
Table of Contents
As a professional manufacturer of PVC electrical conduit and water pipes, we understand that PVC pipe fittings are an integral part of construction projects. While we focus on producing high-quality PVC pipes, we recognize the significant role that fittings play in ensuring successful installations.
Throughout our years of experience, we have received numerous inquiries from clients regarding the types, sizes, applications, manufacturing, and quality of pipe fittings. It has become evident that some customers lack a clear understanding of these aspects. In this article, we aim to provide a comprehensive guide to PVC pipe fittings, addressing these questions and more.
PVC pipe fittings come in a variety of types, each serving specific purposes in different configurations. Understanding the various fittings available and their applications is crucial for any construction project. Additionally, knowing the proper sizes and dimensions of these fittings is essential for seamless integration into the pipeline system.
Why PVC
When it comes to selecting the right material for pipe fittings, PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) stands out for its numerous advantages. PVC pipe fittings offer a range of benefits, especially when compared to alternatives such as iron or metal pipes. The advantages that make PVC the preferred choice include:
- Lightweight: PVC pipe fittings are significantly lighter than metal pipes, making them easier to handle and transport. This characteristic simplifies the installation process, reducing labor and equipment requirements. In addition, the lightweight nature of PVC makes it an ideal choice for overhead installations.
- Cost-Effective: PVC pipe fittings are cost-effective compared to other materials like iron or copper. The raw material used in PVC production is readily available and relatively inexpensive. This affordability extends to the fittings, making PVC a budget-friendly option for both small-scale and large-scale projects.
- Easy Installation: PVC pipe fittings are designed for easy and efficient installation. They feature a simple, push-fit or solvent cement jointing system, eliminating the need for complex welding or threading procedures. This ease of installation saves time and reduces labor costs, making PVC an attractive choice for construction projects with tight schedules.
- Corrosion Resistance: One of the significant advantages of PVC pipe fittings is their resistance to corrosion. Unlike iron or metal fittings, PVC is not susceptible to rust or corrosion caused by moisture or chemical exposure. This resistance ensures the longevity and durability of the fittings, reducing maintenance and replacement costs over time.
- Chemical Resistance: PVC pipe fittings exhibit excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals, acids, and bases. This characteristic makes them suitable for various applications, including chemical processing plants, laboratories, and wastewater treatment facilities. PVC fittings maintain their integrity even when exposed to aggressive substances, ensuring the safety and reliability of the pipeline system.
- Longevity: PVC pipe fittings have a long service life, with an average lifespan of 50 years or more. They are resistant to environmental factors such as sunlight, moisture, and temperature variations, ensuring their performance and structural integrity over extended periods. This longevity translates into long-term cost savings for construction projects.
PVC Vs. CPVC

PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) and CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride) are two commonly used materials for pipe fittings. While they share many similarities in terms of characteristics, there are also some notable differences between them. The most significant difference lies in CPVC’s superior heat resistance and higher mechanical strength. Additionally, they have different standards for their applications.
PVC and CPVC have similar chemical resistance, corrosion resistance, ease of installation, and smooth interior surfaces. Both materials are suitable for a wide range of applications, including electrical systems, water supply, drainage systems, irrigation, and industrial piping. However, when it comes to temperature and mechanical requirements, CPVC outperforms PVC.
CPVC has a higher temperature resistance, allowing it to handle hot water and fluids at elevated temperatures. CPVC can withstand temperatures up to 200°F (93°C) or even higher, depending on the specific product and application. In contrast, PVC has a lower temperature limit, typically around 140°F (60°C). Therefore, if your project involves conveying hot water or fluids at high temperatures, CPVC is the recommended choice.
