
جدول المحتويات
إن توصيل الأسلاك عبر الأنابيب مهمة شائعة في التركيبات الكهربائية، سواء كنت تقوم بتوصيل الأسلاك في مبنى جديد أو توصيل الكابلات الكهربائية للتجديدات أو تركيب خطوط الاتصالات. من الأهمية بمكان أن تتم هذه العملية بشكل صحيح لضمان السلامة والوظائف والامتثال للمعايير. إن استخدام التقنيات المناسبة يمكن أن يمنع تلف الأسلاك والأنابيب مع تقليل العمالة أيضًا. ستغطي هذه المقالة ست طرق فعالة لتوصيل الأسلاك عبر الأنابيب.
قبل البدء في عملية سحب الأسلاك عبر الأنابيب، من الضروري الاستعداد بعناية. فهذا لا يمنع الضغط غير الضروري على الأسلاك والأنابيب فحسب، بل يساعد أيضًا في تجنب المضاعفات مثل الأسلاك المكسورة أو عطل النظام في المستقبل.
يؤثر حجم ونوع الأنابيب (PVC، EMT، مرن) بشكل كبير على سهولة سحب الأسلاك. يمكن أن تستوعب الأنابيب الأكبر عددًا أكبر من الأسلاك، ولكنها تتطلب أيضًا قوة أكبر لسحب الأسلاك من خلالها. يعد فهم إرشادات قانون الكهرباء الوطني (NEC) حول ملء الأنابيب أمرًا بالغ الأهمية لتجنب ارتفاع درجة الحرارة وضمان الامتثال.
تتمتع أنواع مختلفة من الأسلاك (THHN وNM وما إلى ذلك) بمستويات متفاوتة من المرونة والصلابة. قد يكون سحب الأسلاك ذات القياس الأكبر أكثر صعوبة، وخاصة في المسافات الأطول. من الضروري اختيار السلك المناسب للتطبيق المقصود.
يؤثر طول مسار الأنبوب وأي انحناءات أو انعطافات على عملية السحب. فكلما زاد عدد الانحناءات في الأنبوب، زادت صعوبة سحب السلك. إن التخطيط للمسار بأقل عدد ممكن من الانحناءات من شأنه أن يسهل عملية سحب السلك.
يمكن لعوامل مثل درجة الحرارة والرطوبة ووجود الغبار أو الرطوبة أن تؤثر على كل من السلك وعملية السحب. على سبيل المثال، يمكن أن تتسبب الرطوبة العالية في التصاق الأسلاك ببعضها البعض، مما يجعل سحبها أكثر صعوبة.
من الضروري أن يكون لديك الأدوات المناسبة في متناول اليد. ويشمل ذلك أدوات سحب الأسلاك ومواد التشحيم ومعدات السلامة. إن تقييم الأدوات المطلوبة للمهمة مسبقًا يمكن أن يوفر الوقت ويمنع حدوث المضاعفات.
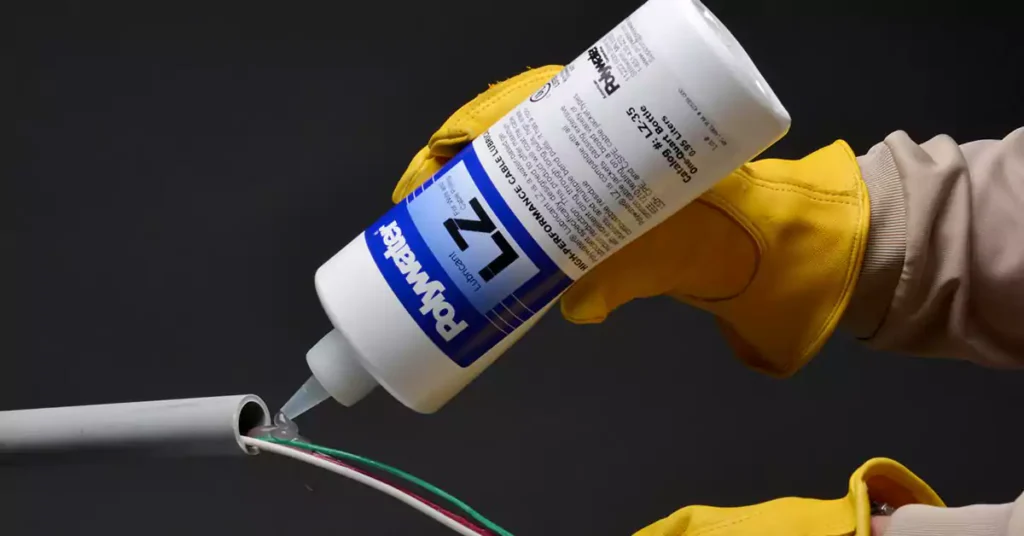

تلعب زيوت التشحيم المستخدمة في سحب الأسلاك (والتي غالبًا ما تسمى زيوت التشحيم المستخدمة في سحب الأسلاك) دورًا أساسيًا في تقليل الاحتكاك بين الأسلاك والأنابيب. فعند سحب الأسلاك عبر مسارات طويلة أو أنابيب ذات انحناءات متعددة، قد يتراكم الاحتكاك، مما يجعل من الصعب سحب الأسلاك بسلاسة. تساعد زيوت التشحيم في ضمان انزلاق الأسلاك بسهولة، مما يحميها من التلف.
