
جدول المحتويات
أنظمة التوصيلات الكهربائية تُعدّ أنظمة الأنابيب الكهربائية العمود الفقري لتمديدات الأسلاك الكهربائية الآمنة والفعّالة في المباني السكنية والتجارية والصناعية. سواءً أكانت لمشروع بناء جديد أم لتحديث مبنى قائم، تُعدّ أنظمة الأنابيب الكهربائية أساسية لحماية الكابلات الكهربائية وضمان السلامة. وفي هذه الأنظمة، يلعب عنصر أساسي، وإن كان غالبًا ما يُغفل عنه، دورًا محوريًا: جسم الأنابيب.
الأهمية في التركيبات الكهربائية
في التركيبات الكهربائية، تُعدّ أجسام الأنابيب ضرورية لتوفير الحماية والوصول إلى الأسلاك داخل الأنابيب. وتتمثل وظيفتها الأساسية في تمكين الكهربائيين من تغيير اتجاهات التوصيلات داخل نظام الأنابيب، مما يوفر مساحة لوصلات الأسلاك، والوصلات، ونقاط السحب. وبدون أجسام الأنابيب، ستفتقر الأنظمة الكهربائية إلى المرونة اللازمة للتنقل بين الزوايا أو المنعطفات، وسيصبح من الصعب صيانة الأسلاك أو استبدالها.
يؤدي هيكل الأنابيب دورًا وقائيًا في ضمان حماية الأسلاك داخل الأنابيب من التلف المادي والمخاطر البيئية والرطوبة. تُعد هذه الحماية أساسية لإطالة عمر النظام وسلامته، ومنع حدوث مشاكل مثل قصر الدوائر الكهربائية أو الحرائق. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، تُساعد هياكل الأنابيب الكهربائيين على استيفاء متطلبات الامتثال للكود، مما يضمن التزام التركيبات بمعايير السلامة المعمول بها.
من خلال توفير كل من التطبيق العملي والسلامة، أصبحت أجسام الأنابيب ضرورية في التركيبات الكهربائية الحديثة، وخاصة في أنظمة الأسلاك المعقدة، مثل تلك المستخدمة في الإعدادات الصناعية أو التجارية.
ما يمكنك تعلمه من هذه المقالة
ستكون هذه المقالة بمثابة دليل شامل لهياكل التوصيلات، مع شرح تفصيلي لأنواعها المختلفة وتطبيقاتها وتوافقها مع التعليمات البرمجية. بنهاية المقالة، ستكون قد اكتسبت فهمًا متينًا لما يلي:
- ما هو جسم القناة وأنواعه المختلفة
- فوائد أجسام القنوات
- الرموز والمعايير الخاصة بأجسام الأنابيب
- كيفية تركيب أجسام الأنابيب
- تطبيقات أجسام الأنابيب
التعريف: ما هو جسم الموصل؟
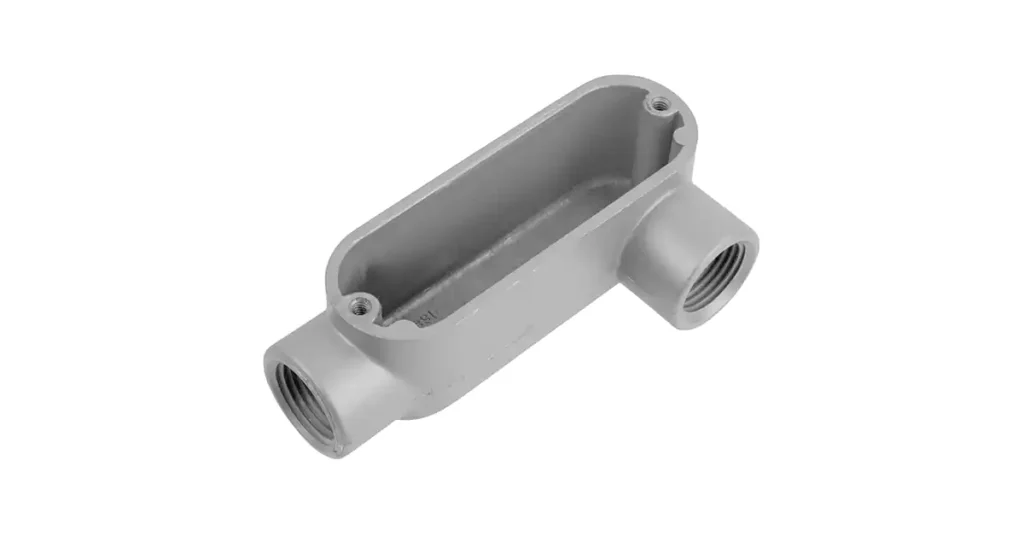

هيكل القناة هو نوع من التركيبات الكهربائية المستخدمة في أنظمة القنوات، وهو مصمم للسماح بتغيير الاتجاه، وتوفير نقاط وصول لسحب الأسلاك، وتسهيل التوصيلات بين أجزاء القناة. وهو في الأساس صندوق أو حاوية تُركّب في مسار القناة، عادةً عند الوصلات أو الزوايا أو النقاط التي تحتاج إلى الوصول إليها للصيانة أو الإصلاح.
تُصنع هياكل الأنابيب من مواد متنوعة، منها الألومنيوم والفولاذ والبلاستيك، وفقًا للمتطلبات الخاصة بالتركيب والبيئة. تُؤوي هذه الهياكل توصيلات الأسلاك، وتوفر مساحة لوصلات الأسلاك، وتُمكّن من توجيه الموصلات الكهربائية عبر النظام بشكل آمن وفعال.
غرض أجسام الأنابيب
تُستخدم أجسام الأنابيب عادةً مع الأنابيب الصلبة من النوعين 40 و80، وكلاهما من نوعي أنابيب كلوريد البوليفينيل (PVC). يُختار هذان النوعان من الأنابيب لمتانتهما ومقاومتهما للتآكل وسهولة تركيبهما.
تُستخدم أجسام الأنابيب بشكل أساسي في التطبيقات التالية:
- التغييرات في الاتجاه: عندما يتطلب نظام الأنابيب انعطافًا أو انحناءً، يسمح هيكل الأنبوب بالانتقال بسلاسة من قسم إلى آخر. فهو يستوعب الانحناءات بدرجات متفاوتة (مثل 90 درجة، 45 درجة)، ويساعد في الحفاظ على المحاذاة الصحيحة للأسلاك الكهربائية.
- أقسام توصيل الأنابيب: تُعدّ أجسام الأنابيب نقاط تقاطع حيث يلتقي قسمان أو أكثر من الأنابيب. تُعد نقاط الوصل هذه أساسية لضمان استمرارية النظام وتمرير الأسلاك بأمان في جميع أنحاء التركيب.
- الوصول إلى الأسلاك والسحب: من أهم وظائف هيكل الموصلات توفير نقاط وصول يستطيع الكهربائيون من خلالها سحب الأسلاك أو فحصها أو تركيبها. تُعد هذه الهياكل مفيدة بشكل خاص عند الحاجة إلى سحب الأسلاك عبر مسارات موصلات طويلة أو معقدة، مما يُسهّل عملية نقل الكابلات وتركيبها.
- توصيل الأسلاك وإنهائها: تتيح هياكل الأنابيب أيضًا توصيل الأسلاك وإنهائها، حيث يمكن إجراء توصيلات كهربائية داخل نظام الأنابيب. يُعد هذا مفيدًا بشكل خاص في الأنظمة التي تتطلب توصيل الأسلاك أو عند الحاجة إلى وصلة لتوصيل دوائر إضافية.
- علب التوصيلات الكهربائية: في بعض الحالات، تعمل هياكل الأنابيب كصناديق توصيل صغيرة ضمن مسار الأنابيب. تساعد هذه الأغطية على حماية الوصلات الكهربائية من التلف المادي والرطوبة والملوثات، مما يضمن سلامة النظام وطول عمره.