In terms of mechanical properties, CPVC has higher impact strength and tensile strength compared to PVC. This enhanced mechanical performance makes CPVC more suitable for applications where higher pressure or mechanical stress is expected. PVC, on the other hand, is suitable for applications with lower pressure requirements. Take the comparison of schedule 40 and schedule 80 tubes as an example:
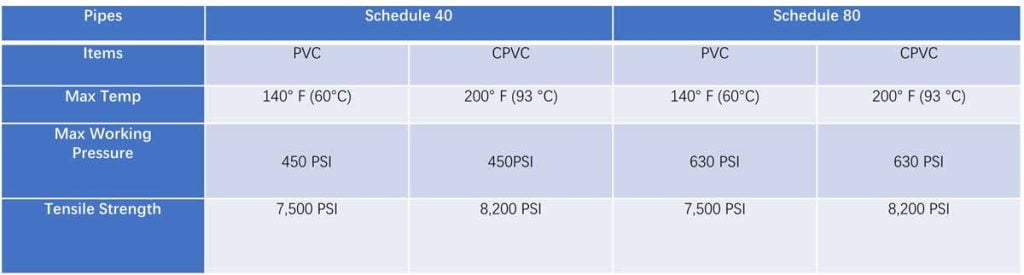
Different Performance of PVC Pipe & CPVC Pipe
While CPVC offers numerous advantages, PVC is significantly more cost-effective, with a price that is typically around 50% lower than CPVC. If PVC meets your project requirements in terms of temperature, pressure, and mechanical stress, it is a more economical option. However, if your project necessitates higher temperature resistance and mechanical performance, CPVC is the recommended choice, despite its higher cost.
PVC Pipe Fitting Sizes
When selecting PVC fittings, it’s important to choose the proper dimensioned units that match your local codes and conduit specifications. Take elbows as an example:
In the America, it’s sizes are ranging from 1/2 inch to 8 inch, and refer to standard UL651, as below:
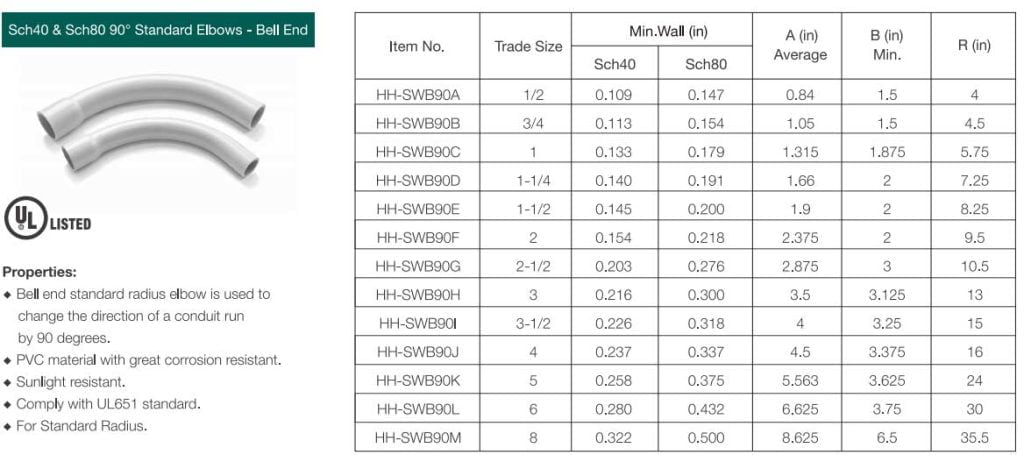
While in Australian, the elbow is ranging from 20mm to 150mm, refer to standard AS/NZS 2053, as below:
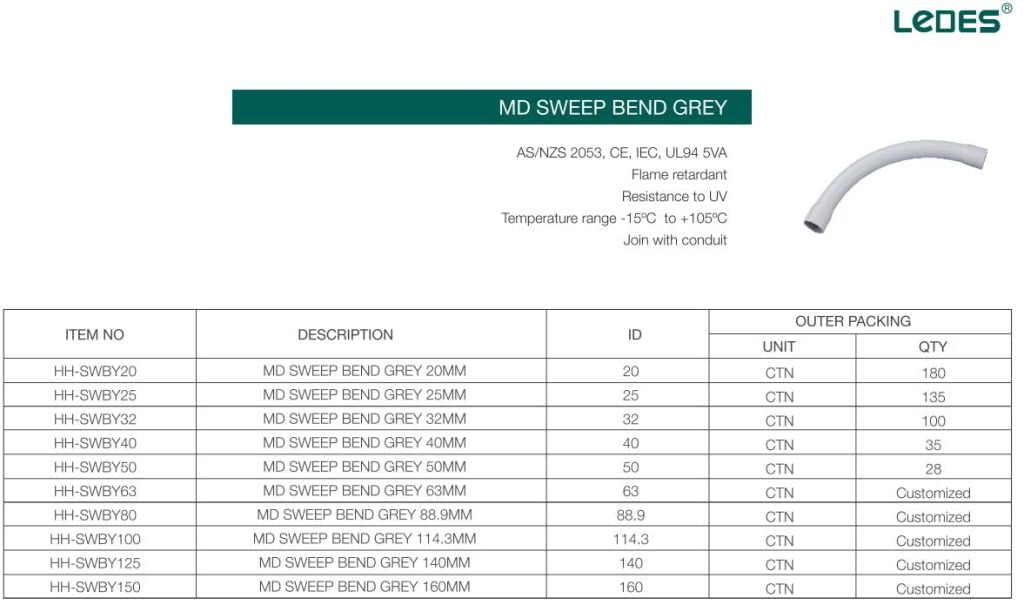
Remember, before purchasing PVC pipe fittings, it is essential to refer to local codes and regulations. This ensures that the fittings are compatible with the PVC pipes used in your project and comply with legal requirements.
