
Table of Contents
Electrical systems form the backbone of modern infrastructure, powering our homes, offices, and industries. Within these systems, various components play crucial roles in ensuring safe and efficient electrical installations. Among these components, electrical raceways, conduit, cable trays, and electrical fittings are essential elements that facilitate the distribution and protection of electrical wiring. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of electrical raceways, conduit, cable trays, and electrical fittings, exploring their definitions, significance, and the various aspects involved in their selection, installation etc.
What is an Electrical Raceway?
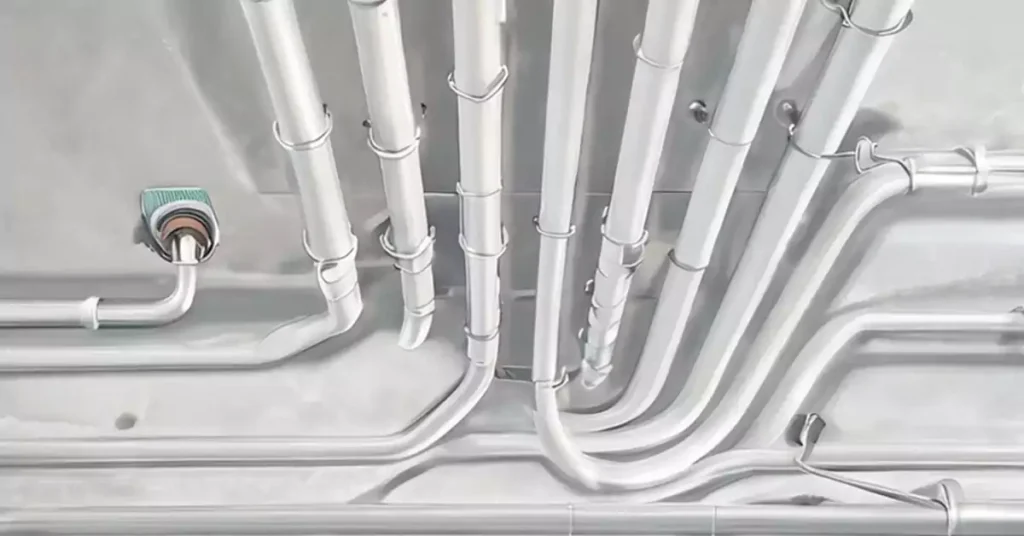

Electrical raceways serve as protective pathways for electrical wires and cables, ensuring safe and organized installations. They protect wires from damage, enhance safety, promote organization, and offer flexibility for future modifications.
A well-designed electrical raceway system offers several benefits, including:
Protection: Electrical raceways shield wires and cables from physical damage, moisture, chemicals, and other external elements. This protection is crucial in harsh environments where wires may be exposed to corrosive substances or mechanical stress.
Safety: By containing electrical conductors within a raceway, the risk of accidental contact or electrical shock is significantly reduced. Raceways provide an added layer of insulation and protection to prevent electrical mishaps.
Organization: Raceways enable the neat and orderly arrangement of wires and cables, minimizing clutter and simplifying maintenance and troubleshooting tasks. This organization enhances the efficiency and accessibility of electrical systems.
Flexibility: Electrical raceways allow for easier modifications, additions, or rerouting of electrical circuits. They offer the flexibility to adapt to changing requirements without the need for extensive rewiring.
Electrical raceways are typically made of metal or non-metallic materials and come in various forms, such as conduits and cable trays. Raceways provide mechanical protection, prevent damage to wires, and offer a neat and organized wiring system. We are going to introduce mainly about the electrical conduit and cable tray two different wiring methods in this article.
Conduit is a type of electrical raceway that provides a protective pathway for electrical conductors. It is commonly used in both residential and commercial settings to route and safeguard electrical wires and cables. Conduit serves multiple purposes:
Protection: Conduit offers physical protection to wires and cables, shielding them from impact, moisture, and other environmental hazards. It prevents accidental damage and extends the lifespan of the electrical system.
Routing: Conduit provides a clearly defined pathway for electrical conductors, ensuring organized and structured installations. It simplifies troubleshooting, maintenance, and future modifications.
Grounding: Metallic conduit, when properly installed and bonded, can serve as an effective grounding pathway, reducing the risk of electrical shocks and providing fault current paths.
4 Common Types of Electrical Conduits
There are four common types of conduit: Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC), Intermediate Metal Conduit (IMC), Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT), and PVC Conduit. Select the appropriate conduit type based on factors like durability, flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and resistance to environmental factors.
Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC):
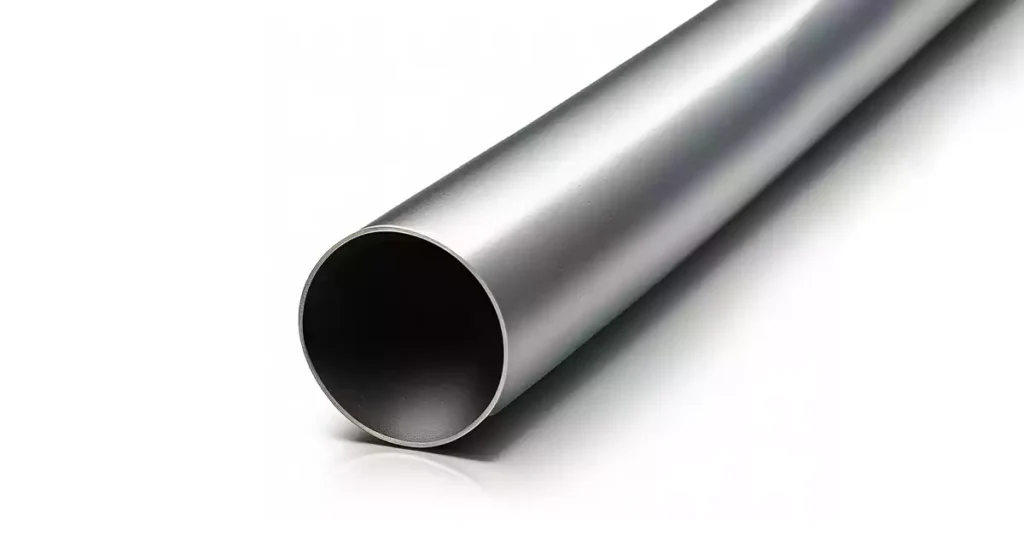

RMC is a heavy-duty conduit made of steel. It provides superior mechanical protection and is highly resistant to impact and compression. RMC is commonly used in industrial and commercial settings where durability and robustness are critical.
Features: Heavy-duty, thick-walled conduit with threaded ends for secure connections. Provides the highest level of mechanical protection and excellent electromagnetic shielding.
Benefits: Superior durability, impact resistance, and EMI protection. Ideal for industrial and high-risk environments.
Considerations: Requires specialized tools for cutting and threading. Susceptible to corrosion without proper coatings. Relatively higher installation labor and cost.
Intermediate Metal Conduit (IMC):
IMC is a lighter-weight conduit also made of steel. It offers similar mechanical protection to RMC but with greater flexibility and ease of installation. IMC is often used in commercial and industrial applications where moderate physical protection is required.
Features: Lighter-weight than RMC with a thinner wall. Uses threaded connections or compression fittings for easy installation.
Benefits: Good mechanical protection while offering greater flexibility and cost-effectiveness compared to RMC. Suitable for commercial and industrial applications.
Considerations: Requires proper grounding for effective fault current paths. Vulnerable to corrosion in certain environments.
Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT):
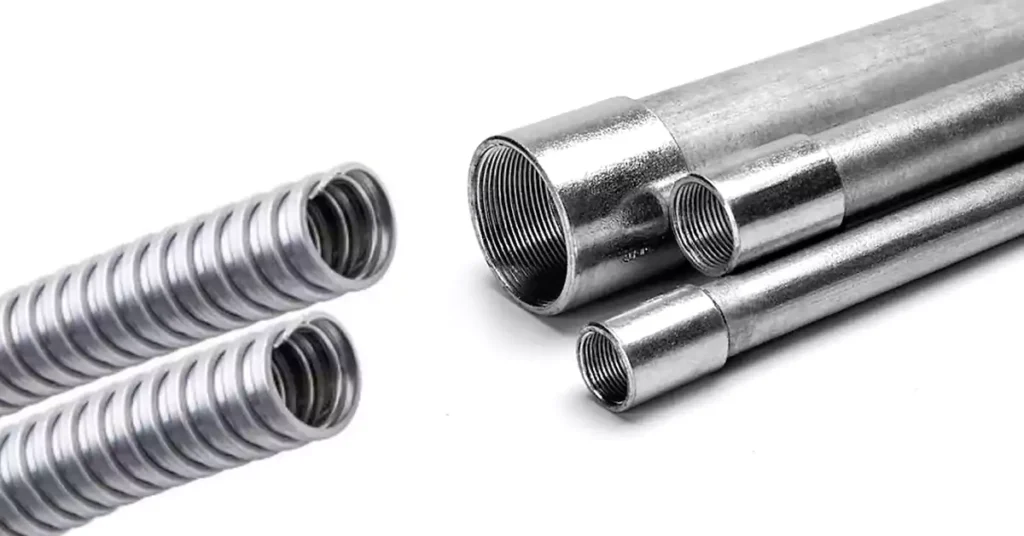

EMT is a thin-walled conduit made of galvanized steel or aluminum. It is lightweight, easy to install, and highly cost-effective. EMT is commonly used in residential and commercial settings where moderate mechanical protection is sufficient.
Features: Thin-walled conduit with a smooth interior for easy wire pulling. Uses compression fittings or set-screw connectors for quick installation.
Benefits: Lightweight, cost-effective, and easy to work with. Ideal for residential and commercial applications where moderate mechanical protection is sufficient.
Considerations: Offers limited protection in harsh environments or areas prone to physical damage.
PVC Conduit:
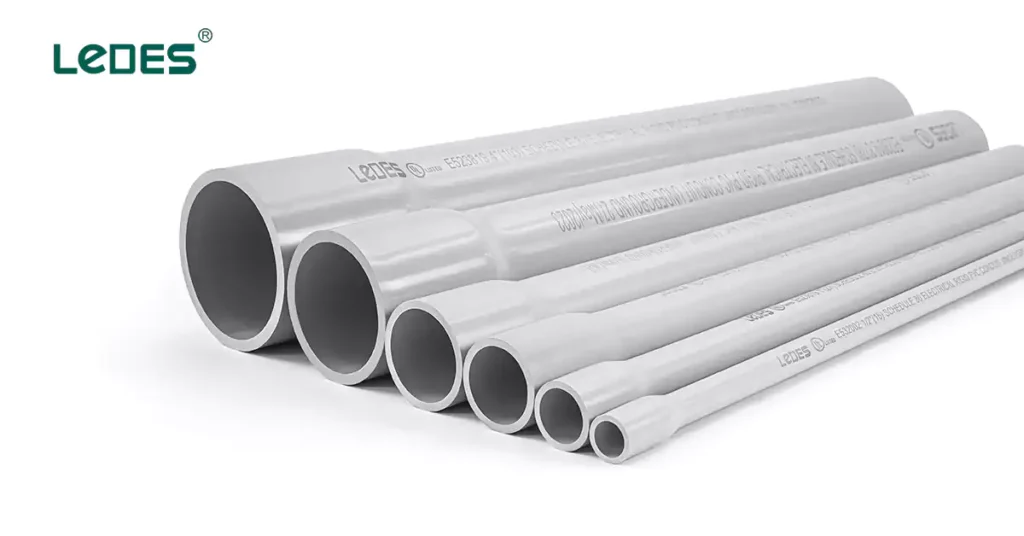

PVC conduit is a non-metallic conduit made of polyvinyl chloride. It is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and offers excellent chemical resistance. PVC conduit is widely used in residential and commercial applications where moderate mechanical protection is required.
