Tabla de contenido
Ya sea que estemos renovando nuestras casas por nuestra cuenta, instalando sistemas de agua o electricidad, o trabajando como ingenieros eléctricos o plomeros, a menudo nos encontramos con tuberías o conductos de PVC. Estos componentes versátiles desempeñan un papel crucial en varios proyectos de construcción. Sin embargo, ¿comprendemos realmente los significados y las diferencias entre las diferentes especificaciones, como las tuberías de PVC Schedule 40 y Schedule 80? ¿Y cuál es mejor?
En este artículo, analizaremos en detalle las diferencias entre las tuberías de PVC Schedule 40 y Schedule 80, así como sus ventajas y desventajas.
¿Qué es una tubería de PVC Schedule 40?

La tubería de PVC Schedule 40 generalmente es de color blanco y se utiliza para aplicaciones de agua. Según los estándares norteamericanos, Las tuberías de PVC se identifican por su tamaño nominal de tubería (NPS), que se refiere al diámetro de la tubería, y el número de Schedule, denotado como “Sched.” o “Sch.”
La tubería de PVC Schedule 40 es un tipo de tubería de PVC muy utilizado con características específicas que la hacen adecuada para diversas aplicaciones. Para comprender su importancia, analicemos su definición y sus características principales.
El número de Schedule para las tuberías de PVC representa el espesor de la pared y determina la clasificación de presión de la tubería. En el caso de la tubería de PVC Schedule 40, tiene un espesor de pared medio en comparación con otras cédulas.
¿Qué es una tubería de PVC Schedule 80?
La tubería de PVC Schedule 80 tiene paredes más gruesas que la tubería de PVC Schedule 40, que generalmente es gris y se utiliza para aplicaciones de agua, como riego o DWV.
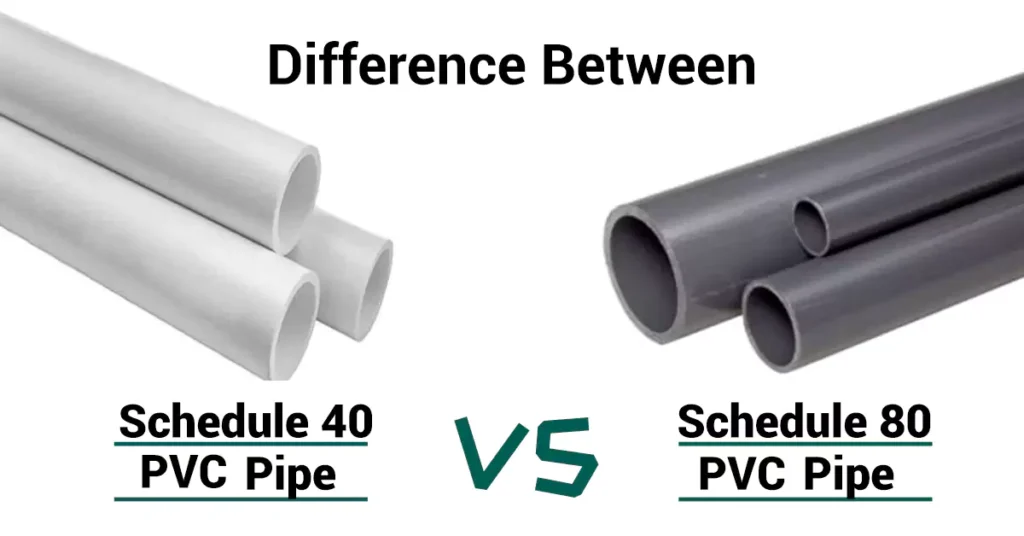
La diferencia clave radica en el espesor de la pared de la tubería en comparación con la tubería de PVC Schedule 40. La tubería de PVC Schedule 80 tiene una pared más gruesa en comparación con la Schedule 40, lo que le permite soportar presiones de agua más altas de hasta 850 PSI. Sin embargo, debido a su pared más gruesa, la tubería de PVC Schedule 80 generalmente es más cara y se usa con menos frecuencia en comparación con la tubería de PVC Schedule 40.
Tubería de PVC Schedule 40 vs Schedule 80, ¿cuál es la diferencia?
Como se mencionó anteriormente, la principal diferencia entre las tuberías de PVC Schedule 40 y Schedule 80 (incluidos los conductos de PVC) radica en el espesor de la pared. A continuación, se indican algunas diferencias clave entre ellas.
1. Espesor de la pared
- Schedule 40: Espesor de pared más delgado
- Schedule 80: Espesor de pared más grueso, lo que proporciona mayor resistencia y durabilidad.
Como sabemos, el espesor de la pared está directamente relacionado con la presión de agua que puede soportar la tubería. Las paredes más gruesas proporcionan mayor resistencia y durabilidad. En esta comparación, la tubería de PVC Schedule 80 tiene una pared más gruesa y, por lo tanto, ofrece ventajas distintivas sobre la tubería de PVC Schedule 40. Es más duradera y resistente.