هناك نوعان رئيسيان من زيوت التشحيم المستخدمة في سحب الأسلاك: زيوت تعتمد على الماء وزيوت تعتمد على الشمع.
- زيوت التشحيم القائمة على الماء: هذه هي أكثر أنواع زيوت التشحيم استخدامًا. فهي سهلة التنظيف وصديقة للبيئة وتعمل بشكل جيد في نطاق واسع من درجات الحرارة.
- زيوت التشحيم القائمة على الشمع: تعتبر هذه الزيوت أكثر سمكًا وقد تكون ضرورية للظروف الأكثر قسوة، مثل البيئات الحارة أو الباردة. تتمتع زيوت التشحيم القائمة على الشمع بمقاومة أكبر للجفاف بمرور الوقت، وهو أمر مفيد للتطبيقات طويلة الأمد.
ضع كمية وفيرة من مادة التشحيم على السلك قبل البدء في السحب. تأكد من تغطية السلك بالتساوي ووضع كمية إضافية من مادة التشحيم عند نقطة دخول الأنبوب لتقليل المقاومة. إذا كانت عملية السحب طويلة أو صعبة بشكل خاص، يمكنك التوقف في منتصف العملية لإضافة المزيد من مادة التشحيم إلى السلك.
توجد عدة تقنيات مختلفة لسحب الأسلاك عبر الأنابيب، وأفضلها بالنسبة لك تعتمد على طول المسار ونوع السلك والمعدات المتوفرة. فيما يلي، نستكشف ست طرق شائعة تستخدم لسحب الأسلاك:

السحب اليدوي هو أبسط وأسهل طريقة، ولكن عادة ما يتم استخدامه فقط للمسارات القصيرة المستقيمة. تتضمن هذه الطريقة إدخال السلك في الأنبوب يدويًا مع توجيهه لتقليل الاحتكاك والمقاومة.
- تحضير القناة: افحص الأنبوب بحثًا عن أي حطام أو حواف حادة قد تتسبب في إتلاف السلك. نظف الجزء الداخلي من الأنبوب إذا لزم الأمر لضمان سحب سلس.
- تزييت السلك: ضع كمية وفيرة من مادة تشحيم سحب الأسلاك على السلك لتقليل الاحتكاك وتسهيل سحبه عبر الأنبوب. قم بتغطية السلك ونقطة دخول الأنبوب.
- تغذية السلك: ابدأ بإدخال السلك في الأنبوب ببطء، مع توجيهه لمنع التشابك. يمكن لشخص واحد إدخال السلك بينما يسحبه شخص آخر من الطرف المقابل.
- الحفاظ على التوتر الثابت: يجب على الشخص الذي يسحب السلك أن يطبق ضغطًا ثابتًا ومتساويًا لتجنب الالتواءات أو الانحناءات. إذا شعرت بمقاومة، فتوقف وقم بالتعديل لمنع تلف عزل السلك.
- أكمل السحب: بمجرد توصيل السلك، افحصه بحثًا عن أي علامات تلف، مثل الخدوش أو القطع. تأكد من أن السلك به مساحة كافية في كلا الطرفين لإجراء التوصيلات الكهربائية اللازمة.
يُعد السحب اليدوي مثاليًا للجري لمسافات قصيرة أو عندما لا تتوفر أدوات متخصصة. ومع ذلك، بالنسبة للجري لمسافات أطول أو أكثر تعقيدًا، قد تكون هذه الطريقة مجهدة جسديًا وأقل كفاءة.