Features: Non-metallic conduit made of PVC, available in various sizes and configurations. Utilizes solvent-welded or push-fit connectors for straightforward installation.
Benefits: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and cost-effective. Offers excellent chemical resistance and is suitable for above-ground installations.
Considerations: Limited mechanical strength and reduced resistance to extreme temperatures compared to metallic conduit.
10 Tips Installation Guidelines and Best Practices for Conduit
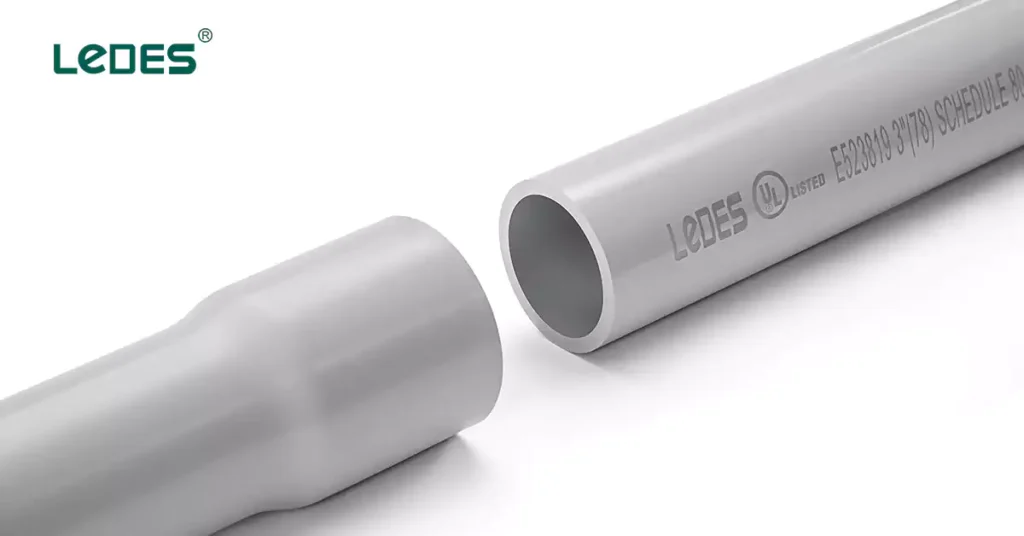

Follow Installation Guidelines and Best Practices for Conduit: Proper installation of conduit is essential for safety and performance. Plan the conduit pathway, consider sizing, ensure secure mounting and support, make accurate connections and fittings, ground the conduit for electrical safety, pull and secure wires, seal the conduit, label the runs, and inspect and test the installation before energizing the system.
- Route Planning: Determine the optimal conduit pathway, considering accessibility, routing constraints, and clearance requirements. Plan for expansion and future maintenance needs.
- Sizing: Select the appropriate conduit size based on the number and size of conductors to be installed. Ensure sufficient space for future expansions. Adhere to local electrical codes and regulations.
- Mounting and Support: Securely attach the conduit to walls, ceilings, or other structural elements using appropriate supports and fasteners. Ensure proper support spacing to avoid sagging or excessive stress. Use clamps or hangers designed for conduit.
- Bending and Cutting: Use specialized tools to correctly bend conduit to the required angles. Follow bending tables or guidelines provided by the conduit manufacturer. Cut conduit to the desired lengths using appropriate cutting tools.
- Connections and Fittings: Use approved connectors, couplings, and fittings suitable for the conduit type. Ensure proper alignment and tight connections. Follow manufacturer instructions for installation.
- Grounding: Ensure proper grounding of metallic conduit to provide effective fault current paths and reduce the risk of electrical shocks. Bond the conduit to grounding conductors using approved methods.
- Pulling and Securing Wires: Install wires and cables inside the conduit carefully to avoid damage. Use appropriate lubricants and pulling tools to minimize friction. Secure the wires at regular intervals to prevent movement and minimize stress on connections.
- Sealing: Seal conduit fittings and connections to prevent the ingress of moisture, dust, or other contaminants. Use approved sealing materials or methods suitable for the specific conduit type and environmental conditions.
- Labeling: Properly label conduit runs and junction boxes for easy identification and troubleshooting. Use permanent markers or labels that withstand environmental conditions.
- Inspection and Testing: Conduct thorough inspections of the conduit installation before energizing the system. Perform continuity and insulation resistance tests to ensure proper electrical connections and safety.
What is the Elctrical Conduit Applications
Electrical Conduit finds various applications in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. Here are some common examples:
Residential Applications:
– Routing electrical wiring in new home construction or renovation projects.
