Inhaltsverzeichnis
Im Bereich der Elektroinstallationsrohre fragen Kunden häufig nach den Unterschieden zwischen DB2- und Schedule-40-Rohren. Beide werden häufig zum Schutz elektrischer Leitungen eingesetzt, verfügen jedoch über einzigartige Eigenschaften, Konformitätsstandards und Anwendungsvorteile. Die Wahl des richtigen Rohrs hängt von den spezifischen Anforderungen eines Projekts ab, wie z. B. Festigkeitsanforderungen, Installationsumgebung und Einhaltung gesetzlicher Vorschriften. Dieser Artikel bietet einen umfassenden Vergleich von DB2- und Schedule-40-Rohren mit Definitionen, Standards, mechanischen Eigenschaften, Montageoptionen und Anwendungen, um Ihnen die Auswahl des richtigen Rohrs für Ihr Projekt zu erleichtern.
DB2-Conduit oder Direktverlegung 2 Leitungenist ein starres, nichtmetallisches Rohr, das speziell für unterirdische Installationen entwickelt wurde. Es ist so konstruiert, dass es äußeren Bodendrücken standhält und korrosionsbeständig ist. Das DB2-Rohr entspricht CSA C22.2 Nr. 211.1, einer kanadischen Norm, die seine Haltbarkeit für die direkte Erdverlegung in unterschiedlichen Bodenverhältnissen zertifiziert.
Schedule 40-Leitungen ist ein starres PVC-Rohr (Polyvinylchlorid) für die ober- und unterirdische Installation. Es ist für seine Langlebigkeit bekannt, kann sowohl sichtbar als auch verdeckt installiert werden und bietet hervorragenden Schutz für elektrische Leitungen im Innen- und Außenbereich. Es eignet sich für Niederspannungskabel und dient zum Schutz von Telefon-, Internet-, Fernseh- und Sicherheitssystemen. Schedule-40-Rohre müssen der Norm UL651 entsprechen, die die Leistungs- und Sicherheitsanforderungen für Kunststoffrohre festlegt.

DB2-Kanal: CSA C22.2 Nr. 211.1, Diese Norm legt Richtlinien für die direkte Verlegung in unterirdischen Anwendungen in Kanada fest.
PVC-Rohrleitung nach Schedule 40: UL651regelt die Norm die Leistungs-, Haltbarkeits- und Sicherheitsanforderungen für PVC-Rohre in den USA
Diese Normen stellen sicher, dass jeder Leitungstyp bestimmte mechanische und sicherheitstechnische Leistungskennzahlen erfüllt, sodass er für den vorgesehenen Anwendungsbereich eine zuverlässige Wahl darstellt.
Sowohl DB2- als auch Schedule 40-Leitungen müssen bestimmte Eigenschaften erfüllen, die in den jeweiligen Normen festgelegt sind. Hier sind einige häufig erforderliche Eigenschaften:

Zeitplan 40 Conduit
Gemäß UL651 müssen starre PVC-Rohre der Klasse 40 bestimmte Zugfestigkeitsanforderungen erfüllen. Diese darf bei ungealterten Proben mindestens 34,5 MPa (5000 psi) betragen. Diese Festigkeit stellt sicher, dass das Rohr erheblichen Belastungen standhält, ohne sich zu dehnen oder zu brechen. Daher eignet es sich sowohl für ober- als auch für unterirdische Anwendungen, bei denen Umwelteinflüsse, Bewegung oder Handhabung zu Zugspannungen führen können. Die Zugfestigkeit des Rohrs darf in jedem Fall nicht geringer sein als:
- a) 5.000 psi (34,5 MN/m2) (3,45 kN/cm2) (3515 gf/mm2) für starre PVC-Rohre der Typen Schedule 40 und 80
- b) 4000 lbf/in2 (27,6 MN/m2 oder 2,76 kN/cm2 oder 2812 gf/mm2) für starre PVC-Rohre vom Typ A und EB
Um diese Anforderung zu erfüllen, werden drei ungealterte Proben von Schedule-40-Rohrleitungen auf ihre Zugfestigkeit geprüft. Anschließend werden diese Proben gealtert, wobei die durchschnittliche Zugfestigkeit der gealterten Proben mindestens 95 % der durchschnittlichen Zugfestigkeit der ungealterten Proben betragen muss. Dieser Alterungstest folgt ähnlichen Verfahren wie die Standardprüfmethode für Zugfestigkeitseigenschaften von Kunststoffen (ASTM D 638) und stellt sicher, dass die Rohrleitung unter verschiedenen Bedingungen ihre Festigkeit behält.
Diese Spezifikationen machen Sch 40-Rohre zu einer ausgezeichneten Wahl für Anwendungen, die langlebige, hochfeste Rohre erfordern, selbst in Umgebungen, in denen Temperaturschwankungen oder eine potenzielle Belastung häufiger vorkommen.
