications that make them suitable for plumbing applications:
- Material: Plumbing PVC pipes are made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC), a thermoplastic material known for its strength, durability, and chemical resistance. PVC pipes used in plumbing applications are typically rigid and referred to as “schedule” pipes. The most common types of plumbing PVC pipes include Schedule 40 and Schedule 80.
- Size and Diameter: PVC pipes for plumbing come in a range of sizes and diameters to accommodate different plumbing needs. The sizes are standardized and are typically designated by their nominal pipe size (NPS) or nominal diameter (ND). Common sizes for plumbing PVC pipes range from ½ inch to 12 inches in diameter, with larger sizes available for specific applications.
- Pressure Rating: PVC pipes used in plumbing applications have specific pressure ratings that indicate their ability to withstand internal pressure. The pressure rating is usually expressed in pounds per square inch (psi) and is determined by the thickness of the pipe walls. Common pressure ratings for plumbing PVC pipes include 125 psi, 160 psi, and 200 psi for Schedule 40 pipes, while Schedule 80 pipes have higher pressure ratings.
- Corrosion Resistance: PVC pipes are highly resistant to corrosion, making them an excellent choice for plumbing systems that transport water and other fluids. Unlike metal pipes, PVC pipes do not rust or corrode when exposed to moisture or certain chemicals, ensuring long-term durability and preventing contamination of the transported fluids.
- Smooth Interior: Plumbing PVC pipes have smooth interior surfaces that facilitate efficient flow and prevent clogs. The smooth surfaces minimize friction and turbulence, allowing water and other fluids to flow smoothly through the pipes. This feature helps prevent blockages and maintain the overall performance of the plumbing system.
- Chemical Resistance: PVC pipes exhibit excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals commonly encountered in plumbing systems. They are unaffected by most acids, alkalis, salts, and other chemicals present in water or wastewater. This chemical resistance ensures the longevity of the pipes and minimizes the risk of degradation or failure due to chemical exposure.
- Ease of Installation: PVC pipes are lightweight, making them easy to handle and install. They can be cut, joined, and connected using various methods such as solvent cementing, threaded fittings, or mechanical couplings. PVC pipes often feature standardized socket or bell ends that allow for convenient connections without the need for special tools or complex techniques.
Pros and Cons of Plumbing PVC Pipe
Pros of Plumbing PVC:
Durability: Plumbing PVC pipes are highly durable and resistant to rust, corrosion, and chemical degradation, ensuring a long lifespan.
Affordability: Plumbing PVC pipes are cost-effective compared to other plumbing pipe materials, making them a popular choice for both residential and commercial plumbing projects.
Lightweight: Plumbing PVC pipes are lightweight, making them easy to handle and install, reducing labor and installation costs.
Cons of Plumbing PVC:
Limited Temperature Range: While plumbing PVC pipes can withstand a wide range of temperatures, they have temperature limitations compared to other pipe materials, such as copper or PEX.
Vulnerability to UV Radiation: Plumbing PVC pipes are susceptible to degradation when exposed to prolonged sunlight or UV radiation. Therefore, they should be properly protected or buried underground in outdoor applications.
Plumbing PVC Installation Tips

Proper installation techniques are crucial for the effective performance of plumbing PVC pipes. Some key considerations include:
Cutting and Joining: Plumbing PVC pipes can be easily cut to the desired lengths using a PVC pipe cutter or a hacksaw. They are typically joined using solvent cement, which creates a strong and leak-proof connection.
Support and Alignment: Proper support and alignment are essential during installation to ensure the pipes are secure and aligned correctly. Adequate supports, such as pipe hangers or brackets, should be used to prevent sagging or misalignment.
Expansion and Contraction: Plumbing PVC pipes have a degree of thermal expansion and contraction. Proper allowances should be made for these movements to prevent stress on the pipes and potential leaks.
Plumbing PVC Code Compliance & Regulations
Plumbing PVC pipes must adhere to specific building codes and regulations to ensure safety and compliance. These codes may vary depending on the region or jurisdiction, but they generally cover aspects such as pipe sizing, installation methods, and material standards.