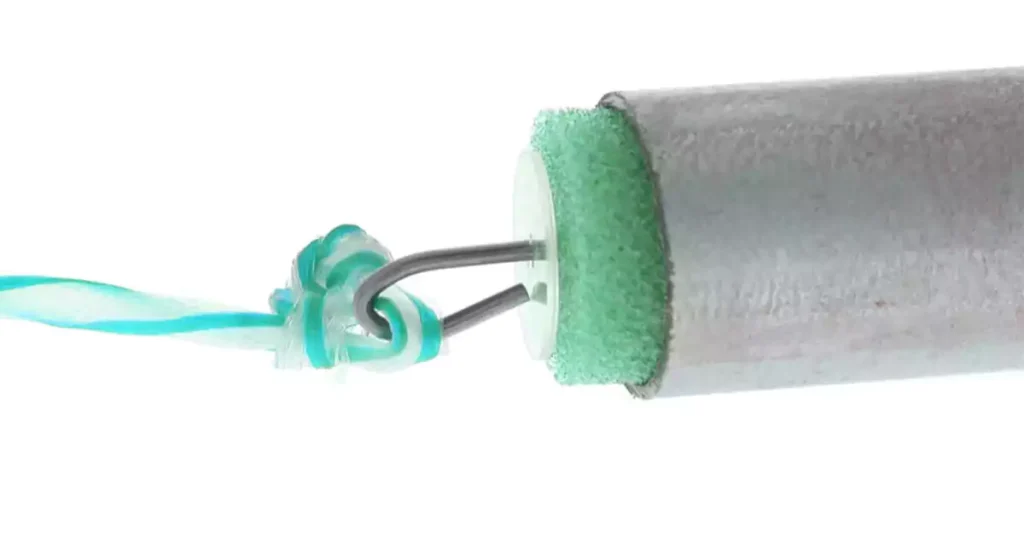
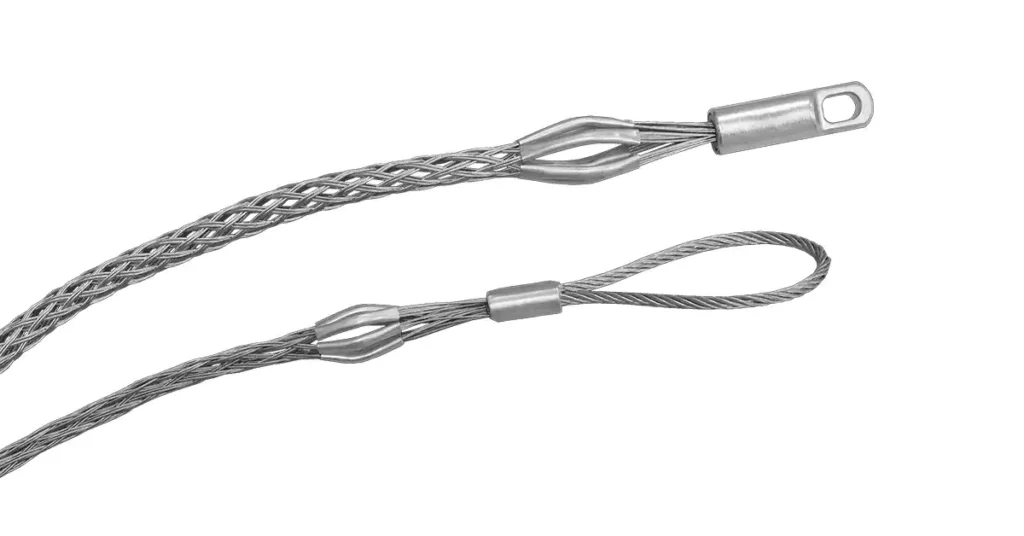
يعد استخدام الفأرة طريقة فعالة للغاية للجري لمسافات متوسطة الطول، وخاصة تلك التي تنطوي على انحناءات. يتم دفع الفأرة، وهي جهاز صغير مصنوع عادة من الرغوة أو المطاط، عبر الأنبوب بواسطة الهواء المضغوط، وسحب خيط يستخدم بعد ذلك لسحب السلك.
- حدد الماوس: اختر فأرة تتناسب بشكل مريح مع الأنبوب دون أن تكون ضيقة للغاية. يجب أن تخلق الفأرة مقاومة كافية ليتم دفعها بواسطة الهواء ولكن ليس كثيرًا بحيث تتعطل.
- قم بربط سلسلة السحب: اربط خيطًا قويًا بالماوس باستخدام عقدة قوية. تأكد من أن الخيط طويل بما يكفي للوصول إلى الطرف الآخر من الأنبوب.
