
Table of Contents
Proper conduit sizing, is a crucial consideration in electrical installations. It involves determining the appropriate size of conduit required to safely house and protect electrical cables. Conduit sizing is essential for maintaining the integrity and efficiency of electrical systems. In this article, we will explore the importance of proper conduit sizing and provide an overview of conduit and cable systems
How Importance of Proper Conduit Sizing?

Proper conduit sizing is of utmost importance for several reasons. Firstly, it ensures the smooth installation of cables within the conduit. If the conduit is too small, it can be challenging to pull the cables through, leading to potential damage or excessive tension. On the other hand, if the conduit is too large, it may not provide adequate support and protection for the cables.
Secondly, proper conduit sizing helps prevent cable overheating. When cables are tightly packed within a conduit, there is limited airflow, which can cause heat buildup. Overheating can lead to insulation degradation, increased resistance, and even fire hazards. By ensuring sufficient conduit fill, heat dissipation is improved, enhancing the overall safety and performance of the electrical system.
Additionally, proper conduit sizing facilitates future maintenance and modifications. If additional cables need to be added or replaced in the future, having ample space within the conduit simplifies the process. It allows for easier access, reducing the time and effort required for troubleshooting, repairs, or upgrades.
What is Conduit Fill?
Conduit fill refers to the maximum amount or percentage of available space within an electrical conduit that can be occupied by cables or wires. It is an important consideration in electrical installations to ensure that the conduit is not overfilled, which can lead to issues such as excessive heat buildup, cable damage, or difficulties during installation or maintenance.
Conduit fill requirements are typically specified by electrical codes and standards, which define the maximum allowable fill based on factors such as the size and type of conduit, the diameter of the cables or wires, and the insulation type. These requirements aim to maintain proper airflow, prevent cable overheating, and allow for future additions or modifications to the electrical system.
Understanding Conduit and Cable Types
2 Types of Conduits (Metal Vs. PVC)
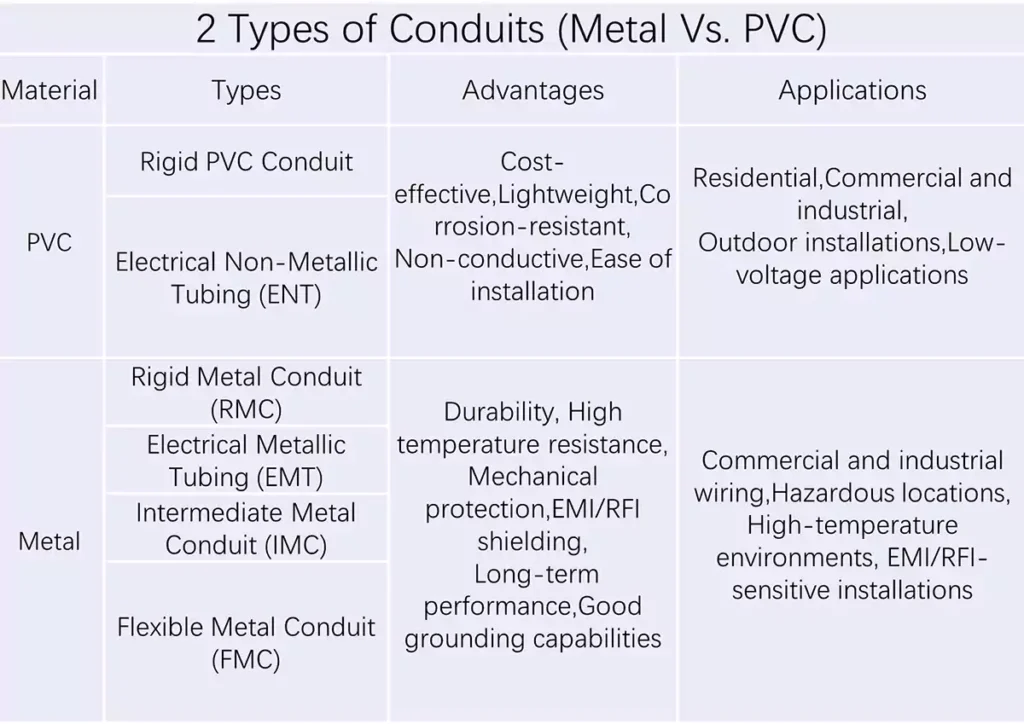
Conduit is an important part to consider in electrical systems, there are many types of conduit available on the market, how to choose a right type for your specific need? Here are some common and basic information you can refer to.