Some common standards include:
ASTM D1785: This is the standard specification for PVC plastic pipe, schedules 40, 80, and 120. It covers the dimensional, performance, and material requirements for PVC pipes used in pressure applications, including water supply and distribution.
NSF/ANSI 14: This standard establishes requirements for plastic pipe and fittings used in potable (drinking) water systems. It covers PVC pipes and fittings that comply with specific health and performance requirements for use in water distribution systems.
NSF/ANSI 61: This standard sets requirements for the chemical leaching and health effects of materials used in drinking water system components, including PVC pipes. It ensures that PVC pipes meet the necessary standards for water quality and safety.
CSA B181.2: This standard, titled “Thermoplastic Drain, Waste, and Vent Pipe and Pipe Fittings,” provides requirements for thermoplastic pipes and fittings used in drain, waste, and vent (DWV) systems in Canada. It covers PVC pipes and fittings, as well as other thermoplastic materials, and establishes specifications for dimensions, materials, performance, and testing methods.
CSA B137.3: This standard, titled “Rigid Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Pipe for Pressure Applications,” specifies requirements for rigid PVC pipes used in pressure applications in Canada. It covers PVC pipes for water distribution, irrigation systems, and other pressure applications, and includes provisions for dimensions, materials, performance, testing, and marking.
International Plumbing Code (IPC): The IPC is a model code adopted by many states and municipalities in the US. It specifies the minimum requirements for plumbing systems, including the use of approved materials, such as PVC pipes, for various plumbing applications.
What is Electrical Conduit PVC?

PVC Electrical Conduit, is a type of PVC pipe specifically designed for electrical installations. It serves as a protective housing for electrical wiring, shielding it from physical damage, moisture, and other environmental factors. PVC electrical conduits non-conductive, meaning it does not conduct electricity, ensuring the safety of the electrical system.
What is the Application of PVC Electrical Conduit?
PVC Electrical Conduit finds extensive use in various electrical applications, some common applications include:
Residential Wiring: PVC electrical conduit is commonly used in residential buildings to protect and route electrical wiring. It is used in both exposed and concealed installations, such as running wiring through walls, ceilings, and floors.
Commercial and Industrial Buildings: PVC conduit finds extensive use in commercial and industrial settings. It is employed for wiring in offices, retail spaces, factories, warehouses, and other structures where electrical systems are required.
Outdoor Installations: PVC conduit is suitable for outdoor applications where electrical wiring needs protection from moisture, sunlight, and other environmental factors. It is commonly used for running electrical lines to outdoor lighting, pumps, air conditioning units, and other outdoor equipment.
Underground Wiring: PVC conduit is often used for underground electrical installations to protect the wiring from soil, moisture, and external damage. It is buried directly in the ground and can be found in applications such as underground electrical service entrances, residential underground feeders, and outdoor lighting systems.
Data and Communication Cabling: PVC conduit is used for routing data and communication cables, such as Ethernet, telephone, and coaxial cables. It provides protection and organization for these cables, ensuring efficient and reliable data transmission.
Solar Power: With the growing popularity of solar power installations, PVC conduit is frequently used to house and protect the electrical wiring in solar panel systems. It helps route the wiring from the panels to the inverters and other components.
What is the Feature of PVC Electrical Conduit

PVC electrical conduit offers several key features that make it a preferred choice for protecting and routing electrical wiring in various applications. Here are some of the key features of PVC electrical conduit:
Durable and Impact-Resistant: PVC conduit is known for its durability and ability to withstand impacts. It provides excellent protection for electrical wiring against physical damage, such as accidental bumps, knocks, or abrasions.
Corrosion-Resistant: PVC is inherently resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor installations. It can withstand moisture, chemicals, and other corrosive elements, ensuring long-term performance and reliability.
Non-Conductive: PVC is a non-conductive material, which means it does not conduct electricity. This property makes PVC conduit an excellent choice for safely routing electrical wiring, reducing the risk of electrical shocks or short circuits.
UV-Resistant: PVC conduit can be manufactured with UV-resistant properties, allowing it to withstand prolonged exposure to sunlight without degrading or becoming brittle. This feature makes it suitable for outdoor applications where protection against UV radiation is required.