- إعداد منفاخ الهواء: أدخل فوهة منفاخ الهواء في الأنبوب، مع التأكد من إحكام الغلق لزيادة ضغط الهواء إلى أقصى حد. قم بتشغيل المنفاخ وادفع الفأرة عبر الأنبوب.
- استرداد الفأرة والخيط: بمجرد خروج الفأر من الطرف الآخر للأنبوب، قم بإخراج الخيط والفأر. افصل الفأر وتأكد من أن الخيط خالٍ من العقد.
- اسحب السلك: قم بربط السلك بخيط السحب ثم اسحبه عبر الأنبوب، مع وضع مادة تشحيم السلك حسب الحاجة للحصول على حركة أكثر سلاسة.
تعتبر هذه الطريقة فعالة للمسافات المتوسطة إلى الطويلة، وخاصة في القنوات ذات المنحنيات، حيث يساعد ضغط الهواء الفأر على التنقل عبر المنحنيات الضيقة.

إن سحب الأسلاك باستخدام خيط هو طريقة مباشرة ومناسبة للمسافات القصيرة أو الأنابيب ذات الانحناءات المحدودة. يتم إدخال الخيط يدويًا أو يتم نفخه عبر الأنابيب، ثم يتم استخدامه لسحب الأسلاك.
- أدخل السلسلة: يمكنك تمرير الخيط يدويًا عبر الأنبوب أو استخدام ضغط الهواء (على غرار طريقة الفأرة) لنفخه. تأكد من أن الخيط طويل بما يكفي ليصل إلى طول الأنبوب بالكامل.
- تأمين السلك إلى الخيط: بمجرد وصول الخيط إلى الطرف الآخر، اربط السلك به بإحكام. استخدم شريطًا كهربائيًا لجعل الاتصال سلسًا ومنعه من الالتصاق بأي مناطق خشنة داخل الأنبوب.
- استخدم مواد التشحيم: بالنسبة للسحوبات الأطول، ضع مادة التشحيم على كل من السلك ونقطة دخول القناة لتقليل الاحتكاك.
- اسحب السلك: اسحب الخيط برفق، لتوجيه السلك عبر الأنبوب. استخدم شدًا ثابتًا لتجنب الالتواءات أو التشابكات. إذا واجهت مقاومة، فتوقف وقم بالتعديل لمنع تلف السلك.
- إنهاء السحب: بمجرد مرور السلك بالكامل عبر الأنبوب، افصله عن الخيط وافحصه بحثًا عن أي تلف. تأكد من وجود سلك كافٍ على كلا الطرفين لإجراء التوصيلات.
يعد سحب الأسلاك باستخدام خيط طريقة سهلة وفعالة من حيث التكلفة، ومفيدة بشكل خاص للمسافات القصيرة والمستقيمة أو عندما لا تتوفر أدوات أخرى.
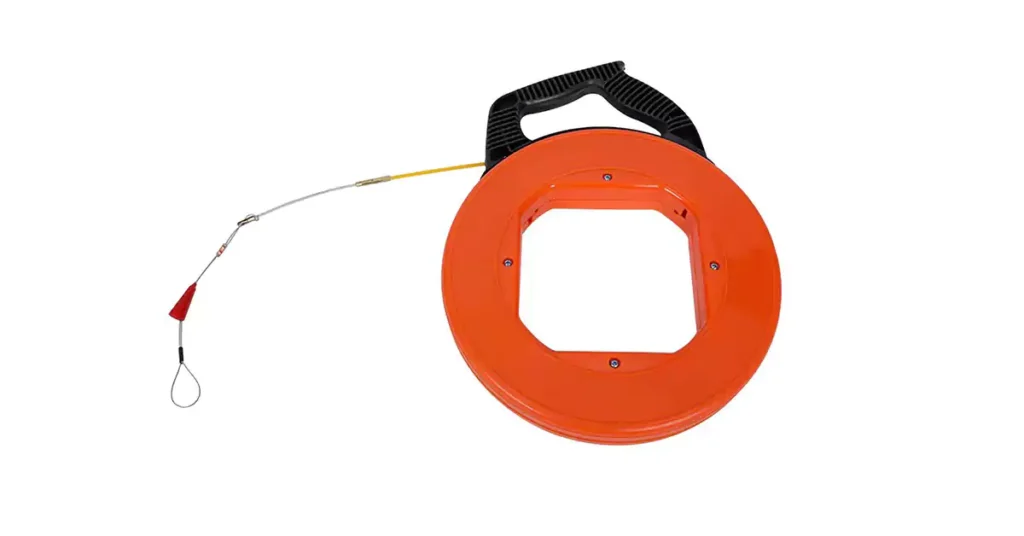

شريط السمك هو أداة شائعة الاستخدام لسحب الأسلاك عبر الأنابيب، وخاصة في الحالات التي يكون فيها السلك طويلاً أو به انحناءات. وهو عبارة عن شريط رفيع ومرن من الفولاذ أو الألياف الزجاجية يتم دفعه عبر الأنابيب ثم استخدامه لسحب السلك للخلف.