11 Different Kinds of Electrical Cable Types and Conductors

There are various types of cables used in electrical and communication systems, each designed for specific applications. Here are some common cable types:
- Non-Metallic Sheathed Cable (NM or Romex): NM cable is commonly used in residential and commercial wiring applications. It consists of two or more insulated conductors (typically copper) surrounded by a non-metallic sheath, providing protection and ease of installation.
- Armored Cable (AC): Armored cable, also known as BX cable, is a flexible metallic cable with conductors encased in a protective metal armor. It provides mechanical protection and is commonly used in commercial and industrial wiring.
- Underground Feeder Cable (UF): UF cable is designed for direct burial applications and is commonly used for outdoor wiring, such as outdoor lighting, underground circuits, and residential landscaping projects. It has insulation suitable for underground use.
- Coaxial Cable (Coax): Coaxial cable consists of a central conductor, insulation, a metallic shield, and an outer insulating layer. It is commonly used for cable television, satellite TV, internet connections, and other high-frequency signal transmissions.
- Ethernet Cable: Ethernet cables, such as Category 5e (Cat 5e) or Category 6 (Cat 6), are used for computer networking and internet connections. They consist of multiple twisted pairs of copper conductors and are terminated with RJ-45 connectors.
- Fiber Optic Cable: Fiber optic cables are designed for high-speed data transmission using light signals. They consist of thin strands of glass or plastic fibers surrounded by protective layers. Fiber optic cables are used for long-distance telecommunications, internet connections, and high-bandwidth applications.
Regarding insulated conductor types, the five most common types include:

- Thermoplastic Insulated Cable (THHN/THWN): THHN (Thermoplastic High Heat-Resistant Nylon) and THWN (Thermoplastic Heat- and Water-Resistant Nylon) are types of insulation commonly used for copper conductors in building wiring. They provide good resistance to heat, moisture, and abrasion.
- Cross-Linked Polyethylene (XLPE): XLPE insulation is commonly used for medium- and high-voltage power cables. It offers excellent electrical properties, thermal stability, and resistance to moisture and chemicals.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): PVC insulation is widely used in a variety of cables due to its excellent electrical properties, low cost, and resistance to moisture, chemicals, and abrasion. It is commonly used in residential and commercial wiring.
- Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR): EPR insulation is commonly used for medium- and high-voltage power cables. It offers good electrical properties, thermal resistance, and flexibility.
- Silicone Rubber: Silicone rubber insulation is known for its excellent high-temperature resistance, flexibility, and electrical properties. It is commonly used in applications where extreme temperatures are encountered, such as in high-temperature environments or industrial settings.
4 Factors Affecting Conduit Sizing
- Cable Type and Size:
The type and size of cables being installed play a significant role in determining the appropriate conduit size. Different cable types, such as power cables, communication cables, and fiber optic cables, have varying outer diameters. Additionally, the insulation thickness of the cables also affects their overall diameter. It is crucial to select a conduit that can accommodate the size of the cables, providing adequate space for easy installation and future maintenance.
- Number of Cables:
The number of cables being installed within a conduit is another crucial factor in conduit sizing. As the number of cables increases, the conduit’s fill capacity decreases. The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines on the maximum fill ratio allowed for different types and sizes of conduits. It is essential to consider the number of cables to ensure proper conduit fill without exceeding the recommended fill ratio.
- Conduit Fill Ratio:
The fill ratio refers to the percentage of the cross-sectional area of the conduit occupied by the cables. The NEC provides specific guidelines for maximum fill ratios to ensure safe and efficient installation. Exceeding the recommended fill ratio can lead to issues such as excessive heat buildup, cable damage, difficulty in future modifications, and reduced airflow for cooling. It is crucial to calculate the conduit fill ratio accurately and select a conduit size that allows for sufficient space for cable installation and maintenance.
- Environmental Considerations:
The environment in which the conduit will be installed is an important consideration for conduit sizing. Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, exposure to chemicals or corrosive substances, and physical hazards can impact the choice of conduit and its size. For example, in high-temperature areas, the conduit may need to accommodate expansion and contraction of cables. In corrosive environments, corrosion-resistant conduits may be necessary. Additionally, outdoor installations may require conduits with UV resistance. Considering the specific environmental conditions helps ensure the longevity and performance of the conduit system.