Espesor de pared de PVC Schedule 40 vs Schedule 80
2. Precio
- El Schedule 80 es generalmente más caro debido a su mayor espesor de pared y los requisitos de material.
Como se indicó en el primer punto, las tuberías de PVC Schedule 80 tienen una pared más gruesa que las tuberías de PVC Schedule 40, lo que genera mayores costos de fabricación. El mayor espesor de la pared requiere más materias primas para la producción, lo que genera mayores costos para los fabricantes. Esto, a su vez, se traduce en precios más altos para los mayoristas y consumidores de tuberías de PVC.
3. Peso
Debido a que la pared es más gruesa por unidad de volumen, las tuberías de PVC Schedule 80 son más pesadas que las tuberías de PVC Schedule 40 del mismo tamaño y longitud. Si bien esto puede no ser una preocupación importante para los consumidores comunes, puede afectar a los distribuidores o fabricantes que necesitan pagar costos de envío más altos para transportar los productos desde las fábricas o almacenes hasta los consumidores. Esto se suma indirectamente a los costos generales.
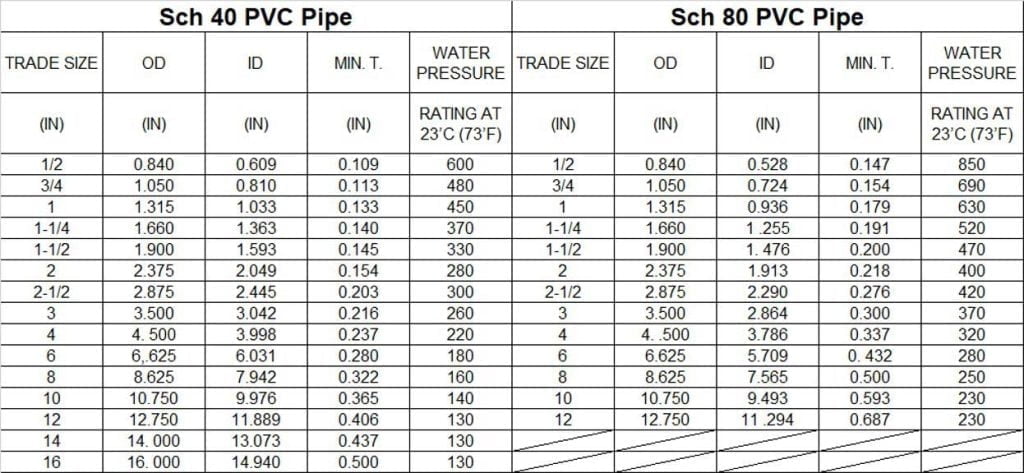
4. Diámetro interior y diámetro exterior
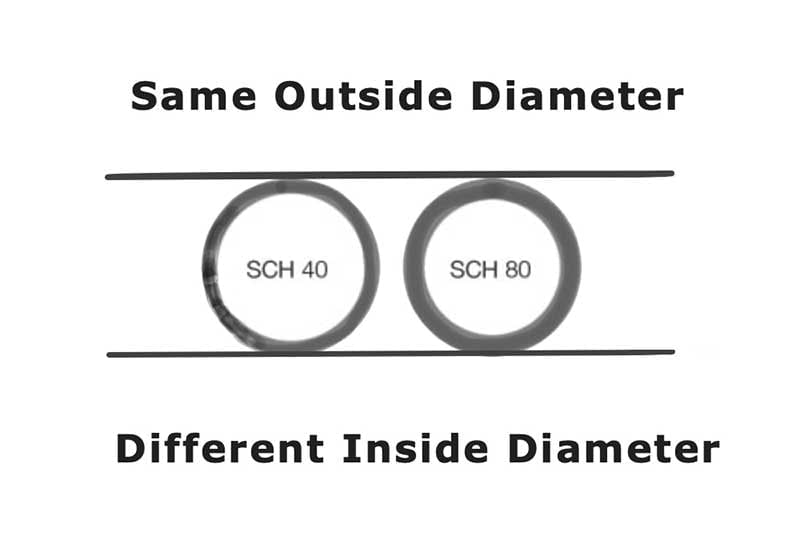
- Tanto las tuberías de PVC Schedule 40 como Schedule 80 tienen el mismo diámetro exterior, lo que permite utilizar los mismos accesorios para las conexiones.
Como se mencionó anteriormente, las dimensiones del diámetro exterior (OD) de las tuberías de PVC Schedule 40 y Schedule 80 son idénticas. Sin embargo, debido a la diferencia en el espesor de la pared, el diámetro interior (DI) también varía. En resumen, debido al mayor espesor de la pared, el DI de las tuberías de PVC Schedule 80 es menor que el de las tuberías de PVC Schedule 40. Esta diferencia se puede ver claramente en el diagrama de comparación proporcionado.