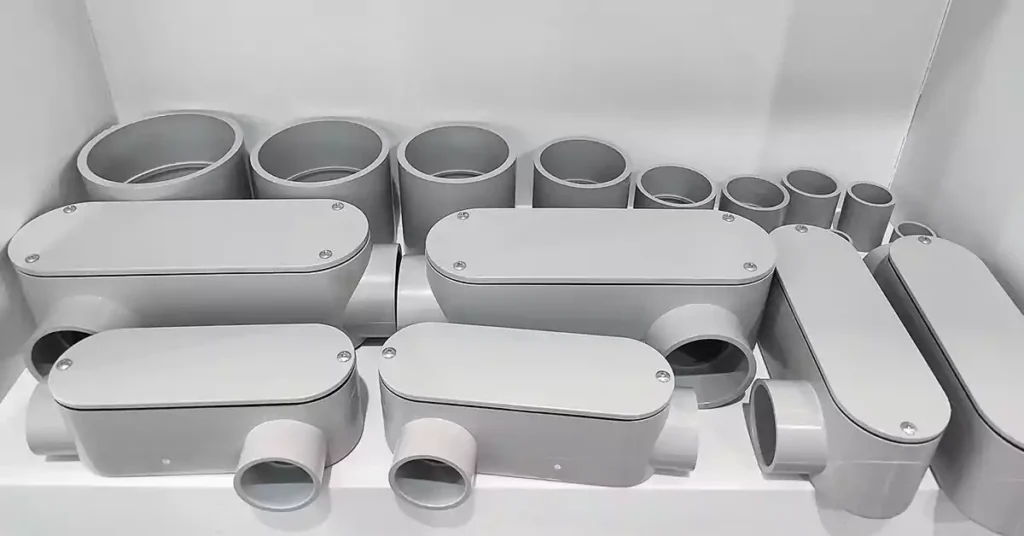
أنواع أجسام الأنابيب
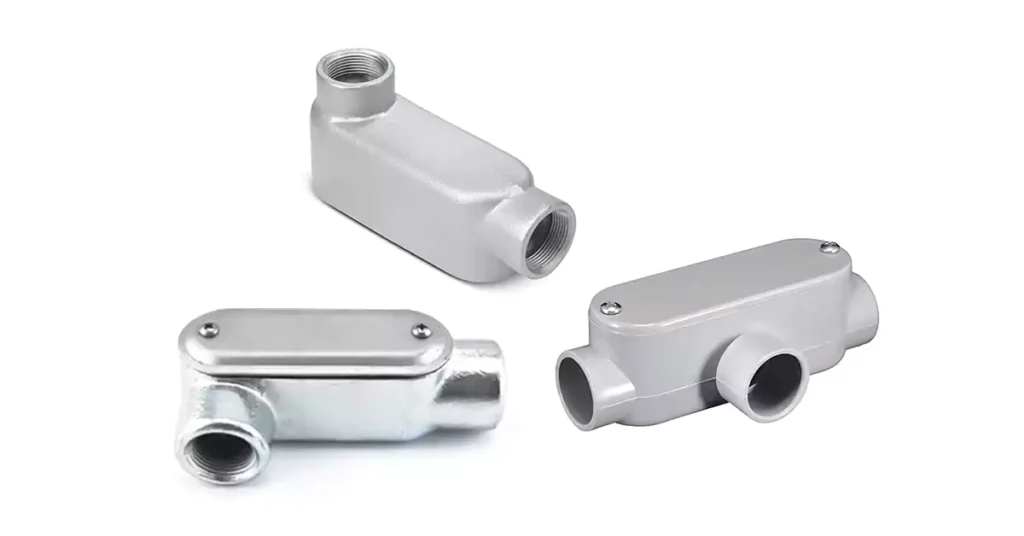
تتوفر أجسام الأنابيب بأشكال وتصاميم متنوعة، كل منها مصمم لتلبية احتياجات محددة في أنظمة الأنابيب الكهربائية. تُستخدم هذه التركيبات لتغيير اتجاه مسارات الأنابيب، وتوفير الوصول للأسلاك، والسماح بوصل الأسلاك أو صيانتها. سنتناول أدناه الأنواع القياسية من أجسام الأنابيب المستخدمة عادةً في التركيبات الكهربائية، بالإضافة إلى نوع أكثر تخصصًا مصمم للأنظمة الأكبر حجمًا. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، سنفرق بين أجسام الأنابيب وصناديق الوصلات، حيث إن هذين المكونين، على الرغم من تشابههما في بعض النواحي، يخدمان أغراضًا مختلفة.
أنواع قياسية من أجسام الأنابيب
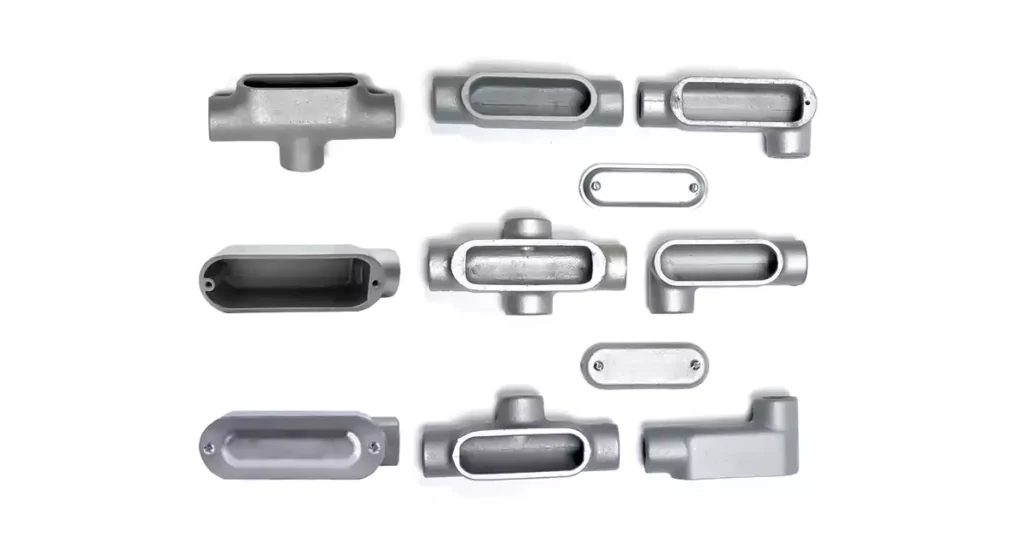

جسم قناة LB (الجانب الخلفي):
يُعدّ هيكل قناة LB من أكثر الأنواع استخدامًا لعمل انعطاف بزاوية 90 درجة في مسار القناة، مع توفير إمكانية الوصول لسحب الأسلاك وتوصيلها. يتضمن الهيكل محورين للقناة - أحدهما للأسلاك الواردة والآخر للأسلاك الصادرة - مما يسمح للكهربائي بتوجيه الأسلاك الكهربائية حول الزاوية. تقع نقطة الوصول في هيكل قناة LB في الجزء الخلفي منه، مما يجعله مثاليًا لتوجيه الأسلاك الكهربائية عبر الجدران أو الأسطح.
الاستخدام الشائع: مثالي للمواقف التي يحتاج فيها الأنبوب إلى تغيير الاتجاه بزاوية 90 درجة، وخاصة عندما يتعين توجيه الأسلاك من خارج الهيكل إلى الداخل.
جسم القناة LL (الجانب الأيسر):
على غرار LB، جسم القناة LL يُشكّل أيضًا انعطافًا بزاوية 90 درجة، لكن الأسلاك تخرج من الجانب الأيسر من الهيكل بدلًا من الأيمن. يتضمن هذا الإصدار محورين للتوصيلات: أحدهما لدخول الأسلاك من الأعلى والآخر لخروج الأسلاك من الجانب الأيسر. وكما هو الحال في هيكل LR، يُعدّ هيكل LL مفيدًا لإعادة توجيه الأسلاك على نفس المستوى.
الاستخدام الشائع: يستخدم عادة في التركيبات حيث يتعين توجيه الأسلاك إلى اليسار بعد الدوران بزاوية 90 درجة.
جسم قناة LR (الجانب الأيمن):
ال جسم قناة LR تركيب كوع بزاوية 90 درجة آخر يسمح للكهربائي بإعادة توجيه أسلاك التوصيل. يتميز هذا الإصدار بمحورين للتوصيل: أحدهما في الأعلى لدخول الأسلاك والآخر على الجانب الأيمن لخروجها. يسمح هذا التصميم بتعديل اتجاه مسار السباق دون تغيير مستوياته.
الاستخدام الشائع: يتم استخدامه عندما يكون من الضروري توجيه الأسلاك من مسار القناة إلى الاتجاه الصحيح، وخاصة في الأماكن الضيقة أو عند التوجيه عبر نفس المستوى.
جسم القناة على شكل حرف T (على شكل حرف T):
يُعدّ هيكل قناة التوصيل على شكل حرف T أول هيكل قناة في هذه القائمة يضم أكثر من محورين. يُشكّل هذا الهيكل تقاطعًا على شكل حرف T، حيث يُشير أحد محوري القناة إلى الخارج بزاوية 90 درجة، بينما يكون المحوران الآخران متوازيين. يُتيح هذا للكهربائي دمج الأسلاك من موقعين مختلفين في قناة واحدة، أو التفرّع من قناة واحدة إلى اتجاهين منفصلين.
الاستخدام الشائع: يتم استخدامه بشكل شائع في المواقف التي يكون فيها من الضروري تقسيم مسار الموصل إلى اتجاهات متعددة، مثل عند إضافة دوائر جديدة إلى نظام موجود.
جسم القناة C (خط مستقيم):
يعمل جسم الأنبوب C كجسم وصل مستقيم. يربط بين قسمين من الأنبوب في خط مستقيم دون تغيير اتجاه الأسلاك. صُمم بألواح قابلة للإزالة لسهولة الوصول إلى الأنبوب، مما يوفر نقطة صيانة على طول مسار التوصيل. يُعد هذا النوع مثاليًا لتوصيل أقسام الأنبوب حيث لا يتطلب تغيير الاتجاه.
الاستخدام الشائع: تُستخدم في الأنظمة التي تحتاج فيها مسارات الأنابيب إلى الوصل أو التمديد في خط مستقيم، مما يوفر نقاط وصول على طول الطريق.
جسم القناة الإلكترونية (الوصول النهائي):
صُمم هيكل قناة التوصيل الكهربائية (E) بنقطة وصول واحدة في نهايته، مما يسمح بسهولة دخول وخروج الأسلاك من نهاية مسار القناة. ورغم بساطة تصميمه، يُعد هيكل قناة التوصيل الكهربائية (E) فعالاً في التركيبات التي تتطلب سحب الأسلاك أو صيانتها في نهاية مقطع القناة.