Fire-Resistant: Fire-resistant PVC electrical conduit variants are available, providing additional fire protection in applications where fire codes or regulations need to be met.
Lightweight and Easy to Install: PVC conduit is lightweight compared to other conduit materials, making it easier to handle and install. Its lightweight nature reduces installation time and effort, making it a preferred choice for both professionals and DIY enthusiasts.
Cost-Effective: PVC conduit is generally more affordable than other conduit materials, such as metal conduits. Its cost-effectiveness makes it an attractive option for various electrical installations, helping to keep project costs lower.
PVC Conduit Installation Tips
Proper installation techniques are crucial for the effective performance of electrical conduit PVC. Some key considerations include:
Planning and Layout: Before installation, careful planning and layout should be done to determine the best route for the electrical conduit PVC. Consider factors such as accessibility, future expansion, and the specific electrical requirements of the project.
Proper Bending: When necessary, electrical conduit PVC can be bent using heat or specialized PVC conduit bending tools. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and maintain the minimum bending radius to prevent damage to the conduit.
Secure Fastening: Electrical conduit PVC should be securely fastened using appropriate straps, clamps, or hangers at regular intervals to prevent sagging and ensure stability.
PVC Electrical Conduit Code Compliance & Regulations

PVC Electrical Conduit installations must adhere to specific electrical codes and regulations to ensure safety and compliance. Some common followed standards include:
ASTM D1784: This ASTM standard specifies the requirements for PVC resin used in the manufacture of PVC electrical conduit. It ensures that the PVC material used in conduit production meets specific quality and performance standards.
UL651: UL651 is a standard developed by Underwriters Laboratories (UL) that covers PVC conduit and fittings for electrical installations. It provides requirements for the physical properties, performance, and testing of PVC conduit to ensure its suitability for use in various electrical applications.
CSA C22.2 No.211.2: This CSA (Canadian Standards Association) standard pertains to rigid PVC conduit, fittings, and accessories used in electrical installations in Canada. It sets requirements for the dimensions, materials, performance, and testing of PVC conduit to ensure its safety and compliance with Canadian electrical standards.
NEMA TC-2: The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) TC-2 standard covers PVC conduit used for electrical applications in the United States. It establishes requirements for the dimensions, performance, and testing of PVC conduit to ensure its suitability for electrical installations.
NEC (National Electrical Code): The NEC is an electrical code widely adopted in the United States, which provides guidelines for safe electrical installations. It includes requirements for conduit installations, including PVC conduit, related to sizing, routing, grounding, and other safety considerations. Compliance with the NEC is essential to ensure safe and code-compliant PVC conduit installations.
Difference Between Plumbing PVC and Electrical Conduit PVC
When it comes to PVC pipes, it’s important to note the distinct characteristics and purposes of plumbing PVC and electrical conduit PVC. While they may appear similar, they serve different functions and have specific features that make them suitable for their respective applications.
Sizes and Dimensions:
Plumbing PVC pipes are available in a wide range of sizes, typically ranging from ½ inch to 24 inches in diameter, there are also other sizes available. These sizes correspond to standard plumbing requirements for water supply lines, drain lines, and venting systems. Electrical conduit PVC pipes, on the other hand, are generally smaller in diameter, typically ranging from ½ inch to 6 inches. The size of electrical conduit PVC pipes is determined by the number and size of electrical wires they are intended to enclose.
● Wall Thickness:
Plumbing PVC pipes typically have a thicker wall compared to electrical conduit PVC pipes. The increased wall thickness of plumbing PVC pipes is necessary to withstand the high water pressures commonly found in plumbing systems. On the other hand, electrical conduit PVC pipes have a thinner wall since their primary purpose is to protect electrical wiring rather than withstand pressure.