5. Instalación
Debido a su mayor peso, las tuberías de PVC Schedule 80 pueden requerir equipos y personal diferentes para proyectos de construcción a gran escala en comparación con las tuberías de PVC Schedule 40. Por ejemplo, es posible que los camiones de transporte o los equipos de elevación deban soportar el mayor peso. Además, tanto las tuberías de PVC Schedule 40 como Schedule 80, que tienen el mismo diámetro exterior, pueden utilizar los mismos accesorios para la instalación, según las pautas ASTM y NEC. Es importante utilizar pegamento especial para PVC para asegurar las conexiones de todos los accesorios y tuberías de PVC durante la instalación.
6. Color

Para diferenciar entre las tuberías de PVC Schedule 40 y Schedule 80, normalmente se fabrican en diferentes colores. Las tuberías de PVC Schedule 40 suelen ser blancas, mientras que las tuberías de PVC Schedule 80 suelen ser de color gris oscuro. Esta distinción de color ayuda a la identificación visual y facilita la instalación y la construcción.
7. Ventajas y desventajas
- Schedule 40: amplia aplicabilidad, espesor de pared más delgado, peso más ligero, precio más bajo, diámetro interior más grande y más opciones de tamaño.
- Schedule 80: amplia aplicabilidad, mayor espesor de pared, mayor peso, diámetro interior más pequeño, menos opciones de tamaño y mayor clasificación de presión de agua.
Al comparar las tuberías de PVC Schedule 40 con las tuberías de PVC Schedule 80, es importante considerar sus respectivas ventajas y desventajas:
Anexo 40 PVC:
Amplia aplicabilidad, adecuado para la mayoría de proyectos de construcción e ingeniería.
Espesor de pared más delgado en comparación con el PVC Schedule 80
Menor peso, menor precio y menores costos de transporte.
Un espesor de pared más delgado da como resultado un diámetro interior más grande
Puede soportar una presión de agua de hasta 600 PSI.
Más opciones de tamaño disponibles
Generalmente de color blanco, pero no siempre.
Anexo 80 PVC:
Amplia aplicabilidad, adecuado para proyectos con mayores requisitos.
Espesor de pared más grueso en comparación con el PVC Schedule 40
Mayor peso, lo que se traduce en precios y costes de transporte más elevados.
Un espesor de pared más grueso da como resultado un diámetro interior más pequeño.
Puede soportar una presión de agua de hasta 850 PSI
Menos opciones de tamaño disponibles
Generalmente de color gris oscuro, pero no siempre
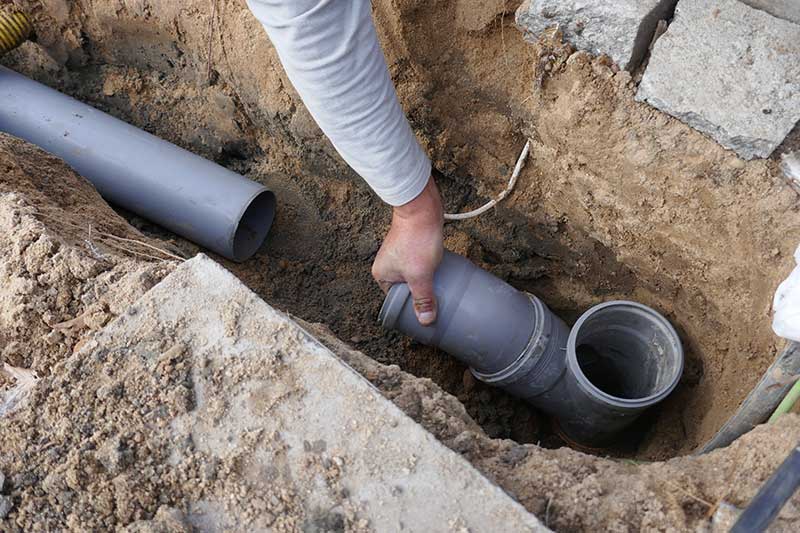

Por lo tanto, para fines generales de drenaje, agua y ventilación, el uso de tuberías de PVC Schedule 40 es más rentable. Sin embargo, si su proyecto tiene requisitos más exigentes, sería mejor utilizar tuberías de PVC Schedule 80.
Tubería de PVC Schedule 40 frente a conducto eléctrico Schedule 40
Según el Código Eléctrico Nacional (NEC) 352, el conducto eléctrico de PVC Schedule 40 está aprobado para varias aplicaciones. Estas incluyen (A) instalaciones ocultas, (B) entornos con influencias corrosivas, (C) áreas con cenizas, (D) lugares húmedos, (E) lugares secos y húmedos, (F) instalaciones expuestas, (G) instalaciones subterráneas, (H) cuerpos de conductos de soporte y (I) cumplimiento de las limitaciones de temperatura de aislamiento. En algunos casos, también puede permitirse para instalaciones sobre el suelo. Sin embargo, es importante tener en cuenta que si el conducto no está diseñado específicamente para soportar la exposición directa a la luz solar, el uso prolongado en aplicaciones al aire libre puede provocar problemas como grietas o daños.