National Electrical Code (NEC) Guidelines for Conduit Fill (6 Steps)

The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines and regulations for electrical installations to ensure safety and efficiency. One important aspect covered by the NEC is conduit fill, which specifies the maximum fill ratio for different types and sizes of conduits. Adhering to these guidelines is crucial for maintaining proper cable installation, preventing overheating, facilitating future modifications, and ensuring compliance with electrical codes. Here are the key details of NEC requirements for conduit fill:
Conduit Fill Tables:
The NEC includes tables that outline the maximum fill ratios for different conduit types and sizes. These tables provide a reference for installers to determine the maximum allowable cable fill based on the conduit size being used. The fill percentages are specified based on conductor size and type, as well as the conduit diameter.
Calculation Methods:
The NEC permits two calculation methods for conduit fill: the actual conductor size method and the adjusted conductor size method. The actual conductor size method requires using the exact outer diameter of the cable and comparing it to the available conduit fill allowance. The adjusted conductor size method involves using the equivalent diameter of the cable, which takes into account the insulation thickness and the shape of the conductor.
Derating Factors:
In some cases, the NEC may require applying derating factors to the cable ampacity due to factors such as ambient temperature, the number of current-carrying conductors in a conduit, and bundling of cables. These derating factors reduce the ampacity of the cables and can impact the conduit fill calculation. It is important to consider the applicable derating factors while determining conduit fill to ensure safe and reliable operation.
Multiple Conduit Runs:
When multiple conduit runs are used in parallel or grouped together, the NEC provides guidelines for calculating the total fill ratio. The combined fill ratio of all the conduits must not exceed the maximum allowable fill ratio for the specific installation.
Equipment and Manufacturer's Specifications:
It is essential to consider the equipment and manufacturer’s specifications when determining conduit fill. Some equipment, such as circuit breakers or termination points, may have specific requirements for conduit fill to maintain proper heat dissipation and avoid operational issues. Manufacturers of cables and conduits may also provide guidelines and recommendations for conduit fill that should be followed.
Future Modifications and Maintenance:
Along with complying with the NEC guidelines for conduit fill, it is important to consider future modifications and maintenance. Leaving sufficient space within the conduit allows for easy cable installation, future additions or upgrades, and maintenance activities. Adequate conduit fill also ensures proper cable bending radius and minimizes the risk of damaging the cables during installation or maintenance.
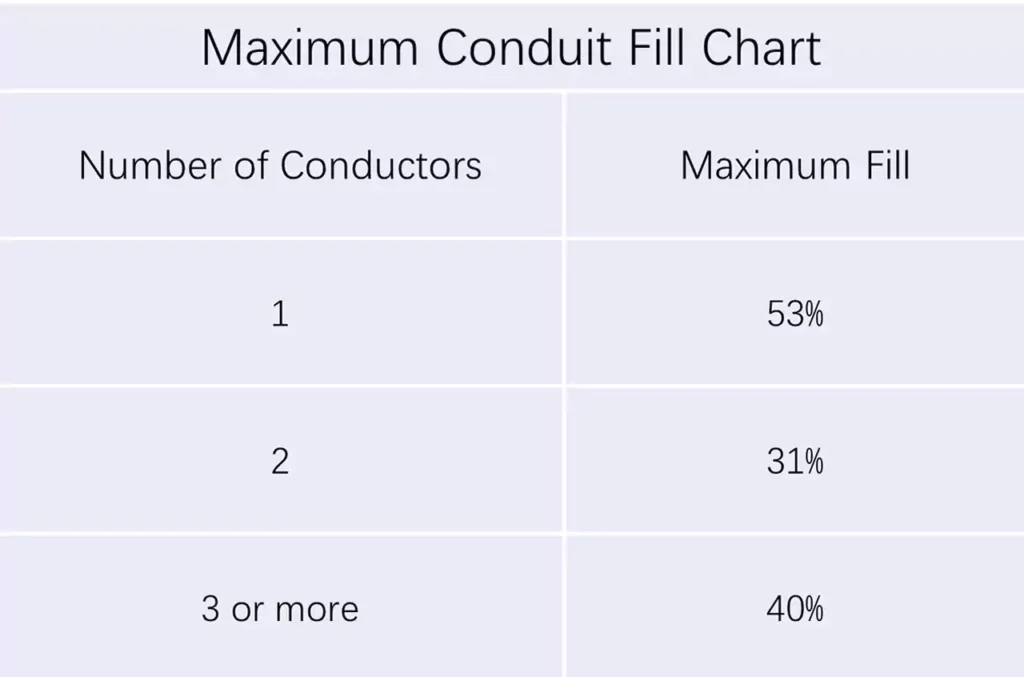
Here are the maximum recommended conduit fill for standard conduit sizes according to NEC:
How to Calculating Conduit Size (Step-by-Step Guideline)
Determining Cable Area:
The first step in calculating conduit size is to determine the total area occupied by the cables that will be installed within the conduit. This can be done by multiplying the cross-sectional area of each cable by the number of cables. The cross-sectional area of a cable can be calculated using the formula:
Area = π * (Diameter/2)^2
Let’s assume we have three power cables with outer diameters of 0.5 inches, 0.75 inches, and 1 inch. Using the cable area formula, we can calculate the individual cable areas as follows:
Cable 1: Area = π * (0.5/2)^2 = 0.19635 square inches
Cable 2: Area = π * (0.75/2)^2 = 0.44178 square inches
Cable 3: Area = π * (1/2)^2 = 0.7854 square inches
Total Cable Area = 0.19635 + 0.44178 + 0.7854 = 1.42353 square inches.