Here are some dimension’s comparison of plumbing Schedule 40 and 80 PVC Pipe and Schedule 40 and 80 Rigid PVC Conduit (part of the sizes):
| Item/Pipe | Sch. 40 PVC Pipe (Inches) | Sch. 40 PVC Electrical Conduit (Inches) | ||||
| Sizes | O.D | Ave. I.D | Min. Wall | Ave. O.D | Min Ave. I.D | Min. Wall |
| 1/2” | 0.840 | 0.602 | 0.109 | 0.840 | 0.578 | 0.109 |
| 3/4” | 1.050 | 0.804 | 0.113 | 1.050 | 0.780 | 0.113 |
| 1” | 1.315 | 1.029 | 0.133 | 1.315 | 1.004 | 0.133 |
| 1-1/4” | 1.660 | 1.360 | 0.140 | 1.660 | 1.335 | 0.140 |
| 1-1/2” | 1.900 | 1.590 | 0.145 | 1.900 | 1.564 | 0.145 |
| 2” | 2.375 | 2.047 | 0.154 | 2.375 | 2.021 | 0.154 |
| 2-1/2” | 2.875 | 2.445 | 0.203 | 2.875 | 2.414 | 0.203 |
| 3” | 3.500 | 3.042 | 0.216 | 3.500 | 3.008 | 0.216 |
| 3-1/2” | 4.000 | 3.521 | 0.226 | 4.000 | 3.486 | 0.226 |
| 4” | 4.500 | 3.998 | 0.237 | 4.500 | 3.961 | 0.237 |
| 5” | 5.563 | 5.016 | 0.258 | 5.563 | 4.975 | 0.258 |
| 6” | 6.625 | 6.031 | 0.280 | 6.625 | 5.986 | 0.280 |
| 8” | 8.625 | 7.942 | 0.322 | — | — | — |
| 10” | 10.750 | 9.976 | 0.365 | — | — | — |
| 12” | 12.750 | 11.889 | 0.406 | — | — | — |
Item/Pipe | Sch. 80 PVC Pipe (Inches) | Sch. 80 PVC Electrical Conduit (Inches) | ||||
Sizes | O.D | Ave. I.D | Min. Wall | Ave. O.D | Min Ave. I.D | Min. Wall |
1/2” | 0.840 | 0.526 | 0.147 | 0.840 | 0.502 | 0.147 |
3/4” | 1.050 | 0.722 | 0.154 | 1.050 | 0.698 | 0.154 |
1” | 1.315 | 0.936 | 0.179 | 1.315 | 0.910 | 0.179 |
1-1/4” | 1.660 | 1.255 | 0.191 | 1.660 | 1.227 | 0.191 |
1-1/2” | 1.900 | 1.476 | 0.200 | 1.900 | 1.446 | 0.200 |
2” | 2.375 | 1.913 | 0.218 | 2.375 | 1.881 | 0.218 |
2-1/2” | 2.875 | 2.290 | 0.276 | 2.875 | 2.250 | 0.276 |
3” | 3.500 | 2.864 | 0.300 | 3.500 | 2.820 | 0.300 |
3-1/2” | 4.000 | 3.326 | 0.318 | 4.000 | 3.280 | 0.318 |
4” | 4.500 | 3.786 | 0.337 | 4.500 | 3.737 | 0.337 |
5” | 5.563 | 4.768 | 0.375 | 5.563 | 4.713 | 0.375 |
6” | 6.625 | 5.709 | 0.432 | 6.625 | 5.646 | 0.432 |
8” | 8.625 | 7.565 | 0.500 | — | — | — |
10” | 10.750 | 9.493 | 0.593 | — | — | — |
12” | 12.750 | 11.294 | 0.687 | — | — | — |
Pressure Rating:
Plumbing PVC pipes are designed with specific pressure ratings, such as Schedule 40 or Schedule 80, indicating their ability to handle different water pressures. These pressure ratings are essential to ensure the integrity and safety of the plumbing system. In contrast, electrical conduit PVC pipes are not pressure-rated since they are not intended to contain fluids under pressure.