Por otro lado, las tuberías de PVC Schedule 40 se utilizan más comúnmente para sistemas de drenaje, agua y ventilación (DWV). Debido a las diferencias en sus aplicaciones previstas, existen variaciones en los procesos de fabricación entre los conductos eléctricos de PVC Schedule 40 y las tuberías de PVC Schedule 40. Por ejemplo, las tuberías de PVC están diseñadas principalmente para soportar la presión de fluidos, por lo que su resistencia a la presión del flujo de agua se convierte en un indicador importante de la calidad del producto. Por el contrario, los conductos eléctricos Schedule 40 se centran principalmente en la protección del cableado interno, lo que hace que la resistencia al impacto sea un factor crucial para evaluar su calidad.
A pesar de sus diferencias, tanto los conductos eléctricos de PVC Schedule 40 como las tuberías de PVC Schedule 40 comparten algunas ventajas comunes. Ambos ofrecen resistencia a la corrosión química, no se oxidan y tienen una excelente durabilidad. Estas características son inherentes al material de PVC.
Aplicaciones de PVC Schedule 40
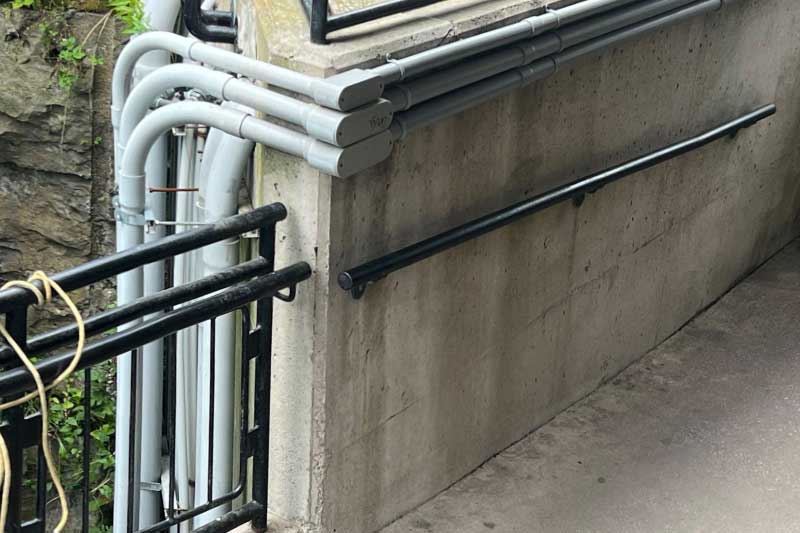

¿Para qué se utiliza la tubería de PVC Schedule 40?
Las tuberías de PVC Schedule 40 se utilizan con mayor frecuencia para el transporte de agua, gas y fluidos en plomería y riego. El PVC Schedule 40 suele ser de color blanco y tiene paredes más delgadas.
¿Dónde se pueden utilizar los conductos de PVC Schedule 40?
Conducto de PVC Schedule 40 Alberga de forma segura sistemas eléctricos tanto de energía como de telecomunicaciones, cumpliendo con los estándares NEC 352 para aplicaciones sobre el suelo, enterradas directamente y revestidas de concreto.
Las tuberías de PVC Schedule 40 y los conductos eléctricos de PVC Schedule 40 se utilizan ampliamente en diversos campos e industrias debido a su versatilidad y confiabilidad. Algunas de las aplicaciones comunes en las que se utilizan con frecuencia las tuberías de PVC Schedule 40 incluyen:
- Sistemas eléctricos y de plomería residenciales: La tubería de PVC Schedule 40 se utiliza comúnmente para instalaciones de cableado y plomería en edificios residenciales, proporcionando un conducto seguro y duradero para el cableado eléctrico y el transporte de agua.
- Sistemas de gestión eléctrica y de plomería de edificios comerciales: En edificios comerciales, como oficinas, espacios comerciales e instalaciones industriales, se utilizan tuberías de PVC Schedule 40 para administrar el cableado eléctrico y los sistemas de plomería, lo que garantiza operaciones eficientes y confiables.
- Riego paisajístico: La tubería de PVC Schedule 40 se utiliza popularmente en sistemas de riego paisajístico para transportar agua a jardines, céspedes y otras áreas al aire libre.
- Riego agrícola: Los agricultores y las empresas agrícolas confían en las tuberías de PVC Schedule 40 para fines de riego, lo que garantiza una distribución adecuada del agua a los cultivos y campos.
- Piscinas y centros de spa: La tubería de PVC Schedule 40 se utiliza comúnmente en la construcción y mantenimiento de piscinas y centros de spa, facilitando la circulación del agua y los sistemas de filtración.