PVC Fittings - Descriptions and Applications
Here provides an overview of some of the most commonly used PVC fittings in construction and electrical applications. Each entry contains a brief description along with typical usage scenarios.
It’s important to note this list is not exhaustive – there are countless fitting variations available depending on specific needs. Always consult technical resources and local codes to select the properly sized and rated fitting for each unique installation.
● Elbows
Used to change the direction of conduit runs, available in standard radii variations. Standard 90° elbows facilitate T-intersections. 45° and 22.5° sweep elbows offer gradual transitions. Commonly used for branch connections and routing around obstructions.

● Coupling
Couplings are used to join two PVC pipes together in a straight line, ensuring a leak-proof connection. It’s one of the most simple types of PVC fittings, easy for handling and installing.

● Male Adapter
Male adapters are important PVC pipe fittings that provide a transition from a male threaded pipe end to a solvent weld connection. They feature a male threaded end that can be screwed into a corresponding female threaded fitting, while the other end is designed for solvent welding to a PVC pipe or fitting. Male adapters enable the connection of different pipe types, such as metal pipes or threaded fittings, to PVC systems, offering versatility and compatibility.

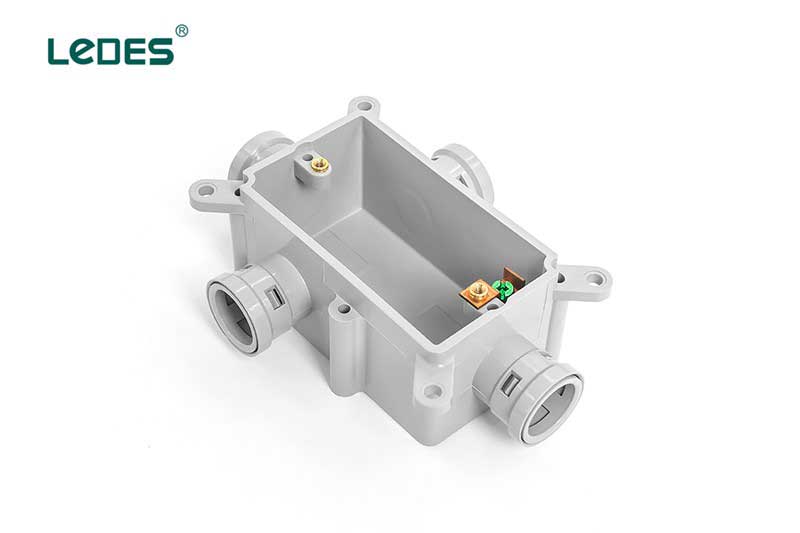
● Junction Box
Junction box provides a secure enclosure for electrical connections and wiring. These boxes are designed to protect the electrical connections from environmental factors, prevent accidents, and facilitate maintenance and troubleshooting. Junction boxes are typically made of durable materials such as PVC and feature multiple openings or knockouts for the entry and exit of electrical cables.