الاستخدام الشائع: تُستخدم عادةً في مسارات الأنابيب المستقيمة، حيث تكون هناك حاجة إلى نقطة وصول واحدة فقط لسحب الأسلاك أو فحصها.
نوع جسم القناة TB:
صُمم هيكل قناة TB بنقاط وصول علوية وسفلية، بالإضافة إلى نقطة وصول خلفية. تُسهّل هذه المرونة الإضافية سحب الأسلاك وتوصيلها من اتجاهات متعددة، وهو أمر مفيد بشكل خاص في المساحات الضيقة أو الأنظمة الكهربائية المعقدة.
مثالي للتركيبات التي تتطلب نقاط وصول متعددة للصيانة أو التفتيش أو عند سحب الأسلاك من اتجاهات مختلفة.
جسم القناة X (على شكل صليب):
يشبه هيكل قناة X هيكل قناة T، ولكنه يتميز بأربعة محاور توصيل - مجموعتان متوازيتان تُشكلان شكلًا متقاطعًا. يسمح هذا التكوين بدخول الأسلاك وخروجها في اتجاهات متعددة من نفس النقطة. يُعد هيكل قناة X حلاً مثاليًا عند الحاجة إلى التقاء مسارات توصيل متعددة عند تقاطع مركزي، مما يجعله مكونًا أساسيًا في الأنظمة الكهربائية المعقدة.
الاستخدام الشائع: تُستخدم عادةً في الأنظمة الكهربائية التجارية أو الصناعية واسعة النطاق حيث تحتاج عدة مسارات توصيل إلى الاتصال أو التفرع من نقطة مركزية.
نوع متخصص من جسم القناة
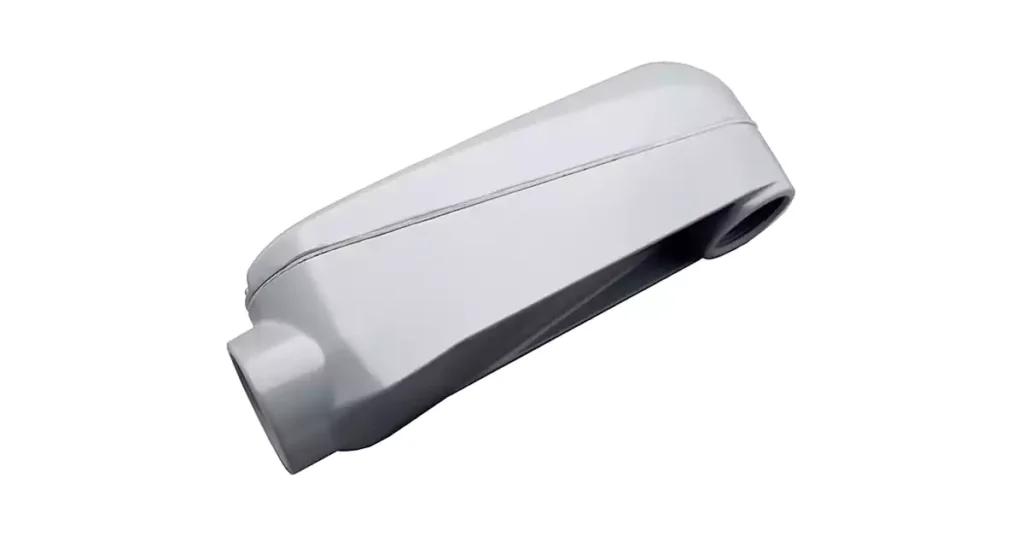

أجسام قنوات موغول
أجسام قنوات موغول هي نسخ أكبر وأكثر متانة من أجسام القنوات القياسية. وهي مصممة لاستيعاب أحجام قنوات أكبر، وتُستخدم عادةً في التطبيقات الصناعية أو التركيبات الكهربائية واسعة النطاق حيث يتحمل نظام القنوات سعات عالية. أجسام قنوات موغول مثالية للحالات التي تتطلب تركيبات أكبر وأكثر متانة لإدارة الأسلاك الكهربائية.
الاستخدام الشائع: تُستخدم عادةً في الأنظمة الكهربائية الصناعية أو التجارية ذات السعة العالية التي تتطلب تجهيزات توصيل كبيرة لإدارة الدوائر الكهربائية الثقيلة.
جسم القناة مقابل صندوق الوصلات
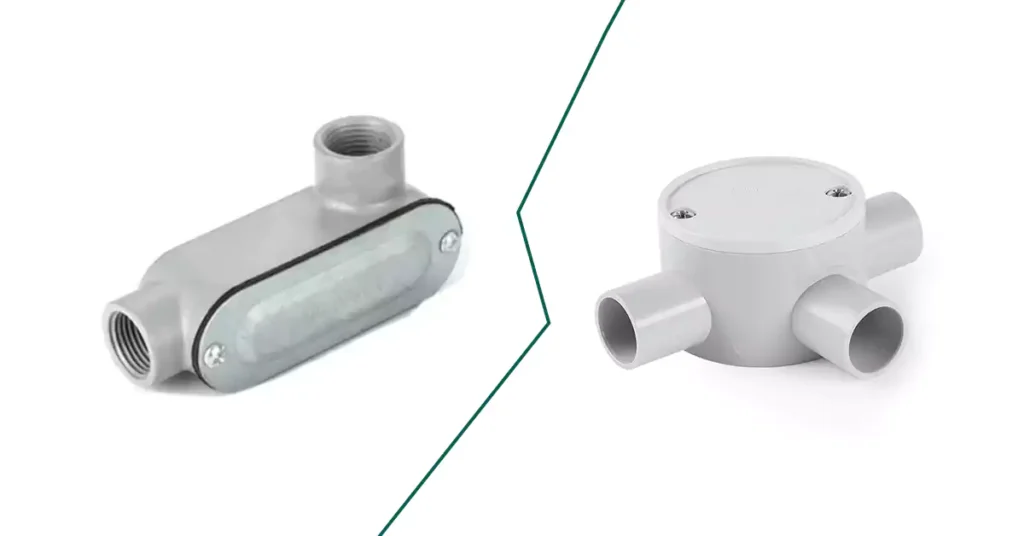

على الرغم من أن كل من أجسام الأنابيب وصناديق الوصلات جزء لا يتجزأ من التركيبات الكهربائية، إلا أنها تخدم أغراضًا مختلفة وتستخدم في سياقات مختلفة.
ميزة | جسم القناة | مربع تقاطع |
غاية | يوفر إمكانية الوصول، ويسمح بتغييرات الاتجاه، أو يوجه الأسلاك داخل نظام القنوات. | يحمي ويحمي التوصيلات والوصلات والوصلات الكهربائية. |
الوظيفة الأساسية | يقوم بتغيير اتجاه الموصل، ويسهل عملية سحب الأسلاك، ويخلق نقاط وصول للتوصيل. | يحمي ويغلف التوصيلات الكهربائية، مما يضمن السلامة والامتثال. |
موقع | مُدمج في نظام القنوات؛ جزء من مسار السباق. | يتم وضعه خارج نظام الأنابيب للحماية والوصول. |
تصميم | يتميز عادةً بوجود محاور متعددة لتوصيل أقسام الأنابيب. | حاوية مغلقة تحتوي على نقطة دخول/خروج واحدة أو أكثر لتوصيلات الأسلاك. |
متطلبات التركيب | لا يلزم دعمها بشكل فردي، لأنها جزء من مضمار السباق. | يجب أن يتم دعمها بشكل مستقل، وغالبًا ما يتم تثبيتها على سطح. |
أنواع | LB، LL، LR، C، T، X، TB، E، إلخ. (أشكال مختلفة لوظائف مختلفة). | صناديق مربعة، أو مستطيلة، أو دائرية، أو بيضاوية، وغالبًا ما تكون أغطيةها قابلة للإزالة. |
نقاط الوصول | يوفر إمكانية الوصول إلى الأسلاك مباشرة من نظام التوصيل نفسه. | يوفر إمكانية الوصول إلى توصيلات الأسلاك للصيانة أو التفتيش. |
مميزات أجسام الأنابيب

تُعدّ أجسام الأنابيب الكهربائية مكونات أساسية في الأنظمة الكهربائية، ويختلف تصميمها باختلاف تركيب المادة، ومقاومتها للعوامل الجوية، وتوافقها مع أنواع الأنابيب، واحتياجات التطبيقات المختلفة. يستعرض هذا القسم خيارات المواد المختلفة، ومزاياها وعيوبها، وخصائص التصميم المتنوعة التي تجعل أجسام الأنابيب الكهربائية مناسبة لمجموعة من التطبيقات.
خيارات المواد لأجسام الأنابيب
تُصنع هياكل الأنابيب من مواد متعددة، ولكل منها مزاياها الخاصة التي تختلف باختلاف البيئة ومتطلبات الاستخدام. المواد الأربع الأكثر شيوعًا هي الألومنيوم، والفولاذ، والبولي فينيل كلوريد (PVC)، والمواد المطلية بالزنك.
أجسام قنوات الألمنيوم
تتميز أجسام أنابيب الألومنيوم بخفة وزنها ومقاومتها للتآكل ومتانتها العالية. تُستخدم على نطاق واسع في التطبيقات التي قد تتعرض فيها أنابيب الألومنيوم للرطوبة أو العوامل البيئية.