- Laboratorios: Las tuberías de PVC Schedule 40 se utilizan en entornos de laboratorio para diversos propósitos, como transporte de productos químicos, sistemas de ventilación y gestión de fluidos.
- Servicios de agua potable: Debido a su resistencia a la corrosión y a la lixiviación química, la tubería de PVC Schedule 40 se utiliza a menudo para transportar agua potable, lo que garantiza un suministro de agua limpia y segura en entornos residenciales y comerciales.
- Sistemas hidrónicos: La tubería de PVC Schedule 40 se utiliza en sistemas de calefacción y refrigeración hidrónicos, facilitando la circulación de agua caliente o fría para regular las temperaturas interiores.
- Sistemas de abastecimiento de agua: Los sistemas de suministro de agua municipales a menudo utilizan tuberías de PVC Schedule 40 para las redes de distribución de agua, proporcionando un suministro de agua confiable y eficiente a las comunidades.
Según las normas ASTM 1785 y ASTM 2665, las tuberías de PVC Schedule 40 están disponibles en tamaños comerciales que van desde 1/2 pulgada hasta 16 pulgadas. La presión nominal del agua puede variar de 130 a 600 PSI, según las dimensiones específicas de la tubería. Las tuberías de PVC Schedule 40 se encuentran comúnmente en color blanco, aunque también pueden estar disponibles en otros colores para aplicaciones específicas.
Tabla de tamaños de tuberías de PVC Schedule 40
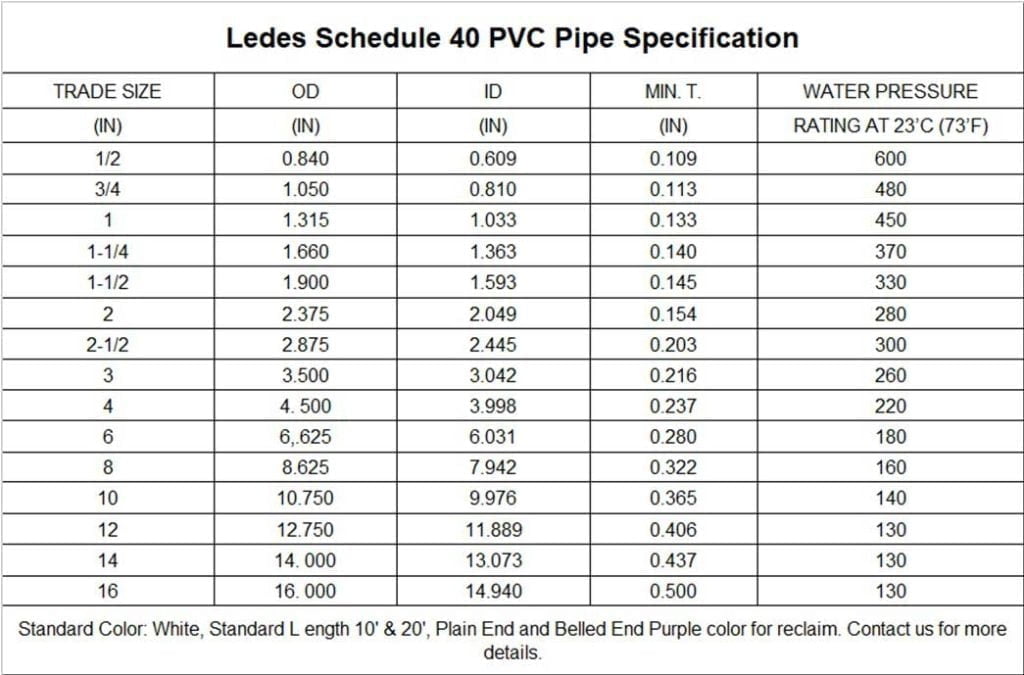
Tabla de tamaños de tuberías de PVC Schedule 80
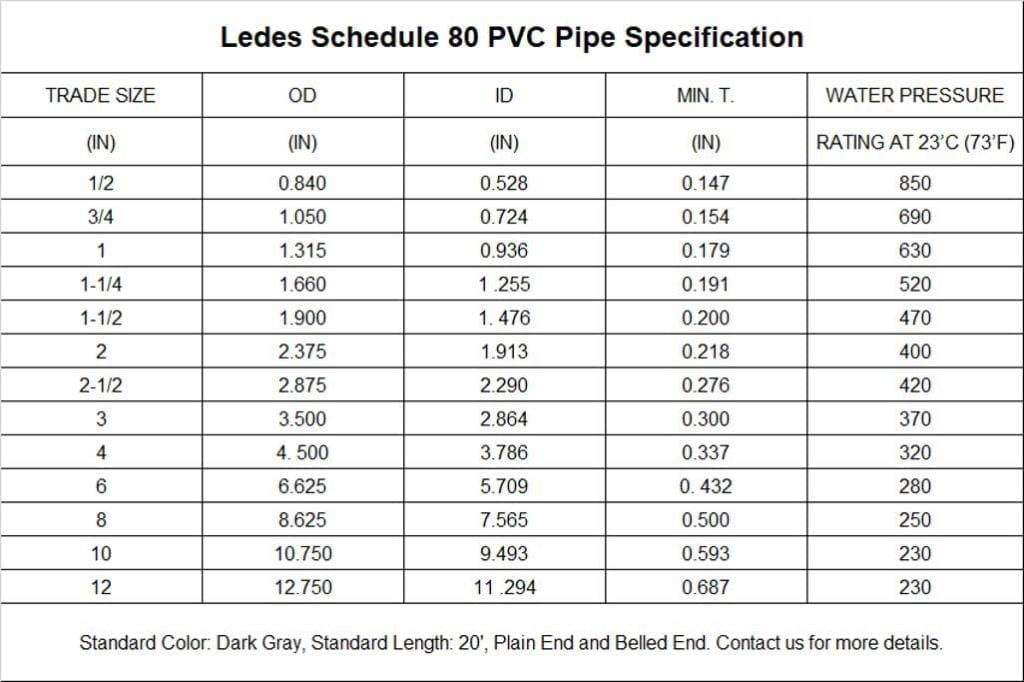
Similar a la tubería de PVC Schedule 40, Conducto de PVC Schedule 80 La tubería de acero inoxidable ofrece las mismas ventajas asociadas con las tuberías de plástico. Presenta resistencia a la corrosión química, no se oxida y tiene una gran durabilidad. Estas características la hacen adecuada para una amplia gama de aplicaciones.
Aplicaciones de tuberías de PVC Schedule 80
La tubería de PVC Schedule 80, con paredes más delgadas que la tubería de PVC Schedule 40, está diseñada para aplicaciones industriales exigentes como procesamiento químico, acuicultura y tratamiento de agua, que requieren tuberías que soporten altas presiones y condiciones adversas.
Los conductos de PVC Schedule 80 se utilizan en diversos campos, entre ellos:
- Sistemas eléctricos y de plomería residenciales: Las tuberías de PVC Schedule 80 se utilizan habitualmente en edificios residenciales para sistemas de conductos eléctricos. Proporcionan un conducto duradero y resistente a la corrosión para enrutar de forma segura los cables eléctricos por toda la casa. Además, se pueden utilizar para aplicaciones de plomería donde se requieren valores de presión de agua más altos, como líneas de suministro de agua principales o sistemas de riego.