- شريط تغذية الأسماك: ابدأ بإدخال شريط السمك في أحد طرفي الأنبوب. ادفع الشريط ببطء عبر الأنبوب، باستخدام مرونته للتغلب على أي انحناءات. استمر في الدفع حتى يصل شريط السمك إلى الطرف الآخر.
- قم بتوصيل السلك: بمجرد الانتهاء من شريط السمك، قم بربط السلك بالحلقة الموجودة في نهاية الشريط. استخدم شريطًا كهربائيًا لتأمين السلك بإحكام وإنشاء انتقال سلس لتجنب التشابك.
- تزييت السلك: إذا كان المسار طويلاً أو يحتوي على العديد من الانحناءات، ضع مادة تشحيم على الأسلاك لتقليل الاحتكاك وجعل السحب أسهل.
- اسحب السلك: قم بسحب شريط السمك، وسحب السلك عبر الأنبوب. قم بتطبيق ضغط ثابت وتوجيه السلك أثناء تحركه. إذا واجهت مقاومة، فتوقف واستخدم المزيد من مواد التشحيم.
- إنهاء السحب: بمجرد الانتهاء من توصيل السلك، افصله عن شريط السمك وافحصه بحثًا عن أي ضرر.
يعد شريط السمك فعالاً للغاية للمسافات الطويلة أو المعقدة وهو أداة متعددة الاستخدامات يمكن إعادة استخدامها في مشاريع متعددة.
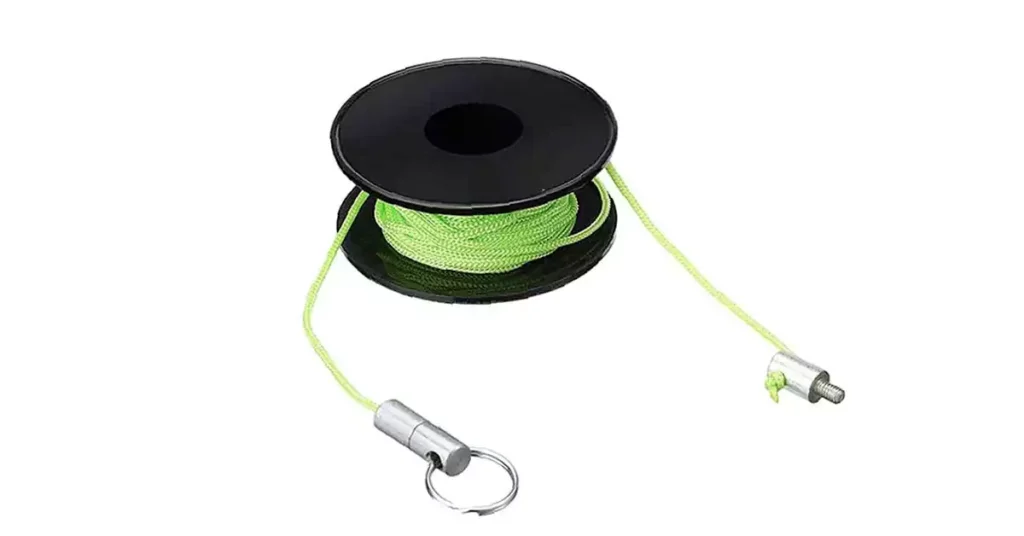

يمكن استخدام وزن الصيد لسحب الأسلاك عبر الأنابيب عن طريق الجاذبية، وخاصة في الأنابيب الرأسية أو المائلة. يتم ربط الوزن بخيط، وتساعد الجاذبية في سحب الخيط من خلاله، والذي يستخدم بعد ذلك لسحب السلك.
- ربط الوزن بالخيط: قم بتثبيت وزن صيد صغير وثقيل في نهاية خيط السحب. تأكد من أن الخيط طويل بما يكفي للوصول إلى قاع الأنبوب.