Here are the pressure requirements for two most widely used plumbing PVC pipe, Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC Pipe:
Pressure Rating (psi) | ||
Norminal Size | Schedule 40 PVC Pipe | Schedule 80 PVC Pipe |
1/2” | 600 | 850 |
3/4” | 480 | 690 |
1” | 450 | 630 |
1-1/4” | 370 | 520 |
1-1/2” | 330 | 470 |
2” | 280 | 400 |
2-1/2” | 300 | 420 |
3” | 260 | 370 |
3-1/2” | 240 | 350 |
4” | 220 | 320 |
5” | 190 | 290 |
6” | 180 | 280 |
8” | 160 | 250 |
10” | 140 | 230 |
12” | 130 | 230 |
Waterproof:
Plumbing PVC pipes are designed to be watertight since their primary function is to transport water. They are constructed to prevent leaks and maintain the flow of water within the plumbing system. On the other hand, electrical conduit PVC pipes do not require the same level of waterproofing since their primary purpose is to protect electrical wiring from physical damage and environmental factors.
Color:
One obvious difference between plumbing PVC pipe and PVC electrical conduit is their colors. Plumbing PVC pipe is usually in white color, but Schedule 80 PVC pipe is usually dark gray. On the other hand, PVC electrical conduit is usually gray, they are light gray not as Schedule 80 PVC pipe’s dark gray. Manufacturers could add different chemicals to create different colors of pipe and conduit.
Fittings:
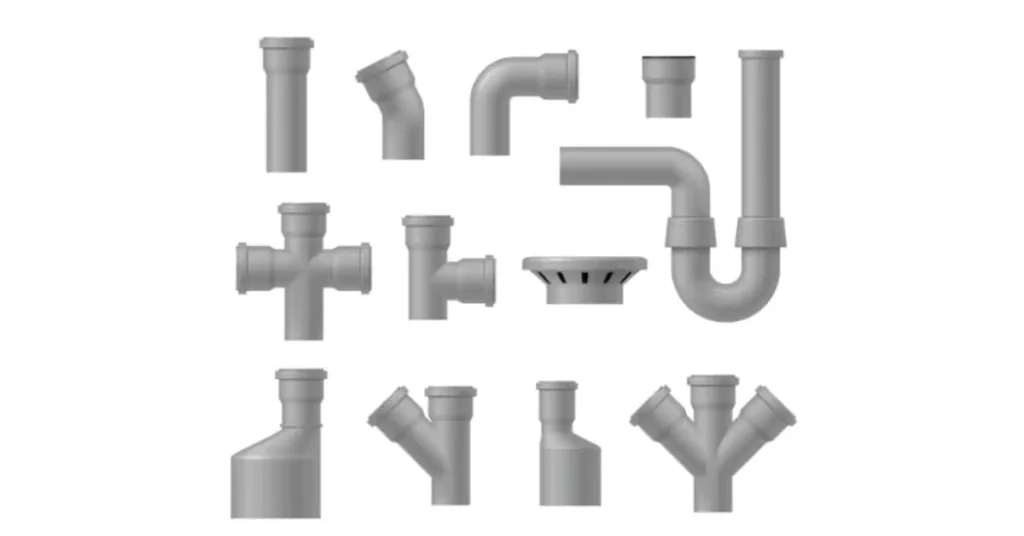
Plumbing PVC and electrical conduit PVC pipes use different types of fittings. Plumbing PVC fittings are designed for water-tight connections and include options such as couplings, elbows, tees, and valves. Electrical conduit PVC fittings, on the other hand, are specifically designed for electrical installations and include connectors, couplings, conduit bodies, and boxes that allow for the proper routing and connection of electrical wires.
Applications:
Plumbing PVC pipes are intended for use in plumbing systems, such as water supply lines, drain lines, and ventilation systems in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. They are compatible with various plumbing fixtures and appliances. Electrical conduit PVC pipes, on the other hand, are used to protect electrical wiring in applications such as residential electrical systems, commercial buildings, and outdoor installations. They are compatible with electrical wires, cables, and electrical boxes.
Can You use Plumbing PVC for Electrical Conduit?

Misusing plumbing PVC or electrical conduit PVC can lead to various consequences, it is essential to understand the potential risks associated with using these types of PVC pipes inappropriately to avoid costly and dangerous outcomes.