- Sistemas de gestión eléctrica y de plomería de edificios comerciales: En edificios comerciales, como oficinas, centros comerciales y hospitales, se utilizan tuberías de PVC Schedule 80 para sistemas de conductos eléctricos a fin de proteger y enrutar el cableado eléctrico. También se emplean para aplicaciones de plomería que exigen clasificaciones de presión más altas, lo que garantiza un suministro de agua y un drenaje confiables en todo el edificio.
- Riego paisajístico: La tubería de PVC Schedule 80 es adecuada para sistemas de riego de jardines, en particular en áreas con mayores requisitos de presión de agua. Puede transportar agua de manera eficiente a jardines, césped y otros espacios al aire libre, lo que garantiza un riego y mantenimiento adecuados de las plantas.
- Riego agrícola: En los entornos agrícolas, las tuberías de PVC Schedule 80 se utilizan habitualmente para fines de riego. Pueden soportar una mayor presión de agua, lo que las hace adecuadas para sistemas de riego a gran escala en granjas y campos.
- Piscinas y centros de spa: La tubería de PVC Schedule 80 es ideal para la construcción y el mantenimiento de piscinas y centros de spa. Puede soportar una mayor presión de agua y proporcionar una circulación y filtración de agua confiables, lo que garantiza el funcionamiento adecuado de estas instalaciones recreativas.
- Laboratorios: Las tuberías de PVC Schedule 80 se utilizan a menudo en laboratorios para diversos fines. Se pueden utilizar para transportar productos químicos, gases o fluidos, así como para sistemas de ventilación o gestión de residuos.
- Servicios de agua potable: La tubería de PVC Schedule 80 se puede utilizar para suministrar agua potable en entornos residenciales, comerciales o industriales. Su resistencia a la corrosión y su durabilidad la hacen adecuada para garantizar un suministro de agua limpia y segura.
- Sistemas hidrónicos: Las tuberías de PVC Schedule 80 se emplean habitualmente en sistemas de calefacción y refrigeración hidrónicos, donde se requieren valores de presión más altos. Hacen circular agua caliente o fría de manera eficiente, lo que ayuda a controlar las temperaturas interiores.
- Sistemas de abastecimiento de agua: Los sistemas de suministro de agua municipales pueden utilizar tuberías de PVC Schedule 80 en áreas donde se espera una mayor presión de agua o en tuberías de mayor diámetro para una distribución eficiente del agua.