● Adaptable Box
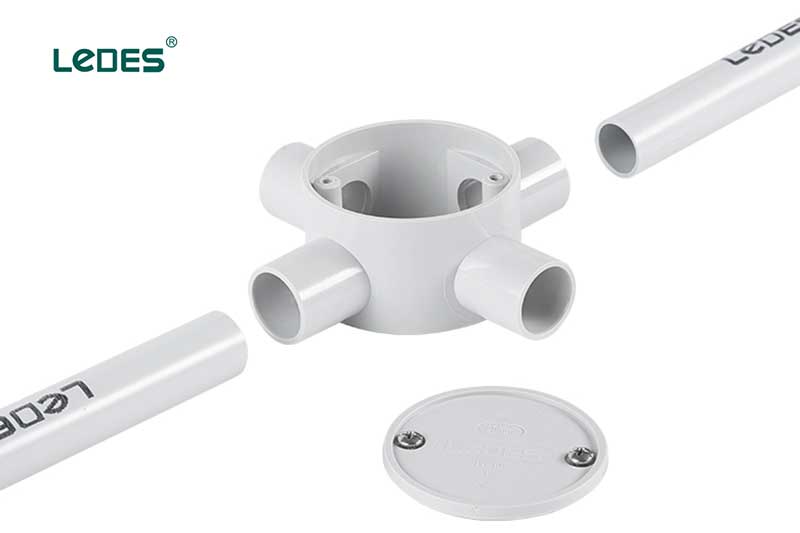
Adaptable boxes are designed to accommodate switches, receptacles, or other electrical devices, providing a secure and organized housing for electrical connections. Adaptable boxes offer flexibility in terms of size and configuration, allowing for easy installation and customization. They are typically made of durable materials like PVC and feature multiple knockouts or openings for cable entry and exit.
● Straight Tee
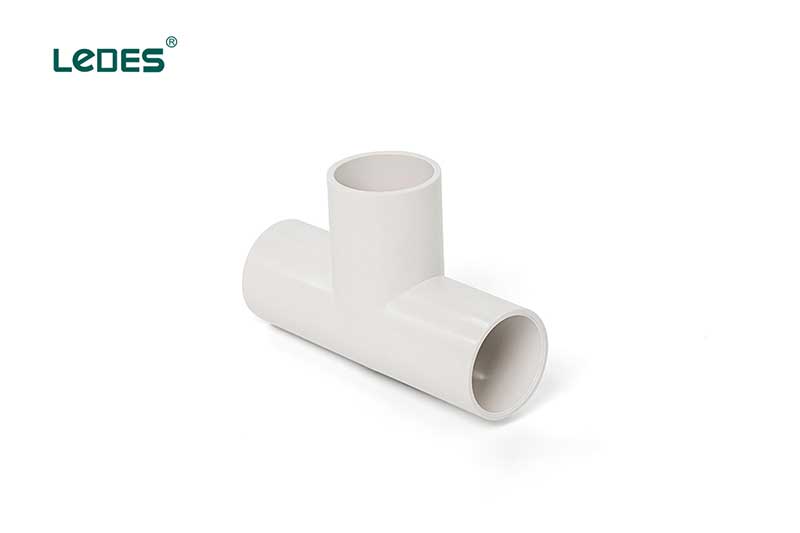
Straight tees are essential PVC pipe fittings that provide a T-shaped intersection in a pipe system. These tees have three openings, with one inlet and two outlets arranged in a straight line. They allow for the branching of pipelines, enabling the distribution or diversion of fluids or materials. Straight tees are commonly used in plumbing, irrigation, and industrial applications where a pipe needs to be split into two separate lines or where additional connections are required. They provide a reliable and leak-proof connection, facilitating the efficient flow of fluids and ensuring the integrity of the pipe system.