Calculating Conduit Fill Ratio:
To calculate the conduit fill ratio, we need to determine the internal cross-sectional area of the conduit and divide the total cable area by it. The formula for the conduit area is:
Conduit Area = π * (Conduit Diameter/2)^2
Let’s assume we are using a conduit with an internal diameter of 2 inches. Using the conduit area formula, we can calculate the internal conduit area as follows:
Conduit Area = π * (2/2)^2 = 3.1416 square inches
Now, we can calculate the conduit fill ratio:
Fill Ratio = (Total Cable Area / Conduit Area) * 100 = (1.42353 / 3.1416) * 100 = 45.33%
Selecting Conduit Size:
Refer to the conduit fill tables in the NEC that correspond to the type and size of conduit being used. Suppose the table specifies a maximum allowable fill ratio of 50%. Since the calculated fill ratio (45.33%) is below the maximum allowable value, the selected conduit size is appropriate for the given cable configuration.
Please note that the provided calculations are for illustrative purposes and may not reflect the exact values for the cables and conduit in your specific scenario. It’s essential to consult the latest edition of the NEC and consider specific requirements, derating factors, and manufacturer’s recommendations for accurate conduit sizing.
How to Conduit Sizing for Different Cable Types

Power Cables:
Power cables are typically used to transmit electrical power in various applications. When sizing conduit for power cables, it is important to consider the cable’s outer diameter, insulation thickness, and the number of cables being installed. The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines for conduit fill based on the cable type and size.
For power cables, the conduit should have sufficient space to accommodate the cables while maintaining the recommended fill ratio. It is crucial to calculate the cable area and determine the appropriate conduit size using the step-by-step methodology mentioned earlier. Additionally, it is important to consider any derating factors specified by the NEC, depending on factors such as ambient temperature and the number of current-carrying conductors.
Communication Cables:
Communication cables, including data cables, telephone cables, and coaxial cables, are used for transmitting signals and data. When sizing conduit for communication cables, the outer diameter of the cables is a key consideration. Communication cables are generally smaller in diameter compared to power cables, so smaller conduit sizes are typically suitable.
It is important to consult the NEC guidelines and manufacturer’s recommendations for communication cables to determine the appropriate conduit fill ratio and conduit size. Following the step-by-step methodology mentioned earlier, calculate the cable area and ensure the fill ratio is within the allowed limits.
Fiber Optic Cables:
Fiber optic cables are used for high-speed data transmission over long distances. They consist of thin glass or plastic fibers encased in protective jackets. When sizing conduit for fiber optic cables, the outer diameter of the cables is the primary consideration.
Fiber optic cables are typically smaller in diameter compared to power and communication cables. As a result, smaller conduit sizes are generally suitable for fiber optic cable installations. It is important to refer to the NEC guidelines and manufacturer’s recommendations to determine the appropriate conduit fill ratio and conduit size for fiber optic cables.
Follow the step-by-step methodology mentioned earlier to calculate the cable area and determine the appropriate conduit size. Consider any derating factors specified by the NEC for the specific type of conductor being used.