- Proyectos de construcción comercial e industrial con mayores exigencias: Las tuberías de PVC Schedule 80 se utilizan a menudo en proyectos comerciales e industriales que requieren índices de presión más altos o donde la aplicación exige mayor durabilidad y resistencia. Esto puede incluir plantas de procesamiento químico, instalaciones de fabricación o entornos industriales donde las tuberías deben soportar condiciones más exigentes.
En términos de tamaño y características, las tuberías de PVC Schedule 80 están disponibles en tamaños que van desde 1/2 pulgada hasta 12 pulgadas. Una distinción importante con respecto a las tuberías Schedule 40 es que las tuberías Schedule 80 suelen ser de color gris oscuro, lo que facilita la diferenciación entre los dos tipos.
Es importante tener en cuenta que las dimensiones del diámetro exterior (OD) de las tuberías de PVC Schedule 40 y Schedule 80 son idénticas. La principal diferencia radica en el espesor de la pared de la tubería, que afecta las dimensiones del diámetro interior (ID).
¿Hay otra opción?
- Tubería de PVC Schedule 80 y 120: Disponible para edificios comerciales más exigentes o aplicaciones específicas
- Tubería CPVC: ofrece un mejor rendimiento, mayor resistencia y mayor durabilidad en comparación con la tubería de PVC.
Sí, además de los tubos de PVC Schedule 40 y 80, también existen los tubos Schedule 120. En comparación con los tubos Schedule 80, los tubos Schedule 120 tienen un espesor de pared aún mayor y son adecuados para edificios comerciales más exigentes o aplicaciones específicas, como plantas químicas o proyectos de drenaje costero.
Además, existen tuberías CPVC disponibles como alternativa. Las tuberías CPVC ofrecen un mejor rendimiento, mayor resistencia y mayor durabilidad en comparación con las tuberías de PVC.
Precio de tuberías de PVC Schedule 40 y 80
Como fabricante, producimos una gama de productos de tuberías de PVC utilizando materiales de alta calidad y las últimas técnicas de fabricación. Nuestra línea de productos incluye conductos y accesorios certificados por UL y CSA, y mejoramos continuamente nuestra oferta en función de los requisitos de los clientes. Si necesita los precios más recientes para distribuidores o mayoristas, no dude en ponerse en contacto con nosotros. Como nuestro distribuidor, también se beneficiará de servicios y asistencia adicionales.
Pensamiento final
Con base en la información proporcionada anteriormente, ahora debería tener una mejor comprensión de las diferencias entre las tuberías de PVC Schedule 40 y Schedule 80. Dependiendo de sus requisitos específicos y las necesidades del proyecto, puede tomar una decisión informada sobre qué producto elegir. Si necesita más información sobre nuestros productos o la industria, no dude en comunicarse con nosotros enviando un formulario de contacto o enviando un correo electrónico. Nuestro objetivo es responder a su consulta dentro de un día hábil.
Preguntas relacionadas
¿El PVC Schedule 40 es seguro para el agua potable?
Si bien el PVC Schedule 40 ha sido aprobado para aplicaciones de agua potable, el cobre generalmente se considera más seguro para la distribución de agua potable y plomería a largo plazo.
No se recomienda el PVC para transportar agua caliente, ya que ciertos productos químicos pueden filtrarse del material a medida que aumentan las temperaturas. Para la distribución de agua fría a temperaturas inferiores a 80 °F, el PVC Schedule 40 presenta riesgos mínimos para la salud cuando se une e instala correctamente de acuerdo con el código.
La Administración de Alimentos y Medicamentos clasifica el PVC rígido (tipos I y II) como aceptable para su uso en la fabricación de piezas de artículos que entran en contacto con alimentos. Sin embargo, el agua muy caliente o hervida puede provocar una mayor extracción de ciertos plastificantes de ftalato del PVC con el tiempo.
Alternativas como el CPVC (cloruro de polivinilo clorado) brindan una resistencia mejorada al agua caliente en comparación con el PVC estándar, lo que lo convierte en una mejor opción cuando se trata de temperaturas de agua más altas.
Para los sistemas de drenaje, desechos y ventilación (DWV), el PVC Schedule 40 es totalmente adecuado y no plantea problemas, ya que no entra en contacto directo con los consumibles. Pero para el agua fría potable, muchos códigos de construcción y plomeros prefieren el cobre o el CPVC debido a su durabilidad superior con exposición prolongada al agua caliente.
¿Cuánto tiempo durarán al sol 40 tuberías de PVC programadas?

Si bien el PVC tiene una vida útil teórica de hasta 100 años con un uso normal, la exposición al aire libre puede reducir significativamente su longevidad. Cuando se expone al sol directo:
- La degradación por rayos ultravioleta de la luz solar hace que el PVC se vuelva quebradizo y se agriete con el tiempo. Los colores más oscuros, como el gris o el negro, brindan más protección contra los rayos ultravioleta que el blanco.