أجسام الأنابيب الفولاذية
تتميز هياكل الأنابيب الفولاذية بالمتانة وتوفر قوة وحماية ممتازتين للأسلاك الكهربائية في البيئات شديدة التأثير أو القاسية. ويُستخدم الفولاذ غالبًا في المنشآت الصناعية أو التجارية التي تتطلب حماية ميكانيكية إضافية.
أجسام قنوات PVC
تُصنع أجسام أنابيب PVC من مادة بلاستيكية توفر مقاومة للتآكل وتُستخدم عادةً في التطبيقات التي تتطلب حلولاً غير معدنية منخفضة التكلفة.
أجسام الأنابيب المطلية بالزنك
تُصنع أجسام الأنابيب المطلية بالزنك (أو المجلفنة) عادةً من الفولاذ، ولكنها مُغطاة بطبقة واقية من الزنك لتحسين مقاومتها للتآكل. تُستخدم هذه الأنابيب في البيئات التي قد تُعرّضها للرطوبة أو المواد الكيميائية أو غيرها من العوامل المسببة للتآكل.
الإيجابيات والسلبيات:
مقاومة للعوامل الجوية ومقاومة للتآكل
من أهم مميزات هياكل الأنابيب قدرتها على تحمل عوامل الطقس، مما يجعلها مناسبة للتطبيقات الداخلية والخارجية. فيما يلي تفصيل لخصائص مقاومة العوامل الجوية والتآكل لمختلف المواد:
- الألومنيوم:مقاوم للتآكل طبيعيًا، ولكنه قابل للتأكسد مع مرور الوقت. يعمل بكفاءة في البيئات الرطبة أو المالحة.
- فُولاَذقوي ومتين، ولكنه عرضة للصدأ ما لم يُجلفن أو يُطلى. مناسب للبيئات الصناعية، ولكنه يتطلب صيانة لتجنب التآكل.
- بولي كلوريد الفينيل:مقاومة ممتازة للتآكل، مثالية للبيئات الرطبة. كما أنها غير تفاعلية، مما يجعلها مثالية للمناطق المعرضة للمواد الكيميائية.
- الفولاذ المطلي بالزنك:يوفر مقاومة معززة للتآكل ولكنه لا يزال يتطلب الصيانة لضمان بقاء طلاء الزنك سليمًا.
عند اختيار المادة لجسم القناة، يجب أن يؤخذ في الاعتبار الظروف الجوية، والتعرض للرطوبة، وإمكانية التآكل المادي.
التوافق مع أنواع الأنابيب
صُممت هياكل الأنابيب لتكون متوافقة مع مختلف أنواع الأنابيب الكهربائية، مما يضمن تكاملاً سلساً في نظام الأنابيب بأكمله. من بين أنواع الأنابيب الشائعة التي تتوافق مع هياكل الأنابيب:
- القناة المعدنية الصلبة (RMC):هذا أنبوب متين يُستخدم في البيئات الصناعية. أجسام الأنابيب مصنوعة من فُولاَذ أو الألومنيوم مثالية لأنظمة RMC.
- القناة المعدنية المتوسطة (IMC):بديل أرق من RMC، فُولاَذ تُستخدم أجسام الموصلات في أغلب الأحيان في أنظمة IMC.
- قناة بي في سي:بالنسبة لأنظمة الأنابيب غير المعدنية، أجسام قنوات PVC يتم استخدامها لضمان التوافق مع القناة والحفاظ على الحماية ضد التآكل في التركيبات الرطبة أو تحت الأرض.
يجب أن تتطابق أجسام الأنابيب مع نوع الأنابيب التي من المفترض أن يتم توصيلها، لذا فإن التوافق هو عامل رئيسي عند اختيار النوع المناسب لمشروعك.
اختلافات التصميم لتطبيقات محددة
تتوفر هياكل الأنابيب بتصاميم متنوعة لتلبية احتياجات تطبيقات محددة. من بين هذه التصاميم:
- الأحجامتتوفر هياكل الأنابيب بأحجام مختلفة تناسب قطر الأنبوب وتستوعب عدد الأسلاك المطلوب مرورها. يضمن اختيار الحجم المناسب توفير مساحة كافية لسحب الأسلاك وصيانتها.
- نقاط الوصول:تأتي العديد من أجسام الأنابيب مع أغطية قابلة للإزالة أو نقاط وصول متعددة لتسهيل سحب الأسلاك، والتوصيل، وفحص النظام. تتيح إمكانية فتح وإغلاق الهيكل سهولة الصيانة بمرور الوقت.
- خيارات الخدمة الشاقة: For harsh environments, heavy-duty فُولاَذ أو zinc-coated conduit bodies may be used. These bodies are designed to withstand high-impact situations and offer enhanced durability.
Each type of conduit body is tailored to meet the needs of specific projects, offering versatility and flexibility in a variety of installations.
Code Compliance and Standards for Conduit Bodies

Conduit bodies must adhere to various regulatory standards to ensure they meet safety, durability, and performance requirements. In this section, we will discuss the NEC (National Electrical Code) requirements for conduit bodies, including the key codes that govern their use, UL (Underwriters Laboratories) Listing, and CSA (Canadian Standards Association) certifications. We will also cover best practices for installation to ensure compliance with these standards.
NEC (National Electrical Code) Requirements
The National Electrical Code (NEC) is a set of regulations used in the United States to ensure safe electrical installations. Several specific NEC sections apply to the use of conduit bodies in electrical systems. These sections outline the necessary safety measures, proper installation practices, and performance criteria.
NEC Article 300.15 Boxes, Conduit Bodies, or Fittings: Where Required
NEC 300.15 provides the general requirements for when a box, conduit body, or fitting is required in an electrical installation. These components are essential for providing proper access and protection for conductors at various points along the wiring system. The code outlines specific requirements for their use at outlet points, splice points, junction points, and other key locations.
General Requirement:
A box or conduit body must be installed at each outlet point, switch point, conductor splice point, conductor junction point, conductor termination point, wiring method transition point, or conductor pull point. This requirement applies when using conduit, tubing, Type AC cable, Type MC cable, Type MI cable, nonmetallic-sheathed cable, or other cables unless an exception is specifically permitted under 300.15(A) through (L).
NEC Article 314
Conduit bodies are essential components used to join, protect, and provide access to electrical conductors in various wiring installations. Under NEC Article 314, conduit bodies are classified as boxes or fittings that serve as junction points for wiring systems, enabling secure connections and ensuring accessibility for future maintenance or modification. The article provides comprehensive guidelines on the installation, sizing, and specific use cases for conduit bodies to maintain safety, efficiency, and code compliance in electrical systems.
Some key points introduced in Article 314:
Types of Conduit Bodies:
Conduit bodies come in various materials, including cast metal, sheet metal, and nonmetallic types. They serve as connection points between raceways and cables.
They must be designed and listed specifically for their intended use, ensuring safety and performance.
Volume Calculations:
Conduit bodies must be large enough to accommodate the number and size of conductors they enclose. The volume of a conduit body must meet the requirements set in 314.16(C), ensuring there is adequate space for all conductors.
Cross-sectional area: For most conduit bodies, the cross-sectional area must be at least twice the area of the largest conduit it is attached to, ensuring that conductors can be routed safely without overcrowding.
Installation and Use:
Conduit bodies are required to be securely supported in a rigid and stable manner. This ensures they can withstand environmental stresses and maintain structural integrity over time.
Short-radius conduit bodies, like elbows, which are intended to change the direction of the conduit system, are exempt from housing splices, taps, or devices.
Damp or Wet Locations: When installed in wet locations, conduit bodies must be designed to prevent moisture from accumulating inside. Drainage openings are allowed in such installations to prevent water ingress.
Conduit Bodies with Splices or Taps:
Only those conduit bodies marked by the manufacturer with their volume are permitted to contain splices, taps, or devices. These must comply with volume requirements and be sized appropriately to handle the electrical load.
Protection and Abrasion:
Conductors entering a conduit body must be protected from abrasion. Insulating bushings should be used where metal conduit bodies are installed with unprotected conductors.
Conduit bodies are also required to have adequate fittings and closures to prevent accidental contact with live conductors and to maintain the integrity of the wiring system.
Conduit Bodies for Larger Conductors:
For installations involving conductors larger than 6 AWG, the conduit body size must be calculated based on the conductors’ total cross-sectional area. This ensures enough space for proper conductor management and heat dissipation.
Maintenance and Accessibility:
Conduit bodies must remain accessible after installation for inspection, maintenance, and potential upgrades. This is essential for ensuring safety and allowing for any future modifications or repairs without significant disruption to the wiring system.
UL Listed Conduit Bodies
The Underwriters Laboratories (UL) is an independent safety certification organization that ensures electrical products meet established safety standards. Conduit bodies are typically UL Listed, which means they have passed rigorous testing and are deemed safe for use in electrical systems. The related UL standards for conduit bodies including UL514C and UL 514B.
UL 514C – Nonmetallic Outlet Boxes, Flush Device Boxes, and Covers
UL514C sets forth the performance and testing requirements for conduit bodies. These standards are critical for ensuring that conduit bodies are safe, reliable, and durable in electrical systems. Some key performance tests and requirements under UL 514C include:
أبعاد: UL 514C specifies the dimension requirements for conduit bodies, including their cross-sectional area requirements, inside volume etc.