– Protecting electrical conductors in outdoor installations, such as landscape lighting or electric vehicle charging stations.
– Securing and organizing cables for home theater systems or computer networks.
Commercial Applications:
– Installing electrical systems in office buildings, retail stores, and educational institutions.
– Routing power and control wiring for HVAC systems, lighting fixtures, and security systems.
– Connecting electrical equipment in data centers or server rooms.
Industrial Applications:
– Managing power distribution in manufacturing facilities and industrial plants.
– Protecting electrical wiring in hazardous environments, such as chemical plants or oil refineries.
– Routing control and instrumentation wiring for industrial machinery and equipment.
What is the Standards for Electrical Conduit
Standards organizations like UL, CSA, NEMA, and IEC provide testing and certification services to ensure safety, performance, and compatibility of electrical conduit.
UL (Underwriters Laboratories): UL is a global safety certification company that provides testing and certification for various electrical products, including conduit. UL standards ensure that the conduit meets specific safety and performance requirements.
CSA (Canadian Standards Association): CSA is an independent organization that develops standards and provides testing and certification services for electrical products in Canada. CSA standards ensure that the conduit meets Canadian safety and performance requirements.
NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association): NEMA is an association of electrical equipment and medical imaging manufacturers. NEMA provides standards for conduit and other electrical products to ensure compatibility, safety, and performance.
IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission): IEC is an international standards organization that develops and publishes standards for various electrical technologies. IEC standards are recognized worldwide and ensure global consistency and interoperability.
Complying with these standards helps ensure the quality and reliability of conduit installations, providing peace of mind and meeting regulatory requirements in different regions.
Cable Tray
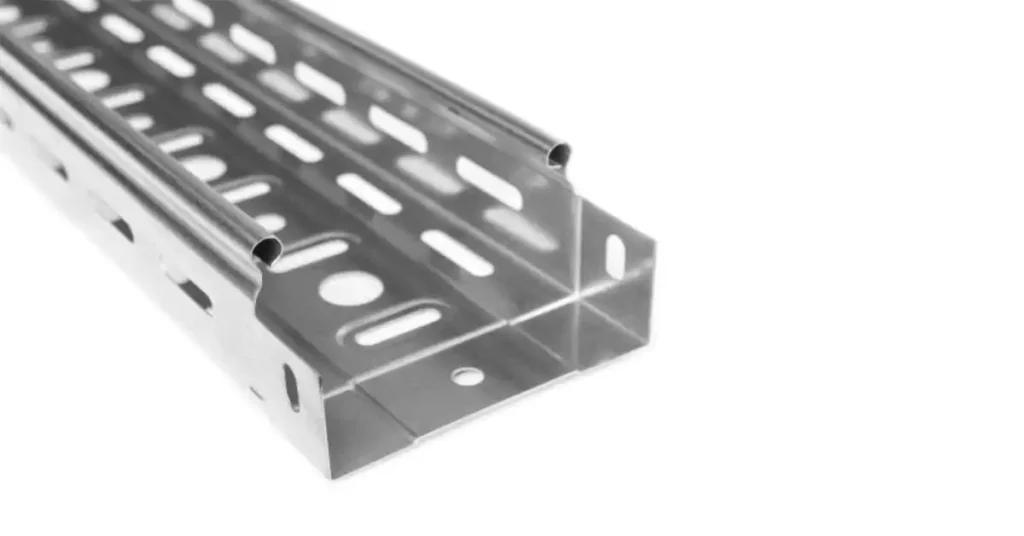

Cable trays are support systems used in electrical installations to organize and protect cables and wires. They offer cable management, mechanical protection, electromagnetic compatibility, and accessibility for maintenance and troubleshooting.
The purposes of cable trays in electrical installations include:
Cable Management: Cable trays offer a structured pathway for routing and supporting cables, keeping them organized and preventing tangling or damage.
Mechanical Protection: Cable trays shield cables from external hazards, such as impact, abrasion, or environmental factors, ensuring their longevity and reliability.
Electromagnetic Compatibility: Cable trays can help manage electromagnetic interference (EMI) by separating and grounding cables appropriately.
Accessibility and Maintenance: Cable trays provide easy access to cables for maintenance, troubleshooting, and future installations or replacements.
6 Different Types of Cable Trays
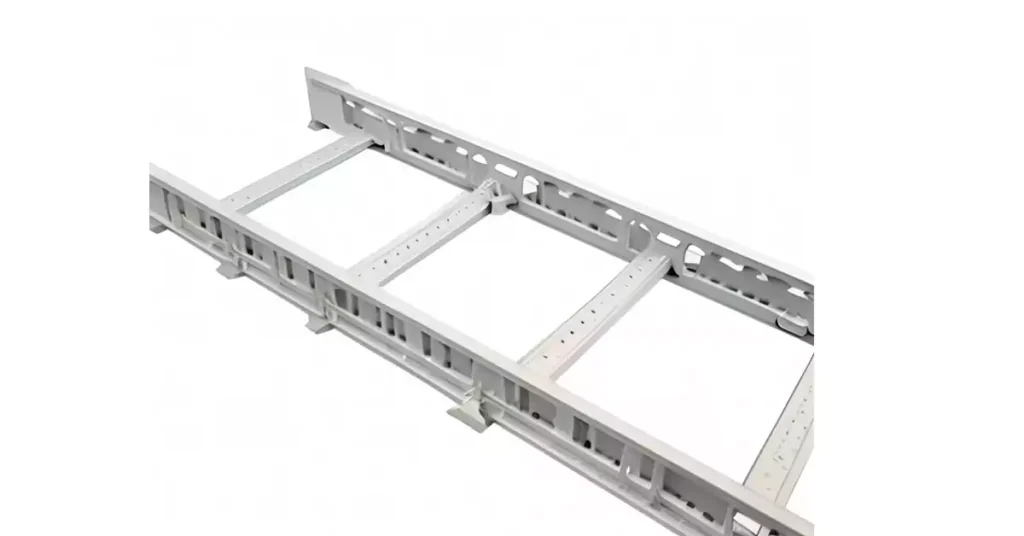

There are six types of cable trays: Ladder Cable Trays, Solid-Bottom Cable Trays, Ventilated Cable Trays, Wire Mesh Cable Trays, Channel Cable Trays, and Trough Cable Trays. Each type has its own design and construction features, making them suitable for specific applications and environmental conditions.