It is important to note that the specific requirements for conduit sizing may vary depending on local electrical codes, project specifications, and other factors. Always consult the latest edition of the NEC and adhere to any additional guidelines provided by relevant authorities and manufacturers for accurate and safe conduit sizing for different cable types.
3 Common Mistakes in Conduit Sizing

Overfilling Conduit:
One common mistake when sizing conduit is overfilling it with cables. Overfilled conduits can lead to excessive heat buildup, increased cable resistance, and potential damage to the cables. It is important to adhere to the fill ratio guidelines provided by the NEC and manufacturer’s recommendations to ensure proper spacing and ventilation within the conduit.
Underestimating Future Expansion:
Failing to consider future expansion needs is another common mistake. As technology advances and electrical requirements change, additional cables may need to be installed in the conduit. It is crucial to plan for future expansion by leaving adequate space within the conduit to accommodate additional cables. This can help avoid the need for costly and time-consuming conduit replacements or upgrades in the future.
Ignoring Environmental Factors:
Environmental factors play a significant role in conduit sizing. Ignoring these factors can lead to detrimental consequences. Some environmental factors to consider include ambient temperature, moisture levels, corrosive substances, and physical stressors. Different cable types and conduit materials have specific temperature rating and environmental requirements. It is essential to select cables and conduits that are suitable for the environmental conditions in which they will be installed.
Ensure that the chosen conduit material is compatible with the surrounding environment and can withstand any anticipated exposure. For example, in areas with high humidity or corrosive substances, selecting corrosion-resistant or moisture-resistant conduits may be necessary. Additionally, consider the impact of physical stressors such as vibrations, bending, or impact, and choose conduits and cable protection methods accordingly.
By taking into account these common mistakes and avoiding them during the conduit sizing process, you can ensure a safe and efficient electrical installation that meets current needs and allows for future expansion while considering environmental factors. Always consult the relevant electrical codes, industry standards, and manufacturer’s guidelines to make informed decisions.
5 Conduit Sizing Tools & Resources
Online Calculators and Software:
Conduit Fill Calculators: Several online tools and software applications are available that can calculate conduit fill ratios based on cable types, sizes, and conduit specifications. These calculators streamline the conduit sizing process and ensure compliance with industry standards and codes. Some popular options include Southwire’s Conduit Fill Calculator, Omni Cable’s Conduit Fill Calculator, and NEC-based conduit fill calculators available on various electrical engineering websites.
Electrical Design Software: Professional electrical design software often includes conduit sizing modules. These software packages provide comprehensive tools for designing electrical systems, including conduit sizing. They allow users to input cable and conduit specifications, calculate fill ratios, and generate detailed reports and drawings. Examples of electrical design software that offer conduit sizing features include AutoCAD Electrical, ETAP, and EasyPower.
Industry Standards and Guidelines:

National Electrical Code (NEC): The NEC is a widely recognized standard for electrical installations in the United States. It includes guidelines and regulations related to conduit sizing, fill ratios, and derating factors. It is essential to consult the relevant sections of the NEC, such as Article 314 (Outlet, Device, Pull, and Junction Boxes; Conduit Bodies) and Article 310 (Conductors for General Wiring), to ensure compliance with industry standards.
Manufacturer’s Documentation: Cable and conduit manufacturers often provide technical documentation that includes information on cable dimensions, allowable fill ratios, and recommended conduit sizes. These resources are valuable references when selecting and sizing conduits for specific cable types. Manufacturers’ websites, product catalogs, and installation guides are good sources of information for conduit sizing recommendations.
Industry Associations and Organizations: Professional associations and organizations related to the electrical industry, such as the National Electrical Contractors Association (NECA) and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), offer resources and publications that cover conduit sizing and related topics. These resources can provide valuable insights and guidance based on industry best practices and standards.
When utilizing conduit sizing tools and resources, it is important to verify the accuracy and applicability of the information provided. Consider factors such as local electrical codes, project specifications, and specific cable and conduit characteristics. Always prioritize safety, compliance, and the specific requirements of the project at hand.
Conclusion
Accurate conduit sizing is crucial for the successful installation of electrical systems. Improper conduit sizing can result in various issues, including overheating, cable damage, increased resistance, and compliance violations. By following the appropriate conduit sizing methodology, considering cable types, fill ratios, and environmental factors, electrical professionals can ensure safe and efficient installations that meet current needs and allow for future expansion.
Any questions, contact Ledes today.