● ENT Slab Box
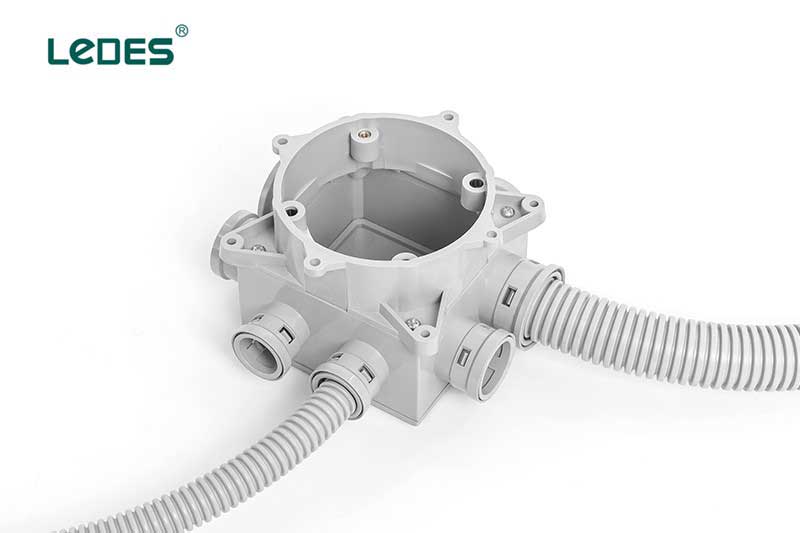
An ENT slab box is an electrical enclosure used in construction projects to safely house electrical connections and wiring within concrete slabs or floors. Its main function is to provide a secure and organized environment for connecting electrical components such as outlets, switches, or data communication outlets. The box is installed during the construction phase, embedded within the concrete structure, and features knockouts or entry points for electrical conduits or cables. It ensures the protection of electrical connections, allows for easy access when needed, and helps maintain a tidy and hazard-free appearance in areas where concrete slabs or raised floors are present. ENT slab boxes are commonly used in commercial buildings, residential complexes, and industrial facilities.

● Concrete Wall Boxes
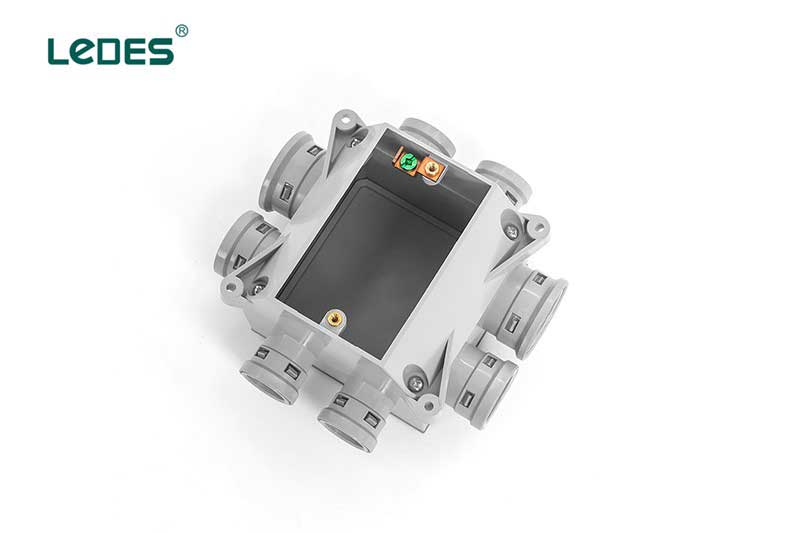
The primary function of an ENT single gang concrete wall box is to provide a secure and protected housing for electrical outlets, switches, or other devices installed on concrete walls. It allows for the safe and organized installation of electrical components while ensuring compliance with electrical codes and safety standards.
ENT single gang concrete wall boxes are typically used in construction projects where concrete walls are present. They are commonly found in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. These boxes are installed by embedding them within the concrete wall during the construction phase.


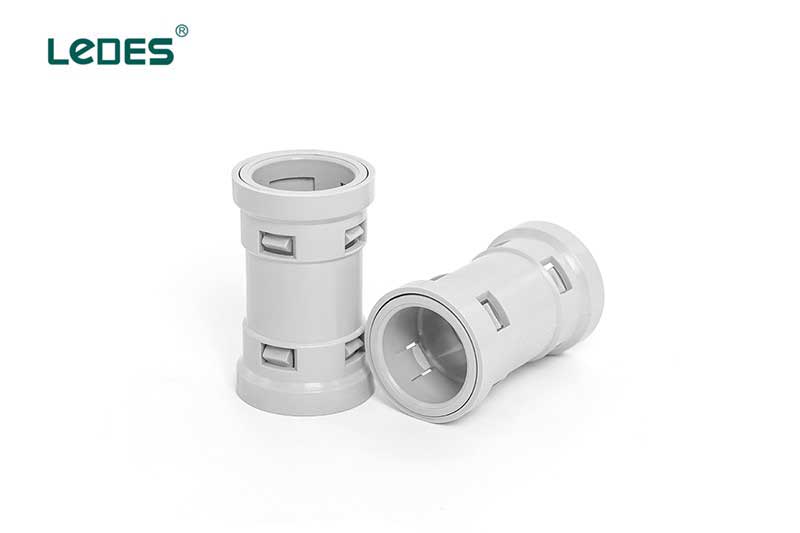
● ENT Coupling
ENT coupling is a fitting used to join or connect two sections of electrical non-metallic tubing (ENT) together. It allows for the extension or joining of electrical conduit runs, ensuring continuous and protected pathways for electrical wiring.