Zugfestigkeit von DB2-Leitungen
Für DB2-Rohre, die hauptsächlich in Erdverlegungsanwendungen eingesetzt werden, gibt es gemäß der Norm CSA C22.2 Nr. 211.1 keine spezifischen Zugfestigkeitsanforderungen. Da DBii-Rohre unterirdisch verlegt werden, wo die Temperatur relativ stabil bleibt und sie vor den oberirdischen Elementen geschützt sind, sind sie weniger Belastungen ausgesetzt, die strenge Zugfestigkeitsanforderungen erfordern könnten. Diese Stabilität in der Installationsumgebung trägt dazu bei, Probleme mit Wärmeausdehnung und -kontraktion zu minimieren, wodurch die Notwendigkeit einer hohen Zugfestigkeit bei DB2-Rohren reduziert wird.
Schedule 40-Stoßfestigkeit von Leitungen
Gemäß UL651 (Artikel 6.6, Tabelle 6.2) müssen Schedule-40-Leitungen einem festgelegten Aufpralltest unterzogen werden. Dabei wird ein 9,1 kg schweres Gewicht aus einer festgelegten Höhe auf die Leitung fallen gelassen. Das Gewicht hat die Form eines Zylinders mit einem Durchmesser von 51 mm. Diese Anforderung stellt sicher, dass Schedule-40-Leitungen physischen Stößen standhalten und sich daher für freiliegende Installationen eignen, bei denen es zu unbeabsichtigten Stößen kommen kann, wie beispielsweise bei oberirdischen Anwendungen.
Handelsgröße | Höhe über der Probe (Anlage 40) | |
Füße | (M) | |
1/2 | 2-1/2 | 0.762 |
3/4 | 4 | 1.22 |
1 | 5 | 1.52 |
1-1/4 | 6 | 1.83 |
1-1/2 | 7-1/2 | 2.29 |
2 | 9-1/2 | 2.90 |
2-1/2 | 10-1/2 | 3.20 |
3 – 6 | 11 | 3.35 |
Schlagfestigkeit von DB2-Kanälen
Für DB2-Rohre schreibt CSA C22.2 Nr. 211.1 (Klausel 6.2) ein anderes Schlagprüfverfahren vor. DB2-Rohre müssen einer Schlagenergie von 61 Joule bei 23 °C (73,4 °F) und 34 Joule bei –18 °C (0 °F) standhalten. Dieses Verfahren stellt sicher, dass DB2-Rohre ihre Integrität bei unterschiedlichen Temperaturen behalten, insbesondere bei kälteren Bedingungen, bei denen das Material spröder sein kann. Aufgrund der direkten Erdverlegung ist die Schlagfestigkeit von DB2-Rohren für unterirdische Umgebungen optimiert, in denen sie Kräften aus dem Boden oder von Geräten ausgesetzt sein können.
Wenn Sie sich für den Abschnitt Schlagfestigkeit interessieren, können Sie hier klicken, um zu lesen Erkenntnisse zur Schlagfestigkeit von PVC-Rohren geschrieben von unserem technischen Team.
Leitungstyp | Schlagprüfverfahren | Gewicht/Kraft | Temperatur |
Zeitplan 40 Conduit | UL651, Artikel 6.6, Tabelle 6.2 | 9,1 kg | 23,0 ± 2,0 °C
|
DB2-Kanal | CSA C22.2 Nr. 211.0, Abschnitt 6.3.1, Methode A | 1,36 kg ± 10 g 61 J bei 23 ℃, 34 J bei -18 ℃ | 23 ℃ und -18 ℃ |
Die Druckfestigkeit ist eine entscheidende Eigenschaft von Leitungen, da sie sicherstellt, dass sie äußeren Drücken standhalten können, ohne sich zu verformen.