Ladder Cable Trays: Ladder cable trays consist of two longitudinal side rails connected by rungs, resembling a ladder-like structure. They offer excellent ventilation and easy access from the top and bottom.
Solid-Bottom Cable Trays: Solid-bottom cable trays have a solid base that provides additional protection against dust, dirt, and moisture. They are suitable for environments where cable protection from external elements is crucial.
Ventilated Cable Trays: Ventilated cable trays have perforations or slots along their length, allowing for increased airflow and heat dissipation. They are often used in areas where cable cooling is essential, such as high-temperature environments.
Wire Mesh Cable Trays: Wire mesh cable trays feature a grid-like structure made of interconnected wires. They provide good cable visibility, flexibility, and airflow while maintaining cable support and protection.
Channel Cable Trays: Channel cable trays have a U-shaped design and are suitable for lightweight cables or conduits. They offer easy cable access from the top.
Trough Cable Trays: Trough cable trays have a deep, rectangular cross-section, making them ideal for managing a large number of cables or bulky cables.
Advantages of Cable Trays:
Cable trays offer flexibility and scalability, improved airflow, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness compared to conduit. However, they may expose cables to external elements and provide limited physical protection.
Flexibility and Scalability: Cable trays allow for easier reconfiguration and future cable additions or modifications, providing flexibility to adapt to changing electrical needs.
Improved Airflow: Cable trays with ventilation enable better airflow around cables, reducing the risk of overheating and improving cable performance.
Accessibility: Cable trays offer easy access to cables, simplifying maintenance, troubleshooting, and upgrades.
Cost-Effective: Cable trays can be more cost-effective than conduit systems, especially for installations requiring a large number of cables.
Disadvantages of Cable Trays:
Exposure to External Elements: Cable trays may expose cables to dust, moisture, and other environmental factors, requiring proper cable selection and periodic inspections.
Limited Protection: Compared to conduit, cable trays provide less physical protection against impact and external hazards.
Visibility: In some cases, cable trays may make it more challenging to visually trace cables’ paths compared to conduit systems.
7 Things You Need to Know Before Selecting and Installing Cable Trays
When selecting and installing cable trays, consider the following factors:
- Load Capacity: Ensure the selected cable tray has sufficient load-bearing capacity to support the weight of the cables and any additional loads that may be applied.
- Environmental Conditions: Choose cable trays suitable for the specific environment, considering factors such as temperature, moisture, corrosive substances, and UV exposure.
- Cable Type and Size: Select cable trays that can accommodate the types and sizes of cables being installed. Consider future cable expansion needs.
- Installation Location: Determine whether the cable tray will be installed indoors, outdoors, or in a hazardous location, and choose appropriate materials and coatings accordingly.
- Support and Mounting: Ensure proper support and mounting methods are used to securely attach the cable tray to walls, ceilings, or other structures. Consider expansion and contraction due to temperature changes.
- Grounding and Bonding: Follow grounding and bonding requirements to maintain electrical safety and minimize electromagnetic interference.
- Code Compliance: Adhere to local electrical codes, regulations, and industry standards when selecting and installing cable trays.
5 Commons Cable Tray Applications
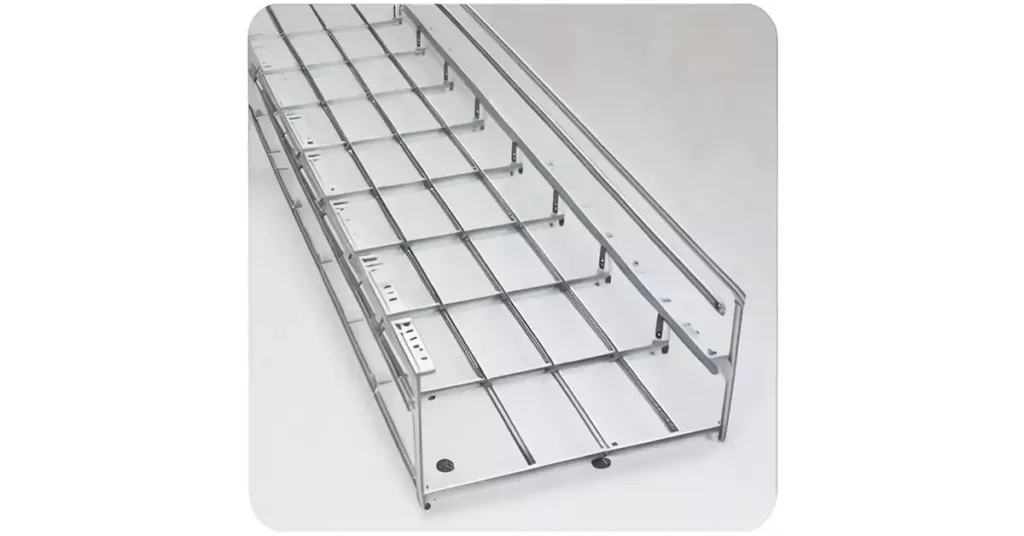

Cable trays find applications in various environments, including:
- Commercial Buildings: Cable trays are used to route and manage cables in office buildings, shopping malls, hospitals, and educational institutions.