Water Pressure Issues:
One of the significant consequences of misusing plumbing PVC or electrical conduit PVC is water pressure problems. Plumbing PVC pipes are specifically designed to handle the high water pressures commonly found in plumbing systems. They have thicker walls and higher pressure ratings to ensure the integrity and functionality of the system. If electrical conduit PVC pipes, which have thinner walls and lack pressure ratings, are used in plumbing applications, they may fail under the sustained water pressure. This can result in burst pipes, leaks, and water damage to the surrounding areas.
Leaks and Water Damage:
Misusing plumbing PVC or electrical conduit PVC can result in leaks and water damage. Plumbing PVC pipes are engineered to be watertight, ensuring the proper containment and flow of water within the plumbing system. In contrast, electrical conduit PVC pipes are not designed with the same level of waterproofing. Using electrical conduit PVC pipes in plumbing applications can lead to leaks due to the lack of proper seals and connections. Prolonged exposure to water leaks can cause structural damage, mold growth, and costly repairs.
Safety Hazards:
Using plumbing PVC in place of electrical conduit PVC or vice versa can create significant safety hazards. Plumbing PVC pipes are not designed to withstand electrical currents and may pose a risk of electrical shock or fire when used for electrical wiring. Similarly, electrical conduit PVC pipes are not intended to handle the high water pressures typically found in plumbing systems. Using electrical conduit PVC for plumbing applications can result in burst pipes, water leaks, and property damage.
Increased Maintenance and Repair Costs:
Misusing PVC pipes can significantly increase maintenance and repair costs in the long run. Water pressure issues, reduced flow, leaks, and water damage often require extensive repairs and replacements. Fixing or replacing incorrectly installed or incompatible PVC pipes can involve significant expenses, including labor costs, material costs, and potential damage to other components of the plumbing system.
Code Violations:
Using plumbing PVC or electrical conduit PVC pipes incorrectly can result in code violations. Building codes and regulations specify the appropriate materials and installation methods for plumbing and electrical systems. Deviating from these guidelines and using the wrong type of PVC pipe can lead to non-compliance with code requirements. Code violations may result in penalties, the need for costly corrections, or difficulties in obtaining insurance coverage.
To avoid water pressure problems and associated consequences, it is crucial to use plumbing PVC pipes specifically designed for plumbing applications. Adhering to plumbing codes and regulations, consulting with professionals, and ensuring proper installation will help maintain the integrity of the plumbing system, prevent water pressure issues, and minimize the risk of damage or safety hazards.
Is PVC Pipe Safe for Drinking Water?
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) pipes are commonly used for various applications, including plumbing systems. When it comes to using PVC pipes for drinking water, it is important to consider certain factors to ensure their safety and suitability for this purpose.
PVC pipes manufactured specifically for plumbing applications are typically safe for transporting drinking water. However, it is vital to use PVC pipes that are approved for potable (drinking) water by regulatory authorities, such as the National Sanitation Foundation (NSF) in the United States. These certified PVC pipes undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet specific safety and performance standards.
However, it is important to note that the safety of PVC pipes for drinking water can be influenced by various factors, including the quality of the water supply, temperature, and the presence of certain chemicals. PVC pipes may not be suitable for conveying extremely hot water or water containing high levels of certain chemicals or solvents. In such cases, alternative materials like CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride) or PEX (Cross-linked Polyethylene) pipes may be more appropriate.
When using PVC pipes for drinking water, it is crucial to follow proper installation practices, including using approved fittings, ensuring adequate support, and avoiding excessive bending or stress on the pipes. Regular maintenance and periodic inspections are also important to detect any potential issues, such as leaks or degradation, that could affect the water quality.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between plumbing PVC and electrical conduit PVC is essential for selecting the appropriate type of PVC pipe for specific applications. Throughout this article, we have discussed the key distinctions between these two types of PVC pipes in terms of sizes and dimensions, pressure ratings, waterproofing, color, design and construction, as well as fittings.
Using the correct type of PVC pipe for a specific application is of utmost importance. Misusing plumbing PVC or electrical conduit PVC can result in many safety problems and increase maintenance costs. When choosing the right pipe, adhering to building codes and regulations, consulting with professionals, and following manufacturers’ guidelines to ensure the proper selection and installation of plumbing PVC or electrical conduit PVC pipes.
Any questions, please contact us at any time.