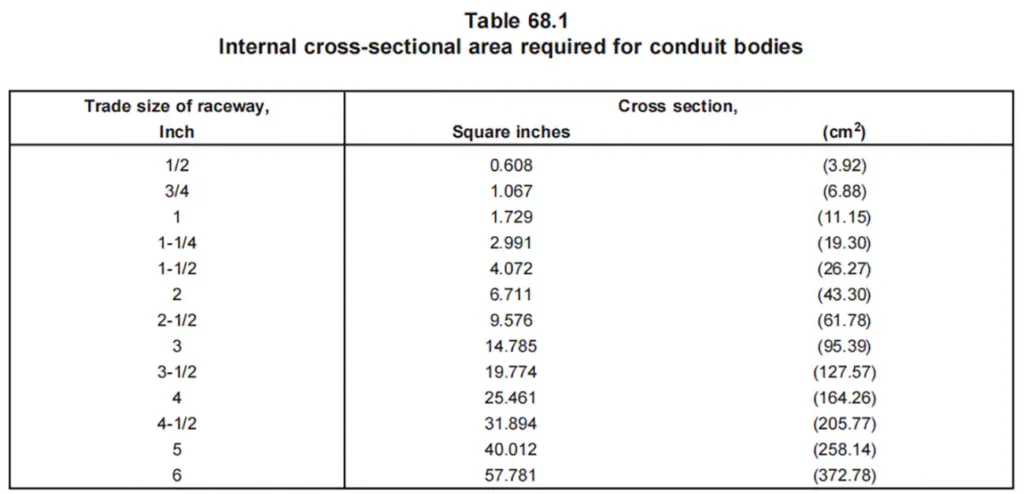
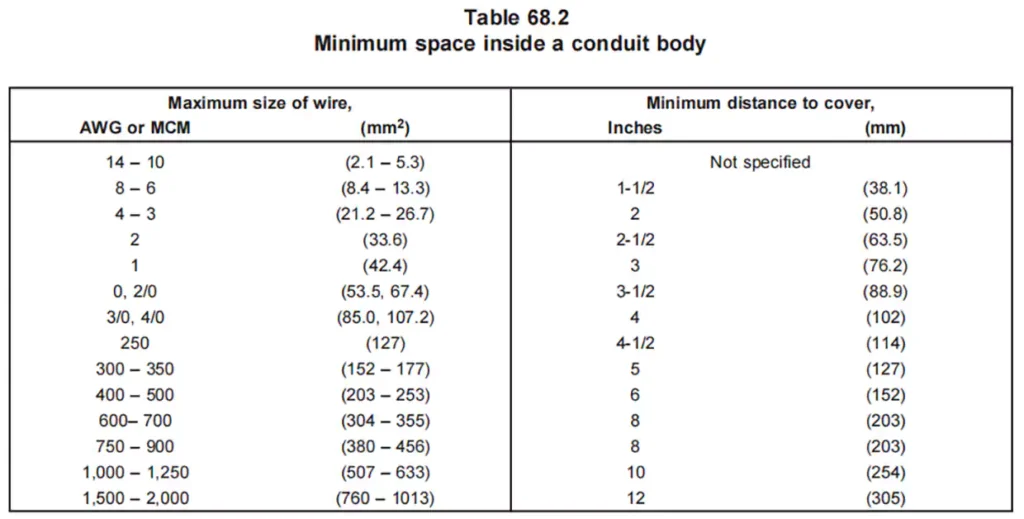
Temperature Endurance: Conduit bodies must withstand elevated temperatures, 92℃ as specified in the standard, without deformation, warping, cracking, or losing their structural integrity. UL 514C tests the ability of conduit bodies to handle extreme conditions, ensuring they perform reliably in both high and low-temperature environments.
Flame Retardant: Require the conduit box do not support combustion for more than 5 seconds after the third application of the flame, and there should be no flame drops, and the box should not be completely consumed.
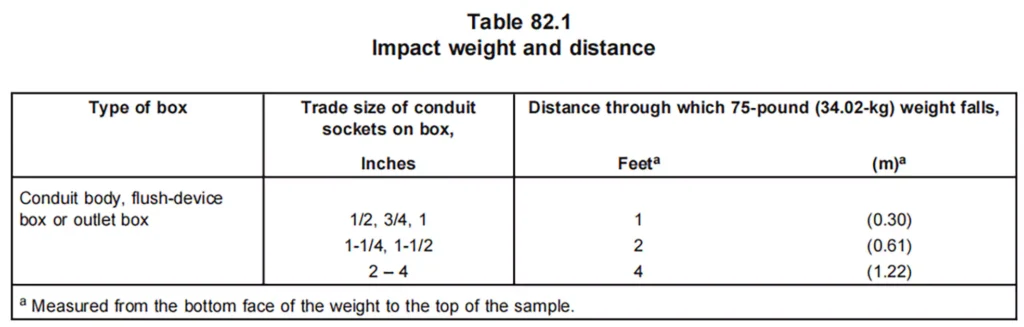
القوة الميكانيكية: Conduit bodies are subject to mechanical stress testing to ensure they can resist physical impacts, vibrations, and other mechanical stresses typically encountered in electrical systems. Including the tensile test, impact test.
المقاومة للتآكل: UL 514C requires that conduit bodies meet specific corrosion resistance standards, particularly for those used in wet or harsh environments. This ensures that the conduit body will not degrade or compromise the integrity of the wiring.
Electrical Insulation and Conductivity: For non-metallic conduit bodies, UL 514C verifies that the material is non-conductive, preventing any risk of electrical shorts or shocks. For metallic bodies, they must be properly insulated or grounded as necessary.
Protection Against Environmental Elements: Conduit bodies used in outdoor or harsh environments must be tested for weatherproofing and resistance to elements like moisture, dust, and chemicals. This ensures that electrical systems remain safe even in challenging environments.
UL 514B – Conduit, Tubing, and Cable Fittings
UL 514B is the Underwriters Laboratories standard that outlines the construction, performance, and safety requirements for conduit bodies, ensuring they are safe for use in electrical installations. This standard applies to all conduit bodies used to connect raceways and cables, including those intended for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. Below is an overview of the key requirements outlined in UL 514B regarding dimensions, construction materials, and performance standards. It covers aspects like:
Dimensions of Conduit Bodies:
UL 514B specifies precise dimensional criteria to ensure conduit bodies are suitable for housing conductors and maintaining their intended function.
Construction and Material Requirements:
The materials and construction methods used in the manufacturing of conduit bodies are crucial for their durability, performance, and safety. UL 514B specifies the following requirements for construction:
Performance Requirements:
UL 514B ensures that conduit bodies meet stringent performance standards to guarantee electrical safety, durability, and overall functionality. These include:
Physical Strength:
مقاومة التأثير: Conduit bodies must be able to withstand physical impact without cracking or failing. This is particularly important in environments subject to mechanical stresses.
Compression Strength: The material must be strong enough to resist deformation when subject to compression, ensuring the conduit body maintains its shape under load and does not collapse or become deformed under normal conditions.
السلامة الكهربائية:
العزل الكهربائي: For nonmetallic conduit bodies, the materials must be electrically insulating to prevent inadvertent short circuits or shock hazards. Metal conduit bodies, on the other hand, must be properly bonded and grounded to ensure that they do not carry stray electrical current that could pose a shock risk.
Moisture and Corrosion Resistance: UL 514B requires that conduit bodies have sufficient protection against moisture and corrosion, particularly when used in damp or wet environments. This includes proper sealing and the use of corrosion-resistant materials to maintain electrical safety over time.
CSA Certified - CSA C22.2 No. 85
In Canada, the Canadian Standards Association (CSA) establishes safety standards for electrical products. Conduit bodies sold in Canada must comply with CSA C22.2 No. 85, which provides the requirements for fittings for electrical conduit and tubing. Some key requirements under CSA C22.2 No. 85 include:
Material and Design Standards:
Similar to UL standards, CSA requires that conduit bodies meet specific material composition and design criteria to ensure they are suitable for safe and reliable use in electrical systems.
Dimensions of Conduit Bodies:
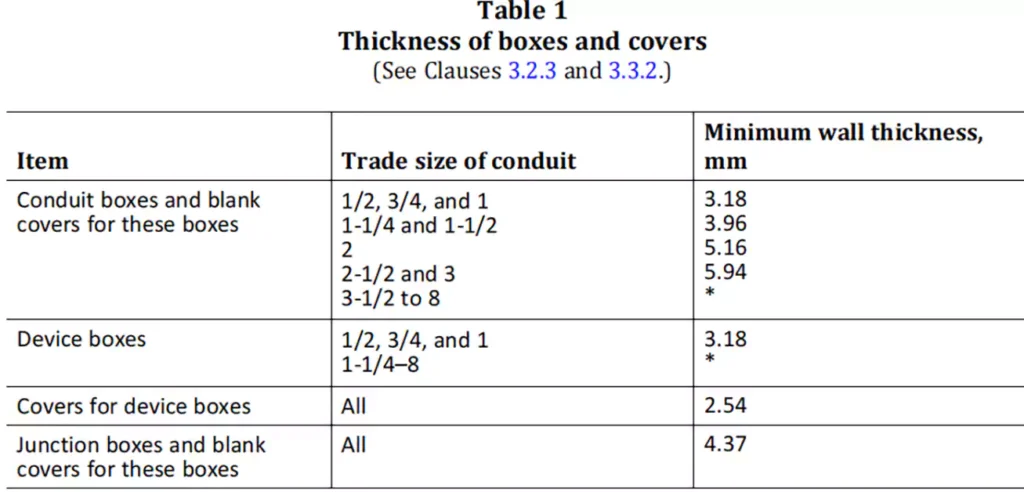
CSA C22.2 No. 85 sets specific dimensional criteria to ensure that conduit bodies have adequate space for wiring and can accommodate the conductors within raceways without risking overcrowding or improper installation.