- Industrial Facilities: Cable trays are commonly employed in manufacturing plants, refineries, powerplants, and chemical processing facilities to organize and protect cables in harsh and demanding environments.
- Data Centers: Cable trays are used extensively in data centers and server rooms to manage the complex network of cables for power distribution, data communication, and cooling systems.
- Transportation Infrastructure: Cable trays are utilized in transportation infrastructure, such as airports, subway systems, and railway stations, to route and protect cables for lighting, signaling, and communication systems.
- Outdoor Installations: Cable trays with appropriate coatings and weatherproofing measures are employed in outdoor installations like street lighting, traffic control systems, and outdoor power distribution.
Categories of Cable Trays
Cable trays can be categorized into covered and uncovered trays, and their selection depends on the application and environmental conditions:
- Covered Trays: Covered cable trays have a protective cover that shields cables from external elements such as dust, moisture, and physical damage. They are suitable for indoor installations or areas where additional protection is required.
- Uncovered Trays: Uncovered or open cable trays provide easy access to cables and are commonly used in indoor settings where cable management and accessibility are priorities. They are not typically suitable for outdoor applications due to exposure to environmental elements.
- Indoor Usage: In indoor applications, cable trays can be selected based on load capacity, cable type, and size requirements, as well as aesthetic considerations. They offer flexibility and easy access to cables while ensuring proper cable management.
- Outdoor Usage: For outdoor installations, cable trays should be selected based on their ability to withstand weather conditions, UV exposure, and corrosive elements. Weatherproof coatings, materials resistant to environmental factors, and proper grounding are essential for outdoor cable tray installations.
It is important to consult local electrical codes, regulations, and manufacturer guidelines to ensure proper selection, installation, and maintenance of cable trays for both indoor and outdoor usage.
Standards for Cable Trays

Standards and codes for cable trays may vary depending on the region and jurisdiction. However, there are several widely recognized standards and codes that provide guidelines for the design, installation, and use of cable trays. Here are some of the commonly referenced standards and codes:
National Electrical Code (NEC)
Underwriters Laboratories (UL)
Canadian Electrical Code (CEC)
International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)
British Standards (BS)
Electrical Fittings
Electrical fittings are components used in electrical installations to connect, secure, and protect electrical equipment, devices, and wiring. They play a crucial role in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of electrical systems. Electrical fittings facilitate the proper installation, routing, and connection of electrical conductors and equipment while maintaining compliance with electrical codes and standards.
The significance of electrical fittings can be summarized as follows:
Safety: Electrical fittings provide mechanical support, protection against environmental factors, and secure electrical connections, minimizing the risk of electrical hazards such as short circuits, electrical shocks, and fires.
Reliability: Properly selected and installed electrical fittings ensure reliable electrical connections, reducing the likelihood of equipment failure, power interruptions, and operational issues.
Convenience: Electrical fittings allow for neat and organized wiring, making it easier to manage and maintain electrical systems. They facilitate troubleshooting, repairs, and upgrades.
Common Types of Electrical Fittings
Here are some common types of electrical fittings used for conduit and cable trays, along with their materials, installation methods, and performance characteristics:
4 Different Conduit Fittings:
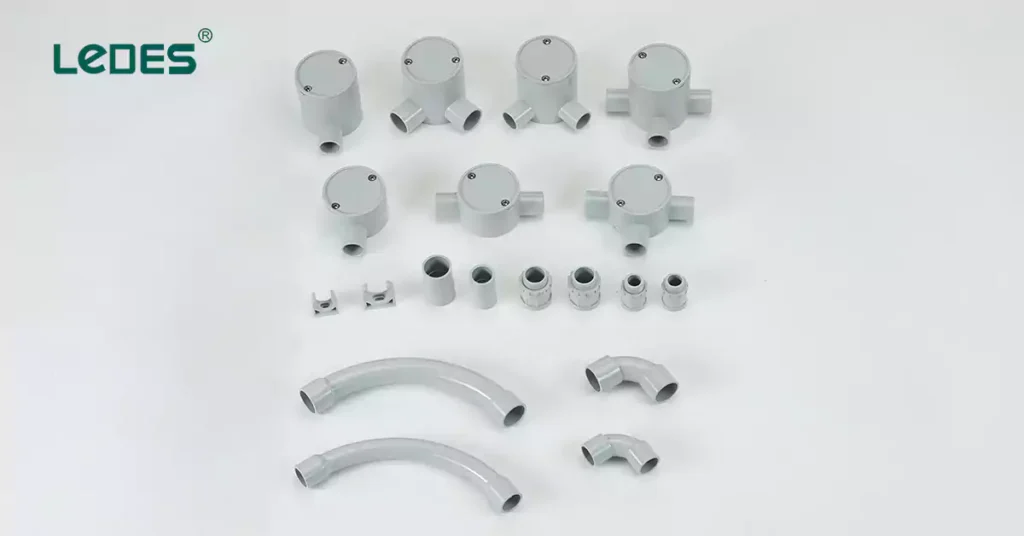

- Conduit Connectors: Conduit connectors are used to join two sections of conduit together or to connect conduit to electrical boxes or enclosures. They are available in various types, such as compression connectors, set-screw connectors, and push-in connectors. Conduit connectors are typically made of materials like steel, aluminum, or PVC. They are installed by tightening screws or compression fittings, ensuring a secure and watertight connection.