- قم بإسقاط الوزن في الأنبوب: أدخل الوزن في الجزء العلوي من الأنبوب واترك الجاذبية تسحبه إلى الأسفل. بالنسبة للمسارات الأفقية أو المنحدرة، قد تحتاج إلى هز الأنبوب برفق لمساعدة الوزن على التحرك من خلاله.
- استرداد الوزن: بمجرد وصول الوزن إلى القاع، قم باستعادته مع سلسلة السحب من الطرف الآخر للأنبوب.
- ربط السلك بالخيط: قم بربط السلك بخيط السحب بشكل آمن، باستخدام شريط كهربائي لضمان اتصال سلس.
- اسحب السلك: اسحب الخيط من الطرف المقابل، مع إدخال السلك في الأنبوب أثناء السحب. ضع مادة تشحيم على السلك إذا لزم الأمر لتسهيل السحب.
تعتبر هذه الطريقة بسيطة ولكنها فعالة في حالة خطوط الأنابيب العمودية أو المائلة قليلاً حيث يمكن للجاذبية أن تساعد في سحب الخيط.
بالنسبة للمسافات الطويلة أو تصميمات الأنابيب الصعبة بشكل خاص، يمكن استخدام آلة السحب. تطبق هذه الآلات قوة سحب ثابتة على السلك، مما يجعلها مثالية للمسافات الطويلة أو المعقدة ذات الانحناءات العديدة.
- إعداد آلة السحب: ضع آلة السحب في أحد طرفي الأنبوب. تأكد من محاذاة الآلة بشكل صحيح لتجنب إتلاف السلك.
- شريط أو خيط تغذية الأسماك: قبل استخدام الجهاز، قم بتمرير شريط السمك أو خيط السحب عبر القناة، إما يدويًا أو بمساعدة فأرة أو وزن الصيد.
- قم بتوصيل السلك: قم بربط السلك بشريط الصيد أو خيط السحب. تأكد من أن الاتصال قوي وسلس، حيث ستمارس آلة السحب قوة كبيرة عليه.
- تفعيل آلة السحب: ابدأ تشغيل الماكينة واتركها تبدأ في سحب السلك عبر الأنبوب. راقب السحب عن كثب للتأكد من عدم تعطل السلك أو تعرضه للتلف أثناء العملية.
- أكمل السحب: بمجرد الانتهاء من السلك، قم بإيقاف تشغيل الجهاز، وفصل السلك من شريط السمك أو الخيط، وافحصه بحثًا عن أي تلف.
تعتبر آلات السحب فعالة للغاية في التشغيلات الطويلة أو المعقدة ولكنها تستخدم عادة في المشاريع التجارية أو الصناعية بسبب حجمها وتكلفتها.

يعد سحب الأسلاك بأمان أمرًا بالغ الأهمية لتجنب التلف وضمان تركيب كهربائي موثوق به وحماية الجميع أثناء العمل. سواء كان الأمر يتعلق بمشروع منزلي صغير أو مشروع تجاري كبير، فإن اتباع خطوات السلامة والامتثال للرموز الكهربائية أمر ضروري. فيما يلي دليل مبسط حول كيفية سحب الأسلاك بأمان.
قبل البدء، تأكد من أن عملية سحب الأسلاك الخاصة بك تتبع الكود الكهربائي الوطني (NEC) أو اللوائح المحلية. هذه الرموز موجودة لضمان السلامة والتركيب السليم. النقاط الرئيسية التي يجب تذكرها:
- أنواع الأسلاك الصحيحة: استخدم الأسلاك المعتمدة للاستخدام في الأنابيب، مثل THHN أو XHHW، اعتمادًا على مشروعك.
- حدود ملء القناة: لا تفرط في ملء الأنبوب. هناك قواعد محددة حول عدد الأسلاك التي يمكن وضعها بأمان داخل الأنبوب لمنع ارتفاع درجة الحرارة.
- حجم الأنابيب والانحناءات المناسبة: تأكد من أن حجم الأنبوب مناسب للأسلاك ولا يحتوي على الكثير من الانحناءات الضيقة، مما قد يجعل السحب صعبًا ويؤدي إلى إتلاف السلك.
إن استخدام معدات الحماية المناسبة يحافظ على سلامتك أثناء العمل. تشمل معدات الحماية الشخصية المهمة لسحب الأسلاك ما يلي:
- القفازات: حماية يديك من الجروح والسحجات.