Physical Performance and Durability Requirements:
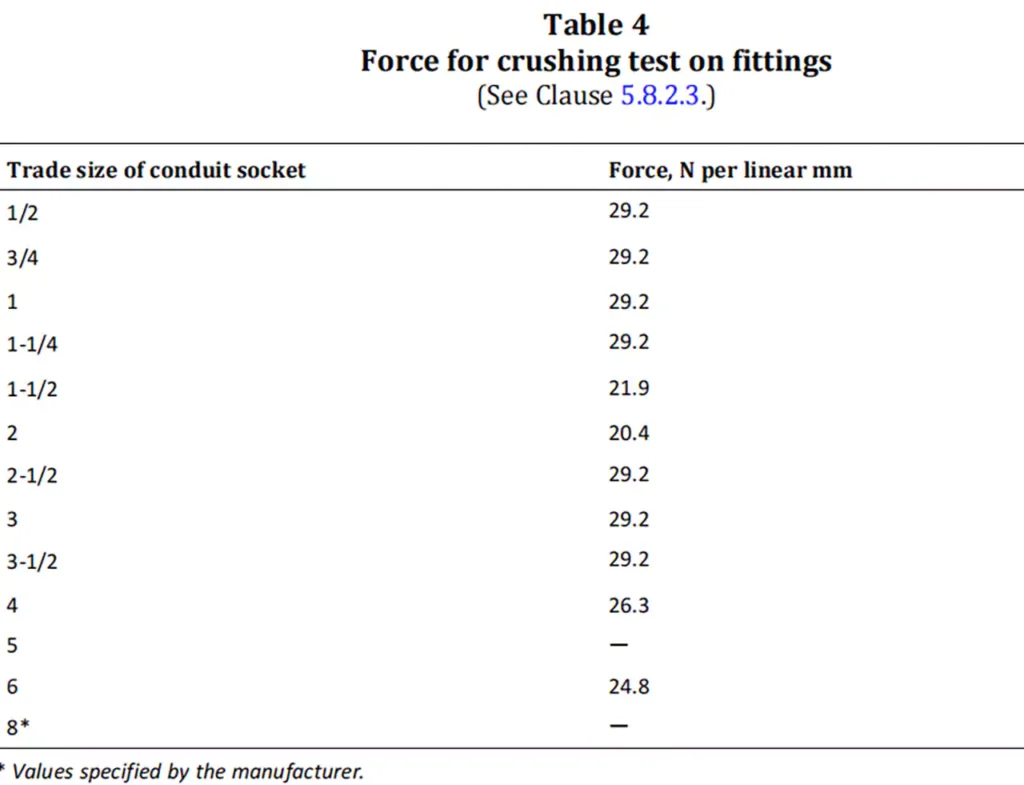
CSA C22.2 No. 85 outlines various physical and environmental performance requirements to ensure that conduit bodies can operate reliably under harsh conditions. These include resistance to heat, flame, impact at -34 Degree Celsius., and crushing.
مقاومة كيميائية:
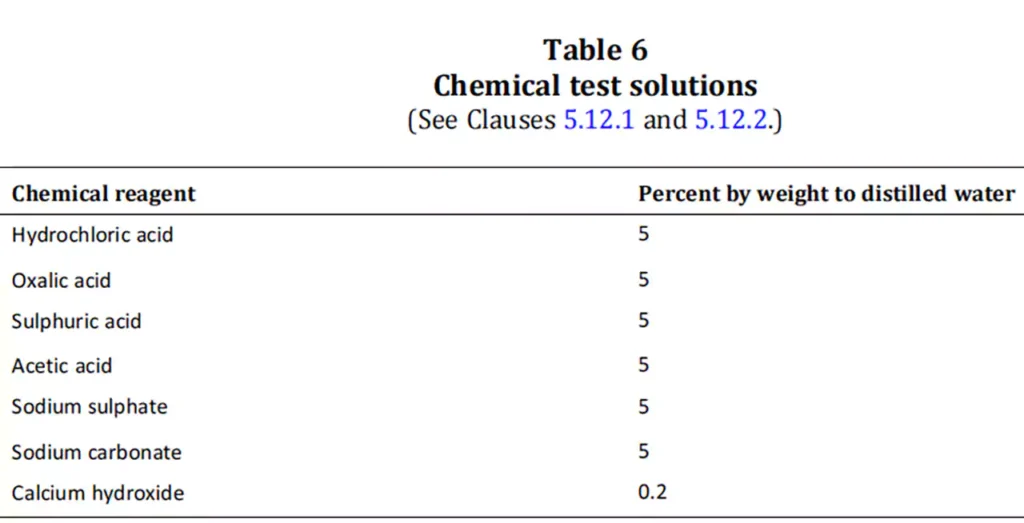
المقاومة للتآكل: Conduit bodies, especially those used in outdoor or industrial applications, must be resistant to corrosion caused by exposure to moisture, chemicals, and pollutants. This is especially true for metallic conduit bodies, which must be treated or coated with corrosion-resistant materials to prevent rusting and deterioration.
التعرض للمواد الكيميائية: Nonmetallic conduit bodies must also exhibit resistance to common industrial chemicals, oils, and solvents that may be encountered in some electrical installations, ensuring they do not degrade or lose their structural integrity.
Marking and Labeling:
Conduit bodies must be clearly marked with manufacturer information, material type, voltage ratings, and CSA certification. Durable labeling ensures that conduit bodies are used properly and meet safety regulations.
Conduit Body Applications
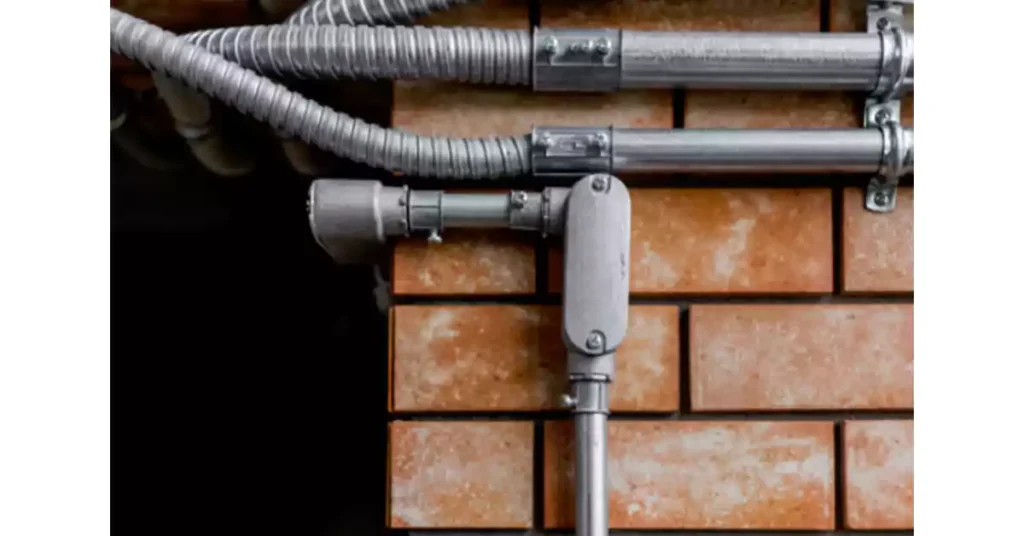
Conduit bodies are essential components used in various electrical installations to protect and organize wiring. Their versatility makes them suitable for a wide range of applications in both residential and industrial environments. Below are some common uses for conduit bodies:
1. Residential Electrical Systems
In homes, conduit bodies are used for:
توصيلات الأسلاك: They provide a secure space for connecting and joining electrical wires. This ensures that wiring is well-organized and accessible for future maintenance.
حماية: They help protect electrical wiring from physical damage and environmental factors like moisture and heat, especially in areas like basements or kitchens.
Branch Circuits: Conduit bodies allow electrical systems to branch out and power multiple circuits, such as outlets, lights, and appliances.
2. Commercial and Industrial Applications
In businesses and factories, conduit bodies are used in:
Control Panels: They house wiring connections and provide easy access to electrical systems, ensuring smooth operations in industrial settings.
Heavy-Duty Systems: They protect wiring from physical damage in environments that involve high mechanical stress, such as factories and warehouses.
Automation Systems: Conduit bodies help route electrical wiring safely to machinery, robots, and automated equipment.
3. Wet and Damp Locations
In areas with exposure to moisture, conduit bodies are designed to meet specific standards for wet and damp locations:
المنشآت الخارجية: Conduit bodies used outdoors—such as for street lighting, signage, or landscape lighting—are built to prevent moisture ingress and protect wiring from weather-related damage.
Damp Environments: In places like basements, parking garages, or laundry rooms, conduit bodies prevent moisture from affecting the wiring, reducing the risk of short circuits or deterioration of the electrical system.