Quetschfestigkeit von Leitungen nach Schedule 40
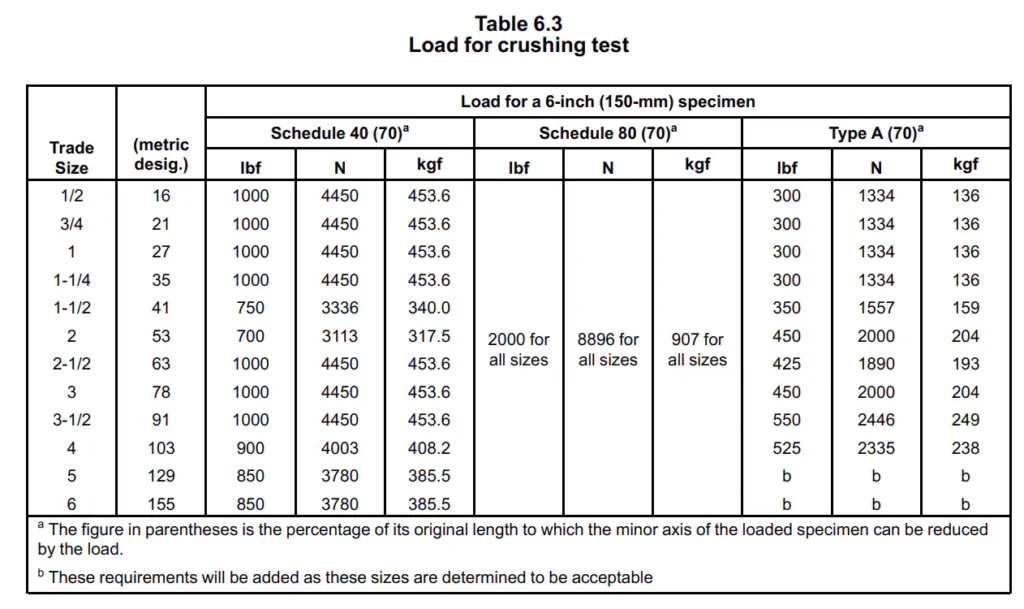
Gemäß UL651 (Artikel 6.9) wird Schedule 40-Leitung einem Druckversuch unterzogen, um ihre Verformungsbeständigkeit zu bewerten. Die Leitung darf sich unter der in Tabelle 6.3 angegebenen Belastung nicht bis zum Knickpunkt abflachen. Die gemessene Nebenachse innerhalb jeder belasteten Probe darf nicht weniger als 70 Prozent des Innendurchmessers der Probe vor der Belastung betragen.
- Plattenbewegungsrate: Die Platte wird mit der Geschwindigkeit von auf die andere zu bewegt 1/2 ±1/8 Zoll (10,0 ±2,5 mm) pro Minute, bis die in Tabelle 6.3 angegebene Last wie auf dem Zifferblatt der Maschine angezeigt aufgebracht wird.
Die Norm schreibt vor, dass Sch 40-Leitungen ihre strukturelle Integrität bis zu einem bestimmten Grenzwert aufrechterhalten müssen. Dieser simuliert reale Bedingungen, unter denen die Leitung dem Gewicht oder Druck von oberirdischen Installationen, wie z. B. Verkehrslasten oder schweren Maschinen, ausgesetzt sein kann. Dadurch wird sichergestellt, dass die Leitung auch in Umgebungen, in denen sie erheblichen physischen Belastungen ausgesetzt sein kann, funktionsfähig und sicher bleibt.
Quetschfestigkeit von DB2-Leitungen
Für DB2-Leitungen enthält CSA C22.2 Nr. 211.1 (Artikel 6.3) die spezifischen Anforderungen an die Druckfestigkeit bei der direkten Erdverlegung. Die prozentuale Durchmesserabnahme unter und nach der Rückverlegung muss darf 10% auf DB2 nicht überschreiten und darf nach der Wiederherstellung 5% nicht überschreiten.
- Lastanwendung: Eine 90 kg schwere Masse (einschließlich der Platte) wird schrittweise aufgebracht und 60 ± 5 Sekunden lang gehalten.
- Durchmessermessung unter Last: Während des Aufbringens der Masse wird der vertikale Innendurchmesser erneut gemessen.
- Erholungsmessung: Nachdem die Last entfernt wurde, erholt sich die Leitung 300 ± 20 Sekunden lang, bevor der Durchmesser erneut gemessen wird.
- Verformungsberechnung: Die prozentuale Verringerung des Durchmessers wird sowohl unter Belastung als auch nach der Rückverformung berechnet und gibt Aufschluss über die Druckfestigkeit des Rohrs.
Diese Norm legt fest, dass DBII-Rohre einer bestimmten Belastung pro Längeneinheit standhalten müssen, um das Gewicht von Erde oder anderen Materialien zu simulieren, das bei unterirdischer Verlegung auf das Rohr wirken kann. Die CSA-Norm soll sicherstellen, dass DB2-Rohre den besonderen Belastungen bei unterirdischen Installationen standhalten. Dabei sind sie nicht nur vor direkten Oberflächenlasten geschützt, sondern auch dem anhaltenden Druck des umgebenden Bodens ausgesetzt.
Steifigkeit von Rohrleitungen nach Schedule 40
Bei PVC-Rohrleitungen der Klasse 40 wird die Rohrsteifigkeit gemäß ASTM D 2412 (Standardprüfverfahren zur Bestimmung der äußeren Belastungseigenschaften von Kunststoffrohren durch Parallelplattenbelastung) bewertet. Rohrleitungen der Klasse 40, die in Richtbohranwendungen eingesetzt werden, müssen eine Mindestrohrsteifigkeit von 120 psi (827 kPa) bei 10%-DurchbiegungDadurch wird sichergestellt, dass Schedule 40 die strukturelle Integrität beibehält und Verformungen unter äußerem Druck widersteht.