- El PVC Schedule 40 está clasificado para aplicaciones subterráneas o enterradas, pero no para exposición prolongada al sol sobre el suelo. Sin inhibidores de rayos UV, podrían producirse grietas o fallas en un plazo de 5 a 10 años.
- Factores como las fluctuaciones de temperatura, los niveles de ozono y los contaminantes del aire pueden acelerar el daño causado por los rayos ultravioleta. En las regiones del sur, la vida útil suele reducirse entre un 30 y un 50 %.
- La adición de estabilizadores UV 2-3% al PVC durante la fabricación prolonga su vida útil cuando se expone al sol. Esto ayuda a prevenir el agrietamiento importante durante 15 a 25 años.
- Cubrir las tuberías de PVC expuestas con una envoltura o cubierta protectora resistente a los rayos UV las protege de los rayos directos y extiende considerablemente su longevidad.
Para maximizar la vida útil de más de 50 años al regar o usar PVC sobre el suelo que esté expuesto a la luz solar, es mejor utilizar tuberías aptas para uso en exteriores que contengan inhibidores de rayos ultravioleta o proporcionar una cobertura total con una envoltura que bloquee los rayos ultravioleta. La selección y protección adecuadas del material son fundamentales.
¿Se puede utilizar un tubo de PVC para conducción eléctrica?
No, no se puede utilizar un tubo de PVC estándar para conductos eléctricos. Si bien ambos están hechos de PVC, los tubos de PVC y los conductos eléctricos tienen diferentes prioridades de diseño:
- Las tuberías de PVC están diseñadas y clasificadas para soportar presiones internas de fluidos y agua durante las aplicaciones de plomería. La tolerancia a la presión es la consideración principal.
- Los conductos eléctricos deben brindar protección y aislamiento resistentes para cableado cerrado según los estándares del código. Su formulación y espesor están optimizados para brindar resistencia mecánica y resistencia a impactos y perforaciones.
- Las paredes de los conductos son más gruesas que las de las tuberías básicas para evitar grietas o roturas que podrían dañar el cableado. A veces se incluye un refuerzo adicional.
- Las clasificaciones de resistencia al fuego son fundamentales para los conductos, ya que los códigos exigen que contengan incendios y permitan una evacuación segura. Las tuberías no enfrentan las mismas demandas de calefacción.
- Los procesos de fabricación también difieren para cumplir con especificaciones de conductos únicas en cuanto a resistencia al aplastamiento, capacidad de tracción, accesorios y facilidad de instalación alrededor de obstrucciones.
Si bien el PVC es una opción eficaz, no conductora ni corrosiva para ambos usos, solo se deben utilizar conductos específicamente aprobados para aplicaciones eléctricas. El uso de tuberías de PVC estándar corre el riesgo de comprometer el aislamiento y la seguridad de los cables a lo largo del tiempo frente a las tensiones mecánicas. La selección adecuada de los componentes garantiza la integridad del sistema eléctrico.
ACERCA DE LEDES

LEDES es un fabricante y mayorista confiable de tuberías plásticas eléctricas y de agua, con años de compromiso con la calidad y la innovación del producto, LEDES se ha convertido en el primer fabricante certificado por UL y CSA en China.
Casos de proyectos
LEDES ofrece una amplia gama de aplicaciones, incluidos productos de conductos y accesorios eléctricos para aplicaciones residenciales, comerciales e industriales. Además, ha sido un proveedor clave para muchos proyectos de construcción importantes, incluido el proyecto CHPE en EE. UU., el proyecto Melbourne Tunnel, el proyecto PV2 en Abu Dhabi y el proyecto fotovoltaico de 2,6 GW en Arabia Saudita. Estos son proyectos bien conocidos que muestran las capacidades de Ledes para proporcionar soluciones de conductos para proyectos de construcción complejos y de gran escala. La trayectoria de la empresa demuestra su capacidad para satisfacer los exigentes requisitos de dichos proyectos y brindar soluciones confiables y eficientes.
Gama de productos
LEDES ofrece una gama completa de productos eléctricos para sistemas eléctricos, que incluye:
- Productos listados por UL según estándar americano: conductos y accesorios de PVC rígido, cédulas 40 y 80, ENT.
- Productos certificados según la norma canadiense CSA: conductos rígidos de PVC, conductos de comunicación DB2, tubos no metálicos, etc.
- Normas de Australia y Nueva Zelanda: conductos, tuberías y accesorios de servicio pesado y mediano.
- Productos estándar británicos;
- Conductos y accesorios libres de halógenos y con baja emisión de humo;
- Conductos y accesorios eléctricos solares fotovoltaicos resistentes a los rayos UV.
Los productos cuentan con certificaciones UL, CSA, AS/NZS, CE, IEC y otras certificaciones, lo que garantiza el cumplimiento de los estrictos estándares de la industria y satisface las necesidades de diversas aplicaciones.
Contacto
Eso es todo. Si aún tienes alguna pregunta, puedes Envíenos un correo electrónico ahora.