الأماكن الرطبة: In locations directly exposed to water, like outdoor swimming pools, fountains, or marine environments, special conduit bodies rated for wet locations provide full protection against moisture, ensuring the safety of electrical systems.
4. Data Centers and Telecommunications
In data centers and telecommunications systems, conduit bodies are used to:
Manage Cables: They keep cables organized and protected while ensuring the safe routing of electrical wiring within the infrastructure of sensitive equipment.
Provide Safety: Conduit bodies help to prevent electrical interference, protect wiring from external elements, and ensure that the electrical systems continue to function smoothly without risk to critical data and communication systems.
5. Hazardous Locations
In environments with a higher risk of fire or explosion, such as chemical plants or oil refineries, conduit bodies are designed to:
Explosion-Proof: Explosion-proof conduit bodies prevent the risk of sparks or electrical arcs from igniting flammable gases or vapors, providing safety in volatile environments.
المقاومة للتآكل: In areas where the electrical system is exposed to harsh chemicals or corrosive elements, conduit bodies are made from corrosion-resistant materials, ensuring they maintain their protective function
4 Benefits of Using Conduit Body

Conduit bodies are not just functional components; they offer a wide range of benefits that enhance the performance, safety, and longevity of electrical installations. Below are some key advantages of using conduit bodies in electrical systems:
1. Flexibility in Conduit Layouts
One of the primary benefits of conduit bodies is the flexibility they provide in designing and modifying electrical conduit systems.
Multiple Entry Points: Conduit bodies offer various openings and configurations, allowing for easy access points at different locations within a system. This flexibility makes it easier to change or expand electrical systems without the need to completely redesign the layout.
Complex Routing: They enable complex wiring configurations, such as sharp bends, branches, or 90-degree turns, without compromising the integrity or performance of the system. This is especially important in spaces with limited access or where the wiring must follow specific paths.
Adaptability: Conduit bodies are available in many sizes and shapes, allowing them to be used in a wide variety of installations, from small residential systems to large commercial and industrial setups.
2. Simplifying Wiring Access
Conduit bodies serve as access points for wiring connections, which simplifies the maintenance, inspection, and modification of electrical systems.
Easy Maintenance: Because they are designed for easy access, conduit bodies make it much simpler to perform electrical maintenance. Technicians can easily access splices, taps, or connections housed within the conduit body without disassembling large portions of the conduit system.
Convenient Modifications: If the electrical system needs to be updated or expanded, conduit bodies provide a convenient place for adding or modifying circuits without the need to disrupt the entire installation.
Safe Access: They also provide safe and organized access to wiring, which can be important for troubleshooting or repairs, reducing the risk of accidental damage to the wiring or the system as a whole.
3. Protection of Electrical Connections
Conduit bodies play a crucial role in protecting electrical connections and ensuring the overall safety of the electrical system.
Shielding from Physical Damage: By enclosing wiring connections, conduit bodies protect them from external forces such as physical impacts, abrasion, or crushing. This is particularly important in environments where cables are at risk of being damaged by equipment, machinery, or everyday wear and tear.
Moisture and Dust Protection: In wet or damp environments, conduit bodies can be designed to prevent moisture or dust from entering the electrical connections, helping to maintain the integrity of the system and reducing the risk of electrical faults or failures.
تحسين السلامة: Conduit bodies help maintain safe electrical systems by ensuring that connections are properly protected from environmental hazards. This contributes to reducing the risk of short circuits, sparks, and potential fire hazards.
4. Reducing Stress on Cables and Wires
Electrical cables and wires are often subjected to mechanical stresses, especially in systems with sharp bends or high traffic areas. Conduit bodies help alleviate this stress, contributing to the longevity of the wiring system.
Preventing Physical Stress: By providing a smooth path for cables and offering space for changes in direction, conduit bodies reduce the risk of kinks, tight bends, or other forms of mechanical stress on the wires. This helps prevent the potential for insulation damage and reduces the risk of wire breakage.
Minimizing Wear and Tear: Conduit bodies can also prevent direct contact between the cables and surfaces that might cause abrasion, further protecting the wiring and extending its service life.
Reducing Tension on Wires: They allow for smoother transitions and more room for wiring within the system, ensuring that wires do not experience undue tension, which can lead to failure or degradation of the cable insulation.
Conduit Body Installation Guide (7 Steps)
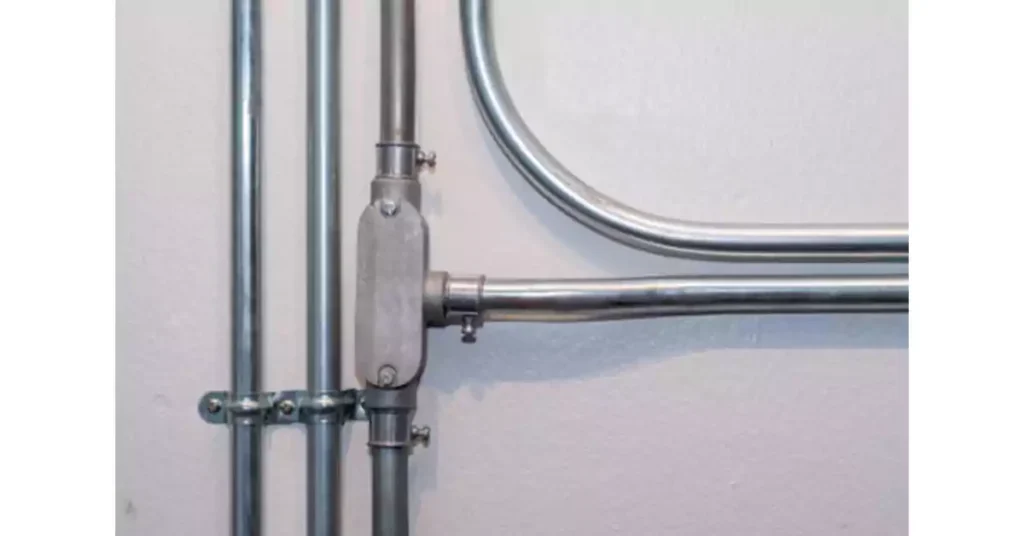

Installing conduit bodies correctly is essential for ensuring a safe and reliable electrical system. Proper installation not only helps maintain code compliance but also ensures the system operates efficiently and minimizes the risks of electrical faults or failures. This section provides a step-by-step guide to installing conduit bodies, highlights the tools needed, and emphasizes key considerations based on relevant codes of such as International Residential Code and NEC.
Tools Required for Installation
Before starting the installation, ensure you have the following tools:
- Measuring Tape: For accurately measuring distances and ensuring conduit bodies are placed in the right location.
- Screwdriver: To secure screws and fasteners in place.
- Wire Strippers: To prepare the conductors before they enter the conduit body.
- Hacksaw or Pipe Cutter: For cutting conduits to the required length.
- Conduit Bender: To bend the conduit to fit the installation layout if required.
- Drill: To create holes for mounting the conduit body if needed.
- Level: To ensure the conduit body is correctly aligned.
- Conduit Wrenches: For tightening connections securely.
Step-by-Step Installation Process (7 Steps)
1. Prepare the Conduit and Conductors
Measure and cut the conduit to the required lengths using a hacksaw or pipe cutter. Make sure the conduit ends are clean and free from burrs.
Strip the insulation from the conductors carefully, ensuring the exposed wires are ready for connection.
2. Position the Conduit Body
Select the appropriate location for the conduit body. Ensure that the position complies with NEC Code Section 314.17 for access and clearance, allowing space for wiring and other connections.
Mount the conduit body securely, using a level to ensure it is aligned correctly. Make sure it is placed at an accessible location for future maintenance.
3. Install the Conduit Entries
Connect the conduit to the conduit body by threading the conduit into the appropriate entry points on the conduit body. Use a conduit wrench to tighten the connections and ensure they are secure.
If using any fittings or bushings, ensure they are installed correctly to avoid damage to the conductors (NEC 300.4(G)).
4. Insert Conductors into the Conduit Body
Insert the prepared conductors into the conduit body, ensuring they pass through any openings smoothly and without damage. According to NEC, conductors entering the conduit body should be protected from abrasion. Use insulating fittings or bushings where necessary.
5. Close Any Openings
If there are unused openings in the conduit body, close them with approved plugs or covers as to prevent any exposure to moisture or dust, which could compromise the safety of the installation.
6. Secure and Seal the Conduit Body
Secure the cover or device to the conduit body, ensuring it is tightly fastened using appropriate screws. Follow manufacturer instructions for any specific sealing requirements.
Use non-corrosive, weather-resistant materials if installing in wet or damp environments.
7. Test the Installation
Once the conduit body and conductors are installed and secured, test the system for continuity and proper operation. Inspect all connections for tightness, ensuring that no part of the system is loose or improperly mounted.
5 Tips for Securing and Sealing
- Tighten Connections Properly: Always ensure that threaded connections between the conduit and the conduit body are tightened securely. Over-tightening can damage threads, while under-tightening can lead to leaks or faults in the system.
- Use Insulated Fittings: To protect the conductors from abrasion when entering the conduit body, use insulated fittings (per NEC 300.4(G)) where appropriate.
- Seal Unused Openings: Unused openings must be sealed using proper plugs or covers to prevent entry of moisture, dust, or debris. Ensure that these covers are properly secured.