DB2-Leitungssteifigkeit
Für DB2-Rohre, die ebenfalls gemäß ASTM D 2412 geprüft wurden, gelten aufgrund ihrer Anwendung bei der direkten Verlegung im Erdreich strengere Anforderungen an die Steifigkeit:
- Leitung Typ EB1: Muss eine Mindestrohrsteifigkeit von 200 kPa bei 5%-Durchbiegung aufweisen.
- Leitung Typ DB2/ES2: Muss einen höheren Grenzwert einhalten, mit einer Mindestrohrsteifigkeit von 300 kPa bei 5%-Durchbiegung.
Diese Werte stellen sicher, dass DB2-Leitungen dem unterirdischen Druck besser standhalten und bieten zusätzliche Widerstandsfähigkeit gegen Bodenlasten und andere Umwelteinflüsse, die bei Verlegung im Erdreich typisch sind.
Leitungstyp | Mindestrohrsteifigkeit | Durchbiegungsprozentsatz | Standardtestmethode |
Anhang 40 | 120 psi (827 kPa) | 10% | ASTM D 2412 |
Typ DB2/ES2 | 300 kPa | 5% | ASTM D 2412 |

Zeitplan 40 Conduit
Für PVC-Rohre der Klasse 40 ist die Sonnenlichtbeständigkeit unerlässlich, um eine langfristige Haltbarkeit bei UV-Strahlung zu gewährleisten. Gemäß UL651 werden Izod-Schlagfestigkeitsprüfungen durchgeführt, um zu messen, wie gut das Material längerer Sonneneinstrahlung standhält.
- Anforderung an die anfängliche Auswirkung: Ungealterte Stabproben aus Schedule 40 oder Schedule 80 Rohren müssen eine durchschnittliche Izod-Schlagzähigkeit von mindestens 0,5 ft-lbf/inch (27 J/m) Kerbbreite. Dadurch ist das Rohr auch vor UV-Belastung widerstandsfähig gegen mechanische Einflüsse.
- Prüfung auf längere Sonneneinstrahlung: Rohrproben nach Schedule 40 werden einer Konditionierung unterzogen für 720, 1080 und möglicherweise 1440 Stunden Zur Simulation längerer UV-Belastung. Nach jedem Zeitintervall wird die durchschnittliche Izod-Schlagzähigkeit gemessen, um die Einhaltung der in Tabelle 6.4 der UL651 angegebenen Werte sicherzustellen. Dieser Test verwendet ein Verfahren ähnlich ASTM D 256 (Prüfmethode zur Bestimmung der Izod-Pendelschlagzähigkeit von Kunststoffen) und stellt sicher, dass das Material auch nach längerer Sonneneinstrahlung seine Schlagfestigkeit behält. Der 1440-Stunden-Test ist besonders streng und bietet Sicherheit für längere Außeninstallationen.
DB2-Kanal
Im Gegensatz zu Schedule 40 ist das DB2-Rohr für die direkte Erdverlegung konzipiert, wo es typischerweise keiner Sonneneinstrahlung ausgesetzt ist. Daher gelten für das DB2-Rohr gemäß CSA C22.2 Nr. 211.1 keine spezifischen Anforderungen an die Sonnenlichtbeständigkeit, da es durch die unterirdische Umgebung vor UV-Strahlung geschützt ist und somit keine Sonnenlichtprüfung erforderlich ist.
Für elektrische Leitungen gibt es immer Anforderungen an die Feuerbeständigkeit. Für Schedule 40- und DB2-Leitungen gelten andere Anforderungen an die Entflammbarkeit.
Tipps: Die Sonnenlichtbeständigkeit und Feuerbeständigkeit ist die wichtigste Leistung für die Haltbarkeit von elektrischen Leitungen. Weitere professionelle Einblicke erhalten Sie in diesem Beitrag für Analyse von Sonnenlicht und UV-Strahlung für elektrische Leitungen.
Zeitplan 40 Conduit
- UL651: Gemäß Artikel 6.11 in UL651 darf ein Leitungsrohr der Spezifikation Schedule 40 nach jeder der drei 60-sekündigen Flammenanwendungen nicht länger als 5 Sekunden brennen und das Leitungsrohr darf während, zwischen oder nach den drei Anwendungen der Testflamme keine brennbaren Materialien in seiner Nähe entzünden können.