ENT couplings are commonly used in electrical installations where non-metallic tubing is employed, such as residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. They are used when there is a need to connect two sections of ENT to create longer conduit runs or to navigate around obstacles in the wiring pathway.

● Conduit Body
Conduit body is to serve as a connection point or access point within a conduit system. It allows for the installation, inspection, and maintenance of electrical wiring and connections. Conduit bodies also provide protection for wire splices and help facilitate changes in conduit direction.
Conduit bodies are available in various shapes and sizes, such as T-shaped (Tee), L-shaped (Elbow), or C-shaped (Pull Box). They are typically made of materials like PVC (polyvinyl chloride). Conduit bodies feature removable covers or access plates that allow for easy access to the interior for wiring, inspections, or troubleshooting.
They are typically installed at strategic points along the conduit system, such as bends, junctions, or access points. Conduit bodies can accommodate wires, splices, and connectors, providing a secure and organized solution for electrical connections.
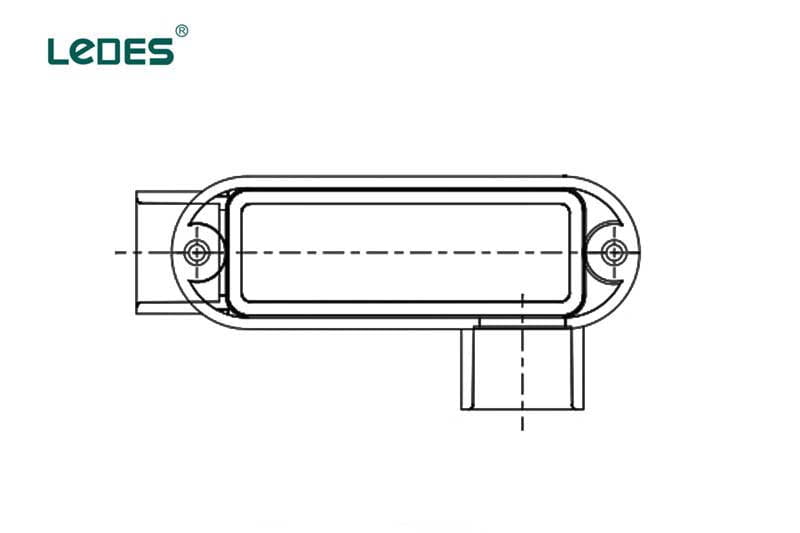
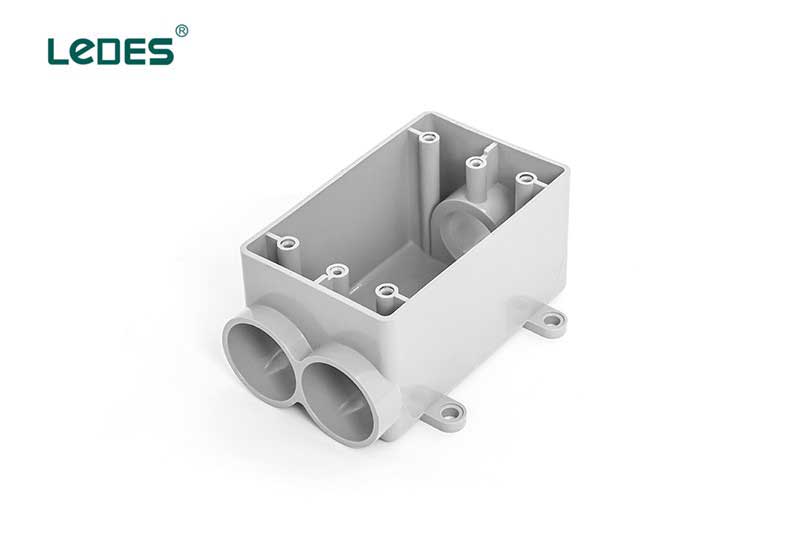
● Gang Box
Single gang box is a specific type of electrical enclosure designed for use with rigid conduits in electrical installations. It is to provide a secure and protected housing for electrical devices, such as switches or outlets, when using rigid conduits. It serves as a junction point or mounting platform for these devices within a rigid conduit system.