- Waterproofing in Wet Locations: In wet or damp environments, be sure to use waterproof conduit bodies and ensure all connections are sealed with a gasket or other weatherproof material.
- Ensure Proper Grounding: Make sure that any metal conduit bodies are properly grounded as per the grounding requirements of the NEC (Section 250).
4 Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Incorrect Placement: Ensure that the conduit body is installed in a location that allows easy access for future maintenance and modification. Avoid placing the conduit body where it is difficult to reach or in locations with poor ventilation.
- Not Sealing Unused Openings: Leaving unused openings in the conduit body open can lead to moisture ingress, which could result in short circuits or corrosion over time.
- Failure to Follow Code: Make sure the installation adheres to the local code, including requirements like those outlined in NEC for securing, sealing, and mounting conduit bodies. Not complying with these can result in unsafe installations or costly repairs.
- Improper Support: Make sure the conduit body is properly supported, especially when mounted in areas with high vibration or movement. According to NEC, all enclosures should be securely mounted to prevent accidental dislodging.
Buying Guide for Conduit Bodies

Choosing the right conduit body is crucial for ensuring the safety, efficiency, and longevity of your electrical installations. With a variety of options available, it’s important to consider the specific requirements of your project, including environmental factors, installation conditions, and compliance with relevant standards. This guide will help you navigate the selection process and make an informed purchase decision.
5 Factors to Consider When Buying Conduit Bodies
1. Size and Capacity
Conduit bodies come in different sizes, often referred to as “trade sizes,” which relate to the diameter of the conduit. You need to pick a size that suits the number of conductors (wires) you will be using, as well as any future wiring that might need to pass through. If the conduit body is too small, it could lead to crowded wires that are difficult to manage. If it’s too large, it may be unnecessary and take up too much space.
2. Material
The material of the conduit body affects its durability and ability to handle environmental factors.
3. Environmental Conditions (Indoor vs. Outdoor Use)
The environment where the conduit body will be installed is crucial. For indoor use, plastic or aluminum is often sufficient. However, for outdoor use or areas exposed to moisture, heat, or chemicals, you’ll need a more rugged material like aluminum or steel. Make sure the conduit body is sealed properly to prevent water or dust from entering.
4. Compatibility with Existing Conduit Systems
Ensure the conduit body matches the size and type of conduit you’re using. Conduit bodies come in different styles (like LB, T, LL) and sizes, so check that the trade size of the conduit body matches your conduit, and that the style works with your wiring layout.
Choosing a conduit body from a reputable manufacturer ensures you’re getting a high-quality, durable product that meets safety standards. Trusted brands typically offer better customer service, warranties, and ensure that their products meet important certifications like UL or CSA.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting for Conduit Bodies
Proper maintenance of conduit bodies is essential to ensure the continued safety and functionality of your electrical system. Regular inspections and prompt attention to any signs of wear or damage can help you avoid costly repairs and potential electrical hazards. In this section, we’ll explore some key tips for maintaining your conduit bodies and troubleshooting common issues.
Routine Inspection Tips
Routine inspections are crucial to ensure that your conduit bodies remain in good condition. Here’s how to go about it:
- Visual Inspection: Start with a visual check to spot any obvious signs of damage or wear. Look for cracks, dents, or deformations in the conduit body. Check the cover and sealing gaskets for any signs of looseness, rust, or corrosion.
- النظافة: Make sure that the conduit body is free from debris, dirt, or any other buildup that could block openings or impede airflow. Dust or dirt can build up over time, which might also affect the performance of the seals or cause overheating.
- Secure Connections: Ensure that all fasteners are tight and that the conduit body is securely mounted. Loose connections or poorly sealed conduit bodies can lead to moisture intrusion, which could damage the wiring inside.
- Check for Ingress: Examine the conduit body for any signs of water, dust, or other contaminants entering. This is especially important for outdoor or wet-location installations. Look for moisture buildup inside the body or at the conduit entry points, as this could indicate a compromised seal.
Identifying Signs of Wear and Damage
Identifying wear and damage early can save you from more serious problems down the line. Here are some common signs to look for:
الأضرار المادية: Look for cracks, splits, or other physical damage to the conduit body. These can weaken the structure and compromise its protective function. Impact damage is particularly common in outdoor installations, so be sure to check for any visible dents or deformations.
تآكل: In wet or outdoor environments, metal conduit bodies can corrode over time. If you notice rust, pitting, or any signs of oxidation, this can lead to structural weaknesses and potential failure. Corrosion can also affect the electrical grounding of the system.
Loosening or Displacement: If the conduit body cover or fittings are loose or have become misaligned, this can lead to improper sealing, exposing the internal wiring to environmental factors. Tighten any loose screws and ensure that all components are properly aligned.
Moisture or Debris Inside: If you find water, rust, or other debris inside the conduit body, it could indicate that the seal is no longer intact. Moisture is especially concerning as it can lead to short circuits or corrosion of the internal wiring.
Repair and Replacement Considerations
When a conduit body shows signs of wear, you may be faced with the decision to repair or replace it. Here are some considerations to guide your decision:
Minor Damage: If the damage is minor (such as a loose cover or a small crack), a simple repair might be sufficient. Tighten any loose fasteners or replace worn seals, gaskets, or screws. For cracks or damage in plastic conduit bodies, you might be able to apply a sealant or patch if the damage is not severe.
Corrosion or Major Damage: If the conduit body is significantly corroded or structurally compromised (such as severe cracking or rusting), it is often best to replace it entirely. Corrosion can weaken the integrity of the conduit body, making it a safety hazard. A replacement ensures that your electrical system remains secure and fully functional.
Old or Outdated Conduit Bodies: If your conduit body is outdated or no longer complies with current electrical codes, it might be worth replacing it with a newer model that meets modern standards. This is particularly true if the conduit body has been in place for a long time and shows signs of aging, such as brittle materials or outdated fittings.
Cost Considerations: While repairs might seem more cost-effective in the short term, it’s important to evaluate the long-term cost. In some cases, replacing a conduit body with a newer, more durable model may be a more cost-effective solution in the long run, as it will likely last longer and require fewer repairs.
FAQs:

كيف تقوم بإغلاق أجسام الأنابيب للاستخدام الخارجي؟
Sealing conduit bodies for outdoor use is essential to protect electrical connections from moisture, dust, and other environmental elements. Here’s how to properly seal them:
- Use Weatherproof Gaskets: When installing conduit bodies outdoors, ensure that the cover and the body are equipped with a weatherproof gasket or sealant. This will help prevent water and dirt from entering the body.
- Apply Silicone Sealant: For additional protection, you can apply silicone or polyurethane sealant around the edges of the conduit body cover before securing it. This creates a more airtight and waterproof seal.
- Use Approved Outdoor-Rated Fittings: When using conduit bodies outdoors, it’s crucial to use components specifically rated for outdoor use, such as weather-resistant covers and corrosion-resistant fittings.
- Check Seals Regularly: Over time, seals and gaskets may wear out, so it’s important to inspect and replace them periodically to ensure a continued waterproof barrier.
ما هي استخدامات أجسام القنوات؟
Conduit bodies serve several functions in electrical systems:
- Junction Points: They act as connection points where different sections of conduit come together. Conduit bodies provide a safe, accessible location for splicing or joining electrical wires and cables.
- Wiring Access: They provide access to the wiring within the conduit system for future maintenance or troubleshooting. This allows electricians to work on the wiring without needing to dismantle large sections of the conduit system.
- Cornering and Bending: Conduit bodies, such as the LB, LR, and LL types, allow for smooth direction changes in the conduit system, helping to run wires around corners and bends.
- حماية: They offer additional protection to wiring from external elements and damage by enclosing the wires in a safe, secure box.
كيف تقوم بتشغيل قناة حول الزوايا؟
Running a conduit around corners requires either using pre-made fittings or bending the conduit manually. Here’s how to do it:
- Use Conduit Bodies: The most common method to run conduit around corners is by using a conduit body, such as the LB, LR, or LL models, which are designed for this purpose. These conduit bodies have built-in angles that allow for smooth changes in direction without the need for bends.
- Use Elbows or 90-Degree Bends: If you’re not using a conduit body, you can use elbows or pre-formed 90-degree bends. These fittings are installed directly into the conduit system to turn the conduit at the desired angle. Ensure that the bend radius meets the requirements for the type of conduit you’re using to prevent damage to the wire inside.
- Manual Bending: For metal conduit (such as EMT or RMC), you can use a conduit bender to create a custom bend around a corner. However, be mindful of the conduit’s minimum bend radius to prevent damaging the conduit or wiring.
خاتمة
In this article, we’ve explored the essential role that conduit bodies play in electrical systems, offering both functional and safety benefits. Conduit bodies are critical for providing accessible junction points, simplifying wiring layouts, protecting electrical connections, and ensuring smooth transitions in conduit systems. Whether you’re working with an LB, LR, or LL type, each conduit body is designed to meet specific needs while adhering to safety codes like NEC and CSA standards.
Understanding the types of conduit bodies, their applications, and the importance of code compliance ensures that your installations are both efficient and safe. Regular maintenance and correct installation will keep your electrical systems functioning smoothly and compliant with industry regulations.
If you’re ready to enhance your electrical systems with high-quality conduit bodies, contact us today or explore our wide selection of conduit bodies and fittings that meet the highest industry standards. Let us help you create safe, reliable, and efficient electrical systems with the right conduit solutions!