- UL94: Neben den Entflammbarkeitsanforderungen nach UL651 verlangen die meisten Kunden auch, dass das Rohr nach Prüfung gemäß UL94 die V0-Klassifizierung erfüllt. Die Entflammbarkeitsklasse UL94 ist ein von Underwriters Laboratories (UL) entwickelter Standard, der die Entflammbarkeitswahrscheinlichkeit eines Kunststoffmaterials misst. Hier sind die in UL94 enthaltenen Entflammbarkeitsklassifizierungen:
UL94-Bewertung | Orientierung | Anforderungen |
5VA | Vertikal | Das Brennen stoppt innerhalb von 60 Sekunden nach fünfmaliger Flammenanwendung (jede Anwendung 5 Sekunden), es tropft kein brennendes Material und die Proben weisen kein Brandloch auf; |
5VB | Vertikal | Das Brennen stoppt innerhalb von 60 Sekunden nach fünfmaliger Flammenanwendung (jede Anwendung 5 Sekunden), es tropft kein brennendes Material und die Proben können ein Brandloch aufweisen; |
V0 | Vertikal | Nach zweimaliger Beflammung (je 10 Sekunden Beflammung) stoppt der Brand innerhalb von 10 Sekunden, kein brennendes Abtropfen; |
V1 | Vertikal | Abbrennen innerhalb von 60 Sekunden nach zweimaliger Flammenbeflammung (je 10 Sekunden Beflammung), kein brennendes Abtropfen; |
V2 | Vertikal | Das Brennen stoppt innerhalb von 60 Sekunden nach zweimaliger Flammenanwendung (jede Anwendung 10 Sekunden), brennendes Abtropfen ist zulässig; |
HB | Horizontal | Das Brennen stoppt vor 100 mm. |
DB2-Kanal
DB2-Leitungen sind in erster Linie für die direkte Erdverlegung konzipiert und entsprechen den kanadischen Normen, zu denen Entflammbarkeitsklassifizierungen wie FT4 und FT6 gehören:
FT4 Flammentest
Die FT4-Zertifizierung genießt aufgrund ihrer strengen Prüfanforderungen hohes Ansehen. Beim FT4-Test werden Kabel in einer vertikalen Schalenkonfiguration einer Flamme mit 70.000 BTU/h ausgesetzt. Das Testverfahren ist anspruchsvoll:
- Testaufbau: Kabel werden auf einer vertikalen Schiene montiert und 20 Minuten lang einer Flamme mit 70.000 BTU/h ausgesetzt. Dieser Aufbau simuliert die intensive Hitze, der ein Kabel oder eine Leitung bei realen Industriebränden ausgesetzt sein kann.
- Kriterien: Damit ein Kabel oder eine Leitung den FT4-Test besteht, darf das verkohlte Material nicht mehr als 1,5 Meter (5 Fuß) über die Unterkante der Brennerfläche hinausragen. Diese Anforderung ist in CSA C22.2 Nr. 38 festgelegt und nahezu identisch mit dem Flammtest nach IEEE 1202. Aufgrund der geringeren Verkohlungshöhengrenzen gilt der FT4-Test als etwas strenger als der vertikale Schalentest nach UL1685.
- Anwendungen: Die FT4-Zertifizierung ist für Industrie- und Gewerberäume unerlässlich, in denen eine vertikale Flammenausbreitung eine Gefahr darstellen könnte. Das Bestehen des FT4-Tests stellt sicher, dass das Kabelrohr die Flammenausbreitung begrenzt und so den Brandschutz in dicht verkabelten Umgebungen erhöht.
FT6 Flammentest
Die FT6-Zertifizierung, oft auch als Steiner-Tunnel-Flammentest bekannt (ähnlich der NFPA 262 in den USA), ist noch strenger und bewertet in erster Linie die Flammenausbreitung und Rauchentwicklung in Lüftungskammern. Dies ist entscheidend für HLK-Systeme und alle Umgebungen mit Umluft, in denen geringe Rauchentwicklung und begrenzte Flammenausbreitung unerlässlich sind.
- Testaufbau: Der Test erfolgt in einem 7,5 Meter langen Steiner-Tunnel mit Zu- und Abluftkanälen zur Steuerung des Luftstroms. Kabel oder Leitungen sind in einer Schiene im Tunnel montiert, an deren Einlass sich zwei kreisförmige Brenner befinden. Methan wird 20 Minuten lang bei einem Luftstrom von 73,3 m/min durch den Tunnel verbrannt.
- Kriterien: Um den FT6-Test zu bestehen, darf die Flammenausbreitungsdistanz 1,52 Meter (5 Fuß) nicht überschreiten. Zusätzlich überwacht der Test die Rauchdichte. Die maximale optische Rauchdichte darf 0,5 nicht überschreiten, die durchschnittliche optische Dichte darf unter 0,15 liegen. Diese Kriterien gewährleisten, dass Materialien der FT6-Klasse eine ausgezeichnete Feuerbeständigkeit und geringe Rauchentwicklung aufweisen und sich für sensible Umgebungen eignen, in denen die Luftqualität gewährleistet sein muss.
- Anwendungen: FT6-zertifizierte Materialien werden in Luftkammern, HLK-Systemen und anderen Bereichen verwendet, in denen die Minimierung der Rauch- und Flammenausbreitung für die Sicherheit und Luftqualität von entscheidender Bedeutung ist.