- Conduit Elbows: Conduit elbows are used to change the direction of conduit runs, providing flexibility in routing electrical wiring. They come in different angles, such as 90 degrees or 45 degrees, and can be made of materials like steel or PVC. Conduit elbows are installed by attaching them to the ends of conduits, allowing for smooth directional changes.
- Conduit Couplings: Conduit couplings are used to connect two sections of conduit in a straight line. They are available in different sizes and materials, including steel, aluminum, or PVC. Conduit couplings are installed by tightening screws or using compression fittings, ensuring a secure and continuous conduit run.
- Conduit Straps: Conduit straps are used to secure conduits to walls, ceilings, or other surfaces. They provide support and prevent excessive movement or vibration. Conduit straps can be made of materials like steel, aluminum, or plastic. They are installed by attaching them to the surface and securing the conduit within the strap.
4 Different Cable Tray Fittings:
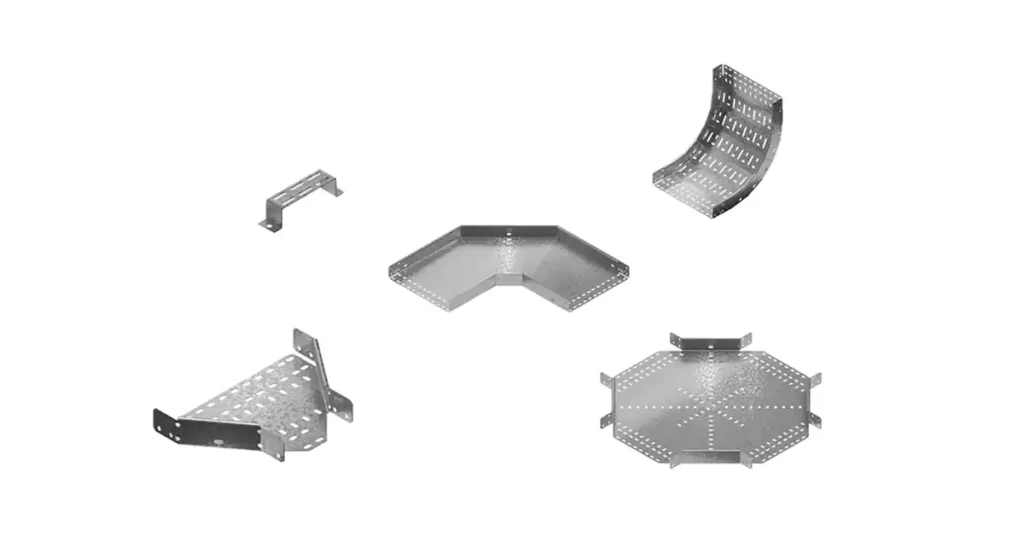
- Straight Sections: Straight sections are the main components of cable trays and provide a pathway for electrical cables. They come in various widths, depths, and materials, such as steel, aluminum, or fiberglass. Straight sections are installed by connecting them together to create a continuous cable tray run.
- Bends and Turns: Bends and turns are used to change the direction of cable tray runs. They are available in different angles, such as 90 degrees or 45 degrees, and can be made of materials like steel or aluminum. Bends and turns are installed by connecting them to the straight sections of the cable tray, allowing for smooth directional changes.
- Tees and Crosses: Tees and crosses are used to create intersections or branching points in cable tray systems. They allow for the separation of cables or the connection of multiple cable tray runs. Tees and crosses are installed by connecting them to the straight sections of the cable tray, providing versatile routing options.
- Support Brackets: Support brackets are used to secure and support cable trays to walls, ceilings, or other structures. They provide stability and prevent sagging or excessive movement. Support brackets can be made of materials like steel or aluminum. They are installed by attaching them to the surface and securing the cable tray within the bracket.
4 Things You Need to Know Before Electrical Fitting Selection
When selecting electrical fittings, consider factors like application and environment, material compatibility, size and capacity, code compliance, and ease of installation. Follow manufacturer’s recommendations for proper fitting selection and compatibility.
Electrical Safety: Choosing fittings that meet electrical codes and standards ensures the integrity of electrical connections and reduces the risk of electrical hazards, such as short circuits, arcing, and overheating.
Reliable Performance: Compatible fittings ensure reliable electrical connections, minimizing the chances of loose connections, voltage drops, and equipment malfunctions. Proper fittings also help maintain the electrical system’s performance over time.
Compliance: Selecting fittings that comply with electrical codes and regulations helps ensure that the installation meets safety requirements and avoids potential legal issues or penalties.
Environmental Protection: Fittings suitable for the installation environment provide protection against moisture, dust, chemicals, and other environmental factors, safeguarding the electrical system from damage or degradation.
Ease of Installation: Compatible fittings are easier to install, reducing installation time and effort. They also allow for efficient routing and connection of electrical conductors, improving overall installation quality.
6 Tips for Choose Right Electrical Fitting
When selecting electrical fittings, 6 factors should be taken into consideration:
Application and Environment: Consider the specific application and environmental conditions in which the fittings will be used. Factors such as temperature, moisture, corrosive elements, and physical stress should be evaluated to ensure the fittings are suitable for the intended environment.