Rigid conduit single gang boxes are commonly used in commercial, industrial, and outdoor applications where a more robust conduit system is required. They are typically used in locations where enhanced protection against physical damage, moisture, or environmental factors is necessary. Rigid conduit single gang boxes are often found in areas such as warehouses, factories, outdoor installations, or high-traffic environments.

PVC Fittings Manufacture
The manufacture process for PVC fittings involves several steps, including material preparation, mold preparation, injection, cooling and solidification, mold opening and ejection, trimming and finishing, quality control and inspection, and packaging and distribution. Each step contributes to the production of high-quality PVC fittings used in plumbing, construction, and industrial applications.
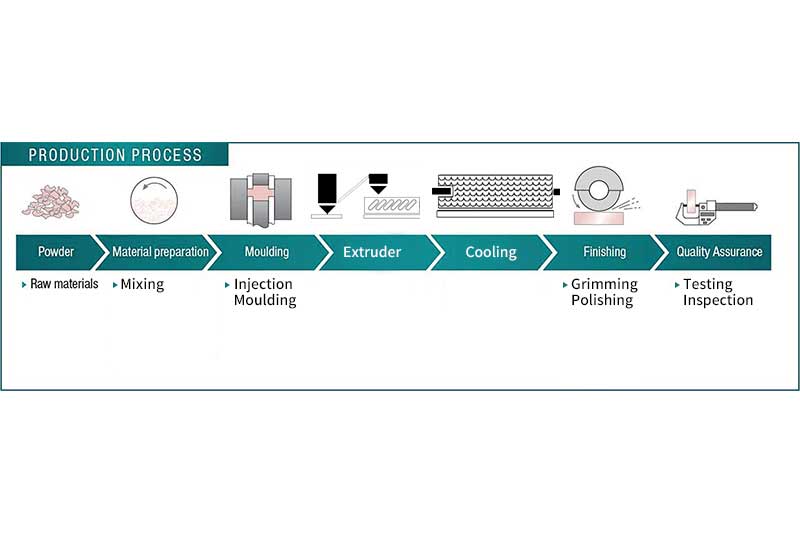
PVC Conduit Pipe Fitting Manufacture Process
1. Material Preparation
- PVC resin, along with additives and plasticizers, is mixed and compounded to create a homogenous PVC compound.
- The compound is typically in pellet form, ready for processing.
- Attention should be paid to accurately measuring and mixing the components to achieve the desired properties and consistency.
2. Mold Preparation
- A mold is designed and created for the specific PVC fitting.
- The mold consists of two halves, an injection side, and a cavity side.
- Proper cleaning and preparation of the mold are crucial to ensure optimal product quality.
- Attention should be given to mold maintenance and proper alignment of the mold halves.
3. Injection Molding
- PVC compound pellets are fed into the hopper of the injection molding machine.
- The pellets are heated and melted in the barrel of the machine.
- The molten PVC is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure.
- Care should be taken to control the temperature, pressure, and injection speed to achieve accurate filling and avoid defects.
4. Cooling and Solidification:
- The mold is cooled through water channels or other cooling methods.
- Cooling helps the molten PVC solidify and maintain the desired shape and dimensions.
- Attention should be given to proper cooling time to ensure complete solidification and dimensional stability.
5. Mold Opening and Ejection
- Once the PVC fitting has solidified, the mold is opened, and the fitting is ejected from the cavity.
- Ejection pins or mechanisms assist in the removal of the fitting without causing damage.
- Attention should be paid to proper alignment and smooth ejection to avoid deformation or breakage.
6. Trimming and Finishing
- Excess material or flash is removed from the fitting.
- Additional processes, such as drilling, threading, or surface finishing, may be performed to meet design requirements.
- Care should be taken to ensure precise trimming and finishing without compromising the structural integrity of the fitting.
7. Quality Control and Inspection
- The finished fittings undergo thorough quality control checks and inspections.
- Dimensional accuracy, strength, and overall product quality are assessed.