DB2-Leitungsverschraubungen
DB2-Rohrverschraubungen sind für die direkte Erdverlegung geeignet. Diese Armaturen sind wasserdicht, verhindern das Eindringen von Feuchtigkeit und schützen die elektrische Verkabelung vor unterirdischen Einflüssen.
Schedule 40-Rohrverschraubungen
Schedule 40-Armaturen bieten Flexibilität sowohl bei ober- als auch unterirdischen Installationen. Sie umfassen Winkelstücke, Kupplungen, Adapter und Anschlusskästen, mit denen sich die Leitung an verschiedene Verlegungsweisen anpassen lässt. Diese Fittings sind einfach zu installieren und mit den meisten Schedule-40-Leitungsrohren kompatibel.
Armaturen-Maßvergleich
Häufig verwendete Klebeverbindungen für beide Leitungstypen, wie Kupplungen, Winkel und Bögen, erfüllen die gleichen Funktionen und sehen möglicherweise auch ähnlich aus, die Anforderungen an die Abmessungen sind jedoch sehr unterschiedlich. Hier nehmen wir als Beispiel Winkel, um einen Größenvergleich durchzuführen:
Handelsgröße | Zeitplan 40 Conduit | DB2-Kanal | ||
Radius R (mm) | Länge Ls (mm) | Radius R (mm) | Länge Ls (mm) | |
1/2 | 100 | 38 | / | / |
3/4 | 114 | 38 | / | / |
1 | 146 | 48 | / | / |
1-1/4 | 184 | 50 | / | / |
1-1/2 | 210 | 50 | / | / |
2 | 241 | 50 | 241 | 38 |
2-1/2 | 267 | 76 | / | / |
3 | 330 | 79 | 330 | 38 |
3-1/2 | 380 | 83 | 381 | 44.5 |
4 | 400 | 86 | 406 | 50.5 |
4-1/2 | / | / | 508 | 57 |
5 | 600 | 92 | 610 | 63.5 |
6 | 760 | 95 | 762 | 82.5 |

DB2 Conduit-Anwendungen: DB2 eignet sich ideal für die direkte Erdverlegung und wird häufig in unterirdischen Infrastrukturprojekten eingesetzt, beispielsweise in Versorgungsleitungen, Straßenbeleuchtung und öffentlichen Bauvorhaben. Dank seiner Korrosionsbeständigkeit und Drucktoleranz eignet es sich für Standorte mit unterschiedlichen Bodenverhältnissen.
Anwendungen für Leitungen nach Schedule 40: Schedule 40-Leitungen werden in Wohn-, Gewerbe- und Industrieanlagen eingesetzt. Dank ihrer Vielseitigkeit können sie in Wänden, Decken und im Außenbereich installiert werden. Sie eignen sich für Anwendungen, die Sonnenlicht ausgesetzt sein können, und werden daher häufig für Gebäudeverkabelungssysteme verwendet.
Gewicht:
Schedule 40 Conduit: Schedule 40-Rohre werden im Vergleich zu DB2 mit einer dickeren Wandstärke hergestellt, was ihnen eine höhere Haltbarkeit und ein geringeres Gewicht verleiht. Diese Konstruktion ermöglicht den Einsatz von Schedule 40 sowohl oberirdisch als auch freiliegend. Aufgrund der dickeren Wandstärken sind Schedule 40-Rohre schwerer als DB2 und dadurch robuster, aber auch in bestimmten Anwendungen schwieriger zu handhaben. Dieses zusätzliche Gewicht trägt zu seiner Haltbarkeit und Festigkeit sowohl im unterirdischen als auch im freiliegenden Bereich bei.
DB2-Kanal: DB2-Rohre sind für die direkte Erdverlegung konzipiert, da hier nicht dieselbe strukturelle Dicke wie bei Schedule 40 erforderlich ist. Dank der dünneren Wände sind DB2-Rohre leichter als Schedule 40 und daher bei unterirdischen Installationsprojekten, bei denen Materialgewicht und Handhabung entscheidende Faktoren sind, einfacher zu handhaben.