Material Compatibility: Ensure that the materials used in the fittings are compatible with the materials of the conduits, cable trays, and other components in the electrical system. Incompatible materials can lead to corrosion, poor electrical conductivity, and reduced performance.
Size and Capacity: Select fittings that are appropriate in size and capacity for the electrical conductors or cables being installed. Oversized or undersized fittings can lead to poor connections, overheating, or constraints on future system expansion.
Code Compliance: Verify that the selected fittings comply with relevant electrical codes and standards. This ensures the installation meets safety requirements and regulatory guidelines.
Ease of Installation: Consider the installation method and requirements of the fittings. Choose fittings that are easy to install and provide secure connections without the need for complicated or time-consuming procedures.
Manufacturer’s Recommendations: Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations and guidelines for fitting selection, installation, and compatibility. Manufacturers often provide valuable information regarding the proper use and limitations of their fittings.
By carefully considering these factors and selecting appropriate electrical fittings, you can ensure a safe, reliable, and compliant electrical installation.
Relationship Between electrical raceways, conduit, cable trays, and fittings
Electrical raceways, conduit, cable trays, and fittings work together to protect, route, and support electrical wires or cables. Conduit is used within raceways to protect individual wires, while cable trays provide a framework for supporting and organizing multiple cables. Fittings play a crucial role in connecting and terminating these components.
The relationship between these components is based on their functional integration. Conduit is used within raceways to protect individual wires, while cable trays provide a framework for supporting and organizing multiple cables. Fittings play a crucial role in connecting and terminating these components, ensuring a secure and reliable electrical installation.
By combining these elements, electrical professionals can create a well-designed and efficient electrical distribution system. The choice of raceways, conduit, cable trays, and fittings depends on factors such as the application, environment, wiring requirements, and local electrical codes.
Conduit vs. Cable Tray: Which One is Better?
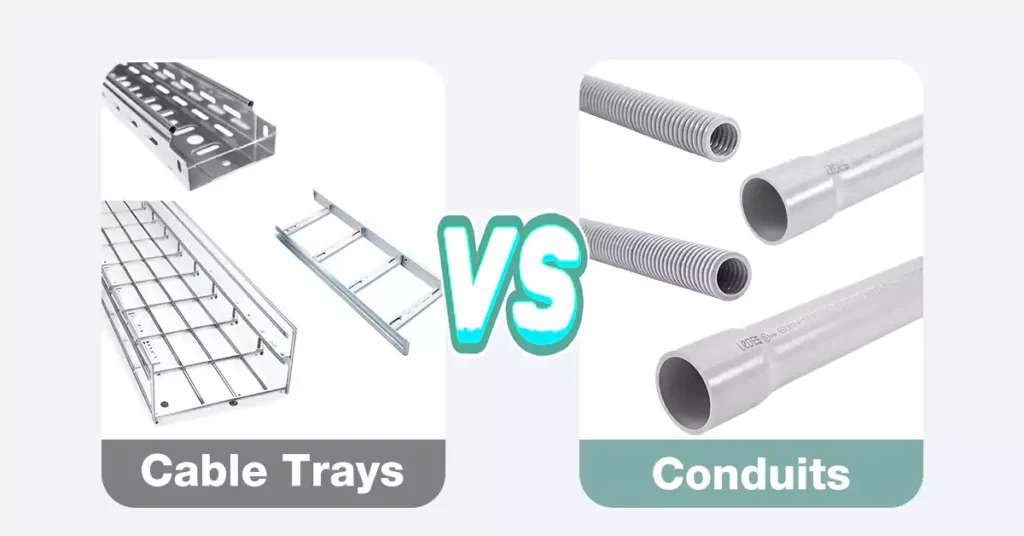
Choose between conduit and cable tray based on the project’s needs, considering factors like environmental conditions, cable capacity, installation flexibility, and code requirements. Consult with electrical professionals or engineers for guidance tailored to your specific project.
Conduit: Ideal for industrial environments, outdoor installations, areas with high vibration, or where EMI shielding and fire resistance are important, such as manufacturing plants, petrochemical facilities, or data centers.
Cable Tray: Well-suited for commercial buildings, large-scale projects with frequent modifications, projects with a high cable density, or applications involving data and communication cables, such as office buildings, universities, or telecommunications facilities.
It is crucial to assess the project’s needs, consider factors like environmental conditions, cable capacity, installation flexibility, and code requirements to make an informed decision between conduit and cable tray. Consulting with electrical professionals or engineers can also provide valuable insights and guidance tailored to your specific project.
Conclusion
In conclusion, these components not only protect the cables from physical damage, moisture, and environmental factors but also ensure proper cable management, accessibility, and EMI shielding. Choosing the right option based on project requirements is vital to ensure efficient and trouble-free electrical installations.
Proper selection and installation of electrical raceways is essential for compliance with industry standards, regulations, and safety guidelines. It ensures the protection of cables, minimizes the risk of electrical faults and failures, and facilitates maintenance and troubleshooting.
Careful consideration of factors such as protection requirements, flexibility, capacity, environmental conditions, and EMI shielding is necessary. This will help in making an informed decision between conduit and cable tray. By selecting and installing the appropriate electrical raceway system, compliance, protection, and trouble-free use of electrical systems can be achieved, ensuring the reliability and longevity of the overall electrical infrastructure. If you have any questions about electrical system protection solutions, contact us at any time by submitting a form or sending us an email.