- نظارات السلامة: احم عينيك من الغبار والحطام ومواد التشحيم.
- أحذية العمل: ارتدِ أحذية مخصصة للسلامة الكهربائية للحماية من الصدمات الكهربائية.
قبل سحب الأسلاك، خذ وقتًا للتخطيط:
- فحص القناة: تأكد من أن الأنبوب خالٍ من الانسدادات أو الحواف الحادة أو الحطام الذي قد يتسبب في تلف السلك. قم بتنظيفه إذا لزم الأمر.
- حساب الانحناءات: حدد عدد الانحناءات أو العوائق الموجودة في الأنبوب. يمكن أن تؤدي الانحناءات إلى زيادة المقاومة، لذا قد تكون هناك حاجة إلى المزيد من مواد التشحيم.
- حساب قوة الشد: إذا كانت المسافة طويلة، تأكد من معرفة حدود شد السلك لتجنب تمدده أو إتلافه.
قد يؤدي السحب بقوة زائدة إلى إتلاف السلك. لمنع ذلك:
- استخدم مقياس التوتر: إذا كنت تستخدم آلة سحب، قم بمراقبة الشد للبقاء ضمن الحدود الآمنة للسلك.
- التوقف والتعديل: إذا شعرت بمقاومة، فلا تجبرها. توقف، أو ضع المزيد من مواد التشحيم، أو اضبط السلك لتجنب إتلاف العزل.
قد يؤدي ملء الأنبوب بأسلاك كثيرة إلى ارتفاع درجة الحرارة وتلفه. اتبع هذه القواعد البسيطة:
- التحقق من حدود ملء القناة: راجع رموز NEC أو الرموز المحلية لمعرفة عدد الأسلاك التي يمكن وضعها بأمان في القناة بناءً على حجمها.
- توفير مساحة لدوران الهواء: تحتاج الأسلاك إلى مساحة لتوزيع الهواء وتبديد الحرارة. قد يؤدي تكديس عدد كبير جدًا من الأسلاك في أنبوب واحد إلى نشوب خطر حريق
من خلال ترك مساحة كافية في القناة، يمكنك ضمان السلامة ومنع ارتفاع درجة الحرارة.
يعد حساب ملء الأنابيب أمرًا ضروريًا لضمان أن التركيب الكهربائي آمن وفعال ومتوافق مع التعليمات. يمكن أن يؤدي ملء الأنابيب بشكل زائد إلى ارتفاع درجة الحرارة وصعوبة سحب الأسلاك وحتى مخاطر الحرائق المحتملة. التعليمات الكهربائية مثل الكود الكهربائي الوطني (NEC) أو ال الكود الكهربائي الكندي (CEC) تحديد الحد الأقصى لعدد الأسلاك والمساحة المقطعية الإجمالية للأسلاك التي يمكن تركيبها بأمان في مجرى.
نسب ملء الأنابيب القصوى:
عدد الموصلات | جميع أنواع الموصلات |
1 | 53% |
2 | 31% |
أكثر من 2 | 40% |
- يمنع ارتفاع درجة الحرارة: يؤدي الإفراط في الملء إلى تراكم مفرط للحرارة، مما قد يؤدي إلى إتلاف عزل الأسلاك ويشكل مخاطر تتعلق بالسلامة.
- يضمن سحب الأسلاك بشكل أسهل: تساعد المساحة الكافية داخل الأنبوب على تقليل الاحتكاك، مما يجعل من السهل سحب الأسلاك دون إتلافها.
- يحافظ على الامتثال للكود: إن إجراء حسابات التعبئة التالية يضمن لك تلبية معايير السلامة وتجنب العقوبات.
تختلف نسبة الملء حسب نوع القناة وعدد الأسلاك. للحصول على المواصفات الدقيقة والإرشادات خطوة بخطوة حول كيفية حساب ملء القناة، راجع مقالتنا السابقة مخطط ملء أنابيب PVC. استشر دائمًا NEC أو CEC للحصول على المعايير الأكثر دقة وقابلية للتطبيق في منطقتك.