Wandstärke und Sockelabmessungen
Um ihre Dimensionsanforderungen besser zu verstehen, vergleichen wir hier einige wichtige Dimensionsdaten:
de Size | Zeitplan 40 Conduit | DB2-Kanal | ||||
Max. Außendurchmesser | Min. Durchschnittliche ID | Min. T | Max. Außendurchmesser | Min. Durchschnittliche ID | Min. T | |
1/2 | 21.54 | 14.68 | 2.77 | / | / | / |
3/4 | 26.92 | 19.81 | 2.87 | / | / | / |
1 | 33.66 | 25.50 | 3.38 | / | / | / |
1-1/4 | 42.47 | 33.90 | 3.56 | / | / | / |
1-1/2 | 48.56 | 39.72 | 3.68 | / | / | / |
2 | 60.63 | 51.33 | 3.91 | 57.30 | 50.80 | 1.78 |
2-1/2 | 73.41 | 61.31 | 5.16 | / | / | / |
3 | 89.28 | 76.40 | 5.49 | 82.75 | 76.20 | 2.03 |
3-1/2 | 102.87 | 88.54 | 5.74 | 95.00 | 88.40 | 2.29 |
4 | 115.57 | 100.60 | 6.02 | 107.30 | 100.10 | 2.67 |
4-1/2 | / | / | / | 121.70 | 114.30 | 2.79 |
5 | 142.57 | 126.36 | 6.55 | 134.85 | 126.35 | 3.81 |
6 | 169.54 | 152.04 | 7.11 | 159.65 | 149.75 | 3.94 |
Handelsgröße | Anhang 40 | DB2-Kanal | ||||
Am Eingang | Im Grunde | Min. Sockeltiefe (mm) | Am Eingang | Im Grunde | Min. Sockeltiefe (mm) | |
1/2 | 21.64 | 21.23 | 16.56 | / | / | / |
3/4 | 27.03 | 26.57 | 18.26 | / | / | / |
1 | 33.78 | 33.27 | 22.22 | / | / | / |
1-1/4 | 42.60 | 42.04 | 23.83 | / | / | / |
1-1/2 | 48.72 | 48.11 | 26.97 | / | / | / |
2 | 60.78 | 60.17 | 28.58 | 57.53 | 57.02 | 18.92 |
2-1/2 | 73.41 | 72.85 | 37.31 | / | / | / |
3 | 89.28 | 88.70 | 40.49 | 83.08 | 82.42 | 37.97 |
3-1/2 | 101.98 | 101.40 | 42.85 | 95.38 | 94.51 | 38.10 |
4 | 114.68 | 114.07 | 44.45 | 107.57 | 106.91 | 43.94 |
4-1/2 | / | / | / | 122.43 | 121.06 | 50.80 |
5 | 142.06 | 141.05 | 49.20 | 135.38 | 134.47 | 62.99 |
6 | 169.11 | 168.00 | 53.98 | 160.15 | 159.26 | 74.93 |
Es gibt unterschiedliche Kennzeichnungsanforderungen für Schedule 40-Leitungen und DB2-Leitungen gemäß UL- und CSA-Standards. Nachfolgend sind die Kennzeichnungsanforderungen von CSA C22.2 Nr. 211.1 und UL651 aufgeführt:
CSA
Jede Standardlänge des Leitungsrohrs und jeder Bogen und jede Biegung müssen leserlich und dauerhaft gekennzeichnet sein, um die
- a) Name, Warenzeichen oder anderes anerkanntes Identifikationssymbol des Herstellers;
- b) Produktbezeichnung;
- c) Handelsgröße;
- d) Herstellungsdatum oder Herstellercode; und
- e) CSA-Standardnummer.
Jede Armatur muss auf ihrer Außenfläche lesbar und dauerhaft gekennzeichnet sein, um die
- a) Name, Warenzeichen oder anderes anerkanntes Identifikationssymbol des Herstellers;
- b) Produktbezeichnung; und
- c) Handelsgröße.
UL
8.1.3 Die Kennzeichnung des Produkts, der Verpackung oder des Etiketts muss Folgendes enthalten:
- a) Der Ausdruck „starres PVC-Rohr“,
- b) Die Handelsgröße des Conduit-Produkts,
- c) Der Name oder die Marke des Herstellers oder jede andere Kennzeichnung, mit der
Die für das Produkt verantwortliche Organisation kann leicht identifiziert werden und
- d) Das Herstellungsdatum oder ein anderer Datierungszeitraum, der drei aufeinanderfolgende Monate nicht überschreiten darf.
Bei einem Winkelstück ist als Herstellungsdatum das Datum zu verstehen, an dem:
1) Das Rohr wird extrudiert, wenn sowohl Extrusion als auch Biegung an der gleichen Stelle erfolgen oder
2) Der Bogen wurde geformt, indem das Schutzrohr an einer anderen Stelle herausgepresst wird.

Berücksichtigen Sie bei der Wahl zwischen DB2- und Schedule-40-Rohren Faktoren wie Umgebungsbedingungen, Budget, Installationsart und behördliche Vorschriften. DB2-Rohren eignen sich besser für unterirdische und Schwerlastanwendungen, bei denen zusätzliche Festigkeit und Umweltschutz erforderlich sind. Schedule 40 ist vielseitig und kostengünstig und ideal für den universellen Einsatz.
- Projektanforderungen
Der erste Schritt besteht darin, den Gesamtbedarf Ihres Projekts zu ermitteln. Für oberirdische Anwendungen eignen sich Schedule-40-Leitungen aufgrund ihrer robusten Struktureigenschaften und der Einhaltung der Anforderungen für den Außenbereich im Allgemeinen gut. Für die direkte Erdverlegung ist jedoch DB2-Leitungen die bessere Wahl. DB2 wurde speziell für unterirdische Installationen entwickelt und bietet optimierte Eigenschaften für Bodenbedingungen und Temperaturstabilität.