- Attention should be given to comprehensive testing, including pressure resistance, chemical compatibility, and other performance criteria.
8. Packaging
- The finalized fittings are carefully packaged to protect them during storage and transportation.
- Attention should be given to proper packaging techniques to prevent damage or contamination.

Throughout the manufacturing process, it is essential to follow established guidelines, maintain equipment, and conduct regular quality control checks to ensure the production of high-quality PVC fittings. Attention to detail and adherence to specific parameters contribute to the consistency and reliability of the final products.
How to Connect PVC Pipe and Fittings
When working on a structural project using PVC pipes and fittings, there are two primary methods for connecting them: the PVC solvent (cement) method and use threaded screws. Although both methods can be effective, we strongly recommend utilizing PVC cement for its superior strength and permanent bond.
Here are the steps to join PVC using PVC cement:
- Test Fit: Before applying any cement, perform a test fit by dry-fitting the pipes and fittings together. This ensures that they align properly and fit snugly.
- Clean the Surfaces: Thoroughly clean the pipe and fitting surfaces that will be joined. Use a clean cloth or rag to remove any dirt, grease, or debris. The surfaces need to be clean for the cement to create a strong bond.
- Apply Primer (Optional): Applying a PVC primer is an optional step but can improve the bond strength. If you choose to use a primer, apply it to the pipe and fitting surfaces according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Allow the primer to dry completely before proceeding.
- Apply PVC Cement: Use a brush or applicator to evenly apply PVC cement to the inside of the fitting and the outside of the pipe. Apply a liberal amount of cement, ensuring that it covers the entire surface that will be joined.
- Insert the Pipe: Immediately after applying the cement, insert the pipe into the fitting. Rotate the pipe slightly to evenly distribute the cement and ensure a proper bond. Push the pipe into the fitting until it reaches the bottom or the desired depth.
- Hold in Place: Hold the pipe and fitting firmly in place for about 15-30 seconds. This allows the cement to set and create a strong bond. Avoid any movement or twisting during this time.
- Wipe Excess Cement: After the bond has formed, use a clean cloth or rag to wipe away any excess cement that may have squeezed out around the joint. It’s important to remove any excess cement before it dries.
- Allow to Cure: Allow the cement to cure for the recommended time specified by the manufacturer. Typically, it takes 24 hours for the cement to fully cure and achieve its maximum strength. Avoid putting any stress or pressure on the joint until it has fully cured.
Steps for connecting PVC Pipe and Fittings with Screws:
- Insert the Pipe into the Fitting: Start by inserting the PVC pipe into the fitting. Ensure that the pipe is fully inserted and seated securely in the fitting. Use a mallet if necessary to ensure a snug fit.
- Create Pilot Holes: Using a power drill with an appropriate drill bit (typically around 1/8″ or as recommended by the screw manufacturer), create pilot holes in the fitting where you want to place the screws. The pilot holes should be positioned evenly on both sides of the fitting, ensuring they align with the pipe.
- Insert Screws: Take self-tapping screws designed for PVC applications and place them into the pilot holes. Use a power drill or screwdriver to drive the screws into the fitting through the pilot holes. Be careful not to overtighten the screws, as this can damage the PVC components.
- Repeat the Process: Depending on the size and complexity of your project, repeat the above steps for any additional pipes and fittings that need to be connected. Ensure that each joint is properly aligned and secured with screws.
Note: When using screws to connect PVC pipes and fittings, keep in mind that this method provides a temporary connection. It is not as strong or permanent as using PVC cement. Screws can be useful for projects that require flexibility and the ability to disassemble the structure later.
Also, make sure to choose screws specifically designed for PVC applications, as they have a thread pattern and point that works well with the material. Regular screws may not provide the same level of grip or may cause damage to the PVC components.
Conclusion
PVC fittings are versatile components widely used in plumbing, irrigation, electrical, and construction applications. They offer numerous advantages, including durability, affordability, and resistance to corrosion and chemicals. In comparison to CPVC, PVC fittings have lower cost, broader compatibility, and are easier to install. The manufacturing process ensures consistent quality and structural integrity. It is advisable to purchase commercially available PVC fittings that meet industry standards for quality and safety. If you have further questions or need assistance, please feel free to contact us through the provided contact form or email Ledes, and our team will respond within one business day.