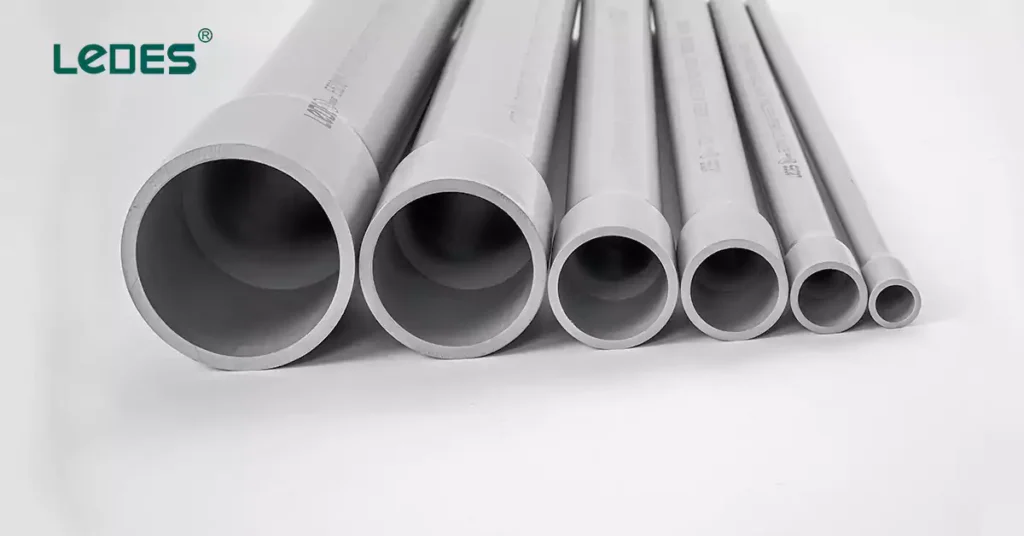

قد يختلف عمر الأنابيب الكهربائية اعتمادًا على المادة المستخدمة وبيئة التركيب والصيانة. تشمل مواد الأنابيب الشائعة أنابيب البولي فينيل كلوريد والفولاذ المجلفن والأنابيب المعدنية المرنة (FMC). فيما يلي فكرة عامة عن مدة عمر الأنابيب:
- قناة بي في سي يمكن أن تدوم لعقود من الزمن، مع عمر افتراضي نموذجي يزيد عن 50 عامًا. وهي مقاومة للرطوبة والتآكل والأضرار الناتجة عن الأشعة فوق البنفسجية، مما يجعلها مثالية للتركيبات الخارجية وتحت الأرض.
- أنابيب فولاذية مجلفنة (مثل EMT أو الأنابيب المعدنية الصلبة) متينة للغاية، خاصة في البيئات المعرضة للتلف المادي أو التعرض للمواد الكيميائية. يمكن أن تدوم لمدة تصل إلى 50 عامًا أو أكثر ولكنها قد تتآكل في البيئات القاسية إذا تآكل الطلاء الواقي.
- الأنابيب المعدنية المرنة (FMC) أكثر عرضة للتآكل والتلف وقد تحتاج إلى الاستبدال في وقت أقرب، وتستمر بشكل عام لمدة 20-30 عامًا حسب ظروف الاستخدام.
يمكن أن تساعد عمليات التفتيش المنتظمة والتركيب المناسب في إطالة عمر نظام التوصيلات الكهربائية، وضمان السلامة وطول عمر الأسلاك الكهربائية التي يحميها.
يتطلب توصيل الأسلاك عبر الأنابيب بشكل فعال استخدام الأساليب والأدوات الصحيحة والتخطيط الدقيق لتجنب إتلاف الأسلاك أو الأنابيب. سواء باستخدام تقنيات يدوية أو أدوات مثل شريط السمك أو حتى آلات السحب، فإن كل طريقة لها مزاياها وتطبيقاتها الفريدة اعتمادًا على تعقيد المهمة. السلامة هي دائمًا أولوية قصوى، لذا تأكد من أن ممارسات سحب الأسلاك الخاصة بك تتبع القواعد الكهربائية، واستخدم معدات السلامة المناسبة، وخطط بشكل صحيح لأي انحناءات أو عوائق أو سحب طويل.
من خلال فهم الطرق المختلفة المتاحة - السحب اليدوي، أو استخدام خيط، أو فأرة، أو شريط صيد السمك، أو وزن الصيد، أو آلة السحب - يمكنك تحسين عملية سحب الأسلاك للمشاريع الصغيرة والكبيرة الحجم. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، فإن معرفة عمر الأنابيب وأهمية حسابات ملء الأنابيب سيضمن تركيبات آمنة طويلة الأمد. باتباع أفضل الممارسات هذه، يمكنك تحسين الكفاءة، وتقليل مخاطر التلف، والحفاظ على تشغيل أنظمتك الكهربائية بسلاسة لسنوات قادمة.