- Umweltaspekte
Die Umgebung, in der das Rohr installiert wird, beeinflusst die Wahl maßgeblich. Beispielsweise ist ein Schedule-40-Rohr UV-beständig und eignet sich daher für oberirdische Installationen im Freien, wo es Sonnenlicht ausgesetzt sein kann. DB2-Rohre hingegen benötigen keine UV-Beständigkeit, da sie für die direkte Erdverlegung konzipiert sind. Berücksichtigen Sie bei der Materialwahl Faktoren wie extreme Temperaturen, Chemikalieneinwirkung und UV-Belastung.
- Einhaltung des Codes
Die Einhaltung von Vorschriften ist unerlässlich, um Sicherheits- und Qualitätsstandards einzuhalten. Schedule 40-Rohre entsprechen den UL651-Standards, während DB2-Rohre CSA C22.2 Nr. 211.1 entsprechen. Diese Standards legen spezifische Anforderungen für jeden Rohrtyp fest, darunter Entflammbarkeit, Schlagfestigkeit und Druckfestigkeit. Wählen Sie ein Rohr, das den lokalen und nationalen Bauvorschriften für Ihren Projektstandort entspricht.
- Kosten
DB2-Rohre sind aufgrund ihres geringeren Gewichts und der dünneren Wandstärke im Allgemeinen günstiger und stellen daher eine kostengünstige Option für unterirdische Installationen dar. Schedule 40 ist robuster und in der Regel teurer. Die Abwägung der Vorlaufkosten mit den Anforderungen an die langfristige Haltbarkeit des Projekts ist ein wichtiger Aspekt bei der Materialbudgetierung.
- Installationskosten
Schedule-40-Leitungen sind schwerer und erfordern möglicherweise mehr Personal und Ressourcen für die Installation, insbesondere bei oberirdischen Installationen, bei denen Stützen erforderlich sind. DB2-Leitungen sind leichter und für die Erdverlegung optimiert und lassen sich oft einfacher unterirdisch verlegen, was die Installationskosten senken kann. Die Bewertung der Installationskosten anhand des Leitungsgewichts, der Zugänglichkeit und der Ausrüstungsanforderungen kann helfen, die beste Wahl für kostenbewusste Projekte zu treffen.
- Vielfalt
Schedule 40 bietet eine größere Auswahl an Fittings und Größen und ist daher vielseitig für verschiedene Anwendungen und Konfigurationen einsetzbar. Wenn Ihr Projekt Flexibilität bei Rohrdurchmessern, Fittings oder Zubehöroptionen erfordert, bietet Schedule 40 möglicherweise mehr Auswahl, um spezifischen Designanforderungen gerecht zu werden. DB2-Rohre haben im Allgemeinen eingeschränktere Größen- und Fittingoptionen, da sie typischerweise für die einfache unterirdische Verlegung optimiert sind.
- Beratung durch Fachleute
Die Beratung durch Branchenexperten oder Rohrlieferanten kann wertvolle Erkenntnisse liefern, die auf Ihre individuellen Projektanforderungen zugeschnitten sind. Experten können Ihre Projektspezifikationen und Umgebungsbedingungen bewerten und Ihnen den am besten geeigneten Rohrtyp empfehlen. Ihr Fachwissen hilft Ihnen außerdem, Ihr Budget einzuhalten und gleichzeitig die Einhaltung von Vorschriften und optimale Leistung sicherzustellen.
Zusammenfassend lässt sich sagen, dass sowohl DB2- als auch Schedule-40-Rohre zuverlässigen Schutz für elektrische Leitungen bieten, jedoch für unterschiedliche Umgebungen und Projektanforderungen optimiert sind. DB2-Rohre sind für die dauerhafte Verlegung im Erdreich konzipiert und zeichnen sich durch höhere Wandstärken und hohe Druckfestigkeit aus. Schedule-40-Rohre hingegen bieten Vielseitigkeit, Erschwinglichkeit und einfache Installation für allgemeine Anwendungen.
Bei Ledes bieten wir hochwertige, zertifizierte Rohrlösungen an, die sowohl den CSA- als auch den UL-Standards entsprechen, einschließlich Optionen in den Typen DB2 und Schedule 40. Unsere Produkte werden strengen Tests unterzogen, um sicherzustellen, dass sie den Industriestandards für Haltbarkeit, Sicherheit und Leistung entsprechen. Das macht sie zu einer zuverlässigen Wahl für Bauunternehmer und Ingenieure in verschiedenen Anwendungsbereichen.
Die Wahl des richtigen Kabelkanals hängt davon ab, die spezifischen Anforderungen jedes Projekts zu verstehen. Bei Ledes unterstützen wir unsere Kunden dabei, die optimale Lösung für ihre Anforderungen an die elektrische Infrastruktur zu finden.



